本次分享主要介绍Mysql数据库的索引、联合查询、自连接、数据库管理及日志配置相关知识。
一、索引
索引就好像书目录,给每页内容按索组织,根据索引快速查找内容。提升查询效率。
如果没有索引,在查询数据时必须扫描表中的所有记录才能找出符合条件的记录,这种全表扫描的查询效率非常低
mysql中索引是以B树结构为索引数据结构,各存储引擎使用的方式有所不同,innodb引擎以B+Tree结构构造索引,除了B索引还要HASH索引
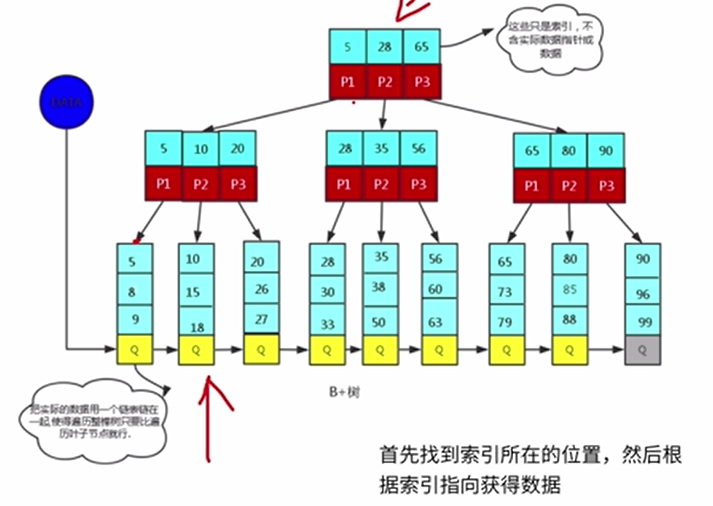
索引策略
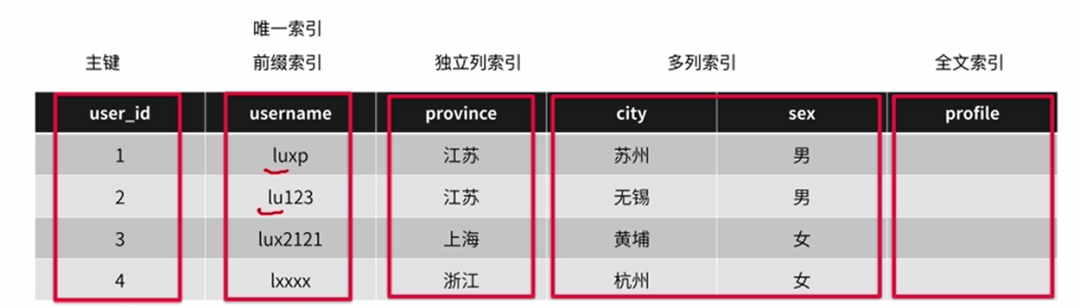
实例,key创建索引

为已经存在的表添加索引
create index index_name on table(field)
alter table "table" add index "index_name"("field");
删除索引:alter table "table" drop index ”index_name";
多列索引注意

索引实战经验:1、选择区分度高的列建立索引2、每次查询每张表仅能使用一个索引;3、避免对索引列进行计算。
show index from employee;
create index idx_name on employee where name="张山";
explain索引分析:分析表的读取顺序;数据读取操作的操作类型;哪些索引可以使用;哪些索引被实际使用;表之间的引用;每张表有多少行被优化器查询。
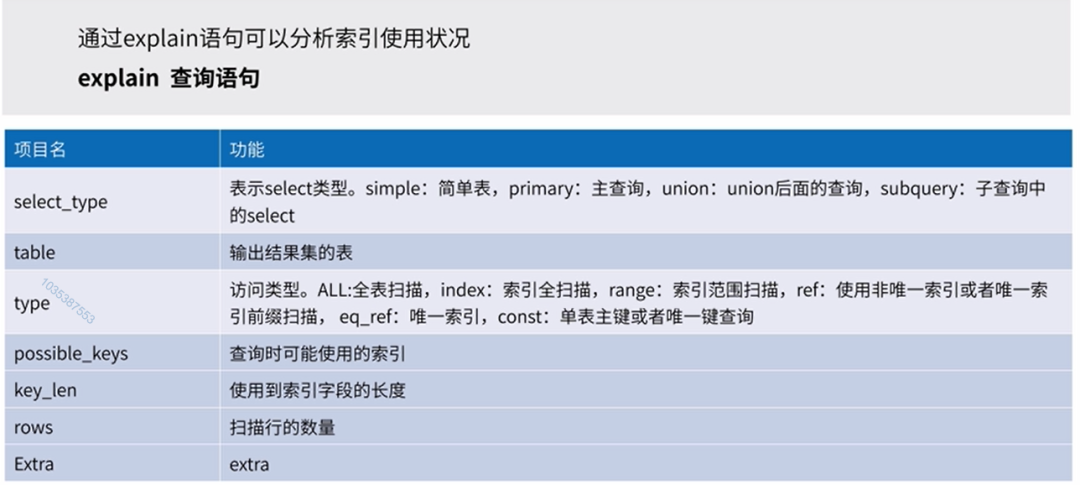

覆盖索引:即select的数据列只从索引中就能得到,不必读取数据行,也就是只需扫描索引就可以得到查询结果。
如何判断使用了覆盖索引,在查询分析器的extra列可以看到“Using index”
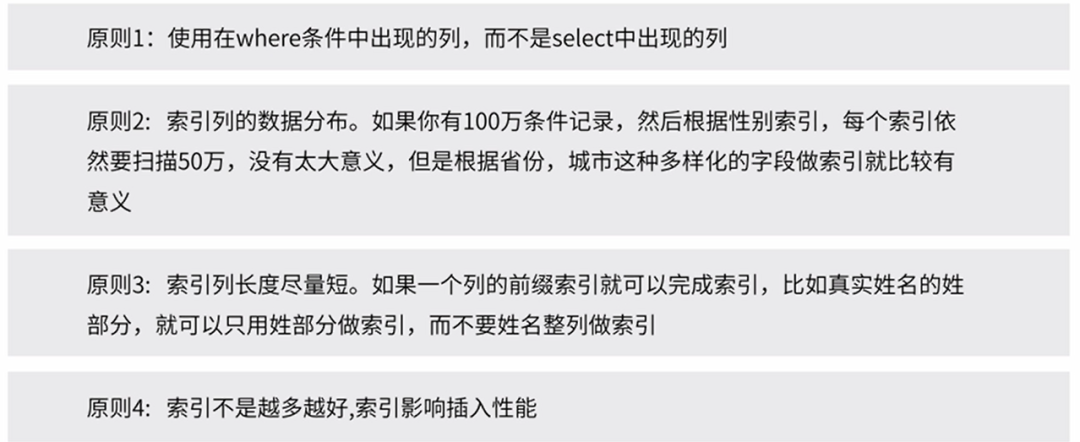
索引设计原则
二、联合查询
(多个表之间)(内连接/左连接)\子查询\拼接
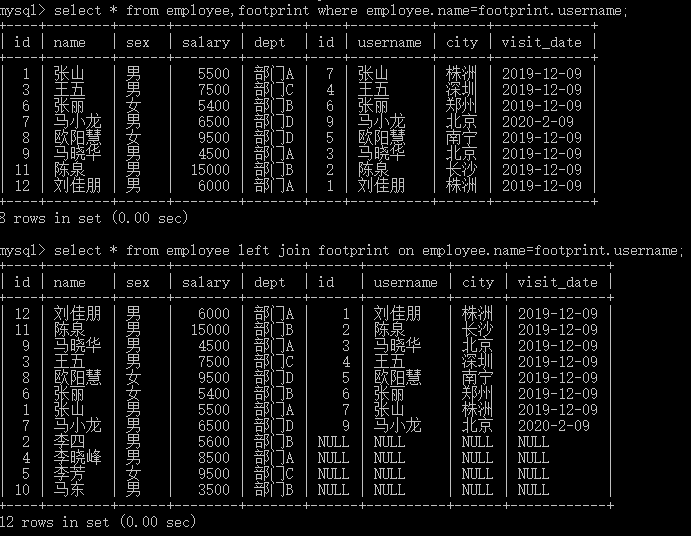
内连接查询,关联表之间必须有相互匹配的记录
隐式语法:select * from users,articles where users.user_id=articles.author
显示语法:select * from users inner join articles on users.user_id=articles.author
外连接查询,关联表之间不需要相互匹配,分左右连接
select * from users left join articles on users.user_id=articles.author
右连接,就是包含右边表查询记录,不管左表有没有对应记录。
全连接(不支持)
子查询-一条查询语句的结果作为另一条查询的条件
select * from table where id in (select id from table)
子查询除了可以用in外,还可以not in,!=,=,exits,not exists
EXISTS是子查询中用于测试内部查询是否返回任何行的布尔运算符。将主查询的数据放到子查询中做条件验证,根据验证结果(TRUE 或 FALSE)来决定主查询的数据结果是否保留。
查询排名靠前的用户文章,查询语句:select * from article where user_id in (select user_id from user_rank)
记录联合即合并拼接-union all (多个查询结构拼接,必须字段数量一致)
select * from table where condition union all select * from table where condition
union:与union all 不同的是去重复
三、自连接
自连接是一种特殊的表连接,它是指相互连接的表在物理上同为一张表,但是逻辑上是多张表。自连接通常用于表中数据有层次结构,如区域表、菜单表、商品分类。
select A.COLUMN,B.column from table A,table B where A.column=B.column;
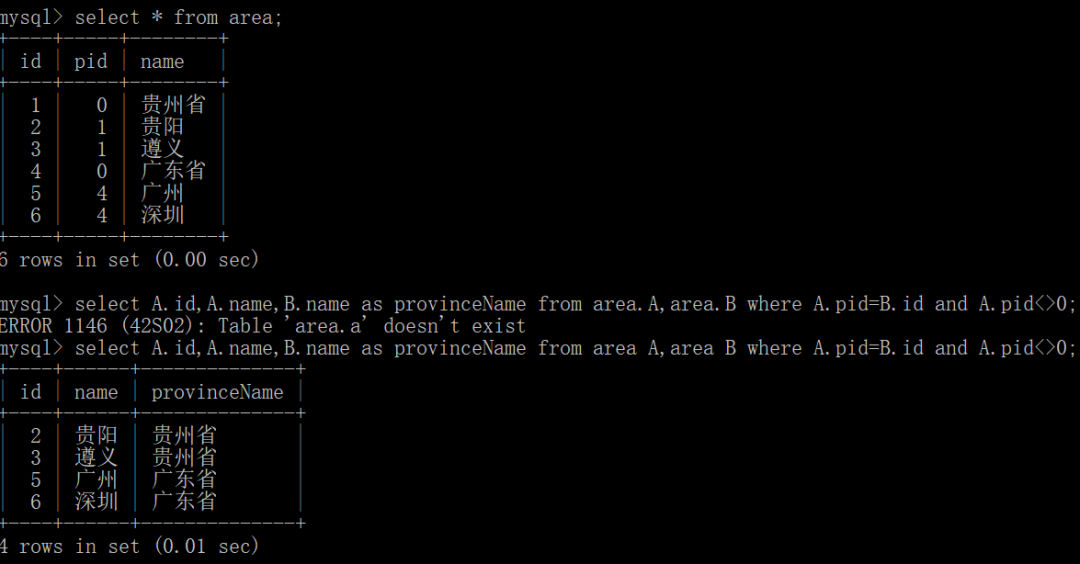
create table area(
id int not null auto_increment primary key comment "区域id",
pid int not null comment "父id(0-省份)",
name varchar(45) comment "区域名称"
);
insert into area(id,pid,name) values(1,0,"贵州省");
insert into area(id,pid,name) values(2,1,"贵阳");
insert into area(id,pid,name) values(3,1,"遵义");
insert into area(id,pid,name) values(4,0,"广东省");
insert into area(id,pid,name) values(5,4,"广州");
insert into area(id,pid,name) values(6,4,"深圳");
四、数据库管理
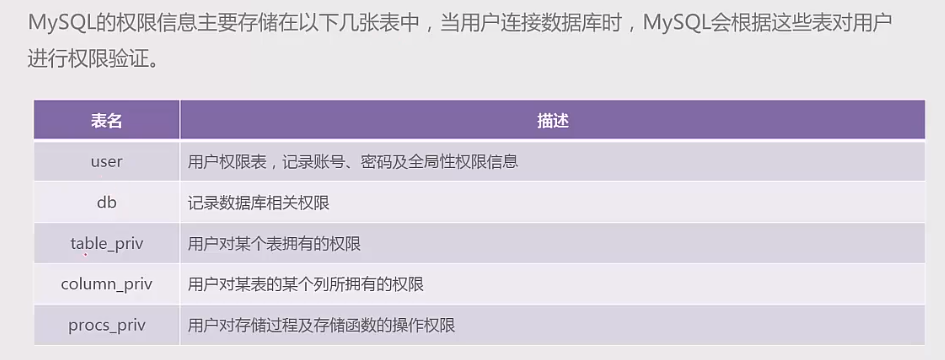
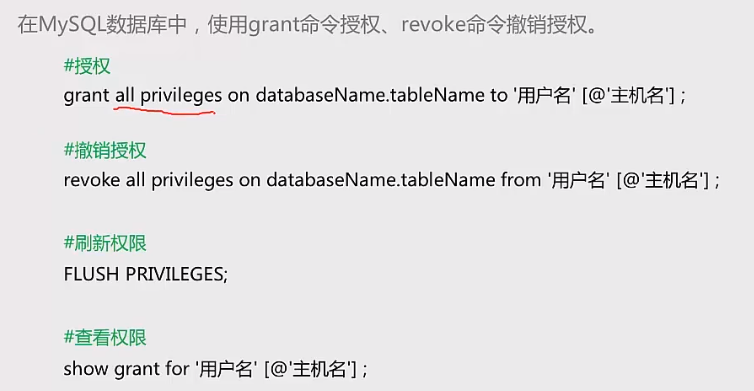
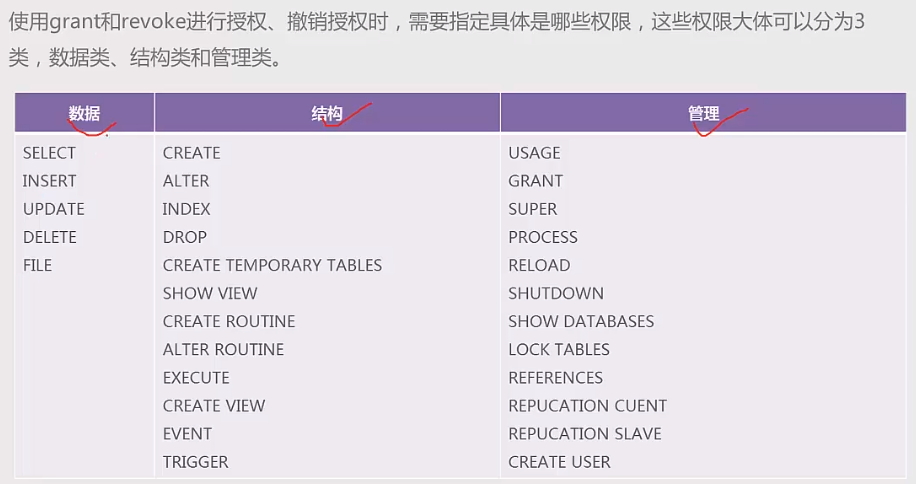
用户授权(DCL)
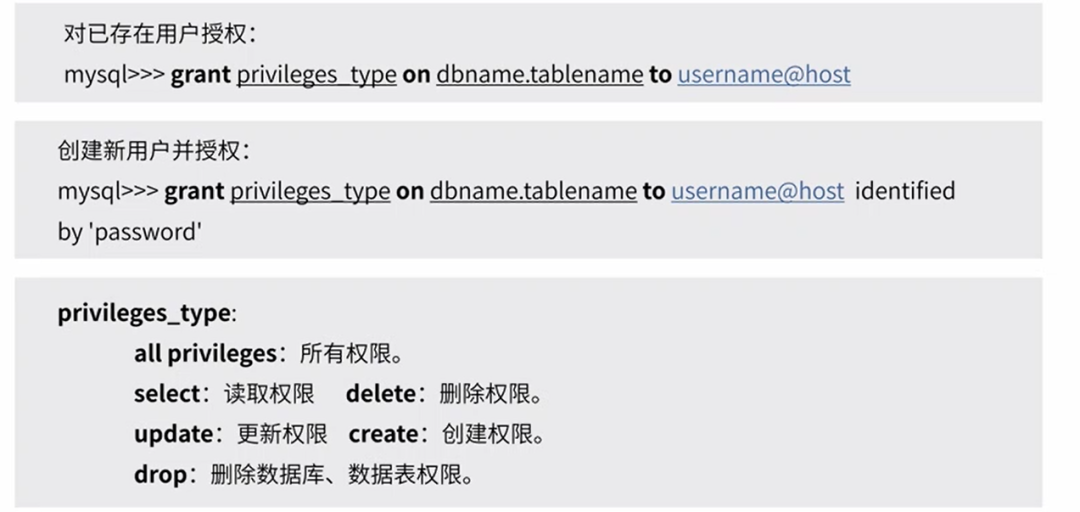
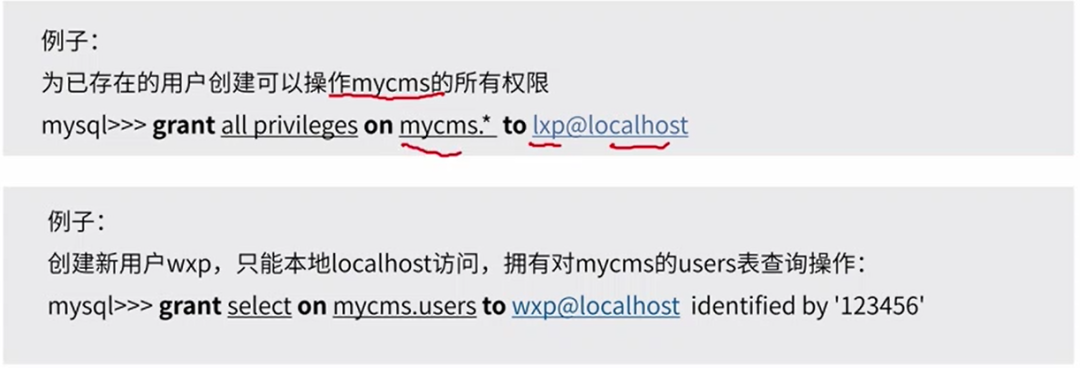
权限体系:全局层级、数据库层级、表层级、列层级、子程序层级

禁止root远程登陆
root是mysql数据库的超级管理员,几乎拥有所有权限
root是mysql数据库默认用户
忘记root密码解决方法
关闭mysql服务-重启mysql时关闭权限验证-修改root密码-正常启动mysql服务。
数据库备份(终端执行,先退出数据库)
数据库备份使用mysqldump命令:mysqldump-u account -p database tablename1 tablename2>mycms.sql
备份mycms库的 users表:mysqldump-u root -p mycms users>mycms.sql
备份database库中所有表:mysqldump-u root -p mycms >mycms.sql
数据库备份与恢复注意事项
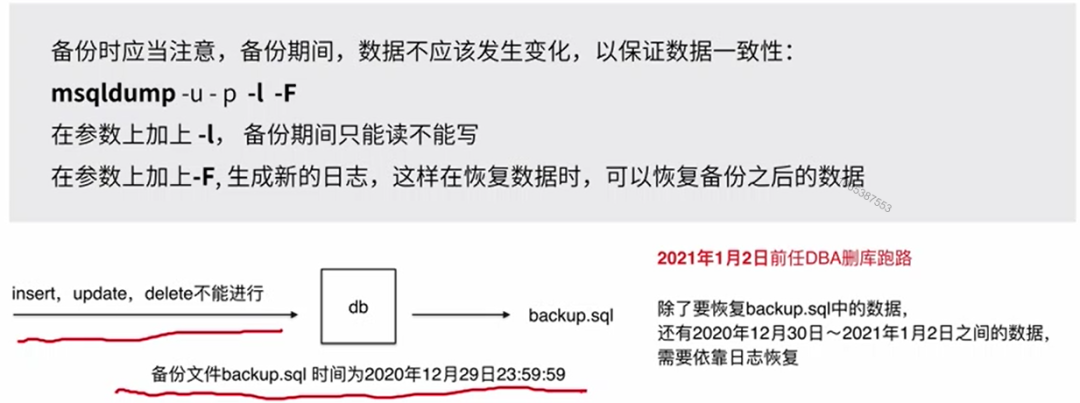
数据库恢复

五、日志配置
日志用于记录数据库的运行情况,以及用户对数据库执行的各类操作。当数据库发生故障时,可以根据日志分析和解决问题,从而对数据库进行恢复。

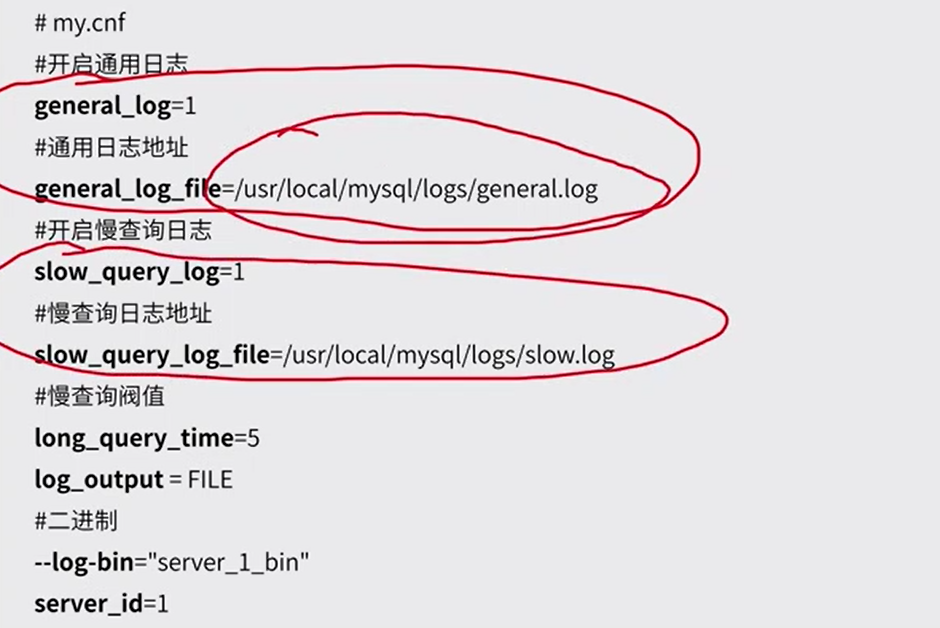
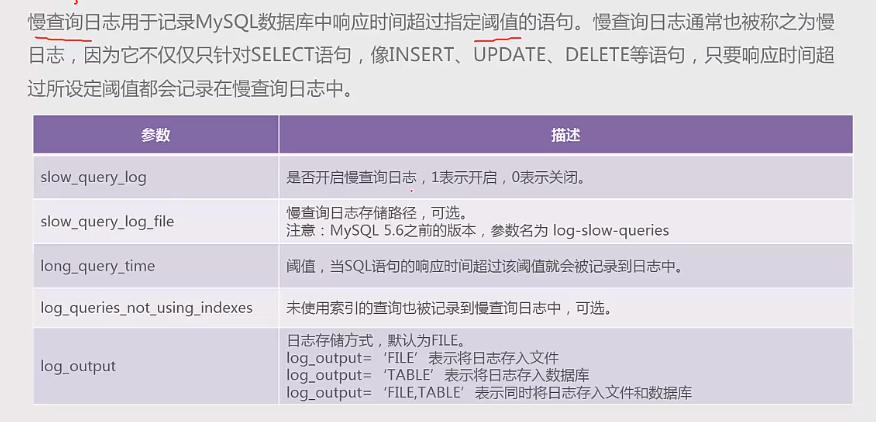
查看是否开启慢查询日志:show variables like "slow%";
临时开启慢查询日志:set global slow_query_log="ON";set long_query_time=1;
慢查询日志文件所在的位置:show variables like "%datadir%";
Python数据分析实例







