hello,大家好,今天为大家介绍广度优先算法,同样通过几个较为经典的算法题进行讲解,本文所用语言为C语言。
前言
广度优先搜索(Breadth-First Search,BFS)是一种较为常见的暴力搜索算法,搜索过程中并不考虑结果的可能位置,而是暴力搜索所有节点直到找到结果为止。
图像渲染
此题为leetcode算法第733题,为经典的广度优先搜索例题,题目给定一个整型二维数组表示的颜色矩阵,同时给定一个坐标[sr, sc]以及此坐标对应的newColor,将与[sr, sc]上下左右相连的oldColor全部染色为newColor,最后返回新的颜色矩阵数组,示意图如下:
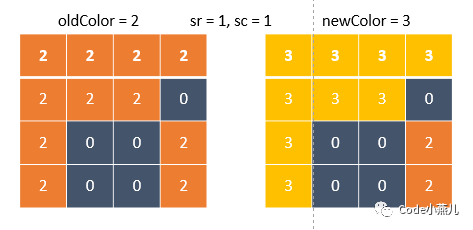
思路解析:显然若newColor==oldColor,则直接返回原数组即可;从起点开始,进行广度优先搜索,若其与oldColor相同,则将其该节点入队,并更新该节点的颜色以防止重复搜索,代码如下:
int** floodFill(int** image, int imageSize, int* imageColSize,int sr, int sc, int newColor, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){*returnSize = imageSize;for(int i = 0; i < imageSize; ++i){*returnColumuSize[i] = imageSize;}int oldColor = image[sr][sc];if(oldColor == newColor) return image;const int dx[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};const int dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};#if 0// 广度优先搜索int front = 0, rear = 0;int queue[imageSize * (*imageColSize)][2];queue[rear][0] = sr, queue[rear++][1] = sc;while(front < rear){int x = queue[front][0], y = queue[front ++][1];for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){int nx = x + dx[i], ny = y + dy[i];if(nx >= 0 && nx < imageSize && ny >= 0 && ny < *imageColSize){queue[rear][0] = nx, queue[rear++][1] = ny;image[nx][ny] = newColor;}}}return image;#else// 深度优先搜索dfs(image, imageSize, imageColSize, sr, sc, oldColor, newColor);return iamge;#endif}void dfs(int **image, int iamgeSize, int *imageColSize,int sr, int sc, int oldColor, int newColor){if(image[sr][sc] != oldColor) return ;image[sr][sc] = newColor;for(int i = 0; i < 4; ++i){int nx = sr + dx[i], ny = sc + dy[i];if(nx >= 0 && nx < imageSize && ny >= 0 && ny < *imageColSize){dfs(image, imageSize, imageColSize, nx, ny, oldColor, newColor);}}}复制
腐烂的橘子
此题为leetcode算法第994题,给定一个数字矩阵,0表示空单元格,1表示好橘子,2表示坏橘子,每一分钟与坏橘子上下左右相邻的所有好橘子都会变为腐烂的坏橘子,要求输出所有好橘子变为坏橘子的分钟数,若存在好橘子与任意坏橘子都不相邻,则输出-1,示意图如下:
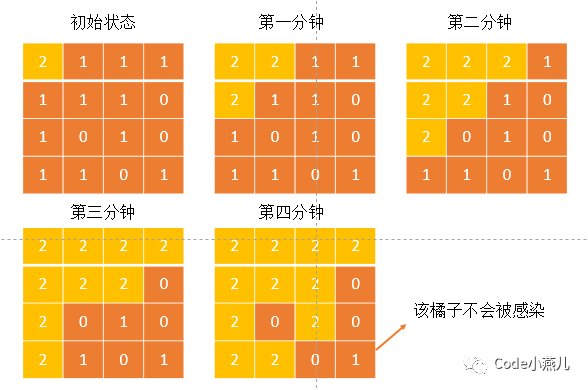
此题为BFS模板题,将所有坏橘子入队,在队列不为空时,将队首坏橘子出队,并将与之相邻的好橘子感染并加入坏橘子队列,最后还需要检查是否存在好橘子未被感染即可,C语言代码如下:
typedef struct{int x;int y;}Queue;const int dx[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};const int dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};int orangesRotting(int** grid, int gridSize, int* gridColSize){int badNum = 0, step = 0;Queue *q = (Queue *)malloc(gridSize * (*gridColSize) * sizeof(Queue));bzero(q, sizeof(q));// 所有的腐烂橘子入队for(int i = 0; i < gridSize; ++i){for(int j = 0; j < *gridColSize; ++j){if(grid[i][j] == 2){q[badNum].x = i;q[badNum++].y = j;}}}int front = 0, rear = badNum;while(front < rear){ // 队列不为空则继续循环int tempFront = front, tempRear = rear;for(int i = tempFront; i < tempRear; ++i){ // 遍历当前队列for(int j = 0; j < 4; ++j){ // 四个方向搜索int nx = q[i].x + dx[j];int ny = q[i].y + dy[j];if(nx < 0 || nx >= gridSize || ny < 0 || ny >= *gridColSize) continue;if(grid[nx][ny] == 1){grid[nx][ny] = 2;q[badNum].x = nx, q[badNum ++].y = ny;}}}front = tempRear, rear = badNum; // 更新队列step ++; // 更新答案}检查是否存在好橘子for(int i = 0; i < gridSize; ++i){for(int j = 0; j < *gridColSize; ++j){if(*(*(grid + i) + j) == 1) return -1;}}return step > 0 ? step - 1 : 0;}复制
01矩阵
此题为leetcode算法第542题,给定一个01矩阵,要求输出每个元素离0最近的距离,示意图如下:
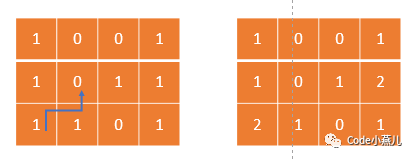
此题同样是BFS的模板题,首先对矩阵进行遍历,将元素为0的位置加入队列,而后广度优先搜索,首先遇到的1为距离为1,将第一层的1入队,而后进行第二次循环,寻找第二层的1,以此类推即可得到结果,代码如下:
const int dx[4] = {0, -1, 0, 1};const int dy[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};int** updateMatrix(int** mat, int matSize, int* matColSize, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){*returnSize = matSize;*returnColumnSizes = matColSize;int queue[matSize * (*matColSize)][2];int visited[matSize][matColSize[0]];bzero(visited, sizeof(visited));int rear = 0, front = 0;int **res = (int **)malloc(sizeof(int *) * matSize);for (int i = 0; i < matSize; i++) {res[i] = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * matColSize[0]);for (int j = 0; j < *matColSize; j++) {if (mat[i][j] == 0) {res[i][j] = 0; // 显然0距离最近0的距离为0queue[rear][0] = i, queue[rear++][1] = j; // 将元素0的位置加入队列visited[i][j] = 2; // 记录遍历状态,为后续剪枝}}}// 广度优先遍历while (front < rear) {int x = queue[front][0], y = queue[front++][1]; // 队首元素出队for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { // 上下左右四个方向搜索int mx = x + dx[i], my = y + dy[i];// 新索引的合法性判断if (mx < 0 || mx >= matSize || my < 0 || my >= (*matColSize) || visited[mx][my] == 2) {continue;}res[mx][my] = res[x][y] + 1; // 更新结果queue[rear][0] = mx, queue[rear++][1] = my; // 将新元素入队visited[mx][my] = 2; // 更新索引状态}}return res;}复制
后记
本文以3个经典的模板题讲述了BFS算法的实现过程,在利用BFS算法时,常用到队列这种数据结构,此外根据题意进行必要的剪枝也是提高时间复杂度的重要方法之一,需要注意的是因本文代码用于leetcode算法求解,在内存申请后,尚未考虑到内存释放的问题。
欢迎大家勘误并提出有效建议(邮箱见往期文章),谢谢大家。







