Oracle update restart特性解析2
概念解析
关于SCN解析
LSN (Log Sequence Number)表示事务日志的写入位置,用于唯一标识事务日志记录(XLOG record),和Oracle中的SCN(System Change Number)类似,但也有不同之处,
LSN表示事务日志的写入位置,在没有新日志写入时,LSN不变。
SCN表示数据库变更操作的逻辑时间点,在没有新日志写入时,SCN是不断增大的。
### pg中的测试结果
postgres=# select pg_current_wal_lsn();
pg_current_wal_lsn
--------------------
3/6000FF8
(1 row)
postgres=# select pg_current_wal_lsn();
pg_current_wal_lsn
--------------------
3/6000FF8
(1 row)
postgres=# select pg_current_wal_lsn();
pg_current_wal_lsn
--------------------
3/6000FF8
(1 row)
postgres=#
### Oracle中的测试结果
SQL> select current_scn from v$database;
CURRENT_SCN
-----------
2487297
SQL> select current_scn from v$database;
CURRENT_SCN
-----------
2487299
SQL> select current_scn from v$database;
CURRENT_SCN
-----------
2487301
SQL>
What is System Change Number (SCN)?
The SCN is a stamp that defines a committed version of a database at a point in time. Oracle assigns every committed
transaction a unique SCN. The value of a SCN is the logical point in time at which changes are made to a database. This number is utilized by Oracle to log the changes made to the database.
Oracle 读一致性
Read Consistency: Example
Figure 9-1 shows a query that uses undo data to provide statement-level read consistency in the read committed isolation level.
Figure 9-1 Read Consistency in the Read Committed Isolation Level
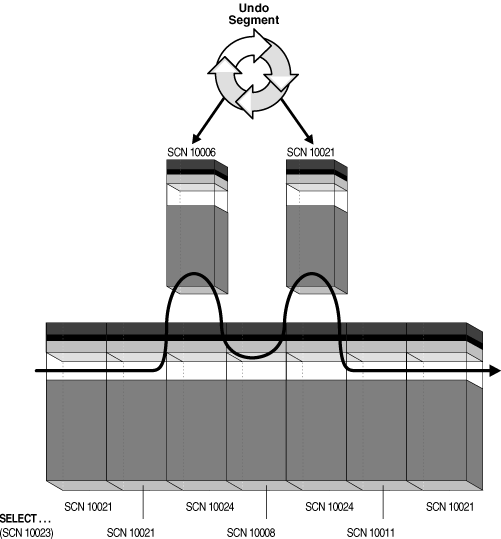
As the database retrieves data blocks on behalf of a query, the database ensures that the data in each block reflects the contents of the block when the query began. The database rolls back changes to the block as needed to reconstruct the block to the point in time the query started processing. The database uses a mechanism called an SCN to guarantee the order of transactions. As the SELECT statement enters the execution phase, the database determines the SCN recorded at the time the query began executing. In Figure 9-1, this SCN is 10023. The query only sees committed data with respect to SCN 10023. In Figure 9-1, blocks with SCNs after 10023 indicate changed data, as shown by the two blocks with SCN 10024. The SELECT statement requires a version of the block that is consistent with committed changes. The database copies current data blocks to a new buffer and applies undo data to reconstruct previous versions of the blocks. These reconstructed data blocks are called consistent read (CR) clones. In Figure 9-1, the database creates two CR clones: one block consistent to SCN 10006 and the other block consistent to SCN 10021. The database returns the reconstructed data for the query. In this way, Oracle Database prevents dirty reads.
关于Oracle锁
写一致性

一致读和当前读


重启动定义
Oracle数据库在执行update操作,一般情况,首先读一致块获取(read-consistent block get),然后读当前块获取(read current block get),将两次获取结果(update查询谓词)进行比较,如果相等则更新,否则(跳过这个记录,并将其忽略,就会有一个不确定的更新。这可能会破坏数据一致性和完整性。)回滚事务后,数据库会重启动更新(修改update执行时间),而且进入SELECT FOR UPDATE模式,再执行UPDATE操作(规避再次重启动)。

总结规律
Oracle数据库在执行update操作,一般情况,首先读一致块获取(read-consistent block get),然后读当前块获取(read current block get),将两次获取结果(update查询谓词)进行比较,如果相等则更新,否则(跳过这个记录,并将其忽略,就会有一个不确定的更新。这可能会破坏数据一致性和完整性。)回滚事务后,数据库会重启动更新(修改update执行时间),而且进入SELECT FOR UPDATE模式,再执行UPDATE操作(规避再次重启动)。 1. update restart分为以下四步 首次变更/回滚过程/锁定行/重做 2. 变更操作是按row的物理位置顺序进行,回滚是按倒序 3. 重做过程会修改update的开始时间 4. sess1 rollback则不restart 5. sess2有谓词但没变化,则不restart 6. sess2没有谓词的影响,则不restart 7. update操作一行锁定一行,不是一次锁定所有行,然后再更新
测试脚本
测试脚本下载地址: https://www.modb.pro/doc/119817
场景测试
场景一、复现重启动过程
场景二、sess1 rollback
场景三、sess3 插入行的影响
场景四、sess2有谓词但没变化
场景五、sess2没有谓词的影响
场景六、restart update 回滚规律
sess_1: update enmo.t set y = 1 where id = 5; sess_2: update enmo.t set y = 1 where id = 7; sess_3: update enmo.t set y = 2,z=3 where y > -1; sess_4: update enmo.t set y = 1 where id = 4;
场景七、自动化批量测试结果
场景八、mread_count=1对批量测试结果影响
场景九、索引+mread_count=1对批量测试结果影响
「喜欢这篇文章,您的关注和赞赏是给作者最好的鼓励」
关注作者
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文章的来源(墨天轮),文章链接,文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






