1、前言
上面文章中总结了Flink 获取 HBase 配置的逻辑和优先级,但是并没有对源码进行分析,本文主要是补充这一部分的源码分析。
2、版本
Flink 1.15.4
HBase 2.0.2
3、入口
从我之前写的文章:Flink用户自定义连接器(Table API Connectors)学习总结 中可知其实Flink Table API 读写 HBase 其实和通过自定义实现一个Table API Connectors ('connector' = 'hbase-2.2')差不多,只不过 HBase Connector 是Flink源码自带的,具体的模块为flink-connector-hbase-2.2,相关的类为HBase2DynamicTableFactory
、HBaseDynamicTableSource
和 HBaseDynamicTableSink
,入口为 HBase2DynamicTableFactory
。并且在Hudi Flink SQL源码调试学习(一)我们也总结了从tableEnv.executeSql
到FactoryUtil.createDynamicTableSink
这部分的源码分析。而在FactoryUtil.createDynamicTableSink
方法中会根据'connector'='hbase-2.2' 找到factory为org.apache.flink.connector.hbase2.HBase2DynamicTableFactory,接着调用 HBase2DynamicTableFactory.createDynamicTableSink
。所以我们前面的源码逻辑已经分析过了,现在只需要从HBase2DynamicTableFactory
开始进行分析就好了。
读:HBase2DynamicTableFactory
.createDynamicTableSource
写:HBase2DynamicTableFactory
.createDynamicTableSink
4、调试代码
代码地址:https://github.com/dongkelun/flink-learning/tree/master/flink-hbase
代码实现了Flink 本地读写远程服务器上带有 kerberos 认证的 HBase ,方便对Flink源码不熟悉的新手调试代码。代码和之前总结的Hudi Flink SQL代码示例及本地调试差不多,用tableEnv执行对应的Flink SQL即可。不同点是之前的读写hudi的路径是在Windows本地(因为hudi支持),但是本地没有 HBase,需要连接远程服务器上的 HBase 服务,我们的环境开启了kerberos认证,所以如何本地认证kerberos是个问题,因为之前用 Flink 本地认证kerberos的经验不多,所以尝试了一下,并总结了一点经验:
Flink 连接 HBase 仅仅有上篇文章 中提到的两个配置项(hbase.security.authentication 和 hbase.regionserver.kerberos.principal)是不够的。
对于在服务器上通过sql-client跑sql来说,以下两个kerberos配置是必要的:security.kerberos.login.keytab 和 security.kerberos.login.principal。对于sql-client而言,如果提交模式是yarn,那么还需要本地通过
kinit
缓存票据,否则提不到yarn上,如果提交模式是其他,比如提到standalone集群(默认提交方式),是不需要通过kinit
缓存票据的,因为standalone集群没有配置kerberos。而对于通过
bin/flink run
命令提交jar包的方式也不需要kinit
缓存票据,因为它会先获取 security.kerberos.login.keytab 和 security.kerberos.login.principal 两个配置项的值先进行kerberos认证。我们在它的提交日志里就可以看出来:
而sql-client的提交日志里就没有这个信息,说明sql-client 和bin/flink run
提交任务时认证kerberos的逻辑是不一致的,具体的原因还要看对应的脚本和源码,本文先不进行研究~对于本地程序而言,又不一样了。因为我最开始不知道本地程序缺少什么配置(本地相对于服务器上面的配置会缺很多,比如flink-conf.yaml),只能从服务端通过sql-client来验证(比如修改flink-conf.yaml,去掉kerberos缓存),最终验证结论如上述所言。所以在本地程序最开始尝试通过添加
security.kerberos.login.keytab 和 security.kerberos.login.principal 两个配置项来解决,但是发现没有效果。添加配置项代码如下:
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.SecurityOptions;
Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
configuration.set(SecurityOptions.KERBEROS_LOGIN_KEYTAB, keytabPath);
configuration.set(SecurityOptions.KERBEROS_LOGIN_PRINCIPAL, principal);
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(configuration);
通过上面的代码添加配置项发现无效后,最终又尝试了通过UserGroupInformation.loginUserFromKeytab
认证kerberos来解决,发现这样就可以解决问题了。附运行成功图:
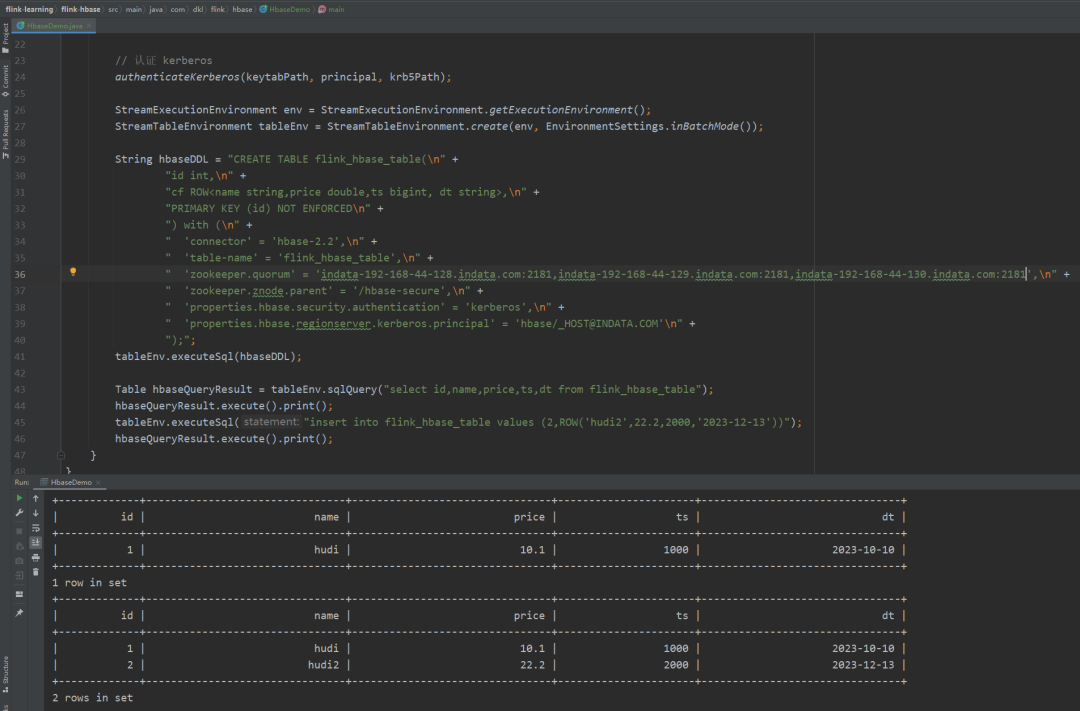
对于上篇文章 提到的不清楚为啥不需要配置:hbase.regionserver.keytab.file,好像也有了答案,只是我的一种推测,不一定是对的。就是认证kerberos是在别的地方提前认证的,比如先缓存票据,或者先获取security.kerberos.login.keytab 和 security.kerberos.login.principal 再认证,然后连接HBase时就不需要了,至于为啥需要hbase.regionserver.kerberos.principal,可能就和连接Spark Thrift Server 一样,需要在url里指定 principal=HTTP/indata-192-168-44-128.indata.com@INDATA.COM,但是这个principal和实际认证keytab的principal的值是可以不一样的。
因为我们本篇文章只是想研究获取HBase配置的部分源码逻辑,所以其实也可以不用连通HBbase就行,因为先获取HBase配置,再去连接。所以获取配置在前面,我们调试的话只需要调试前面获取配置的部分。
5、DynamicTableFactory
HBase2DynamicTableFactory
5.1 tableOptions 我们在建表语句中的配置,如:'connector' = 'hbase-2.2',也就是用户自定义参数,优先级最高的配置
5.2 然后 HBaseConnectorOptionsUtil.getHBaseConfiguration(tableOptions) 获取 hbaseConf
5.3 最后将 hbaseConf 传给 HBaseDynamicTableSource 和 HBaseDynamicTableSink
@Override
public DynamicTableSource createDynamicTableSource(Context context) {
TableFactoryHelper helper = createTableFactoryHelper(this, context);
helper.validateExcept(PROPERTIES_PREFIX);
// tableOptions 我们在建表语句中的配置,如:'connector' = 'hbase-2.2'
// 也就是用户自定义参数,优先级最高的配置
final ReadableConfig tableOptions = helper.getOptions();
validatePrimaryKey(context.getPhysicalRowDataType(), context.getPrimaryKeyIndexes());
String tableName = tableOptions.get(TABLE_NAME);
// 然后 getHBaseConfiguration(tableOptions) 获取 hbaseConf
Configuration hbaseConf = getHBaseConfiguration(tableOptions);
HBaseLookupOptions lookupOptions = getHBaseLookupOptions(tableOptions);
String nullStringLiteral = tableOptions.get(NULL_STRING_LITERAL);
HBaseTableSchema hbaseSchema =
HBaseTableSchema.fromDataType(context.getPhysicalRowDataType());
// 最后将 hbaseConf 传给 HBaseDynamicTableSource
return new HBaseDynamicTableSource(
hbaseConf, tableName, hbaseSchema, nullStringLiteral, lookupOptions);
}
@Override
public DynamicTableSink createDynamicTableSink(Context context) {
TableFactoryHelper helper = createTableFactoryHelper(this, context);
helper.validateExcept(PROPERTIES_PREFIX);
// tableOptions 我们在建表语句中的配置,如:'connector' = 'hbase-2.2'
// 也就是用户自定义参数,优先级最高的配置
final ReadableConfig tableOptions = helper.getOptions();
validatePrimaryKey(context.getPhysicalRowDataType(), context.getPrimaryKeyIndexes());
String tableName = tableOptions.get(TABLE_NAME);
Configuration hbaseConf = getHBaseConfiguration(tableOptions);
// 然后 getHBaseConfiguration(tableOptions) 获取 hbaseConf
HBaseWriteOptions hBaseWriteOptions = getHBaseWriteOptions(tableOptions);
String nullStringLiteral = tableOptions.get(NULL_STRING_LITERAL);
HBaseTableSchema hbaseSchema =
HBaseTableSchema.fromDataType(context.getPhysicalRowDataType());
// 最后将 hbaseConf 传给 HBaseDynamicTableSink
return new HBaseDynamicTableSink(
tableName, hbaseSchema, hbaseConf, hBaseWriteOptions, nullStringLiteral);
}
6、ConnectorOptionsUtil
HBaseConnectorOptionsUtil.getHBaseConfiguration
6.1 首先通过 HBaseConfigurationUtil.getHBaseConfiguration() 获取 hbaseClientConf ,这个方法里就包含了 classpath 和 环境变量两个优先级的获取
6.2 最后根据用户自定义参数更新 hbaseClientConf 并返回。从这里就可以看出用户自定义参数是要比 classpath 和 环境变量 优先级高的。
public static Configuration getHBaseConfiguration(ReadableConfig tableOptions) {
// create default configuration from current runtime env (`hbase-site.xml` in classpath)
// first,
// 首先通过 HBaseConfigurationUtil.getHBaseConfiguration() 获取 hbaseClientConf
// 这个方法里就包含了 classpath 和 环境变量两个优先级的获取
Configuration hbaseClientConf = HBaseConfigurationUtil.getHBaseConfiguration();
// 最后根据用户自定义参数更新 hbaseClientConf 并返回
hbaseClientConf.set(HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_QUORUM, tableOptions.get(ZOOKEEPER_QUORUM));
hbaseClientConf.set(
HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_ZNODE_PARENT, tableOptions.get(ZOOKEEPER_ZNODE_PARENT));
// add HBase properties
final Properties properties =
getHBaseClientProperties(
((org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration) tableOptions).toMap());
properties.forEach((k, v) -> hbaseClientConf.set(k.toString(), v.toString()));
return hbaseClientConf;
}
7、HBaseConfigurationUtil
HBaseConfigurationUtil.getHBaseConfiguration()
7.1 HBaseConfiguration.create() 方法会获取 classpath 中的 hbase-site.xml 和 hbase-default.xml,hbase-site.xml 优先级要高于 hbase-default.xml
7.2 先判断有没有HBASE_HOME环境变量,如果有则读取 hbase-site.xml 和 hbase-default.xml,hbase-site.xml 优先级要高于 hbase-default.xml (具体可以看addHBaseConfIfFound方法)
7.3 然后判断有没有HBASE_CONF_DIR环境变量,如果有则读取 hbase-site.xml 和 hbase-default.xml,hbase-site.xml 优先级要高于 hbase-default.xml (具体可以看addHBaseConfIfFound方法)
后面的配置会覆盖前面的配置,所以从优先级上来看 HBASE_CONF_DIR环境变量 > HBASE_HOME环境变量 >HBaseConfiguration.create() (classpath)
备注:addResource方法会读取新的配置覆盖旧的配置,也就是会更新配置,所以最后读取的配置优先级最高
public static Configuration getHBaseConfiguration() {
// Instantiate an HBaseConfiguration to load the hbase-default.xml and hbase-site.xml from
// the classpath.
// 获取 classpath 中的 hbase-site.xml 和 hbase-default.xml
// hbase-site.xml 优先级要高于 hbase-default.xml
Configuration result = HBaseConfiguration.create();
boolean foundHBaseConfiguration = false;
// We need to load both hbase-default.xml and hbase-site.xml to the hbase configuration
// The properties of a newly added resource will override the ones in previous resources, so
// a configuration
// file with higher priority should be added later.
// Approach 1: HBASE_HOME environment variables
String possibleHBaseConfPath = null;
final String hbaseHome = System.getenv("HBASE_HOME");
// 先判断有没有HBASE_HOME环境变量
if (hbaseHome != null) {
LOG.debug("Searching HBase configuration files in HBASE_HOME: {}", hbaseHome);
possibleHBaseConfPath = hbaseHome + "/conf";
}
// 如果有则读取 hbase-site.xml 和 hbase-default.xml
if (possibleHBaseConfPath != null) {
foundHBaseConfiguration = addHBaseConfIfFound(result, possibleHBaseConfPath);
}
// Approach 2: HBASE_CONF_DIR environment variable
String hbaseConfDir = System.getenv("HBASE_CONF_DIR");
// 然后判断有没有HBASE_CONF_DIR环境变量
// 如果有则读取 hbase-site.xml 和 hbase-default.xml
if (hbaseConfDir != null) {
LOG.debug("Searching HBase configuration files in HBASE_CONF_DIR: {}", hbaseConfDir);
foundHBaseConfiguration =
addHBaseConfIfFound(result, hbaseConfDir) || foundHBaseConfiguration;
}
if (!foundHBaseConfiguration) {
LOG.warn(
"Could not find HBase configuration via any of the supported methods "
+ "(Flink configuration, environment variables).");
}
return result;
}
HBaseConfiguration.create()
public static Configuration create() {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.setClassLoader(HBaseConfiguration.class.getClassLoader());
return addHbaseResources(conf);
}
public static Configuration addHbaseResources(Configuration conf) {
// classpath 中的 hbase-site.xml
conf.addResource("hbase-default.xml");
// classpath 中的 hbase-default.xml
conf.addResource("hbase-site.xml");
checkDefaultsVersion(conf);
HeapMemorySizeUtil.checkForClusterFreeMemoryLimit(conf);
return conf;
}
8、HBaseDynamicTableSink
对于 5.3 提到的 HBaseDynamicTableSource 和 HBaseDynamicTableSink ,我们先只分析 HBaseDynamicTableSink 。我们在 Hudi Flink SQL源码调试学习(一) 有总结过从 tableEnv.executeSql
到 Hudi 的 getSinkRuntimeProvider
的源码分析,类似的HBase也是一样的也会走到 (CommonExecSink)createSinkTransformation
继而调用 HBaseDynamicTableSink
.getSinkRuntimeProvider
。
public SinkRuntimeProvider getSinkRuntimeProvider(Context context) {
HBaseSinkFunction<RowData> sinkFunction =
new HBaseSinkFunction<>(
tableName,
hbaseConf,
new RowDataToMutationConverter(hbaseTableSchema, nullStringLiteral),
writeOptions.getBufferFlushMaxSizeInBytes(),
writeOptions.getBufferFlushMaxRows(),
writeOptions.getBufferFlushIntervalMillis());
return SinkFunctionProvider.of(sinkFunction, writeOptions.getParallelism());
}
8.1 HBaseSinkFunction
在
CommonExecSink
.createSinkTransformation
方法中拿到runtimeProvider
之后会调用applySinkProvider
,从上面代码可知,这里的 runtimeProvider 是 SinkFunctionProvider,所以会先调用 runtimeProvider.createSinkFunction
private Transformation<?> applySinkProvider(
Transformation<RowData> inputTransform,
StreamExecutionEnvironment env,
SinkRuntimeProvider runtimeProvider,
int rowtimeFieldIndex,
int sinkParallelism,
ExecNodeConfig config) {
TransformationMetadata sinkMeta = createTransformationMeta(SINK_TRANSFORMATION, config);
if (runtimeProvider instanceof DataStreamSinkProvider) {
.....
return provider.consumeDataStream(createProviderContext(config), dataStream)
.getTransformation();
} else if (runtimeProvider instanceof TransformationSinkProvider) {
.....
} else if (runtimeProvider instanceof SinkFunctionProvider) {
// 走到这里
// 先调用 runtimeProvider.createSinkFunction
// `createSinkFunction` 返回 `HBaseSinkFunction`
final SinkFunction<RowData> sinkFunction =
((SinkFunctionProvider) runtimeProvider).createSinkFunction();
// 接着调用 `createSinkFunctionTransformation`
return createSinkFunctionTransformation(
sinkFunction,
env,
inputTransform,
rowtimeFieldIndex,
sinkMeta,
sinkParallelism);
} else if (runtimeProvider instanceof OutputFormatProvider) {
.....
} else if (runtimeProvider instanceof SinkProvider) {
.....
} else if (runtimeProvider instanceof SinkV2Provider) {
.....
} else {
throw new TableException("Unsupported sink runtime provider.");
}
}
createSinkFunction
返回HBaseSinkFunction
public SinkFunction<RowData> createSinkFunction() {
return sinkFunction;
}
接着调用
createSinkFunctionTransformation
, 在createSinkFunctionTransformation
会创建Operator
和Transformation
,关于Operator
和Transformation
可以参考 Hudi Flink源码总结(二)-Transformation/Operator总结,关于Function
是如何运行的,会在后面的文章继续总结,本文先不研究~,我们知道后面会运行Function
的open
方法就好了
private Transformation<?> createSinkFunctionTransformation(
SinkFunction<RowData> sinkFunction,
StreamExecutionEnvironment env,
Transformation<RowData> inputTransformation,
int rowtimeFieldIndex,
TransformationMetadata transformationMetadata,
int sinkParallelism) {
// 创建 `Operator`
final SinkOperator operator = new SinkOperator(env.clean(sinkFunction), rowtimeFieldIndex);
if (sinkFunction instanceof InputTypeConfigurable) {
((InputTypeConfigurable) sinkFunction)
.setInputType(getInputTypeInfo(), env.getConfig());
}
// 创建 `Transformation`
final Transformation<?> transformation =
new LegacySinkTransformation<>(
inputTransformation,
transformationMetadata.getName(),
SimpleOperatorFactory.of(operator),
sinkParallelism);
transformationMetadata.fill(transformation);
return transformation;
}
HBaseSinkFunction
.open
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
LOG.info("start open ...");
// 调用 prepareRuntimeConfiguration 获取 配置
org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration config = prepareRuntimeConfiguration();
try {
this.mutationConverter.open();
this.numPendingRequests = new AtomicLong(0);
if (null == connection) {
// 根据 config 连接 HBase
// 所以 config 就是最终配置
this.connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(config);
}
......
LOG.info("end open.");
}
在HBaseSinkFunction
.open
会调用 prepareRuntimeConfiguration 方法返回 config,然后根据 config 连接 HBase,所以 config 就是最终配置了
HBaseSinkFunction
.prepareRuntimeConfiguration
这里一共有两个配置 serializedConfig 和 HBaseConfigurationUtil.getHBaseConfiguration()。这里的 serializedConfig 的优先级要比 HBaseConfigurationUtil.getHBaseConfiguration() 高。我们在 7 中分析了 HBaseConfigurationUtil.getHBaseConfiguration()的逻辑,所以就不用再分析了,也就是它包含 classpath和环境变量两个优先级别的配置信息。serializedConfig。而 serializedConfig 是在 HBase2DynamicTableFactory中通过 HBaseConnectorOptionsUtil.getHBaseConfiguration 获取的,我们在6中分析了,它包含了classpath、环境变量、用户自定义三个优先级的配置信息。所以写 HBase 时连接 HBase 所使用的的配置 就是在6中分析的用 HBaseConnectorOptionsUtil.getHBaseConfiguration 获取的配置,和上篇文章分析的逻辑一致。而后面的 prepareRuntimeConfiguration 并没有改变任何配置信息。
private org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration prepareRuntimeConfiguration() throws IOException {
// create default configuration from current runtime env (`hbase-site.xml` in classpath)
// first,
// and overwrite configuration using serialized configuration from client-side env
// (`hbase-site.xml` in classpath).
// user params from client-side have the highest priority
// 这里一共有两个配置 serializedConfig 和 HBaseConfigurationUtil.getHBaseConfiguration()
// serializedConfig 的优先级要比 HBaseConfigurationUtil.getHBaseConfiguration() 高
org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration runtimeConfig =
HBaseConfigurationUtil.deserializeConfiguration(
serializedConfig, HBaseConfigurationUtil.getHBaseConfiguration());
// do validation: check key option(s) in final runtime configuration
if (StringUtils.isNullOrWhitespaceOnly(runtimeConfig.get(HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_QUORUM))) {
LOG.error(
"Can not connect to HBase without {} configuration",
HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_QUORUM);
throw new IOException(
"Check HBase configuration failed, lost: '"
+ HConstants.ZOOKEEPER_QUORUM
+ "'!");
}
return runtimeConfig;
}
9、DynamicTableSource
HBaseDynamicTableSource
最后总结一下 5.3 提到的 HBaseDynamicTableSource,一开始以为 source 和 sink 是类似的逻辑:getLookupRuntimeProvider
-> HBaseRowDataLookupFunction
-> open
-> prepareRuntimeConfiguration
, 但是调试是发现并不一样。它的调用逻辑为:AbstractHBaseDynamicTableSource
(HBaseDynamicTableSource的父类).getScanRuntimeProvider
-> HBaseDynamicTableSource
.getInputFormat
(返回 HBaseRowDataInputFormat) -> AbstractTableInputFormat
.createInputSplits
(HBaseRowDataInputFormat的父类) -> HBaseRowDataInputFormat
.initTable
-> connectToTable
。
在 connectToTable 通过 getHadoopConfiguration 方法获取配置然后连接 HBase ,这里 getHadoopConfiguration 的逻辑和 HBaseSinkFunction
.prepareRuntimeConfiguration
是一样的。
private void connectToTable() throws IOException {
try {
if (connection == null) {
connection = ConnectionFactory.createConnection(getHadoopConfiguration());
}
TableName name = TableName.valueOf(getTableName());
table = connection.getTable(name);
regionLocator = connection.getRegionLocator(name);
} catch (TableNotFoundException tnfe) {
LOG.error("The table " + tableName + " not found ", tnfe);
throw new RuntimeException("HBase table '" + tableName + "' not found.", tnfe);
}
}
protected org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration getHadoopConfiguration() {
return HBaseConfigurationUtil.deserializeConfiguration(
serializedConfig, HBaseConfigurationUtil.getHBaseConfiguration());
}
分析一下为啥会调用 getScanRuntimeProvider
而不是 getLookupRuntimeProvider
,因为 AbstractHBaseDynamicTableSource 同时实现了 ScanTableSource 和 LookupTableSource,ScanTableSource 对应 getScanRuntimeProvider
,LookupTableSource对应getLookupRuntimeProvider
,可能是因为先实现了 ScanTableSource ,所以会调用 getScanRuntimeProvider
吧(不确定原因,以后再进行研究)。(我们在 Flink用户自定义连接器(Table API Connectors)学习总结 中也是实现了 ScanTableSource ,查询时会调用 getScanRuntimeProvider
~)
public abstract class AbstractHBaseDynamicTableSource
implements ScanTableSource, LookupTableSource, SupportsProjectionPushDown {
10、修改源码添加参数
我们在上篇文章讲到了修改源码,添加参数支持通过参数配置自定义 hbase-site.xml,就是在 HBaseConnectorOptionsUtil
.getHBaseConfiguration
添加了如下代码:
hbaseClientConf.addResource(
new org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path(
tableOptions.get(HBASE_CONF_DIR) + "/hbase-site.xml"));
优先级:如果放在最后那么优先级最高,比通过properties.*
等自定义参数(tableOptions
)要高,如果想比tableOptions
参数优先级低,则可以放在前面。代码:https://github.com/dongkelun/flink/commit/b9db276cc5eb7c68aba029efbac62c7fb9cc46d8
11、相关阅读
🧐 分享、点赞、在看,给个3连击呗!👇






