内容目录
0、前言1、链表介绍2、链表的实现3、测试例子4、运行结果
0、前言
在进行Linux设备驱动开发时,经常会看到链表的使用,链表是一种常见的数据结构,内核中广泛使用链表是因为:
a. 可拓展性
b. 封装
内核源码的可拓展较较好理解,内核庞大但一直在更新,代码不可写死,需要可修改删除,链表很好的符合这个特性。
1、链表介绍
根据链个数分为单链表、双链表,根据是否循环分为单向链表和循环链表。通常定义定义链表结构如下:
typedef struct node
{
ElemType data; //数据域
struct node *next; //指针域
}node, *list;
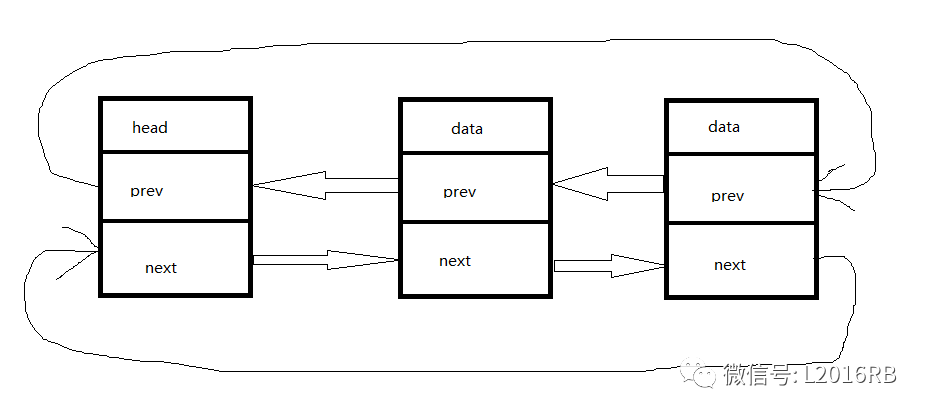
其中,双向循环链表如下图所示:
内核的链表结构也是双向循环链表,但内核的链表不包括数据域,如下图所示:
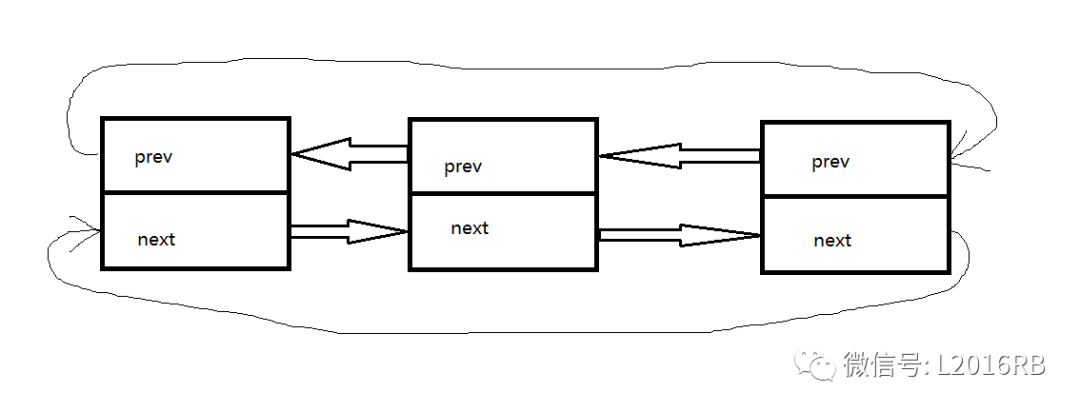
链表结构定义如下:
struct list_head {
struct list_head *next, *prev;
};
不包含数据域
例如,定义一个student 链表
struct student {
char name[32];
int id;
struct list_head list; //链表节点
};
Student 通过list进行链表操作
2、链表的实现
a. 创建链表
a) 使用宏
LIST_HEAD(name); //创建一个名为name的链表,实质上是创建一个头节点,头节点代表一个链表
struct list_head name = LIST_HEAD_INIT(name);
b. 添加节点
i. void list_add(struct list_head *new,struct list_head *head);//添加到首节点前面
ii. void list_add_tail(struct list_head *new, struct list_head *head);//添加到尾节点后面
new是要添加的节点,head是被添加的链表
c. 删除节点
a) void list_del(struct list_head *entry);
b) void list_del_init(struct list_head *entry);
参数entry指向要删除的节点,推荐使用 list_del_init更为安全
d. 对链表的判断
a) 判断节点是否是尾节点:
i. int list_is_last(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
b) 判断链表是否为空:
i. int list_empty(struct list_head *head)
c) 判断链表是否只有一个元素
i. int list_is_singular(struct list_head *head)
e. 遍历链表
list_for_each_entry(pos, head, member) //该宏的展开是一个for循环
f. 替换节点
void list_replace(struct list_head *old,struct list_head *new)
void list_replace_init(struct list_head *old,struct list_head *new)
g. 移动节点
void list_move(struct list_head *list, struct list_head *head)
void list_move_tail(struct list_head *list,struct list_head *head)
移动:从链表中删除,插入一个新的链表中
3、测试例子
代码:
list.h (包含各函数实现)
Student.c
再此给出student.c的代码
/*
* student.c
*
* Created on: 2018.10.14
*
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include "list.h"
struct list_head student_list;//创建链表,链表名是student_list
struct list_head *pos;
LIST_HEAD(student_list);
/* 定义学生的数据类型 */
struct student {
char name[32];
int id;
struct list_head list;
};
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
/* 判断链表是否为空链表 */
if(list_empty(&student_list))
printf("student_list is empty!\n");
else
printf("student_list is not empty!\n");
/* 向链表中添加节点 */
struct student *one = (struct student *)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
strcpy(one->name,"zhangsan");
one->id = 1;
list_add(&(one->list),&student_list); //将one 添加到链表student_list中
one = (struct student *)malloc(sizeof(struct student));
strcpy(one->name,"lisi");
one->id = 2;
list_add_tail(&(one->list),&student_list);//添加到链表student_list的尾部
/* 遍历链表 */
list_for_each(pos,&student_list)
{
one=list_entry(pos,struct student ,list);
printf(" ID: %d\t name:%s\n",one->id,one->name);
}
/* 删除一个节点 */
list_del_init(&(one->list));
/* 再次遍历链表 */
printf("del one node ,list is:\n");
list_for_each(pos,&student_list)
{
one=list_entry(pos,struct student ,list);
printf(" ID: %d\t name:%s\n",one->id,one->name);
}
/* 再次判断链表是否为空 */
if(list_empty(&student_list))
printf("list is empty!\n");
else
printf("list is not empty!\n");
return 0;
}
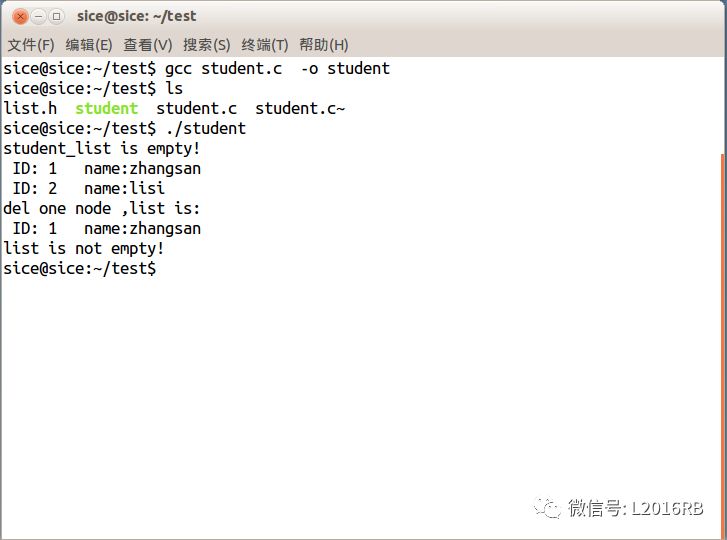
4、运行结果
文章转载自韭黄炒鸡蛋,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






