在阅读本文之前,需要对列存表的存储结构有基本的了解,可以参考列存表的介绍文章:openGauss存储技术(二)——列存储引擎和内存引擎
概述
PSort(Partial sort) Index是在列存表的列上建的聚簇索引。CUDesc 上有每个 CU 的 min 和 max 值,但如果业务的数据模型较为离散,查询时通过 min 和 max 值去过滤 CU 会出现大量的 CU 误读取,例如每个 CU 的 min 和 max跨度都比较大时,其查询效率接近全表扫描。例如下图中的场景,查询2基本命中所有的 CU, 此时查找近似全表扫描。
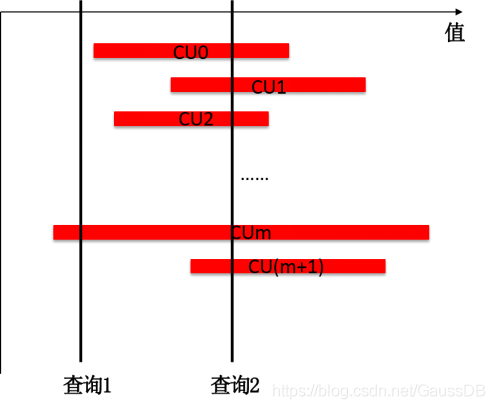
PSort索引可以对部分区间(一般会包含多个CU覆盖的行)内的数据按照索引键进行排序,使得 CU 之间的交集尽量减少,提升查询的效率。
PSort 索引使用
在批量插入列存表的过程中,如果发现有 PSort 索引,会先对这批数据进行排序。PSort索引表的组织形式也是 cstore 表(CUDesc 是 astore 表),表的字段包含了索引键的各个字段,加上对应的行号(TID)字段。插入数据的过程中如果发现有PSort索引,会将一定数量的数据按照PSort索引的索引键进行排序,与 TID 字段共同拼装成向量数组,再插入到 PSort 索引的 cstore 表中。 所以 PSort 索引数据中列数比实际的索引键要多一列,多出的这一列用于存储这条记录在数据 cstore 存储中的位置。
// 构建 PSort 索引过程中构造索引数据
inline void ProjectToIndexVector(VectorBatch *scanBatch, VectorBatch *outBatch, IndexInfo *indexInfo)
{
Assert(scanBatch && outBatch && indexInfo);
int numAttrs = indexInfo->ii_NumIndexAttrs;
AttrNumber *attrNumbers = indexInfo->ii_KeyAttrNumbers;
Assert(outBatch->m_cols == (numAttrs + 1));
// index column
for (int i = 0; i < numAttrs; i++) {
AttrNumber attno = attrNumbers[i];
Assert(attno > 0 && attno <= scanBatch->m_cols);
// shallow copy
outBatch->m_arr[i].copy(&scanBatch->m_arr[attno - 1]);
}
// ctid column
// 最后一列是 tid
outBatch->m_arr[numAttrs].copy(scanBatch->GetSysVector(-1));
outBatch->m_rows = scanBatch->m_rows;
}
cstore 表执行插入流程,如果有 Psort 索引,会先将数据插入排序队列
void CStoreInsert::BatchInsert(_in_ VectorBatch* pBatch, _in_ int options)
{
Assert(pBatch || IsEnd());
/* keep memory space from leaking during bulk-insert */
MemoryContext oldCnxt = MemoryContextSwitchTo(m_tmpMemCnxt);
// Step 1: relation has partial cluster key
// We need put data into sorter contatiner, and then do
// batchinsert data
if (NeedPartialSort()) {
Assert(m_tmpBatchRows);
if (pBatch) {
Assert(pBatch->m_cols == m_relation->rd_att->natts);
m_sorter->PutVecBatch(m_relation, pBatch); // 插入局部排序队列
}
if (m_sorter->IsFull() || IsEnd()) { // 排序队列满了或者插入数据输入结束
m_sorter->RunSort(); // 按照索引键排序
/* reset and fetch next batch of values */
DoBatchInsert(options);
m_sorter->Reset(IsEnd());
/* reset and free all memory blocks */
m_tmpBatchRows->reset(false);
}
}
// Step 2: relation doesn't have partial cluster key
// We need cache data until batchrows is full
else {
Assert(m_bufferedBatchRows);
// If batch row is full, we can do batchinsert now
if (IsEnd()) {
if (ENABLE_DELTA(m_bufferedBatchRows)) {
InsertDeltaTable(m_bufferedBatchRows, options);
} else {
BatchInsertCommon(m_bufferedBatchRows, options);
}
m_bufferedBatchRows->reset(true);
}
// we need cache data until batchrows is full
if (pBatch) {
Assert(pBatch->m_rows <= BatchMaxSize);
Assert(pBatch->m_cols && m_relation->rd_att->natts);
Assert(m_bufferedBatchRows->m_rows_maxnum > 0);
Assert(m_bufferedBatchRows->m_rows_maxnum % BatchMaxSize == 0);
int startIdx = 0;
while (m_bufferedBatchRows->append_one_vector(
RelationGetDescr(m_relation), pBatch, &startIdx, m_cstorInsertMem)) {
BatchInsertCommon(m_bufferedBatchRows, options);
m_bufferedBatchRows->reset(true);
}
Assert(startIdx == pBatch->m_rows);
}
}
// Step 3: We must update index data for this batch data
// if end of batchInsert
FlushIndexDataIfNeed();
MemoryContextReset(m_tmpMemCnxt);
(void)MemoryContextSwitchTo(oldCnxt);
}

图-1 cstore表插入流程示意图
插入流程中更新索引数据的代码
void CStoreInsert::InsertIdxTableIfNeed(bulkload_rows* batchRowPtr, uint32 cuId)
{
Assert(batchRowPtr);
if (relation_has_indexes(m_resultRelInfo)) {
/* form all tids */
bulkload_indexbatch_set_tids(m_idxBatchRow, cuId, batchRowPtr->m_rows_curnum);
for (int indice = 0; indice < m_resultRelInfo->ri_NumIndices; ++indice) {
/* form index-keys data for index relation */
for (int key = 0; key < m_idxKeyNum[indice]; ++key) {
bulkload_indexbatch_copy(m_idxBatchRow, key, batchRowPtr, m_idxKeyAttr[indice][key]);
}
/* form tid-keys data for index relation */
bulkload_indexbatch_copy_tids(m_idxBatchRow, m_idxKeyNum[indice]);
/* update the actual number of used attributes */
m_idxBatchRow->m_attr_num = m_idxKeyNum[indice] + 1;
if (m_idxInsert[indice] != NULL) {
/* 插入PSort 索引 */
m_idxInsert[indice]->BatchInsert(m_idxBatchRow, 0);
} else {
/* 插入 cbtree/cgin 索引 */
CStoreInsert::InsertNotPsortIdx(indice);
}
}
}
}
索引插入流程和普通 cstore 数据插入相同。
使用 PSort 索引查询时,由于 PSort 索引 CU 内部已经有序,因此可以使用二分查找快速找到对应数据在 psort 索引中的行号,这一行数据的 tid 字段就是这条数据在数据 cstore 中的行号。
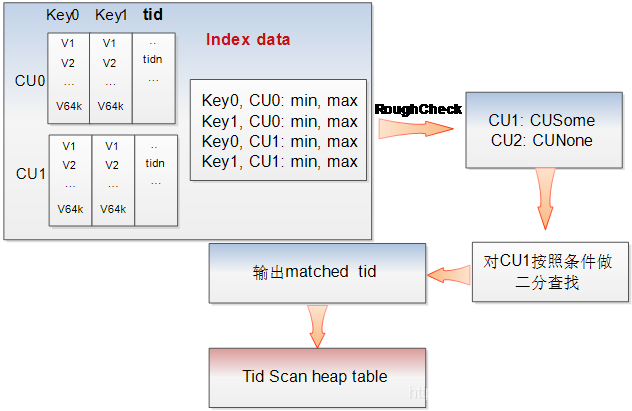
图-2 PSort 索引查询示意图
参考资料:
openGauss存储技术(二)——列存储引擎和内存引擎
openGauss数据库源码解析系列文章——存储引擎源码解析(五)






