前言
和上篇文章Hudi Flink SQL源码调试学习(一)一样:本着学习hudi-flink源码的目的,利用之前总结的文章中的代码进行调试,记录调试学习过程中主要的步骤及对应源码片段。
欢迎关注我的公众号:伦少的博客

本文主要总结 Flink 的 Transformation
、StreamOperator
, 写Hudi与 Transformation
、StreamOperator
的关系以及Hudi有哪些自定义的 StreamOperator
,还有Flink的四层执行图以及 StreamGraph
和 JobGraph
的生成构建过程。
版本
Flink 1.15.4
Hudi 0.13.0
Transformation & Operator
通过阅读Hudi源码,发现写Hudi的主要逻辑在Pipelines
中的hoodieStreamWrite
、append
、bulkInsert
、compact
、cluster
等方法中。而这几个方法的主要逻辑都用到了transform
这个方法,transform
返回结果为DataStream
,执行完transform
方法后最终会执行dataStream.addSink
完成写Hudi逻辑。而transform
和addSink
方法又主要与Transformation
、StreamOperator
(StreamOperatorFactory
)这两个类有关,实际上写Hudi的主要逻辑就是在Hudi自定义的StreamOperator
和SinkFunction
中实现的。
HoodieTableSink.getSinkRuntimeProvider
// bootstrap
final DataStream<HoodieRecord> hoodieRecordDataStream =
Pipelines.bootstrap(conf, rowType, dataStream, context.isBounded(), overwrite);
// write pipeline
pipeline = Pipelines.hoodieStreamWrite(conf, hoodieRecordDataStream);
// compaction
if (OptionsResolver.needsAsyncCompaction(conf)) {
// use synchronous compaction for bounded source.
if (context.isBounded()) {
conf.setBoolean(FlinkOptions.COMPACTION_ASYNC_ENABLED, false);
}
return Pipelines.compact(conf, pipeline);
} else {
return Pipelines.clean(conf, pipeline);
}
Pipelines.hoodieStreamWrite
public static DataStream<Object> hoodieStreamWrite(Configuration conf, DataStream<HoodieRecord> dataStream) {
if (OptionsResolver.isBucketIndexType(conf)) {
WriteOperatorFactory<HoodieRecord> operatorFactory = BucketStreamWriteOperator.getFactory(conf);
int bucketNum = conf.getInteger(FlinkOptions.BUCKET_INDEX_NUM_BUCKETS);
String indexKeyFields = conf.getString(FlinkOptions.INDEX_KEY_FIELD);
BucketIndexPartitioner<HoodieKey> partitioner = new BucketIndexPartitioner<>(bucketNum, indexKeyFields);
return dataStream.partitionCustom(partitioner, HoodieRecord::getKey)
.transform(opName("bucket_write", conf), TypeInformation.of(Object.class), operatorFactory)
.uid(opUID("bucket_write", conf))
.setParallelism(conf.getInteger(FlinkOptions.WRITE_TASKS));
} else {
WriteOperatorFactory<HoodieRecord> operatorFactory = StreamWriteOperator.getFactory(conf);
return dataStream
// Key-by record key, to avoid multiple subtasks write to a bucket at the same time
.keyBy(HoodieRecord::getRecordKey)
.transform(
"bucket_assigner",
TypeInformation.of(HoodieRecord.class),
new KeyedProcessOperator<>(new BucketAssignFunction<>(conf)))
.uid(opUID("bucket_assigner", conf))
.setParallelism(conf.getInteger(FlinkOptions.BUCKET_ASSIGN_TASKS))
// shuffle by fileId(bucket id)
.keyBy(record -> record.getCurrentLocation().getFileId())
.transform(opName("stream_write", conf), TypeInformation.of(Object.class), operatorFactory)
.uid(opUID("stream_write", conf))
.setParallelism(conf.getInteger(FlinkOptions.WRITE_TASKS));
}
}
Pipelines.clean
public static DataStreamSink<Object> clean(Configuration conf, DataStream<Object> dataStream) {
return dataStream.addSink(new CleanFunction<>(conf))
.setParallelism(1)
.name("clean_commits");
}
transform
hudi源码里用到了两个transform
方法,两个方法的区别只是参数不同,一个参数为StreamOperator
,一个为StreamOperatorFactory
,实际都会调用doTransform
方法
@PublicEvolving
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> transform(
String operatorName,
TypeInformation<R> outTypeInfo,
OneInputStreamOperator<T, R> operator) {
return doTransform(operatorName, outTypeInfo, SimpleOperatorFactory.of(operator));
}
@PublicEvolving
public <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> transform(
String operatorName,
TypeInformation<R> outTypeInfo,
OneInputStreamOperatorFactory<T, R> operatorFactory) {
return doTransform(operatorName, outTypeInfo, operatorFactory);
}
doTransform
doTransform的主要逻辑是先构造Transformation
,Transformation
的构造函数中包含StreamOperatorFactory
,然后将Transformation
添加到StreamExecutionEnvironment
的transformations
中,最后返回一个新的DataStream
,这里的DataStream
为SingleOutputStreamOperator
,它是DataStream
的子类(注意SingleOutputStreamOperator
不是上面提到的StreamOperator
),它和之前的DataStream
的不同点是transformation
,新生成的DataStream
的transformation
是这里的resultTransform
protected <R> SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> doTransform(
String operatorName,
TypeInformation<R> outTypeInfo,
StreamOperatorFactory<R> operatorFactory) {
// read the output type of the input Transform to coax out errors about MissingTypeInfo
transformation.getOutputType();
OneInputTransformation<T, R> resultTransform =
new OneInputTransformation<>(
this.transformation,
operatorName,
operatorFactory,
outTypeInfo,
environment.getParallelism());
@SuppressWarnings({"unchecked", "rawtypes"})
SingleOutputStreamOperator<R> returnStream =
new SingleOutputStreamOperator(environment, resultTransform);
getExecutionEnvironment().addOperator(resultTransform);
return returnStream;
}
addSink
可以看到addSink
方法会调用DataStreamSink.forSinkFunction
方法,在forSinkFunction
中也会构建StreamOperator
、Transformation
,然后将Transformation
添加到StreamExecutionEnvironment
的transformations
中,不同的是最后返回DataStreamSink
。这里的StreamOperator
为StreamSink
public DataStreamSink<T> addSink(SinkFunction<T> sinkFunction) {
// read the output type of the input Transform to coax out errors about MissingTypeInfo
transformation.getOutputType();
// configure the type if needed
if (sinkFunction instanceof InputTypeConfigurable) {
((InputTypeConfigurable) sinkFunction).setInputType(getType(), getExecutionConfig());
}
return DataStreamSink.forSinkFunction(this, clean(sinkFunction));
}
static <T> DataStreamSink<T> forSinkFunction(
DataStream<T> inputStream, SinkFunction<T> sinkFunction) {
StreamSink<T> sinkOperator = new StreamSink<>(sinkFunction);
final StreamExecutionEnvironment executionEnvironment =
inputStream.getExecutionEnvironment();
PhysicalTransformation<T> transformation =
new LegacySinkTransformation<>(
inputStream.getTransformation(),
"Unnamed",
sinkOperator,
executionEnvironment.getParallelism());
executionEnvironment.addOperator(transformation);
return new DataStreamSink<>(transformation);
}
Hudi自定义的`StreamOperator`
Pipelines.hoodieStreamWrite
KeyedProcessOperator(BucketAssignFunction)
: KeyedProcessOperator是Flink源码中自带的:org.apache.flink.streaming.api.operators.KeyedProcessOperator。这里的Hudi自定义体现在自定义了Operator的userFunction
: org.apache.hudi.sink.partitioner.BucketAssignFunctionStreamWriteOperator
: org.apache.hudi.sink.StreamWriteOperator,userFunction
为:org.apache.hudi.sink.StreamWriteFunctionBucketStreamWriteOperator
:org.apache.hudi.sink.bucket.BucketStreamWriteOperator,userFunction
为:org.apache.hudi.sink.bucket.BucketStreamWriteFunction
Pipelines.append
AppendWriteOperator
: org.apache.hudi.sink.append.AppendWriteOperator,userFunction
为:org.apache.hudi.sink.append.AppendWriteFunction
Pipelines.bulkInsert
BulkInsertWriteOperator
: org.apache.hudi.sink.bulk.BulkInsertWriteOperator,userFunction
为:org.apache.hudi.sink.bulk.BulkInsertWriteFunctionSortOperator
: org.apache.hudi.sink.bulk.sort.SortOperator
Pipelines.compact
CompactionPlanOperator
: org.apache.hudi.sink.compact.CompactionPlanOperatorCompactOperator
: org.apache.hudi.sink.compact.CompactOperator
Pipelines.cluster
ClusteringPlanOperator
: org.apache.hudi.sink.clustering.ClusteringPlanOperatorClusteringOperator
: :org.apache.hudi.sink.clustering.ClusteringOperator
Hudi自定义的`SinkFunction`
DummySink
: org.apache.hudi.sink.utils.Pipelines.DummySink. Dummy sink that does nothing. (Pipelines.bulkInsert & Pipelines.dummySink)ClusteringCommitSink
: org.apache.hudi.sink.clustering. Function to check and commit the clustering action. (Pipelines.cluster)CompactionCommitSink
: org.apache.hudi.sink.compact.CompactionCommitSink. Function to check and commit the compaction action. (Pipelines.compact)CleanFunction
: org.apache.hudi.sink.CleanFunction. Sink function that cleans the old commits. (Pipelines.clean)
Transformation 类图
StreamOperator 类图
目标
虽然大概知道hudi-flink的主要逻辑就是在Hudi自定义的StreamOperator
和SinkFunction
中实现的,但由于我是个Flink新手,并不知道从DataStream API和 Table API的入口到执行StreamOperator
的调用链或者执行逻辑,所以本篇文章的目的就是研究总结下Flink从最开始入口到StreamOperator
的调用逻辑。这其实都是Flink的源码和Hudi没有关系,但是我们可以结合Hudi自定义的StreamOperator
更好的理解。这块逻辑其实就是研究 Flink 的 Task
或者 Function
是如何运行的(可能描述不准确)。
网上查询相关资料,大概了解了一下相关源码,发现逻辑比较复杂,大概包含StreamGraph
、JobGraph
、ExecutionGraph
、Physical Graph
(没有具体的数据结构,这一步也可以理解为Task的运行)
的生成或者构建,还有JobManager
和TaskManager
的启动,而JobManager
又包含ResourceManager
、Dispatcher
和JobMaster
, 这里涉及Java8异步编程如CompletableFuture
和基于Akka
的RPC
通信,最后才是Task
的的部署和启动,StreamOperator
相关方法的调用最终是通过启动Task.run方法
在StreamTask
中实现的。
可以看出来这块逻辑对于新手来说相当复杂,而且我的精力也有限,所以本篇文章先分析总结StreamGraph
和JobGraph
。
参考资料
Flink 架构官方文档:https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.17/zh/docs/concepts/flink-architecture/
Flink 词汇表官方文档:https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.17/zh/docs/concepts/glossary/
Flink 源码阅读笔记 (Flink Contributor jrthe42):https://blog.jrwang.me/page/3/
Flink 源码分析: https://www.zhihu.com/column/c_1494627744968962048
CompletableFuture: https://blog.csdn.net/qq_31865983/article/details/106137777
CompletableFuture: https://blog.csdn.net/sermonlizhi/article/details/123356877
Akka: https://blog.csdn.net/monokai/category_10204213.html?spm=1001.2014.3001.5515
Transformation: https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_39043378/article/details/123962394
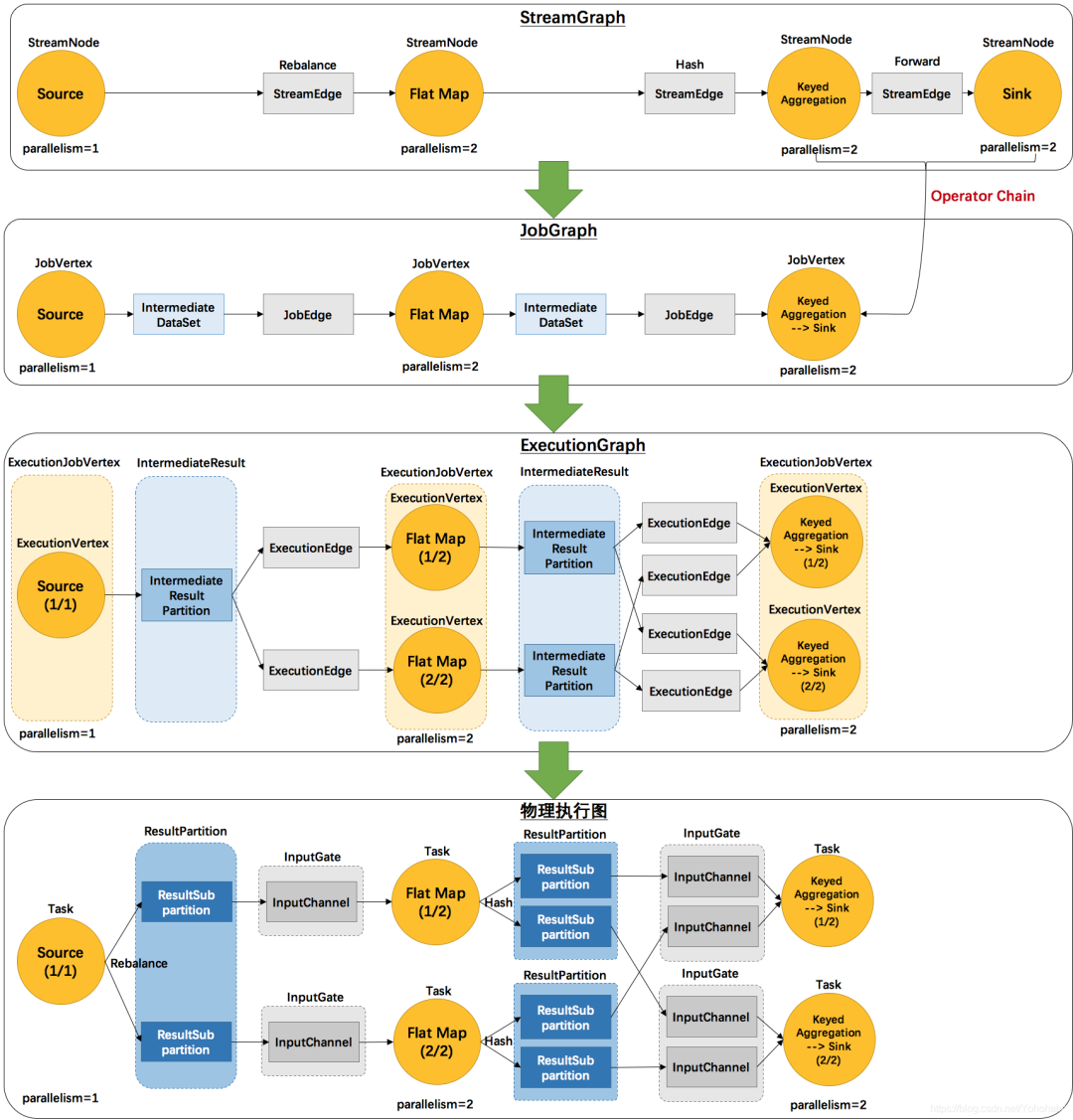
Flink 四层执行图
StreamGraph
(Client端) -> JobGraph
(Client端) -> ExecutionGraph
(JobManager创建JobMaster时) -> Physical Graph
(物理执行图)(TaskManager)(没有具体的数据结构,这一步也可以理解为Task的运行)
由于官方文档对四层执行图的解释不全,且和网上博客资料不太一致,所以我将博客资料和官方文档的解释放在一起了,供大家参考。参考博客:https://blog.csdn.net/Yohohaha/article/details/111400250
StreamGraph
:是根据用户通过 Stream API 编写的代码生成的最初的图,用来表示程序的拓扑结构。每个转换操作会生成一个StreamNode
,两个StreamNodes
之间由StreamEdge
连接在一起,StreamEdge
表示的是算子操作之间的数据传递逻辑,整个图直观表现就是各个算子连接在一起形成一个DAG。官方文档
: 无JobGraph
:StreamGraph
经过优化后生成了JobGraph
,提交给JobManager
的数据结构。在一步做了一个优化,就是将多个符合条件的StreamNode
节点 chain 在一起作为一个JobVertex
节点,这样可以减少数据在节点之间流动所需要的序列化/反序列化/传输消耗。JobGraph在Client端生成。官方文档
: 也叫Logical Graph
,逻辑图是一种有向图,其中顶点是 算子,边定义算子的输入/输出关系,并对应于数据流或数据集。通过从 Flink Application 提交作业来创建逻辑图。逻辑图通常也称为数据流图。ExecutionGraph
:JobManager
根据JobGraph
生成ExecutionGraph
。ExecutionGraph
是JobGraph
的并行化版本:一个JobVertex
对应一个ExecutionJobVertex
,根据一个JobVertex
的并行度(一个Task
可以并行在不同的TaskManager
上执行),生成相对应数量的ExecutionVertex
。同时在这个图中多了一层IntermediateResult
,表示执行的中间结果。IntermediateResult
与ExecutionJobVertex
之间通过ExecutionEdge
形成连接。ExecutionGraph
是调度层最核心的数据结构,JobManager
通过它来调度任务的执行。ExecutionGraph是JobMaster的成员,构建发生在JobMaster的构造方法中。官方文档
:见Physical Graph
。Physical Graph
是一个在分布式运行时,把Logical Graph
转换为可执行的结果。节点是Task
,边表示数据流或数据集的输入/输出关系或partition
。Physical Graph
:JobManager
根据ExecutionGraph
对Job
进行调度后,在各个TaskManager
上部署Task
后形成的“图”,与ExecutionGraph
基本保持一致。它只是一个任务执行状态的逻辑展示,并不是一个具体的数据结构。官方文档
:Physical graph
是一个在分布式运行时,把Logical Graph
转换为可执行的结果。节点是Task
,边表示数据流或数据集的输入/输出关系或partition
。
相关词汇
JobManager
: Flink JobManager 是 Flink Cluster 的主节点。它包含三个不同的组件:Flink Resource Manager、Flink Dispatcher、运行每个 Flink Job 的 Flink JobMaster。TaskManager
: TaskManager 是 Flink Cluster 的工作进程。Task 被调度到 TaskManager 上执行。TaskManager 相互通信,只为在后续的 Task 之间交换数据。
关于
JobManager
和TaskManager
可以查看 Flink 架构官方文档:https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.17/zh/docs/concepts/flink-architecture/
Job
: Flink Job 表示为 runtime 的 logical graph(通常也称为数据流图),通过在 Flink Application 中调用 execute() 方法来创建和提交 。Operator
: Logical Graph 的节点。算子执行某种操作,该操作通常由 Function 执行。Source 和 Sink 是数据输入和数据输出的特殊算子。Function
: Function 是由用户实现的,并封装了 Flink 程序的应用程序逻辑。大多数 Function 都由相应的 Operator 封装。Task
: Task 是 Physical Graph 的节点。它是基本的工作单元,由 Flink 的 runtime 来执行。Task 正好封装了一个 Operator 或者 Operator Chain 的 parallel instance。Transformation
: Transformation 应用于一个或多个数据流或数据集,并产生一个或多个输出数据流或数据集。Transformation 可能会在每个记录的基础上更改数据流或数据集,但也可以只更改其分区或执行聚合。虽然 Operator 和 Function 是 Flink API 的“物理”部分,但 Transformation 只是一个 API 概念。具体来说,大多数(但不是全部)Transformation 是由某些 Operator 实现
相关类
StreamExecutionEnvironmentLocalStreamEnvironmentTableEnvironmentImplDefaultExecutorStreamGraphGeneratorLocalExecutorPipelineExecutorUtilsFlinkPipelineTranslationUtilStreamGraphTranslatorStreamGraphStreamingJobGraphGenerator
调试代码
DataStream API: Hudi Flink SQL代码示例及本地调试
Table API: Flink Hudi DataStream API代码示例
入口
DataStream API 的入口比 Table API 的入口更直观更好找(或者更容易理解)
DataStream API
env.execute
Table API
tableEnv.executeSql
-> TableEnvironmentImpl.executeSql
-> executeInternal(Operation operation)
-> executeInternal(List<ModifyOperation> operations)
tableEnv.executeSql
executeInternal(List<ModifyOperation> operations)
public TableResultInternal executeInternal(List<ModifyOperation> operations) {
List<Transformation<?>> transformations = translate(operations);
List<String> sinkIdentifierNames = extractSinkIdentifierNames(operations);
// 关键步骤:入口
TableResultInternal result = executeInternal(transformations, sinkIdentifierNames);
if (tableConfig.get(TABLE_DML_SYNC)) {
try {
result.await();
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException e) {
result.getJobClient().ifPresent(JobClient::cancel);
throw new TableException("Fail to wait execution finish.", e);
}
}
return result;
}
StreamGraph
虽然入口不一样,但是 DataStream API 和 Table API 最终都是通过 StreamExecutionEnvironment
的 getStreamGraphGenerator(transformations).generate()
继而通过 StreamGraphGenerator.generate
生成 StreamGraph
的
DataStream API
StreamExecutionEnvironment.execute
->StreamExecutionEnvironment.getStreamGraph
env(LocalStreamEnvironment)
public class LocalStreamEnvironment extends StreamExecutionEnvironment {
StreamExecutionEnvironment.execute
public JobExecutionResult execute(String jobName) throws Exception {
Preconditions.checkNotNull(jobName, "Streaming Job name should not be null.");
final StreamGraph streamGraph = getStreamGraph();
streamGraph.setJobName(jobName);
return execute(streamGraph);
}
StreamExecutionEnvironment.getStreamGraph
public StreamGraph getStreamGraph() {
return getStreamGraph(true);
}
public StreamGraph getStreamGraph(boolean clearTransformations) {
// 公共部分
final StreamGraph streamGraph = getStreamGraphGenerator(transformations).generate();
if (clearTransformations) {
transformations.clear();
}
return streamGraph;
}
Table API
TableEnvironmentImpl.executeSql
->executeInternal(Operation operation)
->executeInternal(List<ModifyOperation> operations)
->executeInternal(transformations, sinkIdentifierNames)
->DefaultExecutor.createPipeline
->StreamExecutionEnvironment.generateStreamGraph
private TableResultInternal executeInternal(
List<Transformation<?>> transformations, List<String> sinkIdentifierNames) {
final String defaultJobName = "insert-into_" + String.join(",", sinkIdentifierNames);
// We pass only the configuration to avoid reconfiguration with the rootConfiguration
// 这里的pipeline实际上就是StreamGraph,StreamGraph是 Pipeline 的子类
// execEnv为DefaultExecutor
// 为啥是DefaultExecutor?
// `StreamTableEnvironment.create` -> `StreamTableEnvironmentImpl.create`->`lookupExecutor` -> `DefaultExecutorFactory.create`
Pipeline pipeline =
execEnv.createPipeline(
transformations, tableConfig.getConfiguration(), defaultJobName);
try {
JobClient jobClient = execEnv.executeAsync(pipeline);
final List<Column> columns = new ArrayList<>();
Long[] affectedRowCounts = new Long[transformations.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < transformations.size(); ++i) {
// use sink identifier name as field name
columns.add(Column.physical(sinkIdentifierNames.get(i), DataTypes.BIGINT()));
affectedRowCounts[i] = -1L;
}
return TableResultImpl.builder()
.jobClient(jobClient)
.resultKind(ResultKind.SUCCESS_WITH_CONTENT)
.schema(ResolvedSchema.of(columns))
.resultProvider(
new InsertResultProvider(affectedRowCounts).setJobClient(jobClient))
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new TableException("Failed to execute sql", e);
}
}
DefaultExecutor.createPipeline
@Override
public Pipeline createPipeline(
List<Transformation<?>> transformations,
ReadableConfig tableConfiguration,
@Nullable String defaultJobName) {
// reconfigure before a stream graph is generated
executionEnvironment.configure(tableConfiguration);
// create stream graph
final RuntimeExecutionMode mode = getConfiguration().get(ExecutionOptions.RUNTIME_MODE);
switch (mode) {
case BATCH:
configureBatchSpecificProperties();
break;
case STREAMING:
break;
case AUTOMATIC:
default:
throw new TableException(String.format("Unsupported runtime mode: %s", mode));
}
// 这里的executionEnvironment为LocalStreamEnvironment (Local模式),
// 实际调用父类StreamExecutionEnvironment的generateStreamGraph
final StreamGraph streamGraph = executionEnvironment.generateStreamGraph(transformations);
setJobName(streamGraph, defaultJobName);
return streamGraph;
}
StreamExecutionEnvironment.generateStreamGraph
public StreamGraph generateStreamGraph(List<Transformation<?>> transformations) {
// 公共部分
return getStreamGraphGenerator(transformations).generate();
}
公共部分
StreamExecutionEnvironment.getStreamGraphGenerator
->StreamGraphGenerator.generate
StreamExecutionEnvironment.getStreamGraphGenerator
private StreamGraphGenerator getStreamGraphGenerator(List<Transformation<?>> transformations) {
if (transformations.size() <= 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"No operators defined in streaming topology. Cannot execute.");
}
// We copy the transformation so that newly added transformations cannot intervene with the
// stream graph generation.
return new StreamGraphGenerator(
new ArrayList<>(transformations), config, checkpointCfg, configuration)
.setStateBackend(defaultStateBackend)
.setChangelogStateBackendEnabled(changelogStateBackendEnabled)
.setSavepointDir(defaultSavepointDirectory)
.setChaining(isChainingEnabled)
.setUserArtifacts(cacheFile)
.setTimeCharacteristic(timeCharacteristic)
.setDefaultBufferTimeout(bufferTimeout)
.setSlotSharingGroupResource(slotSharingGroupResources);
}
StreamGraphGenerator.generate
public StreamGraph generate() {
streamGraph = new StreamGraph(executionConfig, checkpointConfig, savepointRestoreSettings);
streamGraph.setEnableCheckpointsAfterTasksFinish(
configuration.get(
ExecutionCheckpointingOptions.ENABLE_CHECKPOINTS_AFTER_TASKS_FINISH));
shouldExecuteInBatchMode = shouldExecuteInBatchMode();
configureStreamGraph(streamGraph);
alreadyTransformed = new IdentityHashMap<>();
for (Transformation<?> transformation : transformations) {
transform(transformation);
}
streamGraph.setSlotSharingGroupResource(slotSharingGroupResources);
setFineGrainedGlobalStreamExchangeMode(streamGraph);
for (StreamNode node : streamGraph.getStreamNodes()) {
if (node.getInEdges().stream().anyMatch(this::shouldDisableUnalignedCheckpointing)) {
for (StreamEdge edge : node.getInEdges()) {
edge.setSupportsUnalignedCheckpoints(false);
}
}
}
final StreamGraph builtStreamGraph = streamGraph;
alreadyTransformed.clear();
alreadyTransformed = null;
streamGraph = null;
return builtStreamGraph;
}
到这里
StreamGraph
就生成了,它是在 Client 端生成的
JobGraph
从分析生成 StreamGraph
的源码中可知,生成StreamGraph
之后接下来就是生成 JobGraph
。
DataStream API 和 Table API 都是在StreamExecutionEnvironment.executeAsync
方法中最终通过 StreamingJobGraphGenerator.createJobGraph
生成JobGraph
的
DataStream API
StreamExecutionEnvironment.execute
->LocalStreamEnvironment.execute(streamGraph)
->StreamExecutionEnvironment.execute(streamGraph)
->StreamExecutionEnvironment.executeAsync
回到
StreamExecutionEnvironment.execute
,LocalStreamEnvironment.execute(streamGraph)
public JobExecutionResult execute(StreamGraph streamGraph) throws Exception {
return super.execute(streamGraph);
}
StreamExecutionEnvironment.execute(streamGraph)
@Internal
public JobExecutionResult execute(StreamGraph streamGraph) throws Exception {
// 关键位置
final JobClient jobClient = executeAsync(streamGraph);
try {
final JobExecutionResult jobExecutionResult;
if (configuration.getBoolean(DeploymentOptions.ATTACHED)) {
jobExecutionResult = jobClient.getJobExecutionResult().get();
} else {
jobExecutionResult = new DetachedJobExecutionResult(jobClient.getJobID());
}
jobListeners.forEach(
jobListener -> jobListener.onJobExecuted(jobExecutionResult, null));
return jobExecutionResult;
} catch (Throwable t) {
// get() on the JobExecutionResult Future will throw an ExecutionException. This
// behaviour was largely not there in Flink versions before the PipelineExecutor
// refactoring so we should strip that exception.
Throwable strippedException = ExceptionUtils.stripExecutionException(t);
jobListeners.forEach(
jobListener -> {
jobListener.onJobExecuted(null, strippedException);
});
ExceptionUtils.rethrowException(strippedException);
// never reached, only make javac happy
return null;
}
}
Table API
executeInternal(transformations, sinkIdentifierNames)
-> DefaultExecutor.executeAsync
-> StreamExecutionEnvironment.executeAsync
private TableResultInternal executeInternal(
List<Transformation<?>> transformations, List<String> sinkIdentifierNames) {
final String defaultJobName = "insert-into_" + String.join(",", sinkIdentifierNames);
// We pass only the configuration to avoid reconfiguration with the rootConfiguration
// 这里的pipeline实际上就是StreamGraph
// execEnv为DefaultExecutor
// 为啥是DefaultExecutor?
// `StreamTableEnvironment.create` -> `StreamTableEnvironmentImpl.create`->`lookupExecutor` -> `DefaultExecutorFactory.create`
Pipeline pipeline =
execEnv.createPipeline(
transformations, tableConfig.getConfiguration(), defaultJobName);
try {
// DefaultExecutor.executeAsync
JobClient jobClient = execEnv.executeAsync(pipeline);
final List<Column> columns = new ArrayList<>();
Long[] affectedRowCounts = new Long[transformations.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < transformations.size(); ++i) {
// use sink identifier name as field name
columns.add(Column.physical(sinkIdentifierNames.get(i), DataTypes.BIGINT()));
affectedRowCounts[i] = -1L;
}
return TableResultImpl.builder()
.jobClient(jobClient)
.resultKind(ResultKind.SUCCESS_WITH_CONTENT)
.schema(ResolvedSchema.of(columns))
.resultProvider(
new InsertResultProvider(affectedRowCounts).setJobClient(jobClient))
.build();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new TableException("Failed to execute sql", e);
}
}
DefaultExecutor.executeAsync
public JobClient executeAsync(Pipeline pipeline) throws Exception {
// 这里的executionEnvironment为LocalStreamEnvironment (Local模式),
// 实际调用父类StreamExecutionEnvironment的generateStreamGraph
return executionEnvironment.executeAsync((StreamGraph) pipeline);
}
公共部分
StreamExecutionEnvironment.executeAsync
->LocalExecutor.execute
->LocalExecutor.getJobGraph
->PipelineExecutorUtils.getJobGraph
->FlinkPipelineTranslationUtil.getJobGraph
->StreamGraphTranslator.translateToJobGraph
->StreamGraph.getJobGraph
->StreamingJobGraphGenerator.createJobGraph
StreamExecutionEnvironment.executeAsync
@Internal
public JobClient executeAsync(StreamGraph streamGraph) throws Exception {
checkNotNull(streamGraph, "StreamGraph cannot be null.");
checkNotNull(
configuration.get(DeploymentOptions.TARGET),
"No execution.target specified in your configuration file.");
final PipelineExecutorFactory executorFactory =
executorServiceLoader.getExecutorFactory(configuration);
checkNotNull(
executorFactory,
"Cannot find compatible factory for specified execution.target (=%s)",
configuration.get(DeploymentOptions.TARGET));
CompletableFuture<JobClient> jobClientFuture =
executorFactory
// 这里的Executor为LocalExecutor
.getExecutor(configuration)
// StreamGraph是Pipeline的实现类
.execute(streamGraph, configuration, userClassloader);
try {
JobClient jobClient = jobClientFuture.get();
jobListeners.forEach(jobListener -> jobListener.onJobSubmitted(jobClient, null));
return jobClient;
} catch (ExecutionException executionException) {
final Throwable strippedException =
ExceptionUtils.stripExecutionException(executionException);
jobListeners.forEach(
jobListener -> jobListener.onJobSubmitted(null, strippedException));
throw new FlinkException(
String.format("Failed to execute job '%s'.", streamGraph.getJobName()),
strippedException);
}
}
LocalExecutor.execute
public CompletableFuture<JobClient> execute(
Pipeline pipeline, Configuration configuration, ClassLoader userCodeClassloader)
throws Exception {
checkNotNull(pipeline);
checkNotNull(configuration);
Configuration effectiveConfig = new Configuration();
effectiveConfig.addAll(this.configuration);
effectiveConfig.addAll(configuration);
// we only support attached execution with the local executor.
checkState(configuration.getBoolean(DeploymentOptions.ATTACHED));
final JobGraph jobGraph = getJobGraph(pipeline, effectiveConfig);
return PerJobMiniClusterFactory.createWithFactory(effectiveConfig, miniClusterFactory)
.submitJob(jobGraph, userCodeClassloader);
}
LocalExecutor.getJobGraph
private JobGraph getJobGraph(Pipeline pipeline, Configuration configuration)
throws MalformedURLException {
// This is a quirk in how LocalEnvironment used to work. It sets the default parallelism
// to <num taskmanagers> * <num task slots>. Might be questionable but we keep the behaviour
// for now.
if (pipeline instanceof Plan) {
Plan plan = (Plan) pipeline;
final int slotsPerTaskManager =
configuration.getInteger(
TaskManagerOptions.NUM_TASK_SLOTS, plan.getMaximumParallelism());
final int numTaskManagers =
configuration.getInteger(ConfigConstants.LOCAL_NUMBER_TASK_MANAGER, 1);
plan.setDefaultParallelism(slotsPerTaskManager * numTaskManagers);
}
return PipelineExecutorUtils.getJobGraph(pipeline, configuration);
}
PipelineExecutorUtils.getJobGraph
public static JobGraph getJobGraph(
@Nonnull final Pipeline pipeline, @Nonnull final Configuration configuration)
throws MalformedURLException {
checkNotNull(pipeline);
checkNotNull(configuration);
final ExecutionConfigAccessor executionConfigAccessor =
ExecutionConfigAccessor.fromConfiguration(configuration);
final JobGraph jobGraph =
FlinkPipelineTranslationUtil.getJobGraph(
pipeline, configuration, executionConfigAccessor.getParallelism());
configuration
.getOptional(PipelineOptionsInternal.PIPELINE_FIXED_JOB_ID)
.ifPresent(strJobID -> jobGraph.setJobID(JobID.fromHexString(strJobID)));
jobGraph.addJars(executionConfigAccessor.getJars());
jobGraph.setClasspaths(executionConfigAccessor.getClasspaths());
jobGraph.setSavepointRestoreSettings(executionConfigAccessor.getSavepointRestoreSettings());
return jobGraph;
}
FlinkPipelineTranslationUtil.getJobGraph
/** Transmogrifies the given {@link Pipeline} to a {@link JobGraph}. */
public static JobGraph getJobGraph(
Pipeline pipeline, Configuration optimizerConfiguration, int defaultParallelism) {
// 这里返回StreamGraphTranslator
FlinkPipelineTranslator pipelineTranslator = getPipelineTranslator(pipeline);
return pipelineTranslator.translateToJobGraph(
pipeline, optimizerConfiguration, defaultParallelism);
}
StreamGraphTranslator.translateToJobGraph
public JobGraph translateToJobGraph(
Pipeline pipeline, Configuration optimizerConfiguration, int defaultParallelism) {
checkArgument(
pipeline instanceof StreamGraph, "Given pipeline is not a DataStream StreamGraph.");
StreamGraph streamGraph = (StreamGraph) pipeline;
return streamGraph.getJobGraph(null);
}
StreamGraph.getJobGraph
public JobGraph getJobGraph(@Nullable JobID jobID) {
return StreamingJobGraphGenerator.createJobGraph(this, jobID);
}
StreamingJobGraphGenerator.createJobGraph
public static JobGraph createJobGraph(StreamGraph streamGraph, @Nullable JobID jobID) {
return new StreamingJobGraphGenerator(streamGraph, jobID).createJobGraph();
}
private StreamingJobGraphGenerator(StreamGraph streamGraph, @Nullable JobID jobID) {
this.streamGraph = streamGraph;
this.defaultStreamGraphHasher = new StreamGraphHasherV2();
this.legacyStreamGraphHashers = Arrays.asList(new StreamGraphUserHashHasher());
this.jobVertices = new HashMap<>();
this.builtVertices = new HashSet<>();
this.chainedConfigs = new HashMap<>();
this.vertexConfigs = new HashMap<>();
this.chainedNames = new HashMap<>();
this.chainedMinResources = new HashMap<>();
this.chainedPreferredResources = new HashMap<>();
this.chainedInputOutputFormats = new HashMap<>();
this.physicalEdgesInOrder = new ArrayList<>();
jobGraph = new JobGraph(jobID, streamGraph.getJobName());
}
到这里
JobGraph
就生成了,它和StreamGraph
都是在 Client 端生成的
小结
本文目标是学习总结从 Flink 入口到执行 Hudi 自定义 StreamOperator
的逻辑的主要调用步骤,也就是研究 Flink 的 Task
或者 Function
是如何运行的。由于这块逻辑比较复杂,本文先主要总结了:
1、Flink 的 Transformation
、StreamOperator
2、阐述了写Hudi逻辑与Transformation
、StreamOperator
的关系,知道了实际上写 Hudi 的主要逻辑就是在 Hudi 自定义的StreamOperator
和SinkFunction
中实现的
3、Flink的四层执行图以及相关词汇概念解释
4、StreamGraph
和 JobGraph
的生成构建过程
对于后面的ExecutionGraph
、Physical Graph
、JobManager
和TaskManager
的启动等还没有分析,等我有空时再分几篇文章来进行总结。
相关阅读
🧐 分享、点赞、在看,给个3连击呗!👇