
作者介绍
2020年8月加入去哪儿网,主要负责公司PostgreSQL和Oracle的运维管理工作。
一、引言
二、Sequence 适用场景
主键
用于整型主键数据的生成,一般 1 个 Sequence 仅用于 1 张表的主键,当然也可以多个表的主键共用 1 个 Sequence (比如分区表),这是最常见的用法。本文讨论的主要是此用途。
非主键
只使用 Sequence 本身自增 (也可自减,但不常用) 的功能,可多表共用一个 Sequence,或整个数据库的应用共用一个全局 Sequence。
需要注意的一点是:无论 Sequence 是否作为表的主键,Sequence 生成时虽然一般是连续的,但由于其值可能随着其所在事务被回滚,或 PostgreSQL 实例某种方式下重启产生跳变等原因,从而导致实际值不一定是连续的,所以应用不应该对 Sequence 的值是否连续作为强依赖。
三、Sequence 用法 1 显式调用
这种方式是单独创建 Sequence 和表,在 INSERT 等语句中显式调用 Sequence 。
3 种数据库中使用情况如下示例。
Oracle
SQL> CREATE SEQUENCE seq_test;Sequence created.SQL> CREATE TABLE tb_test (test_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY); 2 3Table created.SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test (test_id) VALUES (seq_test.nextval);1 row created.SQL> COMMIT;Commit complete.SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test ORDER BY 1 DESC;TEST_ID----------1复制
PostgreSQL 中 Sequence 的创建与 Oracle 很类似。
$ psql -U alvin -d alvindbpsql (11.9)Type "help" for help.alvindb=> CREATE SEQUENCE seq_test;CREATE SEQUENCEalvindb=> CREATE TABLE tb_test (alvindb(> test_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEYalvindb(> );CREATE TABLEalvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test (test_id) VALUES (nextval('seq_test'));INSERT 0 1alvindb=> SELECT * FROM tb_test ORDER BY 1 DESC;test_id---------1(1 row)复制
MySQL
MySQL 未支持显式创建 Sequence,直接支持 AUTO INCREMENT,详见下文用法 4 中所述。
是否可以在 INSERT 语句中不显式调用 Sequence,而使其被自动调用呢?
当然可以!
通常有 3 种方法:
通过触发器
通过 DEFAULT
通过 AUTO INCREMENT
下面我们逐个探讨一下。
四、Sequence 用法 2 隐式调用之触发器
可以在表的 BEFORE INSERT 触发器中,调用 Sequence,从而达到在插入前自动给主键赋值。这样,在 INSERT 中就不需要显式调用 Sequence 了。
Oracle
SQL> CREATE SEQUENCE seq_test2;Sequence created.SQL> CREATE TABLE tb_test2 (test_id NUMBER PRIMARY KEY,test_order NUMBER); 2 3 4Table created.SQL> CREATE OR REPLACE TRIGGER trg_b_ins_tb_test2BEFORE INSERT ON tb_test2FOR EACH ROWBEGINSELECT seq_test2.nextvalINTO :new.test_idFROM dual;END; 2 3 4 5 6 7 89 /Trigger created.SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test2 (test_order) VALUES (1);1 row created.SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test2 ORDER BY 2 DESC;TEST_ID TEST_ORDER---------- ------------1 1复制
下面测试表明,当在 INSERT 中指定列 test_id 为 NULL 时,会从 Sequence 中取值。但这是 trigger 的原理决定的,与传入的值是否为 NULL 无关。
SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test2 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (NULL,2);1 row created.SQL> COMMIT;Commit complete.SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test2 ORDER BY 2 DESC;TEST_ID TEST_ORDER---------- ----------2 21 1复制
alvindb=> CREATE SEQUENCE seq_test2;CREATE SEQUENCEalvindb=> CREATE TABLE tb_test2 (alvindb(> test_id INTEGER PRIMARY KEY,alvindb(> test_order INTEGERalvindb(> );CREATE TABLEalvindb=> CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION trgf_b_ins_tb_test2()alvindb-> RETURNS TRIGGER ASalvindb-> $$alvindb$> BEGINalvindb$> NEW.test_id := nextval('seq_test2');alvindb$> RETURN NEW;alvindb$> END;alvindb$> $$alvindb-> LANGUAGE 'plpgsql';CREATE FUNCTIONalvindb=> CREATE TRIGGER trg_b_ins_tb_test2alvindb-> BEFORE INSERT ON tb_test2alvindb-> FOR EACH ROWalvindb-> EXECUTE PROCEDURE trgf_b_ins_tb_test2();CREATE TRIGGERalvindb=> \d+ tb_test2Table "public.tb_test2"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description------------+---------+-----------+----------+---------+---------+--------------+-------------test_id | integer | | not null | | plain | |test_order | integer | | | | plain | |Indexes:"tb_test2_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (test_id)Triggers:trg_b_ins_tb_test2 BEFORE INSERT ON tb_test2 FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE PROCEDURE trgf_b_ins_tb_test2()alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test2 (test_order) VALUES (1);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> SELECT * FROM tb_test2 ORDER BY 2 DESC;test_id | test_order---------+--------------1 | 1(1 row)复制
alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test2 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (NULL,2);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> SELECT * FROM tb_test2 ORDER BY 2 DESC;test_id | test_order---------+------------2 | 21 | 1(2 rows)复制
MySQL 未支持显式创建 Sequence,直接支持 AUTO INCREMENT,详见下文用法 4 中所述。
五、Sequence 用法 3 隐式调用之 DEFAULT
SQL> CREATE SEQUENCE seq_test3;Sequence created.SQL> CREATE TABLE tb_test3 (test_id NUMBER DEFAULT seq_test3.nextval PRIMARY KEY,test_order NUMBER); 2 3 4test_id NUMBER DEFAULT seq_test3.nextval PRIMARY KEY,*ERROR at line 2:ORA-00984: column not allowed here复制
Restriction on Default Column ValuesA DEFAULT expression cannot contain references to PL/SQL functions or to other columns, the pseudocolumns CURRVAL, NEXTVAL, LEVEL, PRIOR, and ROWNUM, or date constants that are not fully specified.复制
SQL> CREATE SEQUENCE seq_test3;Sequence created.SQL> CREATE TABLE tb_test3 (test_id NUMBER DEFAULT seq_test3.nextval PRIMARY KEY,test_order NUMBER); 2 3 4Table created.SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test3 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (seq_test3.nextval,1);1 row created.SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test3 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (DEFAULT,2);1 row created.SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test3 (test_order) VALUES (3);1 row created.SQL> COMMIT;Commit complete.SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test3 ORDER BY 2 DESC;TEST_ID TEST_ORDER---------- ------------3 32 21 1复制
SQL> SET linesize 100COL table_name FOR a30COL column_name FOR a30COL data_default FOR a30SQL> SELECT table_name,column_name,data_default FROM user_tab_columns WHERE table_name = 'TB_TEST3';TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME DATA_DEFAULT------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------TB_TEST3 TEST_ID "TEST"."SEQ_TEST3"."NEXTVAL"TB_TEST3 TEST_ORDER复制
SQL> DROP SEQUENCE seq_test3;Sequence dropped.复制
那么删除 Sequence 后表列的 DEFAULT 变不变呢?再插入数据会怎么样呢?
如下示例,删除 Sequence 后再插入数据,删除 Sequence 后表列的 DEFAULT 不变!但再插入数据时会报错。
SQL> SELECT table_name,column_name,data_default FROM user_tab_columns WHERE table_name = 'TB_TEST3';TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME DATA_DEFAULT------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------TB_TEST3 TEST_ID "TEST"."SEQ_TEST3"."NEXTVAL"TB_TEST3 TEST_ORDERSQL>SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test3 (test_order) VALUES (5);INSERT INTO tb_test3 (test_order) VALUES (5)*ERROR at line 1:ORA-02289: sequence does not exist复制
如下示例,PostgreSQL 中 DEFAULT 调用 Sequence 与 Oracle 依然很类似。
alvindb=> CREATE SEQUENCE seq_test3;CREATE SEQUENCEalvindb=> CREATE TABLE tb_test3 (alvindb(> test_id INTEGER DEFAULT nextval('seq_test3') PRIMARY KEY,alvindb(> test_order INTEGERalvindb(> );CREATE TABLEalvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test3 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (nextval('seq_test3'),1);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test3 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (DEFAULT,2);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test3 (test_order) VALUES (3);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> SELECT * FROM tb_test3 ORDER BY 2 DESC;test_id | test_order---------+--------------3 | 32 | 21 | 1(3 rows)复制
从下面的示例中可以看出,DEFAULT 中的 Sequence 可以删除。在使用 Cascade 关键字时,表列的 DEFAULT 也被删除了,这个既强大,但也存在一定风险的操作。
alvindb=> CREATE SEQUENCE seq_test3;CREATE SEQUENCEalvindb=> CREATE TABLE tb_test3 (alvindb(> test_id INTEGER DEFAULT nextval('seq_test3') PRIMARY KEY,alvindb(> test_order INTEGERalvindb(> );CREATE TABLEalvindb=> \d+ tb_test3Table "public.tb_test3"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description------------+---------+-----------+----------+--------------------------------+---------+--------------+-------------test_id | integer | | not null | nextval('seq_test3'::regclass) | plain | |test_order | integer | | | | plain | |Indexes:"tb_test3_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (test_id)alvindb=> DROP SEQUENCE seq_test3;ERROR: cannot drop sequence seq_test3 because other objects depend on itDETAIL: default value for column test_id of table tb_test3 depends on sequence seq_test3HINT: Use DROP ... CASCADE to drop the dependent objects too.alvindb=> DROP SEQUENCE tb_test4_test_id_seq CASCADE;NOTICE: drop cascades to default value for column test_id of table tb_test4DROP SEQUENCE复制
那么 PostgreSQL 是哪个版本开始支持的呢?
PostgreSQL 官网文档中列出的最早的版本是 PostgreSQL 7.1(7.1 之前的文档官网中未列出)。
PostgreSQL 7.1 文档中的例子如下:
CREATE TABLE distributors (name VARCHAR(40) DEFAULT 'luso films',did INTEGER DEFAULT NEXTVAL('distributors_serial'),modtime TIMESTAMP DEFAULT now());复制
根据 PostgreSQL 官网, PostgreSQL Release 7.1.3 是 2001-08-15。
根据 Wikipedia, Oracle Database 12c Release 1 是 July 2013 发布的。
即 PostgreSQL 2001 年已支持 Sequence 的 DEFAULT nextval 用法,十二年后,Oracle 也支持了。
MySQL
MySQL 不支持单独创建 Sequence。参考用法 4 AUTO INCREMENT 中 MySQL 部分。
六、Sequence 用法 4 隐式调用之 AUTO INCREMENT
通过 DEFAULT 还是需要事先手动创建 Sequence。是否有更简单的用法呢?
当然,就是通过 AUTO INCREMENT 方式,自动创建 Sequence,并且自动以 DEFAULT 的方式调用!
Oracle
同样,Oracle 也是 12c 开始支持 AUTO INCREMENT。
SQL> CREATE TABLE tb_test4 (test_id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT ON NULL AS IDENTITY,test_order NUMBER); 2 3 4Table created.复制
插入测试数据,可以看到预期的结果。
SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (DEFAULT,1);1 row created.SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (2);1 row created.SQL> COMMIT;Commit complete.SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;TEST_ID TEST_ORDER---------- ------------2 21 1复制
SQL> COL object_name FOR a30COL object_type FOR a30SQL>SQL> SELECT object_name,object_type FROM user_objects;OBJECT_NAME OBJECT_TYPE------------------------------ ------------------------------TB_TEST4 TABLEISEQ$$_254835 SEQUENCESQL> SET linesize 100COL table_name FOR a30COL column_name FOR a30COL data_default FOR a30SQL> SELECT table_name,column_name,data_default FROM user_tab_columns WHERE table_name = 'TB_TEST4';TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME DATA_DEFAULT------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------TB_TEST4 TEST_ID "TEST"."ISEQ$$_254857".nextvalTB_TEST4 TEST_ORDER复制
SQL> SET linesize 200COL table_name FOR a30COL column_name FOR a30COL generation FOR a30COL sequence_name FOR a30SQL> SQL> SQL> SQL>SQL> SELECT table_name,column_name,sequence_name FROM user_tab_identity_cols;TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME SEQUENCE_NAME------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------TB_TEST4 TEST_ID ISEQ$$_254835复制
通过如下实验,可以看到,Oracle 中系统自动生成的 Sequence 不能单独删除。
SQL> DROP SEQUENCE ISEQ$$_254835;DROP SEQUENCE ISEQ$$_254835*ERROR at line 1:ORA-32794: cannot drop a system-generated sequence复制
SQL> DROP TABLE tb_test4;Table dropped.SQL> SELECT table_name,column_name,sequence_name FROM user_tab_identity_cols;TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME SEQUENCE_NAME------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------BIN$vXiAW/32gIHgU5KhXwowkg==$0 TEST_ID ISEQ$$_254835SQL> SELECT object_name,object_type FROM USER_OBJECTS;OBJECT_NAME OBJECT_TYPE------------------------------ ------------------------------ISEQ$$_254835 SEQUENCE复制
SQL> PURGE RECYCLEBIN;Recyclebin purged.SQL> SELECT object_name,object_type FROM USER_OBJECTS;no rows selectedSQL> SELECT table_name,column_name,sequence_name FROM user_tab_identity_cols;no rows selected复制
这是 Oracle 中 GENERATED BY DEFAULT ON NULL 中的 ON NULL 决定的。
SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;TEST_ID TEST_ORDER---------- ----------6 8SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (NULL,9);1 row created.SQL> COMMIT;Commit complete.SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;TEST_ID TEST_ORDER---------- ----------7 96 8复制
GENERATED BY DEFAULT 与 GENERATED BY DEFAULT ON NULL 区别是,当主键插入 NULL 值时,GENERATED BY DEFAULT 会报错,如下:
SQL> CREATE TABLE tb_test5 (test_id NUMBER GENERATED BY DEFAULT AS IDENTITY,test_order NUMBER); 2 3 4Table created.SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test5 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (NULL,1);INSERT INTO tb_test5 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (NULL,1)*ERROR at line 1:ORA-01400: cannot insert NULL into ("TEST"."TB_TEST5"."TEST_ID")复制
若主键指定值会报错:
SQL> CREATE TABLE tb_test6 (test_id NUMBER GENERATED ALWAYS AS IDENTITY,test_order NUMBER); 2 3 4Table created.SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test6 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (1,1);INSERT INTO tb_test6 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (1,1)*ERROR at line 1:ORA-32795: cannot insert into a generated always identity columnSQL> INSERT INTO tb_test6 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (NULL,2);INSERT INTO tb_test6 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (NULL,2)*ERROR at line 1:ORA-32795: cannot insert into a generated always identity column复制
SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test6 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (DEFAULT,3);1 row created.SQL> COMMIT;Commit complete.SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test6 ORDER BY 2 DESC;TEST_ID TEST_ORDER---------- ----------1 3复制
创建表
alvindb=> CREATE TABLE tb_test4 (alvindb(> test_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,alvindb(> test_order INTEGERalvindb(> );CREATE TABLE复制
alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (DEFAULT,1);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (2);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;test_id | test_order---------+--------------2 | 21 | 1(2 rows)复制
alvindb=> \d+ tb_test4Table "public.tb_test4"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description------------+---------+-----------+----------+-------------------------------------------+---------+--------------+-------------test_id | integer | | not null | nextval('tb_test4_test_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |test_order | integer | | | | plain | |Indexes:"tb_test4_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (test_id)复制
即 'Owned by' 也代表删除表或列的时候,对应的 Sequence 也会被删除。
alvindb=> \d+ tb_test4_test_id_seqSequence "public.tb_test4_test_id_seq"Type | Start | Minimum | Maximum | Increment | Cycles? | Cache---------+-------+---------+------------+-----------+---------+-------integer | 1 | 1 | 2147483647 | 1 | no | 1Owned by: public.tb_test4.test_id复制
alvindb=> DROP TABLE tb_test4;DROP TABLEalvindb=> \d+ tb_test4_test_id_seqDid not find any relation named "tb_test4_test_id_seq".alvindb=>复制
alvindb=> CREATE TABLE tb_test4 (alvindb(> test_id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,alvindb(> test_order INTEGERalvindb(> );CREATE TABLEalvindb=> DROP SEQUENCE tb_test4_test_id_seq;ERROR: cannot drop sequence tb_test4_test_id_seq because other objects depend on itDETAIL: default value for column test_id of table tb_test4 depends on sequence tb_test4_test_id_seqHINT: Use DROP ... CASCADE to drop the dependent objects too.alvindb=> DROP SEQUENCE tb_test4_test_id_seq CASCADE;NOTICE: drop cascades to default value for column test_id of table tb_test4DROP SEQUENCEalvindb=> \d+ tb_test4Table "public.tb_test4"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description------------+---------+-----------+----------+-------------------------------------------+---------+--------------+-------------test_id | integer | | not null | nextval('tb_test4_test_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |test_order | integer | | | | plain | |Indexes:"tb_test4_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (test_id)复制
a. 自动生成的 Sequence 与对应列是绑定的
b. 删除表后,自动生成的 Sequence 也会被删除,避免无用的 Sequence 的存在
根据 PostgreSQL 官方文档
CREATE TABLE tablename (colname SERIAL);复制
CREATE SEQUENCE tablename_colname_seq AS integer;CREATE TABLE tablename (colname integer NOT NULL DEFAULT nextval('tablename_colname_seq'));ALTER SEQUENCE tablename_colname_seq OWNED BY tablename.colname;复制
从上面 SERIAL 等价的 SQL 中可以看出,PostgreSQL 只是将上述 3个 SQL 整合为 SERIAL 关键字,与 Oracle 中 AUTO INCREMENT 本质是不同的。
alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (NULL,9);ERROR: null value in column "test_id" violates not-null constraintDETAIL: Failing row contains (null, 9).alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test3 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (NULL,9);ERROR: null value in column "test_id" violates not-null constraintDETAIL: Failing row contains (null, 9).复制
PostgreSQL 官网文档中列出的最早的版本是 PostgreSQL 8.0,在这个文档中,已支持这种用法。
这是 PostgreSQL 8.0 文档中的例子
CREATE TABLE cinemas (id serial,name text,location text) TABLESPACE diskvol1;复制
根据 Wikipedia, Oracle Database 12c Release 1 是 July 2013 发布的。
即 PostgreSQL 2005 年已支持 Sequence 的 AUTO INCREMENT 用法,八年后,Oracle 也支持了。
MySQL
MySQL 用 AUTO_INCREMENT 关键字。
如下示例。
mysql> CREATE TABLE tb_test4 (-> test_id INTEGER NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,-> test_order INTEGER-> );Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.01 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (DEFAULT,1);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (2);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+--------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+--------------+| 2 | 2 || 1 | 1 |+---------+--------------+2 rows in set (0.00 sec)复制
mysql> SHOW CREATE TABLE tb_test4;+----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+| Table | Create Table |+----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+| tb_test4 | CREATE TABLE `tb_test4` (`test_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`test_order` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`test_id`)) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=102 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 |+----------+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)复制
mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (NULL,9);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test5 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 1 | 8 |+---------+------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)复制
INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (1);INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (100,2);INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (3);UPDATE tb_test4 SET test_id = 200 WHERE test_order = 3;INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (5);INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (6);SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;DELETE FROM tb_test4 WHERE test_order = 5;DELETE FROM tb_test4 WHERE test_order = 6;INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (7);TRUNCATE TABLE tb_test4;INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (8);复制
以下是 MySQL 5.7 InnoDB ENGINE 中的运行结果。
mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (1);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 1 | 1 |+---------+------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| LAST_INSERT_ID() |+------------------+| 1 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (100,2);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 1 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (3);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 101 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 101 | 3 || 100 | 2 || 1 | 1 |+---------+------------+3 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> UPDATE tb_test4 SET test_id = 200 WHERE test_order = 3;Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 101 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (5);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 102 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 102 | 5 || 200 | 3 || 100 | 2 || 1 | 1 |+---------+------------+4 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (6);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 103 | 6 || 102 | 5 || 200 | 3 || 100 | 2 || 1 | 1 |+---------+------------+5 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 103 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> DELETE FROM tb_test4 WHERE test_order = 5;Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 103 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> DELETE FROM tb_test4 WHERE test_order = 6;Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 103 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 200 | 3 || 100 | 2 || 1 | 1 |+---------+------------+3 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (7);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 104 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 104 | 7 || 200 | 3 || 100 | 2 || 1 | 1 |+---------+------------+4 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> TRUNCATE TABLE tb_test4;Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 104 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (8);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 1 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 1 | 8 |+---------+------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)复制
以下是 MySQL 5.7 MYISAM ENGINE 中的运行结果
mysql> CREATE TABLE tb_test5 (-> test_id INTEGER NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,-> test_order INTEGER-> ) ENGINE = MYISAM;Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SHOW CREATE TABLE tb_test5;+----------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+| Table | Create Table |+----------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+| tb_test5 | CREATE TABLE `tb_test5` (`test_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,`test_order` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,PRIMARY KEY (`test_id`)) ENGINE=MyISAM DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1 |+----------+------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test5 (test_order) VALUES (1);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 1 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test5 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (100,2);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 1 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test5 (test_order) VALUES (3);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 101 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql>mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test5 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 101 | 3 || 100 | 2 || 1 | 1 |+---------+------------+3 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> UPDATE tb_test5 SET test_id = 200 WHERE test_order = 3;Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)Rows matched: 1 Changed: 1 Warnings: 0mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 101 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test5 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 200 | 3 || 100 | 2 || 1 | 1 |+---------+------------+3 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test5 (test_order) VALUES (5);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 201 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test5 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 201 | 5 || 200 | 3 || 100 | 2 || 1 | 1 |+---------+------------+4 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test5 (test_order) VALUES (5);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test5 (test_order) VALUES (6);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 203 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test5 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 203 | 6 || 201 | 5 || 202 | 5 || 200 | 3 || 100 | 2 || 1 | 1 |+---------+------------+6 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> DELETE FROM tb_test5 WHERE test_order = 5;Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.00 sec)mysql> DELETE FROM tb_test5 WHERE test_order = 6;Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 203 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test5 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 200 | 3 || 100 | 2 || 1 | 1 |+---------+------------+3 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test5 (test_order) VALUES (7);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 204 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test5 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 204 | 7 || 200 | 3 || 100 | 2 || 1 | 1 |+---------+------------+4 rows in set (0.00 sec)mysql> TRUNCATE TABLE tb_test5;Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 204 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO tb_test5 (test_order) VALUES (8);Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT last_insert_id();+------------------+| last_insert_id() |+------------------+| 1 |+------------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SELECT * FROM tb_test5 ORDER BY 2 DESC;+---------+------------+| test_id | test_order |+---------+------------+| 1 | 8 |+---------+------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql>复制
以下是 Oracle 12c(Release 12.2.0.1.0) 中的运行结果
SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (1);1 row created.SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (100,2);1 row created.SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (3);1 row created.SQL> COMMIT;Commit complete.SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;TEST_ID TEST_ORDER---------- ----------2 3100 21 1SQL> COL table_name FOR a30COL column_name FOR a30COL generation FOR a30COL sequence_name FOR a30SELECT table_name,column_name,sequence_name FROM user_tab_identity_cols;SQL> SQL> SQL> SQL>SQL> SELECT table_name,column_name,sequence_name FROM user_tab_identity_cols;TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME SEQUENCE_NAME------------------------------ ------------------------------ ------------------------------TB_TEST4 TEST_ID ISEQ$$_254864SQL>SQL> SELECT ISEQ$$_254864.currval FROM dual;CURRVAL----------2SQL> UPDATE tb_test4 SET test_id = 200 WHERE test_order = 3;1 row updated.SQL> SELECT ISEQ$$_254864.currval FROM dual;CURRVAL----------2SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (5);1 row created.SQL> SELECT ISEQ$$_254864.currval FROM dual;CURRVAL----------3SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;TEST_ID TEST_ORDER---------- ----------3 5200 3100 21 1SQL>SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (6);1 row created.SQL> COMMIT;Commit complete.SQL> SELECT ISEQ$$_254864.currval FROM dual;CURRVAL----------4SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;TEST_ID TEST_ORDER---------- ----------4 63 5200 3100 21 1SQL>SQL> DELETE FROM tb_test4 WHERE test_order = 5;1 row deleted.SQL> DELETE FROM tb_test4 WHERE test_order = 6;1 row deleted.SQL> COMMIT;Commit complete.SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (7);1 row created.SQL> COMMIT;Commit complete.SQL> SELECT ISEQ$$_254864.currval FROM dual;CURRVAL----------5SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;TEST_ID TEST_ORDER---------- ----------5 7200 3100 21 1SQL> TRUNCATE TABLE tb_test4;Table truncated.SQL> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (8);1 row created.SQL> SELECT ISEQ$$_254864.currval FROM dual;CURRVAL----------6SQL> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;TEST_ID TEST_ORDER---------- ----------6 8复制
PostgreSQL 11
以下是 PostgreSQL 11 中的运行结果
alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (1);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_id,test_order) VALUES (100,2);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (3);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;test_id | test_order---------+------------2 | 3100 | 21 | 1(3 rows)alvindb=>alvindb=> \d+ tb_test4Table "public.tb_test4"Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default | Storage | Stats target | Description------------+---------+-----------+----------+-------------------------------------------+---------+--------------+-------------test_id | integer | | not null | nextval('tb_test4_test_id_seq'::regclass) | plain | |test_order | integer | | | | plain | |Indexes:"tb_test4_pkey" PRIMARY KEY, btree (test_id)alvindb=> SELECT currval('tb_test4_test_id_seq');currval---------2(1 row)alvindb=> UPDATE tb_test4 SET test_id = 200 WHERE test_order = 3;UPDATE 1alvindb=> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;test_id | test_order---------+------------200 | 3100 | 21 | 1(3 rows)alvindb=> SELECT currval('tb_test4_test_id_seq');currval---------2(1 row)alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (5);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> SELECT currval('tb_test4_test_id_seq');currval---------3(1 row)alvindb=> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;test_id | test_order---------+------------3 | 5200 | 3100 | 21 | 1(4 rows)alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (6);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> SELECT currval('tb_test4_test_id_seq');currval---------4(1 row)alvindb=> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;test_id | test_order---------+------------4 | 63 | 5200 | 3100 | 21 | 1(5 rows)alvindb=> DELETE FROM tb_test4 WHERE test_order = 5;DELETE 1alvindb=> DELETE FROM tb_test4 WHERE test_order = 6;DELETE 1alvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (7);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> SELECT currval('tb_test4_test_id_seq');currval---------5(1 row)alvindb=> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;test_id | test_order---------+------------5 | 7200 | 3100 | 21 | 1(4 rows)alvindb=>alvindb=> TRUNCATE TABLE tb_test4;TRUNCATE TABLEalvindb=> INSERT INTO tb_test4 (test_order) VALUES (8);INSERT 0 1alvindb=> SELECT currval('tb_test4_test_id_seq');currval---------6(1 row)alvindb=> SELECT * FROM tb_test4 ORDER BY 2 DESC;test_id | test_order---------+------------6 | 8(1 row)复制
通过上述详细的测试,可得出如下结论:
Oracle 和 PostgreSQL 测试结果相同,INSERT 比当前 Sequence 大的值, 还有 UPDATE/DELETE/TRUNCATE,均对其 Sequence 无影响。
而在MySQL 5.7 InnoDB ENGINE 中,INSERT 比当前 Sequence 大的值和 TRUNCATE 对其 Sequence 有影响,而 UPDATE/DELETE 对其 Sequence 无影响。
Sequence 调用方式对比
从下表可以看出,Oracle 与 PostgreSQL 对以下 Sequence 的调用方式都支持。MySQL 直接支持 AUTO INCREMENT 方式。
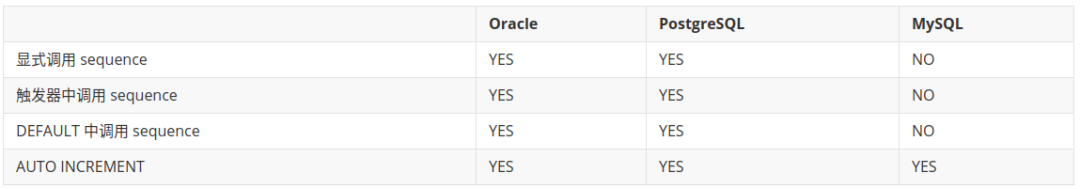
AUTO INCREMENT 方式对比
AUTO INCREMENT 主键创建方式对比如下:
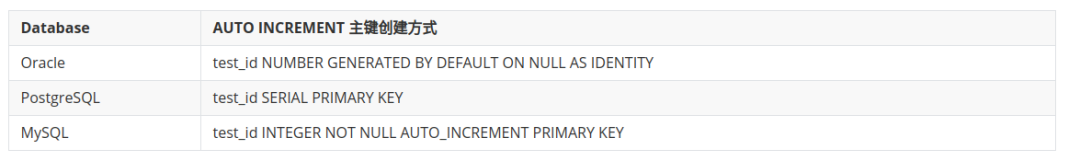
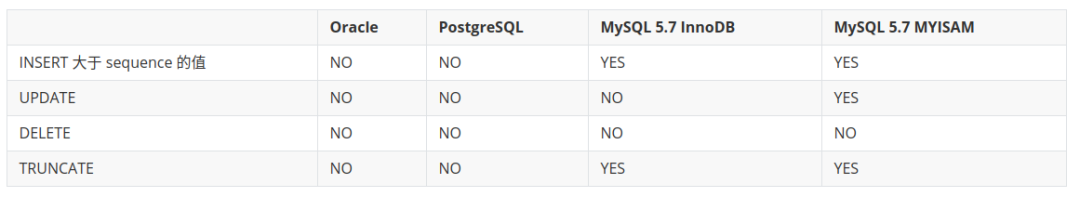
可以看出,AUTO INCREMENT 方式中,Oracle 和 PostgreSQL中,Sequence 与 UPDATE/DELETE/TRUNCATE 相对独立的,仅会在 INSERT 时自增,且在INSERT 大于 当前Sequence 的值时,并不会重置 Sequence。
在 MySQL 中,Sequence 的重置与否,不但与 MySQL DML/DDL 有关,还与表使用的 ENGINE有关,使用时需要特别注意。
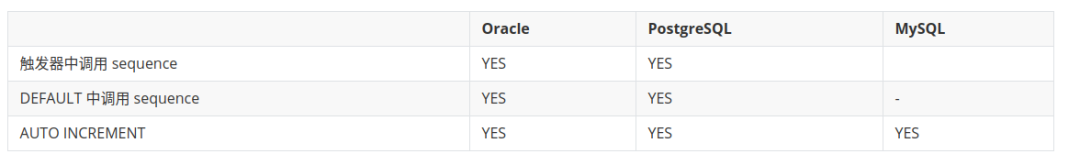
INSERT 方式对比
INSERT WITH SEQUENCE
以下方式在 SQL 中指明了 Sequence。
这种使用方式相对灵活,基本适用各种场景,尤其是大型复杂数据库应用中。
如果使用的数据库是 Oracle 或 PostgreSQL,推荐这种方式。
--OracleINSERT INTO tb_test (test_id) VALUES (seq_test.nextval);--PostgreSQLINSERT INTO tb_test (test_id) VALUES (nextval('seq_test'));复制
SQL 如下
INSERT INTO tb_test (test_order) VALUES (1);复制
可以看出,这种 INSERT 方式对以下三种数据库支持良好,且好记好理解。
从 SQL 对各数据库的兼容性考虑,推荐这种省略列名的方式。
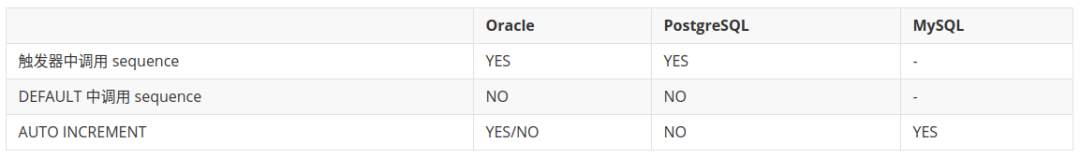
INSERT NULL
SQL 如下
INSERT INTO tb_test (test_id,test_order) VALUES (NULL,1);复制
从以下对比表格可以看出,支持不统一。
从 SQL 对各数据库的兼容性考虑,除非特意使用,一般不作推荐。
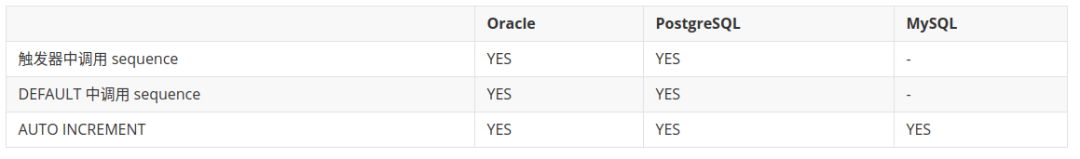
INSERT DEFAULT
SQL 如下
INSERT INTO tb_test (test_id,test_order) VALUES (DEFAULT,1);复制
但在触发器调用 Sequence 的方式中,DEFAULT 并不是专门用来插入 Sequence 的下一个值的,此时就没必要使用 DEFAULT 了。
DEFAULT 一般仅在定义了列的 DEFAULT 值时使用。
具体对比如下表所示。
招募贴:












