
一 背景和架构
Transformation
remove_redundant_subquery_clause : Permanently remove redundant parts from the query if 1) This is a subquery 2) Not normalizing a view. Removal should take place when a query involving a view is optimized, not when the view is created.
remove_base_options: Remove SELECT_DISTINCT options from a query block if can skip distinct
resolve_subquery : Resolve predicate involving subquery, perform early unconditional subquery transformations
Convert subquery predicate into semi-join, or Mark the subquery for execution using materialization, or Perform IN->EXISTS transformation, or Perform more/less ALL/ANY -> MIN/MAX rewrite Substitute trivial scalar-context subquery with its value
transform_scalar_subqueries_to_join_with_derived: Transform eligible scalar subqueries to derived tables.
flatten_subqueries : Convert semi-join subquery predicates into semi-join join nests. Convert candidate subquery predicates into semi-join join nests. This transformation is performed once in query lifetime and is irreversible.
apply_local_transforms :
delete_unused_merged_columns : If query block contains one or more merged derived tables/views, walk through lists of columns in select lists and remove unused columns. simplify_joins : Convert all outer joins to inner joins if possible. prune_partitions :Perform partition pruning for a given table and condition.
push_conditions_to_derived_tables : Pushing conditions down to derived tables must be done after validity checks of grouped queries done by apply_local_transforms();
Window::eliminate_unused_objects: Eliminate unused window definitions, redundant sorts etc.
二 详细转换过程
1 解析子查询(resolve_subquery)
标记subquery是否变成semi-join
转换判断条件 检查OPTIMIZER_SWITCH_SEMIJOIN和HINT没有限制 子查询是IN/=ANY和EXIST subquery的谓词 子查询是简单查询块而不是UNION 子查询无隐形和显性的GROUP BY 子查询没有HAVING、WINDOW函数 Resolve的阶段是Query_block::RESOLVE_CONDITION和Query_block::RESOLVE_JOIN_NEST并且没有用到最新的Hyper optimizer优化器。 外查询块可以支持semijoins 至少要一个表,而不是类似"SELECT 1" 子查询的策略还没有指定Subquery_strategy::UNSPECIFIED 父查询也至少有一个表 父查询和子查询都不能有straight join 父查询块不禁止semijoin IN谓词返回值是否是确定的,不是RAND 根据子查询判断结果是否需要转成true还是false以及是否为NULL,判断是可以做antijoin还是semijoin Antijoin是可以支持的,或者是semijoin offset和limit对于semjoin是有效的,offset是从第一行开始,limit也不是0 设置Subquery_strategy::CANDIDATE_FOR_SEMIJOIN并添加sj_candidates
标记subquery是否执行时采用materialization方案
如果不符合转换semijoin,尝试使用物化方式,转换判断条件 Optimzier开关subquery_to_derived=on 子查询是IN/=ANY or EXISTS谓词 子查询是简单查询块而不是UNION 如果是[NOT] EXISTS,必须没有聚合 Subquery谓词在WHERE子句(目前没有在ON子句实现),而且是ANDs or ORs的表达式tree 父查询块支持semijoins 子查询的策略还没有指定Subquery_strategy::UNSPECIFIED 父查询也至少有一个表,然后可以做LEFT JOIN 父查询块不禁止semijoin IN谓词返回值是否是确定的,不是RAND 根据子查询判断结果是否需要转成true还是false以及是否为NULL,判断是可以做antijoin还是semijoin 不支持左边参数不是multi-column子查询(WHERE (outer_subq) = ROW(derived.col1,derived.col2)) 该子查询不支持转换为Derived table(m_subquery_to_derived_is_impossible) 设置Subquery_strategy::CANDIDATE_FOR_DERIVED_TABLE并添加sj_candidates
如果上面两个策略无法使用,根据类型选择transformer
Item_singlerow_subselect::select_transformer 对于简单的标量子查询,在查询中直接用执行结果代替
select * from t1 where a = (select 1);=>select * from t1 where a = 1;
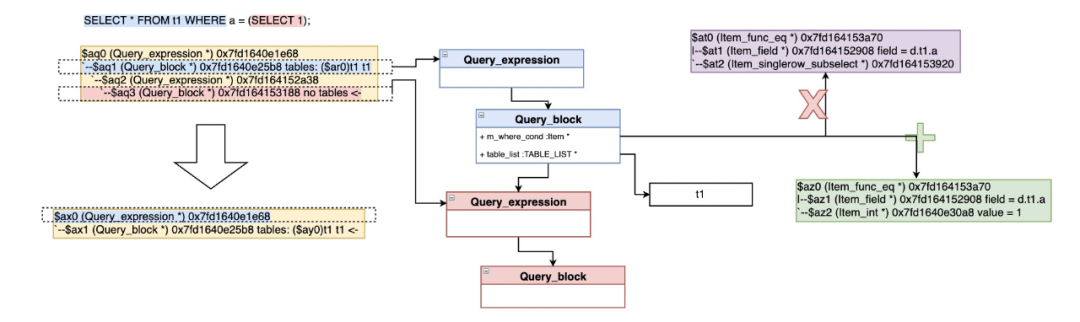
Item_in_subselect/Item_allany_subselect::select_transformer->select_in_like_transformer
select_in_like_transformer函数来处理 IN/ALL/ANY/SOME子查询转换transformation
处理"SELECT 1"(Item_in_optimizer)
如果目前还没有子查询的执行方式,也就是无法使用semijoin/antijoin执行的子查询,会做IN->EXISTS的转换,本质是在物化执行和迭代式循环执行中做选择。IN语法代表非相关子查询仅执行一次,将查询结果物化成临时表,之后需要结果时候就去物化表中查找;EXISTS代表对于外表的每一条记录,子查询都会执行一次,是迭代式循环执行。子查询策略设定为Subquery_strategy::CANDIDATE_FOR_IN2EXISTS_OR_MAT
重写single-column的IN/ALL/ANY子查询(single_value_transformer)
oe $cmp$ (SELECT ie FROM ... WHERE subq_where ... HAVING subq_having)=>- oe $cmp$ (SELECT MAX(...) ) handled by Item_singlerow_subselect- oe $cmp$ \<max\>(SELECT ...) handled by Item_maxmin_subselectfails=>Item_in_optimizer- 对于已经是materialized方案,不转换- 通过equi-join转换IN到EXISTS
如果是ALL/ANY单值subquery谓词,尝试用MIN/MAX子查询转换
SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE a < ANY (SELECT a FROM t1);=>SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE a < (SELECT MAX(a) FROM t1)
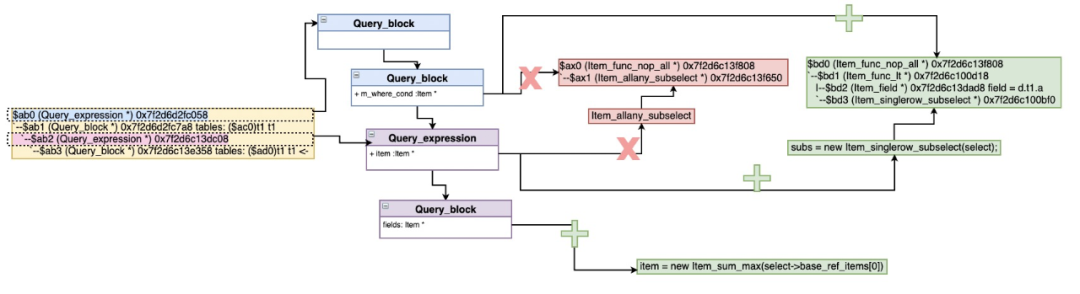
不满足上面,调用single_value_in_to_exists_transformer转换IN到EXISTS
转换将要将子查询设置为相关子查询,设置UNCACHEABLE_DEPENDENT标识 如果子查询包含聚合函数、窗口函数、GROUP语法、HAVING语法,将判断条件加入到HAVING子句中,另外通过ref_or_null_helper来区分NULL和False的结果,如需要处理NULL IN (SELECT ...)还需要封装到Item_func_trig_cond触发器中。
SELECT ... FROM t1 WHERE t1.b IN (SELECT <expr of SUM(t1.a)> FROM t2)=>SELECT ... FROM t1 WHERE t1.b IN (SELECT <expr of SUM(t1.a)> FROM t2[trigcond] HAVING t1.b=ref-to-<expr of SUM(t1.a)>)
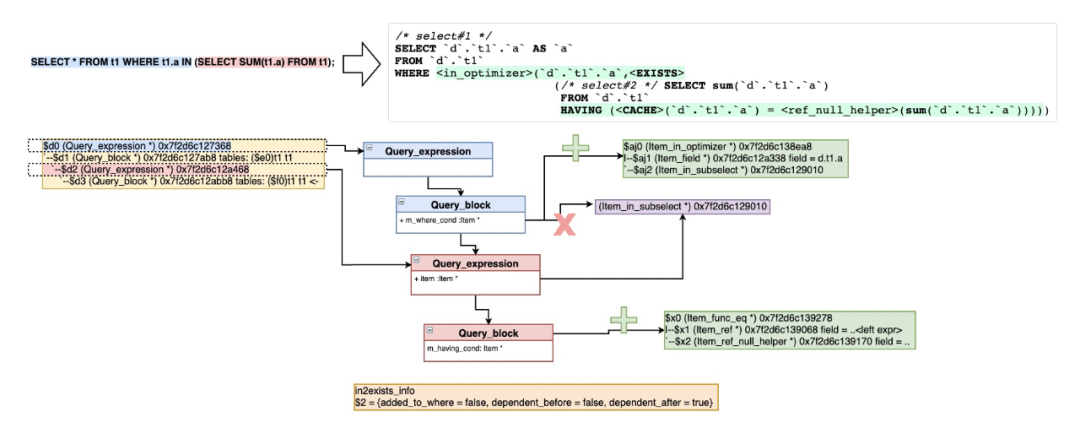
如果子查询不包含聚合函数、窗口函数、GROUP语法,会放在WHERE查询条件中,当然如果需要处理NULL情况还是要放入HAVING子句(Item_func_trig_cond+Item_is_not_null_test)。
不需要区分NULL和FALSE的子查询:SELECT 1 FROM ... WHERE (oe $cmp$ ie) AND subq_where需要区分的子查询:SELECT 1 FROM ...WHERE subq_where AND trigcond((oe $cmp$ ie) OR (ie IS NULL))HAVING trigcond(@<is_not_null_test@>(ie))
JOIN::optimize()会计算materialization和EXISTS转换的代价进行选择,设置m_subquery_to_derived_is_impossible = true
ROW值转换,通过Item_in_optimizer,不支持ALL/ANY/SOME(row_value_transformer)
Item_in_subselect::row_value_in_to_exists_transformer
for (each left operand)create the equi-join conditionif (is_having_used || !abort_on_null)create the "is null" and is_not_null_test itemsif (is_having_used)add the equi-join and the null tests to HAVINGelseadd the equi-join and the "is null" to WHEREadd the is_not_null_test to HAVING
没有HAVING表达式
(l1, l2, l3) IN (SELECT v1, v2, v3 ... WHERE where) =>EXISTS (SELECT ... WHERE where and(l1 = v1 or is null v1) and(l2 = v2 or is null v2) and(l3 = v3 or is null v3)[ HAVING is_not_null_test(v1) andis_not_null_test(v2) andis_not_null_test(v3)) ] <-- 保证不为NULL可以去掉HAVING
有HAVING表达式
(l1, l2, l3) IN (SELECT v1, v2, v3 ... HAVING having) =>EXISTS (SELECT ... HAVING having and(l1 = v1 or is null v1) and(l2 = v2 or is null v2) and(l3 = v3 or is null v3) andis_not_null_test(v1) andis_not_null_test(v2) andis_not_null_test(v3))
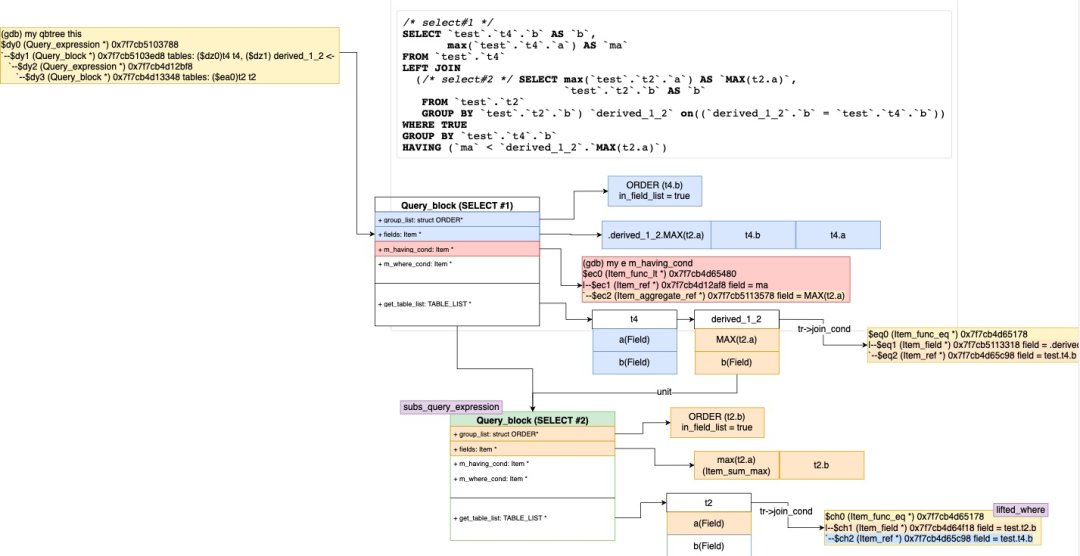
2 转换的标量子查询转换成Derived Table(transform_scalar_subqueries_to_join_with_derived)
root:test> set optimizer_switch = 'subquery_to_derived=off';Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)root:test> EXPLAIN SELECT b, MAX(a) AS ma FROM t4 GROUP BY b HAVING ma < (SELECT MAX(t2.a) FROM t2 WHERE t2.b=t4.b);+----+--------------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+--------------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------+| 1 | PRIMARY | t4 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | Using temporary || 2 | DEPENDENT SUBQUERY | t2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 33.33 | Using where |+----+--------------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------+2 rows in set, 3 warnings (0.00 sec)root:test> set optimizer_switch = 'subquery_to_derived=on';Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)root:test> EXPLAIN SELECT b, MAX(a) AS ma FROM t4 GROUP BY b HAVING ma < (SELECT MAX(t2.a) FROM t2 WHERE t2.b=t4.b);+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+| 1 | PRIMARY | t4 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 10 | 100.00 | Using temporary || 1 | PRIMARY | <derived2> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (hash join) || 2 | DERIVED | t2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 3 | 100.00 | Using temporary |+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+3 rows in set, 3 warnings (0.01 sec)
transform_scalar_subqueries_to_join_with_derived具体转换的过程如下:
首先从JOIN条件、WHERE条件、HAVING条件和SELECT list中收集可以转换的标量子查询(Item::collect_scalar_subqueries)。 遍历这些子查询,判断是否可以增加一个额外的转换(transform_grouped_to_derived):把隐性的GROUP BY标量子查询变成Derived Table。
SELECT SUM(c1), (SELECT SUM(c1) FROM t3) scalar FROM t1;转换为=>SELECT derived0.summ, derived1.scalarFROM (SELECT SUM(a) AS summ FROM t1) AS derived0LEFT JOIN(SELECT SUM(b) AS scalar FROM t3) AS derived1ON TRUE执行计划如下:explain SELECT SUM(a), (SELECT SUM(c1) FROM t3) scalar FROM t1;+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+| 1 | PRIMARY | <derived3> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | NULL || 1 | PRIMARY | <derived4> | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using where; Using join buffer (hash join) || 4 | DERIVED | t3 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | NULL || 3 | DERIVED | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | NULL |+----+-------------+------------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+--------------------------------------------+
收集唯一的聚合函数Item列表(collect_aggregates),这些Item将会被新的Derived Table的列代替。
还需要添加所有引用到这些Item的fields,包括直接在SELECT列表的,Window函数参数、ORDER by、Partition by包含的,还有该查询块中ORDER BY的列,因为他们都会引动到Derived Table里。 创建Derived Table需要的Query_expression/Query_block(create_query_expr_and_block)。 添加Derived Table到查询块和top_join_list中。 保留旧的子查询单元块,如果包含可以转化的Derived的移到Derived Table下面的Query_block,如果不包含,保留到原来的子查询块中。 将之前的聚合函数Item列表插入到Derived Table的查询块中。 收集除GROUP AGG表达式中的列,由于这些fields已经移动到Derived Table中,删除不合理的fields引用。 收集所有唯一的列和View的引用后,将他们加到新的Derived Table列表中。 对新的新的Derived Table进行flatten_subqueries/setup_tables 重新resolve_placeholder_tables,不处理进行转换后的子查询。 处理Derived Table中,新加入的HAVING条件中的聚合函数Item,并通过Item_aggregate_refs引用到new_derived->base_ref_items而不是之前的父查询块base_ref_items。 永久代替父查询块中的聚合函数列表,变成Derived Table的列,并删除他们。 之前保存和加入到Derived Table的唯一的列和View的引用,也要替换新的fields代替他们的引用。

但目前不支持HAVING表达式中包含该子查询,其实也是可以转换的。
SELECT SUM(a), (SELECT SUM(b) FROM t3) scalarFROM t1HAVING SUM(a) > scalar;转换为=>SELECT derived0.summ, derived1.scalarFROM (SELECT SUM(a) AS summ FROM t1) AS derived0LEFT JOIN(SELECT SUM(b) AS scalar FROM t3) AS derived1ON TRUEWHERE derived0.sum > derived1.scalar;
接下来遍历所有可以转换的子查询,把他们转换成derived tables,并替换相应的表达式变成列(transform_subquery_to_derived)。
生成derived table的TABLE_LIST(synthesize_derived)。 将可以移动到derived table的where_cond设置到join_cond上。 添加derived table到查询块的表集合中。 decorrelate_derived_scalar_subquery_pre 添加非相关引用列(NCF)到SELECT list,这些条件被JOIN条件所引用,并且还有另外一个fields包含了外查询相关的列,我们称之为'lifted_where' 添加COUNT(*)到SELECT list,这样转换的查询块可以进行cardinality的检查。比如没有任何聚合函数在子查询中。如果确定包含聚合函数,返回一行一定是NCF同时在GROUP BY列表中。 添加NCF到子查询的GROUP列表中,如果已经在了,需要加到最后,如果发生GROUP BY的列由于依赖性检查失败,还要加Item_func_any_value(非聚合列)到SELECT list。对于NCF会创建 derived.field和derived.`count(field)` 。 设置物化的一些准备(setup_materialized_derived)。 decorrelate_derived_scalar_subquery_post: 创建对应的'lifted_fields'。 更新JOIN条件中相关列的引用,不在引用外查询而换成Derived table相关的列。
代替WHERE、JOIN、HAVING条件和SELECT list中的子查询的表达式变成对应的Derived Table里面列。
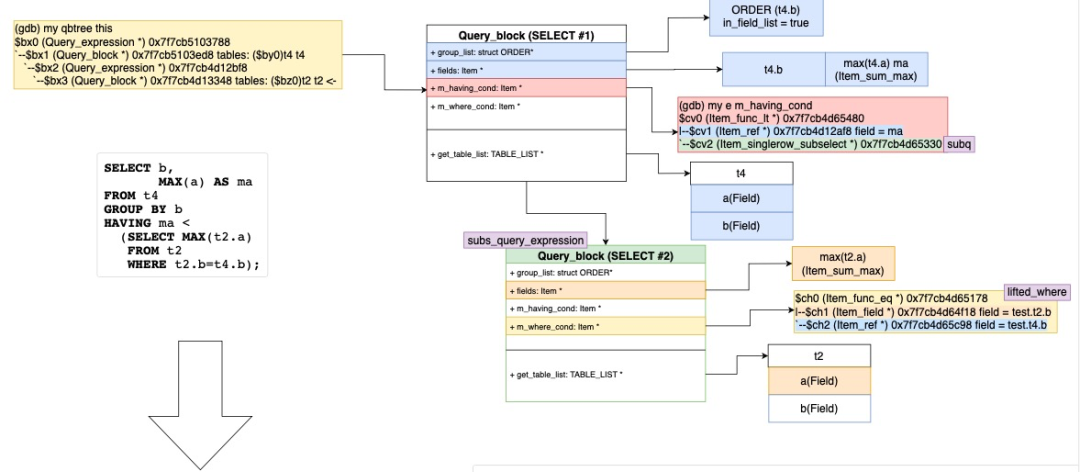
3 扁平化子查询(flatten_subqueries)
简单来讲步骤可以简化理解为:
创建SEMI JOIN (it1 ... itN)语以部分,并加入到外层查询块的执行计划中。 将子查询的WHERE条件以及JOIN条件,加入到父查询的WHERE条件中。 将子查询谓词从父查询的判断谓词中消除。
由于MySQL在一个query block中能够join的tables数是有限的(MAX_TABLES),不是所有sj_candidates都可以做因此做flatten_subqueries 的,因此需要有优先级决定的先后顺序先unnesting掉,优先级规则如下:
相关子查询优先于非相关的 inner tables多的子查询大于inner tables少的 位置前的子查询大于位置后的
subq_item->sj_convert_priority =(((dependent * MAX_TABLES_FOR_SIZE) + // dependent subqueries firstchild_query_block->leaf_table_count) *65536) + // then with many tables(65536 - subq_no); // then based on position
另外,由于递归调用flatten_subqueries是bottom-up,依次把下层的子查询展开到外层查询块中。
for SELECT#1 WHERE X IN (SELECT #2 WHERE Y IN (SELECT#3)) :Query_block::prepare() (select#1)-> fix_fields() on IN condition-> Query_block::prepare() on subquery (select#2)-> fix_fields() on IN condition-> Query_block::prepare() on subquery (select#3)<- Query_block::prepare()<- fix_fields()-> flatten_subqueries: merge #3 in #2<- flatten_subqueries<- Query_block::prepare()<- fix_fields()-> flatten_subqueries: merge #2 in #1
遍历子查询列表,删除Item::clean_up_after_removal标记为Subquery_strategy::DELETED的子查询,并且根据优先级规则设置sj_convert_priority。根据优先级进行排序。
遍历排序后的子查询列表,对于Subquery_strategy::CANDIDATE_FOR_DERIVED_TABLE策略的子查询,转换子查询([NOT] {IN, EXISTS})为JOIN的Derived table(transform_table_subquery_to_join_with_derived)
FROM [tables] WHERE ... AND/OR oe IN (SELECT ie FROM it) ...=>FROM (tables) LEFT JOIN (SELECT DISTINCT ie FROM it) AS derivedON oe = derived.ie WHERE ... AND/OR derived.ie IS NOT NULL ...
设置策略为Subquery_strategy::DERIVED_TABLE
semijoin子查询不能和antijoin子查询相互嵌套,或者外查询表已经超过MAX_TABLE,不做转换,否则标记为Subquery_strategy::SEMIJOIN策略。 判断子查询的WHERE条件是否为常量。如果判断条件永远为FALSE,那么子查询结果永远为空。该情况下,调用Item::clean_up_after_removal标记为Subquery_strategy::DELETED,删除该子查询。 如果无法标记为Subquery_strategy::DELETED/设置Subquery_strategy::SEMIJOIN策略的重新标记会Subquery_strategy::UNSPECIFIED继续下一个。 替换外层查询的WHERE条件中子查询判断的条件(replace_subcondition) 子查询内条件并不永远为FALSE,或者永远为FALSE的情况下,需要改写为antijoin(antijoin情况下,子查询结果永远为空,外层查询条件永远通过)。此时将条件改为永远为True。 子查询永远为FALSE,且不是antijoin。那么将外层查询中的条件改成永远为False。
Item_subselect::EXISTS_SUBS不支持有聚合操作
convert_subquery_to_semijoin函数解析如下模式的SQL IN/=ANY谓词
如果条件满足解关联,解关联decorrelate_condition
添加解关联的内表表达式到 SELECT list
收集FROM子句中的外表相关的 derived table或join条件
去掉关联标识UNCACHEABLE_DEPENDENT,更新used table
Derived table子查询增加SELECT_DISTINCT标识
转换子查询成为一个derived table,并且插入到所属于的查询块FROM后(transform_subquery_to_derived)
创建derived table及其join条件
遍历父查询块的WHERE,替换该子查询的Item代替成derived table(replace_subcondition)
遍历排序后的子查询列表,对于Subquery_strategy::CANDIDATE_FOR_SEMIJOIN策略的子查询。
判断是否可以转换为semijoin
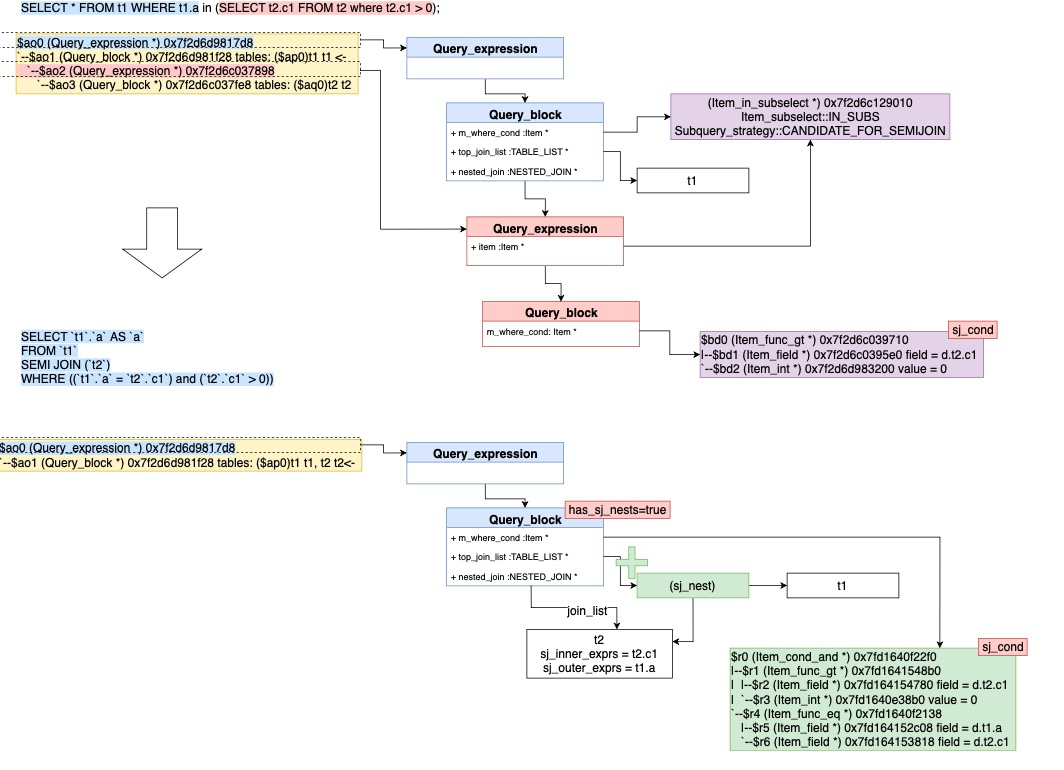
遍历排序后的子查询列表,对于Subquery_strategy::SEMIJOIN的子查询,开始转换为semijoin/antijoin(convert_subquery_to_semijoin)
convert_subquery_to_semijoin函数解析如下模式的SQL IN/=ANY谓词
SELECT ...FROM ot1 ... otNWHERE (oe1, ... oeM) IN (SELECT ie1, ..., ieMFROM it1 ... itK[WHERE inner-cond])[AND outer-cond][GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]=>SELECT ...FROM (ot1 ... otN) SJ (it1 ... itK)ON (oe1, ... oeM) = (ie1, ..., ieM)[AND inner-cond][WHERE outer-cond][GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]
EXISTS谓词
SELECT ...FROM ot1 ... otNWHERE EXISTS (SELECT expressionsFROM it1 ... itK[WHERE inner-cond])[AND outer-cond][GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]=>SELECT ...FROM (ot1 ... otN) SJ (it1 ... itK)[ON inner-cond][WHERE outer-cond][GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]
NOT EXISTS谓词
SELECT ...FROM ot1 ... otNWHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT expressionsFROM it1 ... itK[WHERE inner-cond])[AND outer-cond][GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]=>SELECT ...FROM (ot1 ... otN) AJ (it1 ... itK)[ON inner-cond][WHERE outer-cond AND is-null-cond(it1)][GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]
NOT IN谓词
SELECT ...FROM ot1 ... otNWHERE (oe1, ... oeM) NOT IN (SELECT ie1, ..., ieMFROM it1 ... itK[WHERE inner-cond])[AND outer-cond][GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]=>SELECT ...FROM (ot1 ... otN) AJ (it1 ... itK)ON (oe1, ... oeM) = (ie1, ..., ieM)[AND inner-cond][WHERE outer-cond][GROUP BY ...] [HAVING ...] [ORDER BY ...]
查找可以插入semi-join嵌套和其生成的条件的位置,比如对于 t1 LEFT JOIN t2, embedding_join_nest为t2,t2也可以是nested,如t1 LEFT JOIN (t2 JOIN t3))
生成一个新的semijoin嵌套的TABLE_LIST表
处理Antijoin
将子查询中潜在的表合并到上述join表(TABLE_LIST::merge_underlying_tables)
将子查询的叶子表插入到当前查询块的叶子表后面,重新设置子查询的叶子表的序号和依赖的外表。将子查询的叶子表重置。
如果是outer join的话,在join链表中传递可空性(propagate_nullability)
将内层子查询中的关联条件去关联化,这些条件被加入到semijoin的列表里。这些条件必须是确定的,仅支持简单判断条件或者由简单判断条件组成的AND条件(Query_block::decorrelate_condition)
判断左右条件是否仅依赖于内外层表,将其表达式分别加入到semijoin内外表的表达式列表中(decorrelate_equality)
解关联内层查询的join条件(Query_block::decorrelate_condition)
移除该子查询表达式在父查询的AST(Query_express::exclude_level)
根据semi-join嵌套产生的WHERE/JOIN条件更新对应的table bitmap(Query_block::fix_tables_after_pullout)
将子查询的WHERE条件上拉,更新使用表的信息(Item_cond_and::fix_after_pullout())
根据semijoin的条件列表创建AND条件,如果有条件为常量True,则去除该条件;如果常量为False,则整个条件都去除(Query_block::build_sj_cond)
将创建出来的semijoin条件加入到外层查询的WHERE条件中
最后遍历排序后的子查询列表,对于没有转换的子查询,对于Subquery_strategy::UNSPECIFIED的策略,执行IN->EXISTS改写(select_transformer),如果确实原有的子查询已经有替代的Item,调用replace_subcondition解析并把他们加入到合适的WHERE或者ON子句。
清除所有的sj_candidates列表
Semi-join有5中执行方式,本文并不介绍Optimizer和Execution过程,详细可以参考引用文章中关于semijoin的介绍,最后引入下控制semijoin优化和执行的优化器开关,其中semijoin=on/off是总开关。
SELECT @@optimizer_switch\G*************************** 1. row ***************************@@optimizer_switch: ......materialization=on,semijoin=on,loosescan=on,firstmatch=on,subquery_materialization_cost_based=on,......
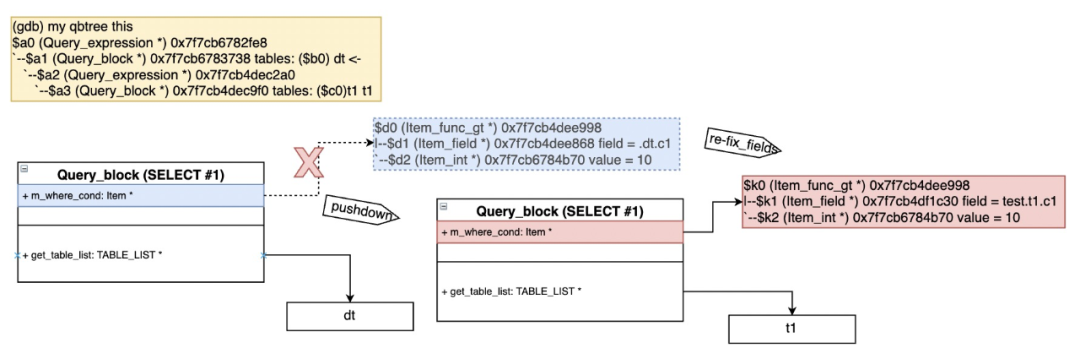
下图举例说明该转换过程:
SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE t1.a in (SELECT t2.c1 FROM t2 where t2.c1 > 0);=>/* select#1 */SELECT `t1`.`a` AS `a`FROM `t1`SEMI JOIN (`t2`)WHERE ((`t1`.`a` = `t2`.`c1`) and (`t2`.`c1` > 0))执行计划如下:explain SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE t1.a in (SELECT t2.c1 FROM t2 where t2.c1 > 0);+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+| 1 | SIMPLE | t2 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 1 | 100.00 | Using where; Start temporary || 1 | SIMPLE | t1 | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 50.00 | Using where; End temporary; Using join buffer (hash join) |+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+------+----------+-----------------------------------------------------------+
4 应用当前查询块转换(apply_local_transforms)
删除无用列(delete_unused_merged_columns)
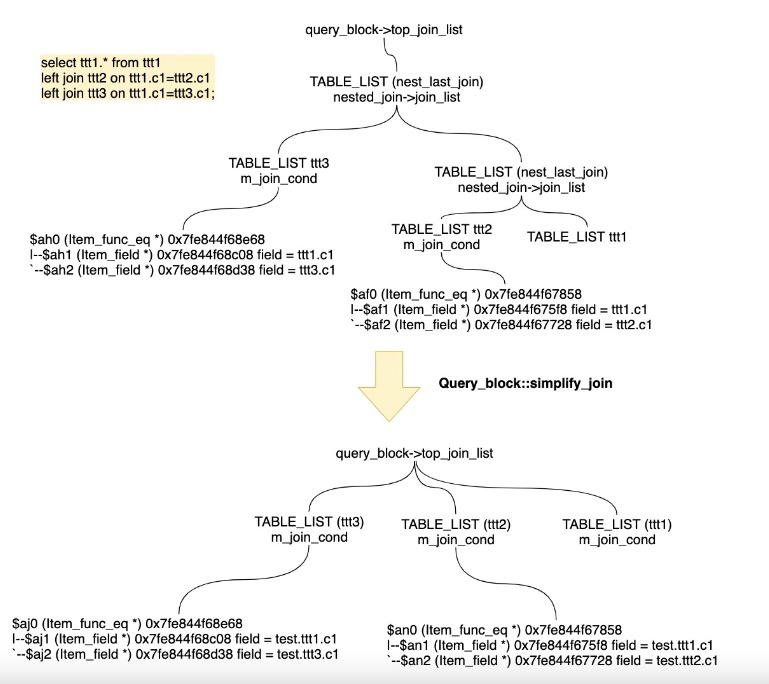
简化JOIN(simplify_joins)
分区表的静态剪枝(prune_partitions)
struct TABLE {......partition_info *part_info{nullptr}; /* Partition related information *//* If true, all partitions have been pruned away */bool all_partitions_pruned_away{false};......}SQL tranformation phaseSELECT_LEX::apply_local_transforms--> prune_partitionsfor example, select * from employee where company_id = 1000 ;SQL optimizer phaseJOIN::prune_table_partitions--> prune_partitions------> based on tbl->join_cond_optim() or JOIN::where_condfor example, explain select * from employee where company_id = (select c1 from t1);
举例下面RANGE剪枝的过程:
root:ref> CREATE TABLE R2 (-> a INT,-> d INT-> ) PARTITION BY RANGE(a) (-> PARTITION p20 VALUES LESS THAN (20),-> PARTITION p40 VALUES LESS THAN (40),-> PARTITION p60 VALUES LESS THAN (60),-> PARTITION p80 VALUES LESS THAN (80),-> PARTITION p100 VALUES LESS THAN MAXVALUE-> );Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.09 sec)root:ref> Select * From R2 where a > 40 and a < 80;
剪枝详细过程如下:
由于剪枝需要根据不同条件产生的pruning结果进行交集,因此剪枝过程中需要使用read_partitions这样的bitmap来保存是否使用该对应分区。另外剪枝过程类似迭代判断,因此引入了part_iterator来保存开始、结束和当前,以及对应需要获取区间范围的endpoint函数和获取下一个值next的迭代器函数。这里巧妙的运用了指针,来兼容不同分区类型Hash/Range/List类型,如下图所示:
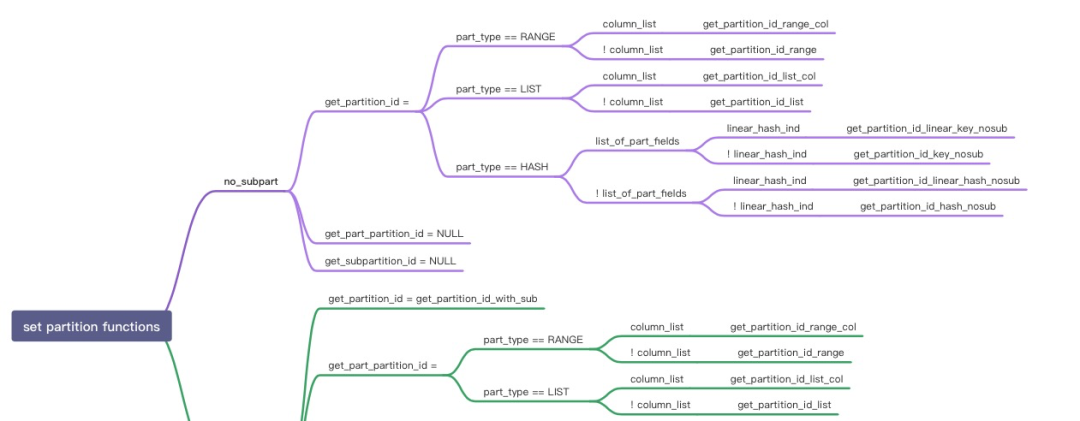
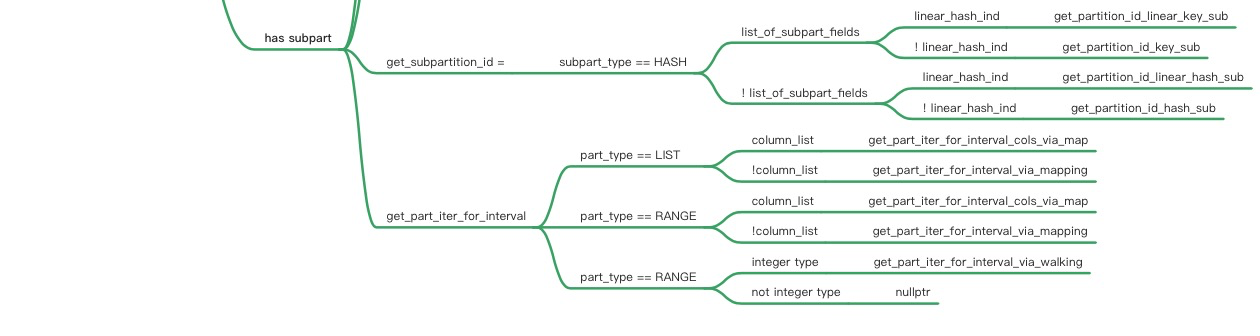
获取join_cond或者m_where_cond的SEL_TREE红黑树(get_mm_tree)
调用find_used_partitions来获取满足的分区,对于SEL_TREE的每个区间(interval):1. 获取区间的左右端点 2.从左边继续获取下一个满足的分区,直到到右边端点结束,每次调用完满足条件的分区需要使用bitmap_set_bit设置该分区在part_info->read_partitions上的位点。 find_used_partitions是根据SEL_TREE的结构进行递归,如图从左到右遍历next_key_part(and condition),然后再遍历SEL_TREE的左右(也就是上下方向,or condition)深度递归。
(start)| $| Partitioning keyparts $ subpartitioning keyparts| $| ... ... $| | | $| +---------+ +---------+ $ +-----------+ +-----------+\-| par1=c1 |--| par2=c2 |-----| subpar1=c3|--| subpar2=c5|+---------+ +---------+ $ +-----------+ +-----------+| $ | || $ | +-----------+| $ | | subpar2=c6|| $ | +-----------+| $ || $ +-----------+ +-----------+| $ | subpar1=c4|--| subpar2=c8|| $ +-----------+ +-----------+| $| $+---------+ $ +------------+ +------------+| par1=c2 |------------------| subpar1=c10|--| subpar2=c12|+---------+ $ +------------+ +------------+| $... $例如第一行(par1=c1 and par2=c2 and subpar1=c3 and subpar2=c5)的遍历的stack将是:in find_used_partitions(key_tree = "subpar2=c5") (***)in find_used_partitions(key_tree = "subpar1=c3")in find_used_partitions(key_tree = "par2=c2") (**)in find_used_partitions(key_tree = "par1=c1")in prune_partitions(...)然后是继续下面的条件,以此类推or(par1=c1 and par2=c2 and subpar1=c3 and subpar2=c6)or(par1=c1 and par2=c2 and subpar1=c4 and subpar2=c8)or(par1=c2 and subpar1=c10 and subpar2=c12)
下图来展示了pruning的结构和过程:

5 下推条件到Derived Table(push_conditions_to_derived_tables)
root:test> set optimizer_switch = 'derived_merge=off'; // 关闭dervied_merge 测试下推能力Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)root:test> EXPLAIN FORMAT=tree SELECT * FROM (SELECT c1,c2 FROM t1) as dt WHERE c1 > 10;+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+| EXPLAIN |+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+| -> Table scan on dt (cost=2.51..2.51 rows=1)-> Materialize (cost=2.96..2.96 rows=1)-> Filter: (t1.c1 > 10) (cost=0.35 rows=1)-> Table scan on t1 (cost=0.35 rows=1)|+-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
遍历derived table列表,判断是否可以下推(can_push_condition_to_derived),如果包括下面的情况则不能下推:
Derived table有UNION Derived table有LIMIT Derived table不能是outer join中的内表,会导致更多NULL补偿的行 不能是CTE包含的Derived table
创建可以下推到的Derived table的where cond(Condition_pushdown::make_cond_for_derived)
保留剩余不能下推的条件(Condition_pushdown::get_remainder_cond)
Top-down递归调用push_conditions_to_derived_tables
三 综述
四 参考资料
WL#3740: Subquery optimization: Semijoin: Pull-out of inner tables WL#3741: Subquery optimization: Semijoin: Duplicate elimination strategy WL#3750: Subquery optimization: Semijoin: First-match strategy WL#3751: Subquery optimization: Semijoin: Inside-out strategy
《WL#4389: Subquery optimizations: Make IN optimizations also handle EXISTS》
《WL#4245: Subquery optimization: Transform NOT EXISTS and NOT IN to anti-join》
推荐阅读


点击“阅读原文”了解PolarDB更多信息
文章转载自阿里云数据库,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






