01
—
一、什么是时间轮
02
—
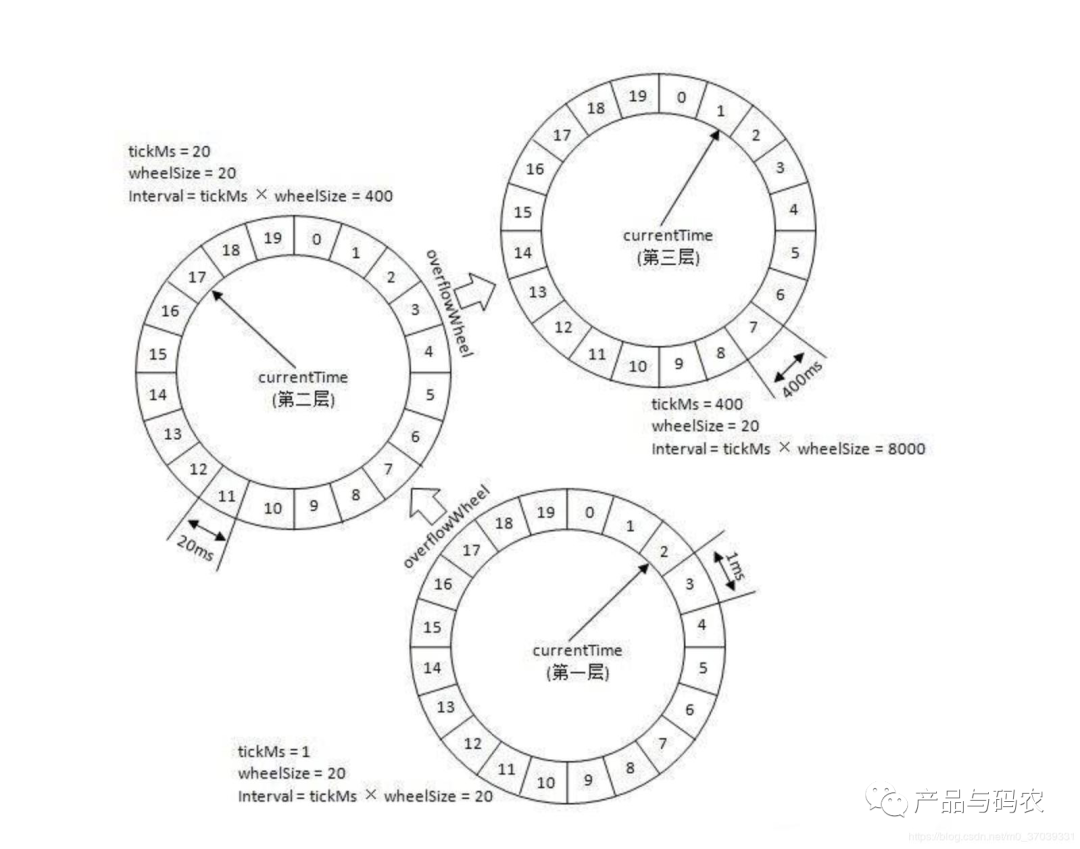
二、kafka时间轮实现原理
> 本文将kafka源码迁移到java再进行解读,方便理解
DelayedOperationPurgatory --- 启动类,可以理解为时间推进,实例化该类的时候,就会启动定时器,最终通过timeoutTimer.advanceClock(timeoutMs)进行时间推进。
public class DelayedOperationPurgatory {Timer timeoutTimer;// 实例化public DelayedOperationPurgatory(Timer timeoutTimer) {this.timeoutTimer = timeoutTimer;ExpiredOperationReaper expirationReaper = new ExpiredOperationReaper("ExpirationReaper");// ExpiredOperationReaper 继承自 Thread 这个位置启动线程expirationReaper.start();}void advanceClock(long timeoutMs) {timeoutTimer.advanceClock(timeoutMs);}private class ExpiredOperationReaper extends ShutdownableThread {public ExpiredOperationReaper(String name) {super(name);}@Overridepublic void doWork() {advanceClock(200L);}}}abstract class ShutdownableThread extends Thread {Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());CountDownLatch shutdownInitiated = new CountDownLatch(1);CountDownLatch shutdownComplete = new CountDownLatch(1);public ShutdownableThread(String name) {super(name);this.setDaemon(false);}Boolean isShutdownInitiated() {return shutdownInitiated.getCount() == 0;}Boolean isRunning() {return !isShutdownInitiated();}@Overridepublic void run() {logger.info("Starting");try {while (isRunning()) {// 通过一个可终止的死循环进行时间推进doWork();}} catch (Error e) {shutdownInitiated.countDown();shutdownComplete.countDown();logger.info("stopped");System.exit(1);} catch (Throwable t) {if (isRunning()) {logger.error("error due to", t);}} finally {shutdownComplete.countDown();}logger.info("Stopped");}public abstract void doWork();}
Timer(SystemTimer) --- 计时器,包含2个功能:1.添加延迟任务;2.时间推进
public interface Timer {void add(TimerTask timerTask);Boolean advanceClock(Long timeoutMs);}class SystemTimer implements Timer {Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());String executorName;long tickMs;int wheelSize;long startMs;DelayQueue<TimerTaskList> delayQueue = new DelayQueue<>();AtomicInteger taskCounter = new AtomicInteger(0);TimingWheel timingWheel;// 延迟任务到期执行线程ExecutorService taskExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1, new ThreadFactory() {@Overridepublic Thread newThread(Runnable r) {return KafkaThread.nonDaemon("executor-" + executorName, r);}});ReentrantReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock = readWriteLock.readLock();ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock = readWriteLock.writeLock();public SystemTimer(String executorName, long tickMs, int wheelSize, long startMs) {this.executorName = executorName;this.tickMs = tickMs;this.wheelSize = wheelSize;this.startMs = startMs;timingWheel = new TimingWheel(tickMs,wheelSize,startMs,taskCounter,delayQueue);}@Overridepublic void add(TimerTask timerTask) {readLock.lock();try {// 添加延迟任务到时间轮addTimerTaskEntry(new TimerTaskEntry(timerTask, timerTask.delayMs + System.currentTimeMillis()));} finally {readLock.unlock();}}private void addTimerTaskEntry(TimerTaskEntry timerTaskEntry) {// 执行添加延迟任务到时间轮if (!timingWheel.add(timerTaskEntry)) {// 添加失败,要么是任务已经取消,要么是已到期if (!timerTaskEntry.cancelled()) {// 如果任务已到期,异步执行任务taskExecutor.submit(timerTaskEntry.timeTask);}}}// 将延迟任务重新插入新的时间轮槽位,以此来触发到期Consumer<TimerTaskEntry> reinsert = this::addTimerTaskEntry;// 时间推进@Overridepublic Boolean advanceClock(Long timeoutMs) {try {// 通过阻塞的方式获取到期的槽位,减少循环的次数TimerTaskList bucket = delayQueue.poll(timeoutMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);if (bucket != null) {writeLock.lock();try {while (bucket != null) {// 将时间轮指针指向当前槽位的位置,最终就是修改currentTimetimingWheel.advanceClock(bucket.getExpiration());// 清空该槽,重新将槽内的任务插入到时间轮新的位置,将到期的任务直接执行// 重新加入的原因是,上层时间轮的间隔不是1ms了,所以存在一个槽位存在多个不同延迟的任务,// 通过重新加入时间轮,就会对该槽位所有的任务进行时间轮降级// 比方有2个任务,一开始延迟时间为25ms,36ms,这两个就会加入同一个槽位[20, 40)// 当时间推进到20的时候就会,该槽位就会取出,当前时间加了20ms,然后这2个任务就会加入到第一层时间轮对应的位置,// 下次再推进到[5, 6),就会执行25ms这个任务了。同理[16, 17)的时候就会执行36ms任务了bucket.flush(reinsert);// 再次尝试立刻获取过期的任务,因为存在前面重新入时间轮刚好没过期,这里再次取一次有任务可以直接获取到// 这里为了提高性能,所以直接使用最快捷的poll()也就是尝试取第一个槽对象判断是否过期bucket = delayQueue.poll();}} finally {writeLock.unlock();}return true;}} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}return false;}}
TimerWheel --- 时间轮对象,有个固定的数组TimerTaskList[wheelSize],保存延迟任务的时间轮对象
public class TimingWheel {// 精度 也就是 两个刻度之间的时间差,这里第一层就是1ms,第二层20ms,第三层400ms以此类推Long tickMs;// 时间轮槽刻度数,也就是槽数,int wheelSize;// 时间推进起始时间 也就是当前时间Long startMs;// 任务计数器AtomicInteger taskCounter;// 根据延迟时间槽位刻度值,保存槽位FIFO延迟队列DelayQueue<TimerTaskList> queue;// 当前层时间轮总共时间 tickMs * wheelSizeLong interval;// 推进到的当前时间Long currentTime;/*** 父级时间轮*/volatile TimingWheel overflowWheel;// 当面时间轮保存延迟任务的固定大小数字,TimerTaskList是一个双向链表TimerTaskList[] buckets;public TimingWheel(Long tickMs, int wheelSize, Long startMs,AtomicInteger taskCounter, DelayQueue<TimerTaskList> queue) {this.tickMs = tickMs;this.wheelSize = wheelSize;this.startMs = startMs;this.taskCounter = taskCounter;this.queue = queue;interval = tickMs * wheelSize;currentTime = startMs - (startMs % tickMs);buckets = new TimerTaskList[wheelSize];// 初始化时间轮存储数组for (int i = 0; i < wheelSize; i++) {buckets[i] = new TimerTaskList(taskCounter);}}// 延迟时间超出当前时间轮,进行时间轮升级public synchronized void addOverflowWheel() {if (overflowWheel == null) {overflowWheel = new TimingWheel(interval,wheelSize,currentTime,taskCounter,queue);}}// 在时间轮中执行加入延迟任务操作public Boolean add(TimerTaskEntry timerTaskEntry) {// 获取到加入的热舞的延迟时间ms数long expiration = timerTaskEntry.expirationMs;// 已经取消加入失败if (timerTaskEntry.cancelled()) {return false;}// 过期时间小于下一个刻度,说明已经过期if (expiration < currentTime + tickMs) {return false;}// 过期时间没有超出当前层时间轮的总时长if (expiration < currentTime + interval) {// 计算出可插入的槽位long virtualId = expiration / tickMs;int index = (int) (virtualId % wheelSize);TimerTaskList bucket = buckets[index];// 将任务加入到对应的槽位bucket.add(timerTaskEntry);// 设置槽的过期时间,如果设置成功,说明原来这个槽位的链表是没有任务的if (bucket.setExpiration(virtualId * tickMs)) {// 如果设置成功说明是新槽位,加入到延迟队列中等待时间推进queue.offer(bucket);}return true;} else {// 如果超出当前时间轮,加入到上层时间轮,逻辑一样if (overflowWheel == null) {addOverflowWheel();}return overflowWheel.add(timerTaskEntry);}}// 时间推进逻辑public void advanceClock(Long timeMs) {// 判断时间推进的距离if (timeMs>= currentTime + tickMs) {// 如果超过当前时间轮的一个刻度数,将当前时间推进到timeMs向下取整的刻度上currentTime = timeMs - (timeMs% tickMs);if (overflowWheel != null) {// 如果有上层,也需要往上时间推进overflowWheel.advanceClock(currentTime);}}}}
TimerTaskList --- 时间轮槽位双向链表,实现了Delayed接口,双向链表,每个节点保存一个持有延迟任务的entry
public class TimerTaskList implements Delayed {// 根节点private final TimerTaskEntry root;// 这个槽位对应的延迟时间,经过类似向下取整的方式的刻度上的值// 打个比方, 钟表2020-02-26 01:20:30,假设是只看小时指针,那么这个值就是取 2020-02-26 01:00:00转换为的ms数,// 其他层逻辑一致AtomicLong expiration = new AtomicLong(-1);// 全局任务计数器private final AtomicInteger taskCounter;// 初始化 root是一个空节点public TimerTaskList(AtomicInteger taskCounter) {this.taskCounter = taskCounter;this.root = new TimerTaskEntry(null, -1);this.root.next = root;this.root.prev = root;}// 设置槽位过期时间,如果有更新说明是新的槽位public Boolean setExpiration(Long expirationMs) {return expiration.getAndSet(expirationMs) != expirationMs;}public Long getExpiration() {return expiration.get();}// 加入一个延迟任务节点public synchronized void add(TimerTaskEntry timerTaskEntry) {boolean done = false;while (!done) {timerTaskEntry.remove();synchronized (this) {if (timerTaskEntry.list == null) {TimerTaskEntry tail = root.prev;timerTaskEntry.next = root;timerTaskEntry.prev = tail;timerTaskEntry.list = this;tail.next = timerTaskEntry;root.prev = timerTaskEntry;taskCounter.incrementAndGet();done = true;}}}}// 移除一个链表节点public synchronized void remove(TimerTaskEntry timerTaskEntry) {synchronized (this) {// 判断是属于当前链表的才能移除if (timerTaskEntry.list.compareTo(this) == 0) {timerTaskEntry.next.prev = timerTaskEntry.prev;timerTaskEntry.prev.next = timerTaskEntry.next;timerTaskEntry.next = null;timerTaskEntry.prev = null;timerTaskEntry.list = null;taskCounter.decrementAndGet();}}}// 由于时间推进,将当前链表的任务重新插入到时间轮,以此来触发到期任务执行public synchronized void flush(Consumer<TimerTaskEntry> consumer) {TimerTaskEntry head = root.next;while (!head.equals(root)) {remove(head);consumer.accept(head);head = root.next;}expiration.set(-1L);}@Overridepublic long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {return unit.convert(Math.max(getExpiration() - System.currentTimeMillis(), 0), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);}@Overridepublic int compareTo(Delayed d) {TimerTaskList other = (TimerTaskList) d;if (getExpiration() < other.getExpiration()) {return -1;} else if (getExpiration() > other.getExpiration()) {return 1;}return 0;}}
TimerTaskEntry --- 时间轮槽链表对象的节点
class TimerTaskEntry implements Comparable<TimerTaskEntry> {TimerTask timeTask;volatile TimerTaskList list = null;TimerTaskEntry next = null;TimerTaskEntry prev = null;/*** 过期时间*/Long expirationMs;public TimerTaskEntry(TimerTask timeTask, long expirationMs) {this.timeTask = timeTask;this.expirationMs = expirationMs;if (timeTask != null) {timeTask.setTimerTaskEntry(this);}}public Boolean cancelled() {return timeTask.getTimerTaskEntry() != this;}public void remove() {TimerTaskList currentList = list;while (currentList != null) {currentList.remove(this);currentList = list;}}// 实现了comparable@Overridepublic int compareTo(TimerTaskEntry that) {return this.expirationMs.compareTo(that.expirationMs);}}
TimerTask --- 时间轮槽链表对象的节点上的延迟任务
abstract class TimerTask implements Runnable {Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());long delayMs;String name;TimerTaskEntry timerTaskEntry;public TimerTask(long delayMs, String name) {this.delayMs = delayMs;this.name = name;}public void cancel() {synchronized (this) {if (timerTaskEntry != null) {timerTaskEntry.remove();}timerTaskEntry = null;}}// 将延迟任务关联上链表上的一个节点public void setTimerTaskEntry(TimerTaskEntry entry) {synchronized (this) {if (timerTaskEntry != null && timerTaskEntry != entry) {timerTaskEntry.remove();}timerTaskEntry = entry;}}public TimerTaskEntry getTimerTaskEntry() {return timerTaskEntry;}}
DelayQueue --- 延迟队列,元素是时间轮槽位bucket (也就是TimerTaskList对象)
这是java包自带的一种特殊队列,插入的元素必须实现Delayed,按照时间先后出队列
03
—
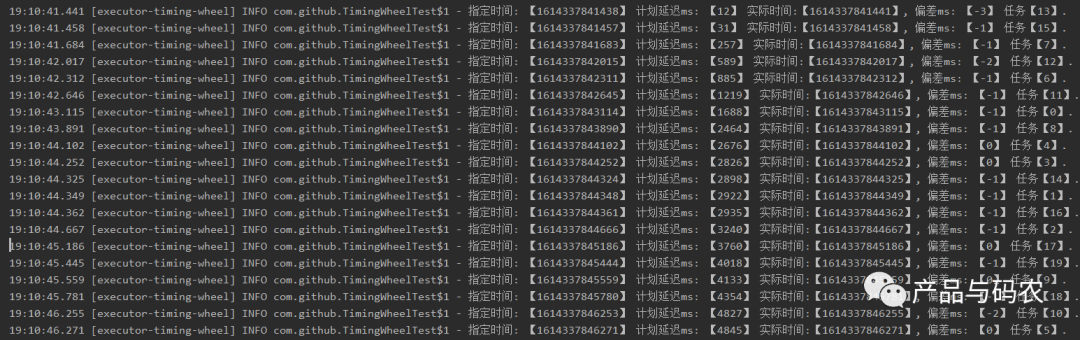
三、测试结果
增加测试代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {Timer systemTimer = new SystemTimer("timing-wheel", 1, 20, System.currentTimeMillis());new DelayedOperationPurgatory(systemTimer);for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {TimerTask timerTask = new TimerTask(new Random().nextInt(5000), i + "") {@Overridepublic void run() {long now = System.currentTimeMillis();logger.info("" +"指定时间: 【{}】 " +"计划延迟ms: 【{}】 " +"实际时间:【{}】, " +"偏差ms: 【{}】 " +"任务【{}】.",timerTaskEntry.expirationMs,delayMs,now,(timerTaskEntry.expirationMs - now),name);}};systemTimer.add(timerTask);}}
测试结果,加入20个延迟任务,延迟时间随机,电脑性能问题存在在很小的误差;
04
—
四、总结与思考
kakfa通过时间轮来处理延迟任务,只将时间轮的槽保存到延迟队列,大大的减少了延迟队列的元素数量,这样对于元素的增加删除性能有很大提高;
kafka通过阻塞的方式poll延迟队列的,减少了大量的空转;
为了保证线程安全,灵活运用读写锁、原子对象、synchronized控制时间轮的操作;
文章转载自产品与码农,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






