翻译:尚凯
审核:魏波
目录
1 属性
2 运算符类和族
3 系统目录
属性
访问方法的所有属性都存储在«pg_am»表中(“am”代表访问方法)。我们还可以从同一个表中获取可用方法的列表:
postgres=# select amname from pg_am;amname--------btreehashgistginspgistbrin(6 rows)复制
虽然顺序扫描可以正确地引用访问方法,但由于历史原因,它不在此列表中。
在PostgreSQL9.5及更低版本中,每个属性都用«pg_am»表的单独字段表示。从9.6版本开始,属性使用特殊函数进行查询,并被分为多个层:
(1)访问方法属性 - «pg_indexam_has_property»
(2)特定索引的属性 - «pg_index_has_property»
(3)索引各列的属性 - «pg_index_column_has_property»
展望未来,访问方法层和索引层是分开的:到目前为止,所有基于一种访问方法的索引始终具有相同的属性。
1.以下是访问方法的4个属性(通过«btree»的示例)
postgres=# select a.amname, p.name, pg_indexam_has_property(a.oid,p.name)from pg_am a,unnest(array['can_order','can_unique','can_multi_col','can_exclude']) p(name)where a.amname = 'btree'order by a.amname;amname | name | pg_indexam_has_property--------+---------------+-------------------------btree | can_order | tbtree | can_unique | tbtree | can_multi_col | tbtree | can_exclude | t(4 rows)复制
(1) can_order
访问方法使我们能够在创建索引时指定值的排序顺序(目前仅适用于«btree»)。
(2) can_unique
支持唯一约束和主键(仅适用于«btree»)。
(3) can_multi_col
可以在多个列上构建索引。
(4) can_exclude
支持排除约束EXCLUDE。
2.以下属性与索引有关(让我们以一个现有的索引为例)
postgres=# select p.name, pg_index_has_property('t_a_idx'::regclass,p.name)from unnest(array['clusterable','index_scan','bitmap_scan','backward_scan']) p(name);name | pg_index_has_property---------------+-----------------------clusterable | tindex_scan | tbitmap_scan | tbackward_scan | t(4 rows)复制
(1) clusterable
可以根据索引重新排序行(使用同名命令CLUSTER进行)。
(2) index_scan
支持索引扫描。尽管此属性可能看起来很奇怪,但并非所有索引都可以逐个返回TID-有些索引一次返回所有结果,并且只支持位图扫描。
(3) bitmap_scan
支持位图扫描。
(4) backward_scan
可以按照构建索引时指定的顺序返回结果。
3.以下是列属性
postgres=# select p.name,pg_index_column_has_property('t_a_idx'::regclass,1,p.name)from unnest(array['asc','desc','nulls_first','nulls_last','orderable','distance_orderable','returnable','search_array','search_nulls']) p(name);name | pg_index_column_has_property--------------------+------------------------------asc | tdesc | fnulls_first | fnulls_last | torderable | tdistance_orderable | freturnable | tsearch_array | tsearch_nulls | t(9 rows)复制
(1) asc,desc,nulls_first,nulls_last,orderable
这些属性与值的排序有关(我们将在讨论«btree»索引时进一步描述)。
(2) distance_orderable
结果可以按操作确定的排序顺序返回(目前仅适用于GiST和RUM索引)。
(3) returnable
可以在不访问表的情况下使用索引,即支持仅索引扫描。
(4) search_array
支持使用表达式:
« indexed-field IN(list_of_constants)» 搜索多个值,
该表达式
与« indexed-field=ANY(array_of_constants)»相同。
(5)search_nulls
可以通过IS NULL和IS NOT NULL条件进行搜索。
我们已经详细讨论了一些属性。有些属性是特定于某些访问方法的。我们将在考虑这些具体方法时进一步展开描述。
运算符类和族
除了由所描述的接口公开的访问方法的属性之外,还需要信息来了解访问方法接受哪些数据类型和哪些操作符。为此,PostgreSQL引入了运算符类和运算符族概念。
运算符类包含用于操作特定数据类型的索引的最小运算符集(可能还有辅助函数)。
运算符类包含在某些运算符族中。此外,如果一个公共运算符族具有相同的语义,则它们可以包含多个运算符类。
例如,«integer_ops»系列:
包括«int8_ops»,«int4_ops»和«int2_ops»类,
用于类型«bigint»,«integer»和«smallint»,它们的大小不同,但含义相同:
postgres=# select opfname, opcname, opcintype::regtypefrom pg_opclass opc, pg_opfamily opfwhere opf.opfname = 'integer_ops'and opc.opcfamily = opf.oidand opf.opfmethod = (select oid from pg_am where amname = 'btree');opfname | opcname | opcintype-------------+----------+-----------integer_ops | int2_ops | smallintinteger_ops | int4_ops | integerinteger_ops | int8_ops | bigint(3 rows)复制
另一个例子:«datetime_ops»系列包括操作日期的运算符类(有时间和无时间):
postgres=# select opfname, opcname, opcintype::regtypefrom pg_opclass opc, pg_opfamily opfwhere opf.opfname = 'datetime_ops'and opc.opcfamily = opf.oidand opf.opfmethod = (select oid from pg_am where amname = 'btree');opfname | opcname | opcintype--------------+-----------------+-----------------------------datetime_ops | date_ops | datedatetime_ops | timestamptz_ops | timestamp with time zonedatetime_ops | timestamp_ops | timestamp without time zone(3 rows)复制
运算符族还可以包括其他运算符来比较不同类型的值。将谓词分组为多个族,使计划器能够为具有不同类型值的谓词使用索引。一个族也可以包含其他辅助功能。
在大多数情况下,我们不需要了解有关运算符族和类的任何信息。通常我们只是创建一个索引,默认情况下使用某个运算符类。
但是,我们可以显式指定运算符类。这是一个简单的示例,说明何时需要显式规范:在排序规则与C不同的数据库中,常规索引不支持LIKE操作:
postgres=# show lc_collate;lc_collate-------------en_US.UTF-8(1 row)postgres=# explain (costs off) select * from t where b like 'A%';QUERY PLAN-----------------------------Seq Scan on tFilter: (b ~~ 'A%'::text)(2 rows)复制
我们可以通过使用运算符类«text_pattern_ops»创建索引来克服此限制(注意计划中的条件如何更改):
postgres=# create index on t(b text_pattern_ops);postgres=# explain (costs off) select * from t where b like 'A%';QUERY PLAN----------------------------------------------------------------Bitmap Heap Scan on tFilter: (b ~~ 'A%'::text)-> Bitmap Index Scan on t_b_idx1Index Cond: ((b ~>=~ 'A'::text) AND (b ~<~ 'B'::text))(4 rows)复制
系统目录
在本文的结尾,我们提供了系统目录中与运算符类和族直接相关的表的简化图。
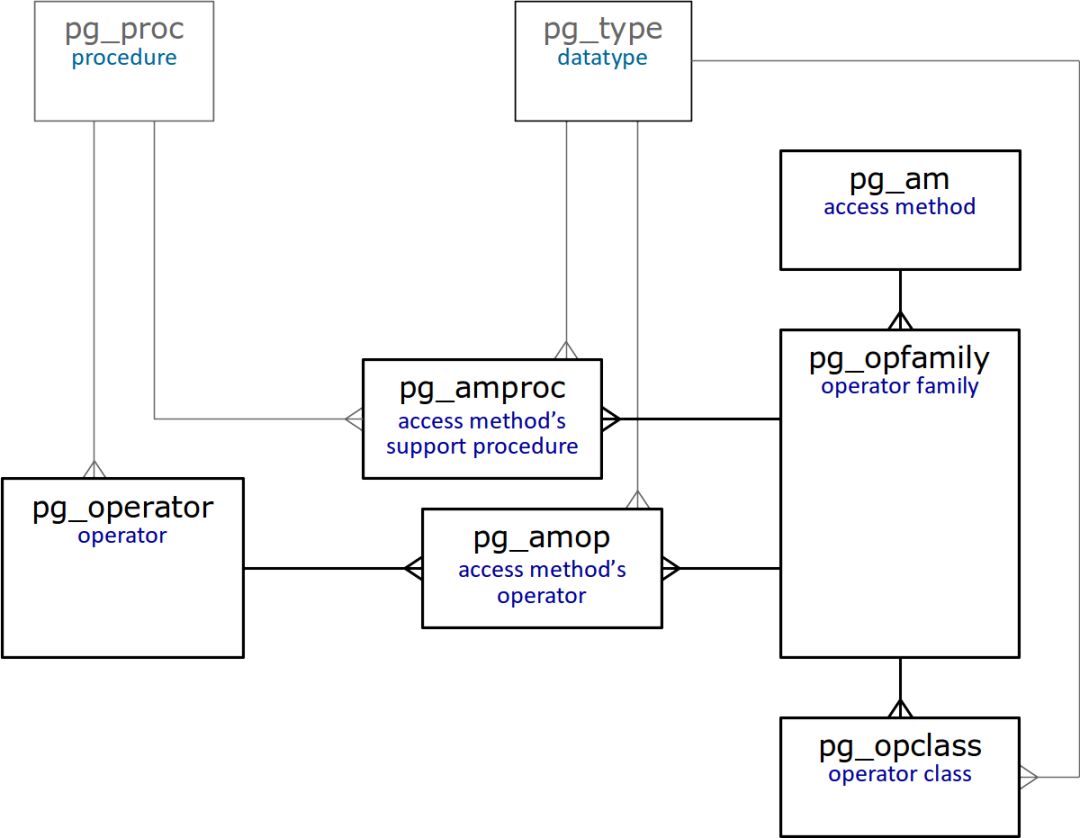
不用多说,所有这些表都有详细的描述。
系统目录使我们无需查找文档即可找到许多问题的答案。例如,某种访问方法可以操纵哪些数据类型?
postgres=# select opcname, opcintype::regtypefrom pg_opclasswhere opcmethod = (select oid from pg_am where amname = 'btree')order by opcintype::regtype::text;opcname | opcintype---------------------+-----------------------------abstime_ops | abstimearray_ops | anyarrayenum_ops | anyenum...复制
运算符类包含哪些运算符(因此,索引访问可用于包含此类运算符的条件)?
postgres=# select amop.amopopr::regoperatorfrom pg_opclass opc, pg_opfamily opf, pg_am am, pg_amop amopwhere opc.opcname = 'array_ops'and opf.oid = opc.opcfamilyand am.oid = opf.opfmethodand amop.amopfamily = opc.opcfamilyand am.amname = 'btree'and amop.amoplefttype = opc.opcintype;amopopr-----------------------<(anyarray,anyarray)<=(anyarray,anyarray)=(anyarray,anyarray)>=(anyarray,anyarray)>(anyarray,anyarray)(5 rows)复制
下期预告
下篇文章将关于“特种类型的索引介绍之哈希索引”
原文请点击下方“阅读原文”获取










