
为了使Kubernetes具有更高的可扩展性,在Kubernetes 1.5版本中以Alpha的形式发布了一种新的插件API —— Container Runtime Interface(容器运行时接口)
CRI概述
Kubelet使用gRPC框架通过Unix套接字与容器运行时(或Runtime CRI shim)进行通信。Container Runtime实现了CRI gRPC Server,包括RuntimeService和ImageService。该gRPC Server需要监听本地的Unix socket,而kubelet则作为gRPC Client运行,CRI shim充当服务器。
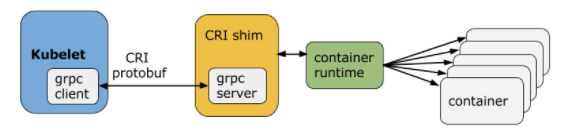
CRI中定义了容器服务(RuntimeService)和镜像服务(ImageService)的接口,因为容器运行时与镜像的生命周期是彼此隔离的,因此需要定义两个服务。ImageService提供RPC,以从存储库中提取图像,检查并删除图像。RuntimeService包含用于管理容器和容器的生命周期的RPC,以及与容器进行交互的调用(exec/attach等)
CRI接口
CRI使用Protocol Buffer,基于gRPC,源码在:
https://github.com/kubernetes/cri-api/blob/master/pkg/apis/runtime/v1alpha2/api.proto
RuntimeService:容器和Sandbox运行时管理。
ImageService:提供了从镜像仓库拉取、查看、和移除镜像的RPC。
// Runtime service defines the public APIs for remote container runtimesservice RuntimeService {// Version returns the runtime name, runtime version, and runtime API version.rpc Version(VersionRequest) returns (VersionResponse) {}// RunPodSandbox creates and starts a pod-level sandbox. Runtimes must ensure// the sandbox is in the ready state on success.rpc RunPodSandbox(RunPodSandboxRequest) returns (RunPodSandboxResponse) {}// StopPodSandbox stops any running process that is part of the sandbox and// reclaims network resources (e.g., IP addresses) allocated to the sandbox.// If there are any running containers in the sandbox, they must be forcibly// terminated.// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if all relevant// resources have already been reclaimed. kubelet will call StopPodSandbox// at least once before calling RemovePodSandbox. It will also attempt to// reclaim resources eagerly, as soon as a sandbox is not needed. Hence,// multiple StopPodSandbox calls are expected.rpc StopPodSandbox(StopPodSandboxRequest) returns (StopPodSandboxResponse) {}// RemovePodSandbox removes the sandbox. If there are any running containers// in the sandbox, they must be forcibly terminated and removed.// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the sandbox has// already been removed.rpc RemovePodSandbox(RemovePodSandboxRequest) returns (RemovePodSandboxResponse) {}// PodSandboxStatus returns the status of the PodSandbox. If the PodSandbox is not// present, returns an error.rpc PodSandboxStatus(PodSandboxStatusRequest) returns (PodSandboxStatusResponse) {}// ListPodSandbox returns a list of PodSandboxes.rpc ListPodSandbox(ListPodSandboxRequest) returns (ListPodSandboxResponse) {}// CreateContainer creates a new container in specified PodSandboxrpc CreateContainer(CreateContainerRequest) returns (CreateContainerResponse) {}// StartContainer starts the container.rpc StartContainer(StartContainerRequest) returns (StartContainerResponse) {}// StopContainer stops a running container with a grace period (i.e., timeout).// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the container has// already been stopped.// TODO: what must the runtime do after the grace period is reached?rpc StopContainer(StopContainerRequest) returns (StopContainerResponse) {}// RemoveContainer removes the container. If the container is running, the// container must be forcibly removed.// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the container has// already been removed.rpc RemoveContainer(RemoveContainerRequest) returns (RemoveContainerResponse) {}// ListContainers lists all containers by filters.rpc ListContainers(ListContainersRequest) returns (ListContainersResponse) {}// ContainerStatus returns status of the container. If the container is not// present, returns an error.rpc ContainerStatus(ContainerStatusRequest) returns (ContainerStatusResponse) {}// UpdateContainerResources updates ContainerConfig of the container.rpc UpdateContainerResources(UpdateContainerResourcesRequest) returns (UpdateContainerResourcesResponse) {}// ReopenContainerLog asks runtime to reopen the stdout/stderr log file// for the container. This is often called after the log file has been// rotated. If the container is not running, container runtime can choose// to either create a new log file and return nil, or return an error.// Once it returns error, new container log file MUST NOT be created.rpc ReopenContainerLog(ReopenContainerLogRequest) returns (ReopenContainerLogResponse) {}// ExecSync runs a command in a container synchronously.rpc ExecSync(ExecSyncRequest) returns (ExecSyncResponse) {}// Exec prepares a streaming endpoint to execute a command in the container.rpc Exec(ExecRequest) returns (ExecResponse) {}// Attach prepares a streaming endpoint to attach to a running container.rpc Attach(AttachRequest) returns (AttachResponse) {}// PortForward prepares a streaming endpoint to forward ports from a PodSandbox.rpc PortForward(PortForwardRequest) returns (PortForwardResponse) {}// ContainerStats returns stats of the container. If the container does not// exist, the call returns an error.rpc ContainerStats(ContainerStatsRequest) returns (ContainerStatsResponse) {}// ListContainerStats returns stats of all running containers.rpc ListContainerStats(ListContainerStatsRequest) returns (ListContainerStatsResponse) {}// UpdateRuntimeConfig updates the runtime configuration based on the given request.rpc UpdateRuntimeConfig(UpdateRuntimeConfigRequest) returns (UpdateRuntimeConfigResponse) {}// Status returns the status of the runtime.rpc Status(StatusRequest) returns (StatusResponse) {}}// ImageService defines the public APIs for managing images.service ImageService {// ListImages lists existing images.rpc ListImages(ListImagesRequest) returns (ListImagesResponse) {}// ImageStatus returns the status of the image. If the image is not// present, returns a response with ImageStatusResponse.Image set to// nil.rpc ImageStatus(ImageStatusRequest) returns (ImageStatusResponse) {}// PullImage pulls an image with authentication config.rpc PullImage(PullImageRequest) returns (PullImageResponse) {}// RemoveImage removes the image.// This call is idempotent, and must not return an error if the image has// already been removed.rpc RemoveImage(RemoveImageRequest) returns (RemoveImageResponse) {}// ImageFSInfo returns information of the filesystem that is used to store images.rpc ImageFsInfo(ImageFsInfoRequest) returns (ImageFsInfoResponse) {}}
无论是docker、rkt或cri-o,只要能实现这个接口,谁都可以做Container Runtime。
启用CRI接口
Kubernetes默认启用了CRI,除非集成了rktnetes,且1.7版本开始,旧的预集成的docker CRI已经被移除。
配置CRI只需要在kubelet的启动参数传入参数:--container-runtime-endpoint远程运行时服务的端点。
Linux上支持unix socket,如: unix:///var/run/dockershim.sock
windows上支持tcp,如tcp://localhost:373
默认是unix:///var/run/dockershim.sock,即默认使用本地的docker作为容器运行时。
如cri-o替换docker作为容器运行时的配置
--container-runtime=remote \
--container-runtime-endpoint=/var/run/crio/crio.sock \
--runtime-request-timeout=5m \
--image-service-endpoint=/var/run/crio/crio.sock \
通过CRI接口可以指定使用其它容器运行时作为Pod的后端,目前支持 CRI 的后端有:
docker:kuberentes最初就开始支持的容器运行时,也是默认的容器运行时,目前还没完全从kubelet中解耦。
cri-o:Kubernetes的CRI标准的实现,并且允许Kubernetes间接使用OCI兼容的容器运行时。
cri-containerd:基于Containerd的Kubernetes CRI实现。
rkt:由CoreOS主推的用来跟docker抗衡的容器运行时。
frakti:基于hypervisor的CRI。
当前同样存在一些只实现了OCI标准的容器,但是它们可以通过CRI-O来作为Kubernetes的容器运行时。因为CRI-O是Kubernetes的CRI标准的实现,并且允许Kubernetes间接使用OCI兼容的容器运行时。
Clear Containers:由Intel推出的兼容OCI容器运行时,可以通过CRI-O来兼容CRI。
Kata Containers:符合OCI规范,可以通过CRI-O或Containerd CRI Plugin来兼容CRI。
gVisor:由谷歌推出的容器运行时沙箱(Experimental),可以通过CRI-O来兼容CRI。
一个Kubernetes集群中,Node节点可以使用不同的容器运行时
[root@k8s-test09 ~]# kubectl get nodes -o wide
NAME STATUS ROLES AGE VERSION INTERNAL-IP EXTERNAL-IP OS-IMAGE KERNEL-VERSION CONTAINER-RUNTIME
k8s-test09 Ready <none> 24d v1.19.2 172.31.250.215 <none> CentOS Linux 8 (Core) 4.18.0-193.14.2.el8_2.x86_64 cri-o://1.19.0
k8s-test10 Ready <none> 24d v1.19.2 172.31.250.214 <none> CentOS Linux 8 (Core) 4.18.0-193.14.2.el8_2.x86_64 docker://19.3.13
[root@k8s-test09 ~]#
CRI API
前面我们说过只要实现CRI接口谁都可以做容器运行时,那么我们也可以通过CRI API接口去操作或获取遵循CRI接口规范的容器运行时的容器。
参考cri-tools工具的实现,写一个简单程序获取容器标准输出的日志文件和容器挂载的端点。
package main
import (
"context"
"fmt"
"log"
"net"
"net/url"
"os"
"time"
"github.com/pkg/errors"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
pb "k8s.io/cri-api/pkg/apis/runtime/v1alpha2"
)
const (
// unixProtocol is the network protocol of unix socket.
unixProtocol = "unix"
)
var (
// RuntimeEndpoint is CRI server runtime endpoint
RuntimeEndpoint = []string{"unix:///var/run/dockershim.sock", "unix:///run/crio/crio.sock", "unix:///run/containerd/containerd.sock"}
//RuntimeEndpoint = []string{"unix:///run/crio/crio.sock"}
// Timeout of connecting to server (default: 10s)
Timeout = 10 * time.Second
)
func getConnection(endPoints []string) (*grpc.ClientConn, error) {
if endPoints == nil || len(endPoints) == 0 {
return nil, fmt.Errorf("endpoint is not set")
}
endPointsLen := len(endPoints)
var conn *grpc.ClientConn
for indx, endPoint := range endPoints {
_, sock, _ := parseEndpoint(endPoint)
if isExist(sock)==false{
log.Printf("sock: %s No such file or directory\n",sock)
continue
}
log.Printf("connect using endpoint '%s' with '%s' timeout", endPoint, Timeout)
addr, dialer, err := GetAddressAndDialer(endPoint)
if err != nil {
if indx == endPointsLen-1 {
return nil, err
}
log.Fatal(err)
continue
}
conn, err = grpc.Dial(addr, grpc.WithInsecure(), grpc.WithBlock(), grpc.WithTimeout(Timeout), grpc.WithContextDialer(dialer))
if err != nil {
errMsg := errors.Wrapf(err, "connect endpoint '%s', make sure you are running as root and the endpoint has been started", endPoint)
if indx == endPointsLen-1 {
return nil, errMsg
}
log.Println(errMsg)
} else {
log.Printf("connected successfully using endpoint: %s", endPoint)
break
}
}
return conn, nil
}
// GetAddressAndDialer returns the address parsed from the given endpoint and a context dialer.
func GetAddressAndDialer(endpoint string) (string, func(ctx context.Context, addr string) (net.Conn, error), error) {
protocol, addr, err := parseEndpointWithFallbackProtocol(endpoint, unixProtocol)
if err != nil {
return "", nil, err
}
if protocol != unixProtocol {
return "", nil, fmt.Errorf("only support unix socket endpoint")
}
return addr, dial, nil
}
func dial(ctx context.Context, addr string) (net.Conn, error) {
return (&net.Dialer{}).DialContext(ctx, unixProtocol, addr)
}
func parseEndpointWithFallbackProtocol(endpoint string, fallbackProtocol string) (protocol string, addr string, err error) {
if protocol, addr, err = parseEndpoint(endpoint); err != nil && protocol == "" {
fallbackEndpoint := fallbackProtocol + "://" + endpoint
protocol, addr, err = parseEndpoint(fallbackEndpoint)
if err == nil {
log.Printf("Using %q as endpoint is deprecated, please consider using full url format %q.", endpoint, fallbackEndpoint)
}
}
return
}
func parseEndpoint(endpoint string) (string, string, error) {
u, err := url.Parse(endpoint)
if err != nil {
return "", "", err
}
switch u.Scheme {
case "tcp":
return "tcp", u.Host, nil
case "unix":
return "unix", u.Path, nil
case "":
return "", "", fmt.Errorf("using %q as endpoint is deprecated, please consider using full url format", endpoint)
default:
return u.Scheme, "", fmt.Errorf("protocol %q not supported", u.Scheme)
}
}
func main() {
runtimeClient, runtimeConn, err := getRuntimeClient()
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
defer closeConnection(runtimeConn)
request := &pb.ListContainersRequest{}
listContainers, err := runtimeClient.ListContainers(context.Background(), request)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
for _, container := range listContainers.Containers {
id := substr(container.GetId(), 12)
var request = &pb.ContainerStatusRequest{ContainerId: id}
info, err := runtimeClient.ContainerStatus(context.Background(), request)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
fmt.Println(info.Status.LogPath)
var req = &pb.ContainerStatsRequest{ContainerId: id}
stat, _ := runtimeClient.ContainerStats(context.Background(), req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
}
if container.State.String() != "CONTAINER_RUNNING" {
fmt.Printf("container %s it's not RUNNING, there are no log files and mount points\n", container.Metadata.Name)
continue
}
fmt.Println(stat.Stats.WritableLayer.FsId.Mountpoint)
}
}
func getRuntimeClient() (pb.RuntimeServiceClient, *grpc.ClientConn, error) {
// Set up a connection to the server.
conn, err := getConnection(RuntimeEndpoint)
if err != nil {
return nil, nil, errors.Wrap(err, "connect")
}
runtimeClient := pb.NewRuntimeServiceClient(conn)
return runtimeClient, conn, nil
}
func closeConnection(conn *grpc.ClientConn) error {
if conn == nil {
return nil
}
return conn.Close()
}
func substr(s string, l int) string {
if len(s) <= l {
return s
}
ss, sl, rl, rs := "", 0, 0, []rune(s)
for _, r := range rs {
rint := int(r)
if rint < 128 {
rl = 1
} else {
rl = 2
}
if sl+rl > l {
break
}
sl += rl
ss += string(r)
}
return ss
}
func isExist(fileName string) bool{
_,err := os.Stat(fileName)
if err!=nil{
if os.IsExist(err){
return true
}
return false
}
return true
}
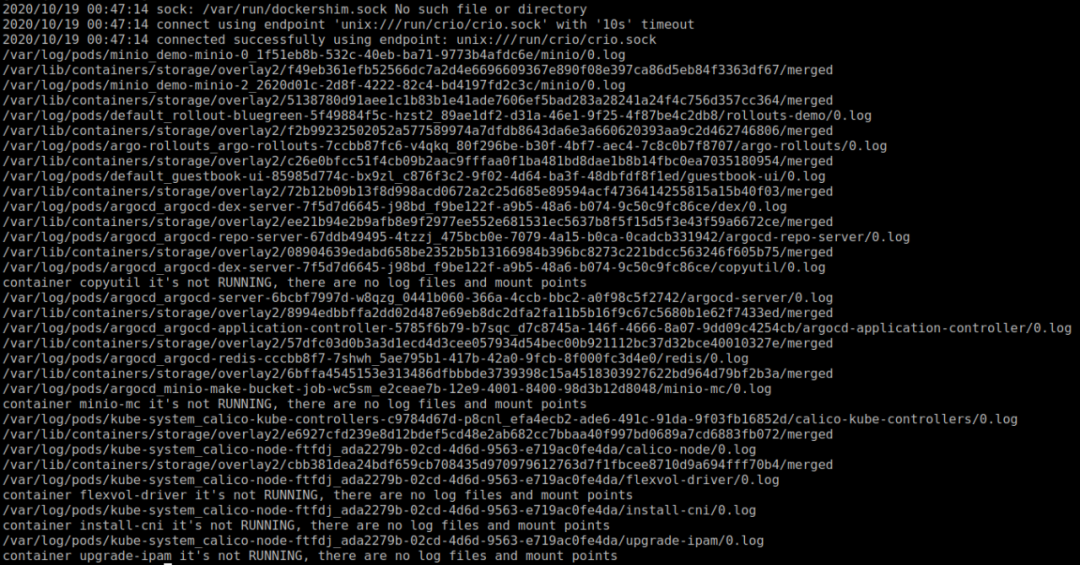
cri-o节点的运行结果
docker节点运行结果
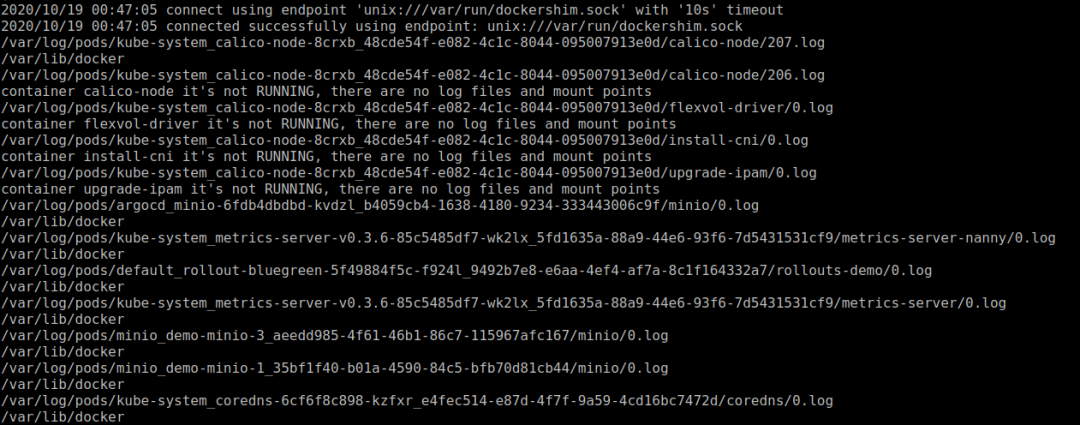
值得注意的是dockert通过cri api不能获取容器完整的挂载点路径,需要调用docker自身的API。
往期回顾






