原标题:Conditional RandomFields: Probabilistic Models for Segmenting and Labeling Sequence Data
作者:John Lafferty, Andrew McCallum &FernandoC.N. Pereira
会议:ICML 2001
中文摘要:
我们提出了条件随机场,这是一个用于建立概率模型以分割和标记序列数据的框架。与隐马尔可夫模型和随机语法相比,条件随机场在这类任务中具有一些优势,包括能够放松在这些模型中做出的强独立性假设。条件随机场还避免了最大熵马尔可夫模型(MEMMs)和其他基于有向图形模型的区别性马尔可夫模型的基本限制,这些模型可能偏向于具有少数后续状态的状态。我们提出了条件随机场的迭代参数估计算法,并在合成和自然语言数据上比较了所得到的模型与HMMs和MEMMs的性能。
英文摘要:
We presentconditional random fields, a framework for building probabilistic models tosegment and label sequence data. Conditional random fields offer severaladvantages over hidden Markov models and stochastic grammars for such tasks,including the ability to relax strong independence assumptions made in thosemodels. Conditional random fields also avoid a fundamental limitation ofmaximum entropy Markov models (MEMMs) and other discriminative Markov modelsbased on directed graphical models, which can be biased towards states with fewsuccessor states. We present iterative parameter estimation algorithms forconditional random fields and compare the performance of the resulting modelsto HMMs and MEMMs on synthetic and natural-language data.
原标题:STRUCTPOOL:STRUCTURED GRAPH POOLING VIA CONDITIONAL RANDOM FIELDS
作者:Hao Yuan, Shuiwang Ji
会议:ICLR 2020
中文摘要:
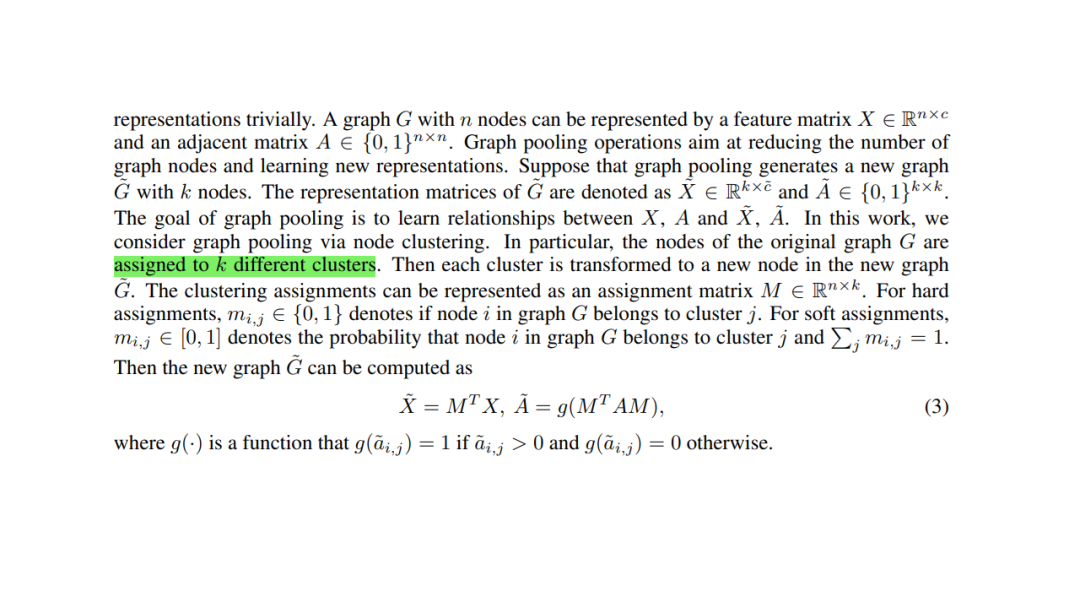
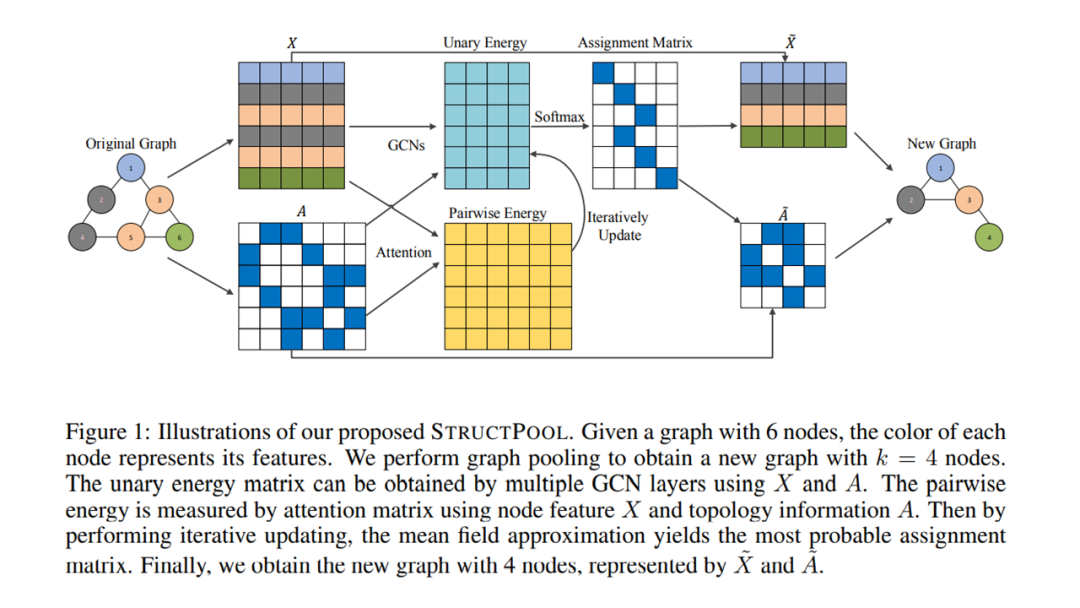
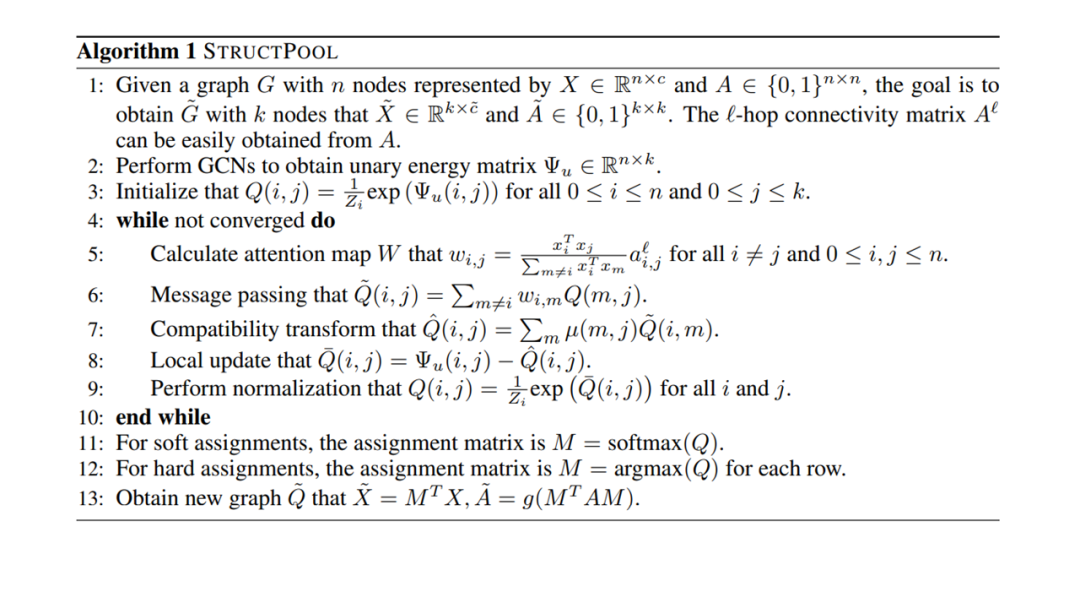
学习图形的高级表示对于图形分析任务非常重要。除了图卷积之外,图池也是一个重要但探索较少的研究领域。特别是,大多数现有的图形池技术不考虑图形结构信息明确。我们认为这些信息很重要,并在这项工作中开发了一种新的图池技术,称为STRUCTPOOL。我们认为图池是一个节点聚类问题,它需要学习一个聚类分配矩阵。我们建议将其表述为一个结构化预测问题,并使用条件随机场来捕获不同节点的分配之间的关系。我们还推广了我们的方法,在设计吉布斯能量函数时加入了图形拓扑信息。在多个数据集上的实验结果证明了我们提出的STRUCTPOOL的有效性。
英文摘要:
Learning high-levelrepresentations for graphs is of great importance for graph analysis tasks. Inaddition to graph convolution, graph pooling is an important but less exploredresearch area. In particular, most of existing graph pooling techniques do notconsider the graph structural information explicitly. We argue that suchinformation is important and develop a novel graph pooling technique, know asthe STRUCTPOOL, in this work. We consider the graph pooling as a nodeclustering problem, which requires the learning of a cluster assignment matrix.We propose to formulate it as a structured prediction problem and employconditional random fields to capture the relationships among the assignments ofdifferent nodes. We also generalize our method to incorporate graph topologicalinformation in designing the Gibbs energy function. Experimental results onmultiple datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed STRUCTPOOL.
文献总结: