目录:
曲线拟合多项式拟合多项式拟合正弦函数最小二乘拟合Scipy.linalg.lstsq 最小二乘解Scipy.stats.linregress 线性回归更高级的拟合Scipy.optimize.leastsqScipy.optimize.curve_fit
曲线拟合
导入基础包:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams["font.family"] = "SimHei"
plt.rcParams["axes.unicode_minus"] = False
多项式拟合
# 导入线多项式拟合工具:
from numpy import polyfit, poly1d
# 产生数据:
x = np.linspace(-5, 5, 100)
y = 4 * x + 1.5
noise_y = y + np.random.randn(y.shape[-1]) * 2.5
# 画出数据:
%matplotlib inline
p = plt.plot(x, noise_y, 'rx')
p = plt.plot(x, y, 'b:')

进行线性拟合,polyfit
是多项式拟合函数,线性拟合即一阶多项式:
coeff = polyfit(x, noise_y, 1)
print(coeff)
[3.81313227 1.53189309]
一阶多项式 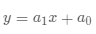 拟合,返回两个系数 。
拟合,返回两个系数 。
画出拟合曲线:
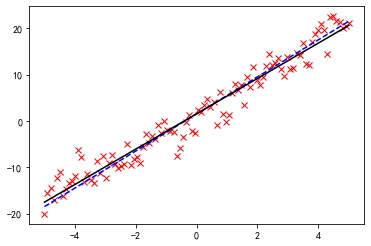
p = plt.plot(x, noise_y, 'rx')
p = plt.plot(x, y, 'b--')
p = plt.plot(x, coeff[0] * x + coeff[1], 'k-')
还可以用 poly1d
生成一个以传入的 coeff
为参数的多项式函数:
f = poly1d(coeff)
p = plt.plot(x, noise_y, 'rx')
p = plt.plot(x, f(x))
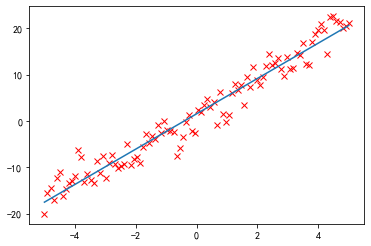
display(f)
print(f)
poly1d([3.81313227, 1.53189309])
3.813 x + 1.532
还可以对它进行数学操作生成新的多项式:
print(f + 2 * f ** 2)
2
29.08 x + 27.18 x + 6.225
多项式拟合正弦函数
正弦函数:
x = np.linspace(-np.pi, np.pi, 100)
y = np.sin(x)
用一阶到九阶多项式拟合,类似泰勒展开:
y1 = poly1d(polyfit(x, y, 1))
y3 = poly1d(polyfit(x, y, 3))
y5 = poly1d(polyfit(x, y, 5))
y7 = poly1d(polyfit(x, y, 7))
y9 = poly1d(polyfit(x, y, 9))
x = np.linspace(-3 * np.pi, 3 * np.pi, 300)
p = plt.plot(x, np.sin(x), 'k', label="sin(x)")
p = plt.plot(x, y1(x), label="1")
p = plt.plot(x, y3(x), label="3")
p = plt.plot(x, y5(x), label="5")
p = plt.plot(x, y7(x), label="7")
p = plt.plot(x, y9(x), label="9")
a = plt.axis([-3 * np.pi, 3 * np.pi, -1.25, 1.25])
plt.legend()
plt.show()
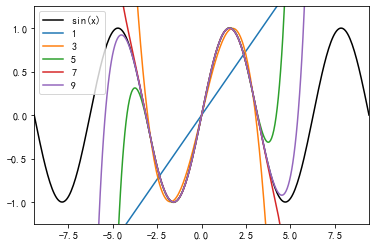
黑色为原始的图形,可以看到,随着多项式拟合的阶数的增加,曲线与拟合数据的吻合程度在逐渐增大。
最小二乘拟合
导入相关的模块:
from scipy.linalg import lstsq
from scipy.stats import linregress
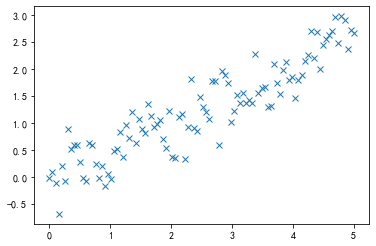
x = np.linspace(0, 5, 100)
y = 0.5 * x + np.random.randn(x.shape[-1]) * 0.35
plt.plot(x, y, 'x')
[<matplotlib.lines.Line2D at 0x1757efd0>]
Scipy.linalg.lstsq 最小二乘解
一般,当使用一个 N-1 阶的多项式拟合这 M 个点时,有这样的关系存在:
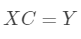
即
要得到 C
,可以使用 scipy.linalg.lstsq
求最小二乘解。
这里,我们使用 1 阶多项式即 N = 2
,先将 x
扩展成 X
:
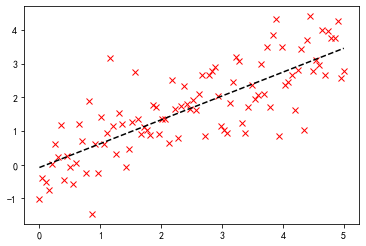
x = np.linspace(0, 5, 100)
h = np.random.randn(x.shape[-1]) * 0.8
y = 0.7 * x + h
print(f"原函数f(x)=0.7x+0.8*N(0,1)")
X = np.hstack((x[:, np.newaxis], np.ones((x.shape[-1], 1))))
# 求解:
C, resid, rank, s = lstsq(X, y)
print(f"拟合函数f(x)={C[0]}x+{C[1]}")
print(f"残差平方和(sum squared residual) = {resid:.3f}")
print(f"矩阵X的秩(rank of the X matrix) = {rank}")
print(f"奇异值分解(singular values of X) = {s}")
# 画图:
p = plt.plot(x, y, 'rx')
p = plt.plot(x, C[0] * x + C[1], 'k--')
原函数f(x)=0.7x+0.8*N(0,1)
拟合函数f(x)=0.7074763635934755x+-0.08249211243588586
残差平方和(sum squared residual) = 63.276
矩阵X的秩(rank of the X matrix) = 2
奇异值分解(singular values of X) = [30.23732043 4.82146667]
Scipy.stats.linregress 线性回归
slope, intercept, r_value, p_value, stderr = linregress(x, y)
print("原函数f(x)=0.7x+0.8*N(0,1)")
print(f"拟合函数f(x)={slope}x+{intercept}")
print(f"R-value = {r_value:.3f}")
print(f"p-value (probability there is no correlation) = {p_value:.3e}")
print(f"均方误差RMSE(Root mean squared error of the fit) = {np.sqrt(stderr):.3f}")
p = plt.plot(x, y, 'rx')
p = plt.plot(x, slope * x + intercept, 'k--')
原函数f(x)=0.7x+0.8*N(0,1)
拟合函数f(x)=0.7074763635934755x+-0.08249211243588661
R-value = 0.792
p-value (probability there is no correlation) = 1.036e-22
均方误差RMSE(Root mean squared error of the fit) = 0.235
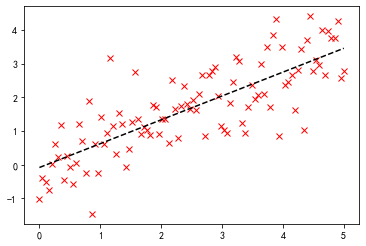
可以看到,两者求解的结果是一致的,但是出发的角度是不同的。
更高级的拟合
定义非线性函数: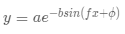
def function(x, a , b, f, phi):
result = a * np.exp(-b * np.sin(f * x + phi))
return result
from scipy.optimize import leastsq
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 50)
actual_parameters = [3, 2, 1.25, np.pi / 4]
y = function(x, *actual_parameters)
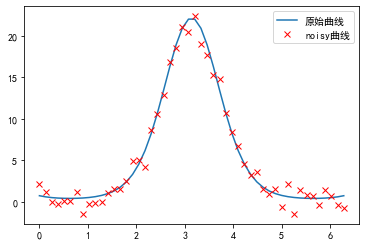
# 画出原始曲线:
p = plt.plot(x, y, label="原始曲线")
# 加入噪声:
from scipy.stats import norm
y_noisy = y + 0.9 * norm.rvs(size=len(x))
p = plt.plot(x, y_noisy, 'rx', label="noisy曲线")
plt.legend()
<matplotlib.legend.Legend at 0xfea9ef0>
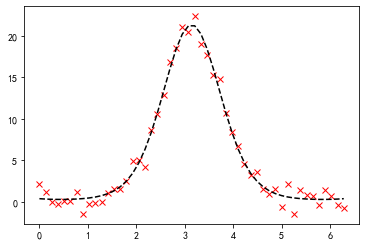
Scipy.optimize.leastsq
定义误差函数,将要优化的参数放在前面:
def f_err(p, y, x):
return y - function(x, *p)
将这个函数作为参数传入 leastsq
函数,第二个参数为初始值:
c, ret_val = leastsq(f_err, [1, 1, 1, 1], args=(y_noisy, x))
c, ret_val
(array([2.45649947, 2.16216292, 1.1618549 , 1.06139211]), 1)
ret_val
是 1~4 时,表示成功找到最小二乘解:
p = plt.plot(x, y_noisy, 'rx')
p = plt.plot(x, function(x, *c), 'k--')
Scipy.optimize.curve_fit
更高级的做法:
from scipy.optimize import curve_fit
# 不需要定义误差函数,直接传入 function 作为参数:
p_est, err_est = curve_fit(function, x, y_noisy)
# 函数的参数
print("函数的参数:", p_est)
print("协方差矩阵:\n", err_est)
p = plt.plot(x, y_noisy, "rx")
p = plt.plot(x, function(x, *p_est), "k--")
函数的参数: [2.45649949 2.16216291 1.1618549 1.0613921 ]
协方差矩阵:
[[ 0.56326029 -0.22664715 0.07116718 -0.22363429]
[-0.22664715 0.0915539 -0.02843914 0.08936659]
[ 0.07116718 -0.02843914 0.00955867 -0.03003698]
[-0.22363429 0.08936659 -0.03003698 0.09462869]]

协方差矩阵的对角线为各个参数的方差:
print("协方差矩阵的对角线为各个参数的方差(normalized relative errors for each parameter):")
print(" a\t b\t f\tphi")
print(np.sqrt(err_est.diagonal()) / p_est)
协方差矩阵的对角线为各个参数的方差(normalized relative errors for each parameter):
a b f phi
[0.30551876 0.13994263 0.0841486 0.28982481]
文章转载自漫谈大数据与数据分析,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






