📢📢📢📣📣📣
哈喽!大家好,我是【IT邦德】,江湖人称jeames007,10余年DBA及大数据工作经验
一位上进心十足的【大数据领域博主】!😜😜😜
中国DBA联盟(ACDU)成员,目前服务于工业互联网
擅长主流Oracle、MySQL、PG、高斯及Greenplum运维开发,备份恢复,安装迁移,性能优化、故障应急处理等。
✨ 如果有对【数据库】感兴趣的【小可爱】,欢迎关注【IT邦德】💞💞💞
❤️❤️❤️感谢各位大可爱小可爱!❤️❤️❤️
文章目录
运用时间模型来构造的应用非常需要时序数据库的加持,包括未来大数据的趋势,时序数据库必然会成为一个新潮流。
📣 1.时序数据库
什么是时序数据库?顾名思义,用于处理按照时间变化顺序的数据的数据库即为时序数据库(time-series database),时序数据库专门优化处理带时间标签的数据,为什么会衍生时序数据库这一种新趋势呢?我们知道像PostgreSQL和MySQL这种关系型数据库对于短期需求不大的情况下下还是可以满足的,但是一旦数据量增长,其性能不足以支持频繁的添加和读取需求。运用时间模型来构造的应用非常需要时序数据库的加持,包括未来大数据的趋势,时序数据库必然会成为一个新潮流。
📣 2.TimescaleDB
对于TimescaleDB来说,在功能的丰富程度上战胜了排名更靠前的几位选手,但是对于性能上可能处于下风,因此TimescaleDB如何持续地发展下去、如何发展地更好,除了探寻在性能等综合素质方面的提升外,在PostgreSQL的肩膀上怎么样更好地适应现代化需求才是重中之重。
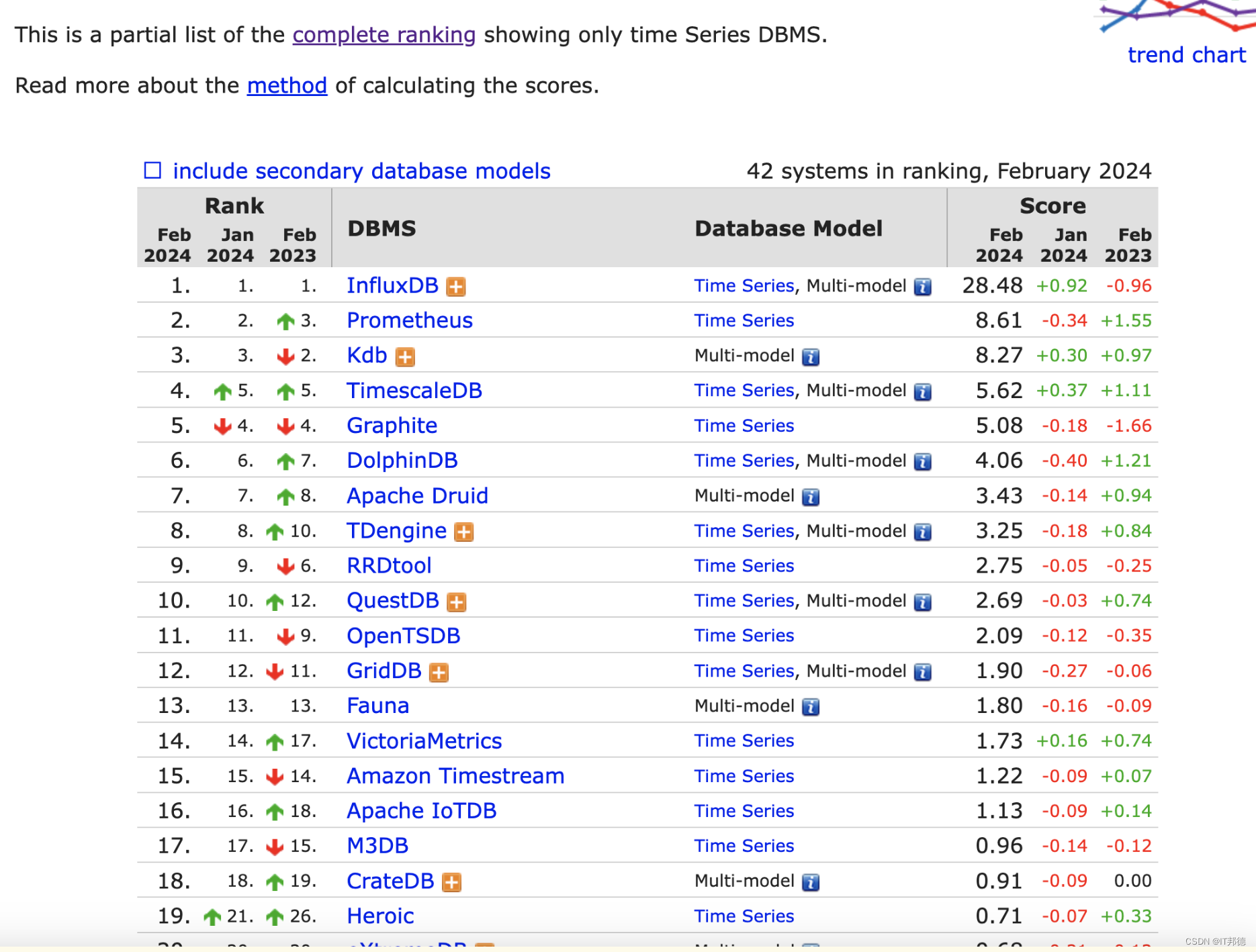
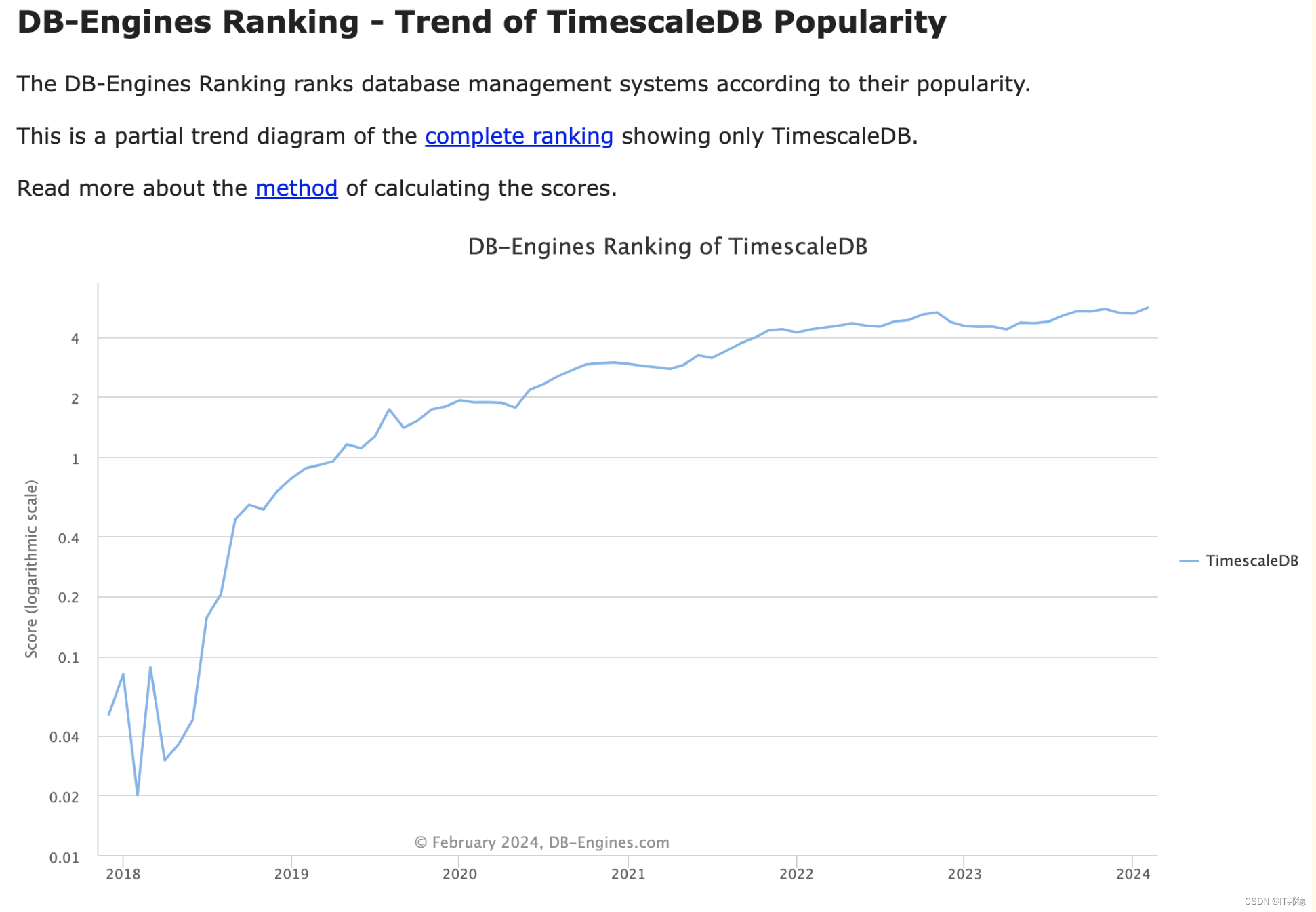
截止2024年2月,TimescaleDB在DB-Engines中排名的处于第4位,并一直处于上升的趋势。
TimescaleDB是基于PostgreSQL数据库打造的一款时序数据库,插件化的形式,随着PostgreSQL的版本升级而升级,不会因为另立分支带来麻烦。
📣 3.安装PG
✨3.1. rpm包下载
https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/14/redhat/rhel-8.1-x86_64/
下载lib
wget https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/14/redhat/rhel-8.1-x86_64/postgresql14-libs-14.9-2PGDG.rhel8.x86_64.rpm
下载客户端和库
wget https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/14/redhat/rhel-8.1-x86_64/postgresql14-14.9-2PGDG.rhel8.x86_64.rpm
下载service
wget https://ftp.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/14/redhat/rhel-8.1-x86_64/postgresql14-server-14.9-2PGDG.rhel8.x86_64.rpm
✨3.2 安装依赖包
yum install -y cmake make gcc zlib gcc-c++ perl readline readline-devel
yum install -y zlib-devel perl python36 tcl openssl ncurses-devel openldap pam
yum install -y zlib libicu
rpm -ivh postgresql14-libs-14.9-2PGDG.rhel8.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh postgresql14-14.9-2PGDG.rhel8.x86_64.rpm
rpm -ivh postgresql14-server-14.9-2PGDG.rhel8.x86_64.rpm
✨3.3 始化安装
/usr/pgsql-14/bin/postgresql-14-setup initdb
systemctl enable postgresql-14
systemctl start postgresql-14
systemctl status postgresql-14
✨3.4 配置参数
cat >> /var/lib/pgsql/14/data/postgresql.conf <<"EOF"
listen_addresses = '*'
port=5432
logging_collector = on
log_directory = 'pg_log'
log_filename = 'postgresql-%a.log'
log_truncate_on_rotation = on
EOF
cat << EOF > /var/lib/pgsql/14/data/pg_hba.conf
# TYPE DATABASE USER ADDRESS METHOD
local all all trust
host all all 127.0.0.1/32 trust
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
host replication all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
local replication all trust
EOF
✨3.5 重启
systemctl restart postgresql-14
ALTER USER postgres WITH PASSWORD ‘123456’;
psql -U postgres -h 192.168.3.10 -d postgres -p 5432
📣 4.TimescaleDB部署
✨ 4.1 repository
tee /etc/yum.repos.d/timescale_timescaledb.repo <<EOL
[timescale_timescaledb]
name=timescale_timescaledb
baseurl=https://packagecloud.io/timescale/timescaledb/el/$(rpm -E %{rhel})/\$basearch
repo_gpgcheck=1
gpgcheck=0
enabled=1
gpgkey=https://packagecloud.io/timescale/timescaledb/gpgkey
sslverify=1
sslcacert=/etc/pki/tls/certs/ca-bundle.crt
metadata_expire=300
EOL
✨ 4.2 yum在线安装
1.Update your local repository list:
yum update --skip-broken --nobest
2.Install TimescaleDB:
yum install timescaledb-2-postgresql-14
在Red Hat Enterprise Linux 8上安装时,需要使用:
sudo dnf module disable postgresql
命令禁用系统中内置的PostgreSQL模块。
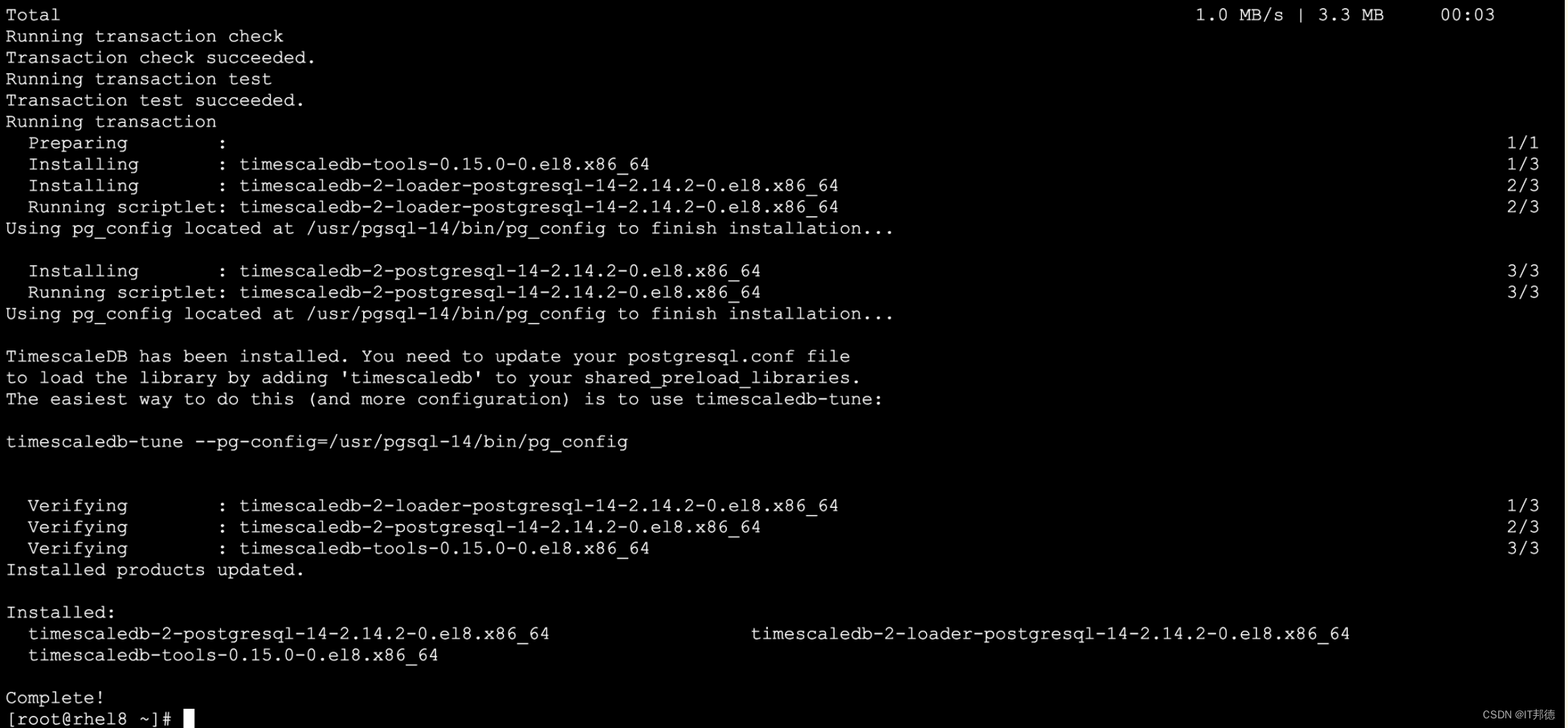
✨ 4.3 插件配置
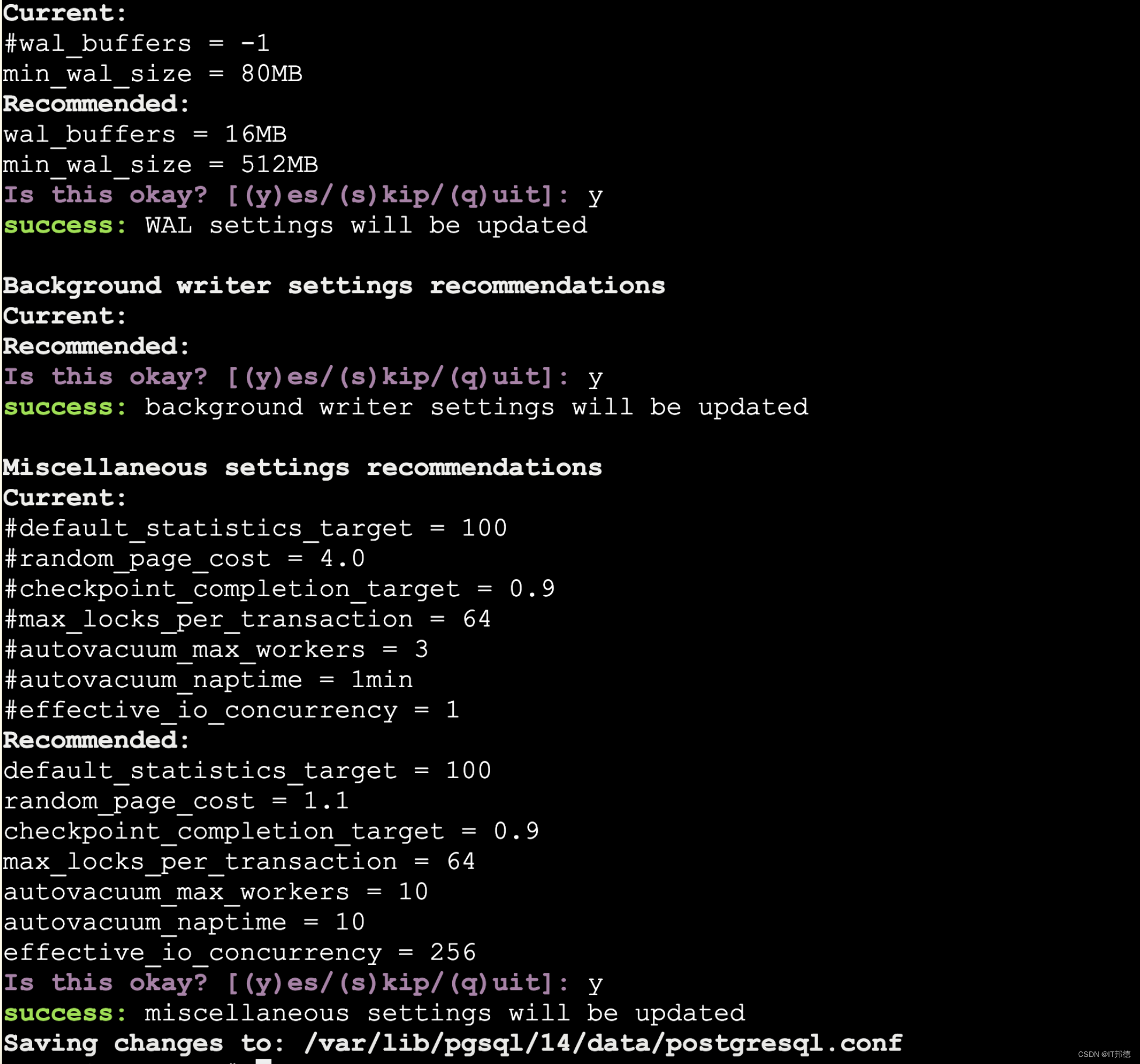
修改postgresql config文件,使timescaledb这个插件能正常工作,通过调优脚本来配置数据库
[root@rhel8 ~]# find / -name pg_config
/usr/pgsql-14/bin/pg_config
sudo timescaledb-tune --pg-config=/usr/pgsql-14/bin/pg_config
📣 5.TimescaleDB使用
✨ 5.1 登陆PG
[root@rhel8 ~]# su - postgres
[postgres@rhel8 ~]$
[postgres@rhel8 ~]$ psql
psql (14.10)
Type "help" for help.
postgres=# create database jemdb;
CREATE DATABASE
postgres=# \c jemdb
You are now connected to database "jemdb" as user "postgres".
✨ 5.2 创建插件
1.创建插件
CREATE EXTENSION IF NOT EXISTS timescaledb;
2.删除插件
DROP EXTENSION IF EXISTS timescaledb;
jemdb=# \dx
List of installed extensions
Name | Version | Schema | Description
-------------+---------+------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
plpgsql | 1.0 | pg_catalog | PL/pgSQL procedural language
timescaledb | 2.14.2 | public | Enables scalable inserts and complex queries for time-series data (Apache 2 Edition)
(2 rows)
✨ 5.3 使用超表
1、创建普通测试表
CREATE TABLE conditions (
time TIMESTAMPTZ NOT NULL,
location TEXT NOT NULL,
temperature DOUBLE PRECISION NULL,
humidity DOUBLE PRECISION NULL
);
2、基于time分区将上一步创建的普通表转换为超表
jemdb=# SELECT create_hypertable('conditions', 'time');
create_hypertable
-------------------------
(1,public,conditions,t)
(1 row)
3、插入数据并查询
jemdb=# INSERT INTO conditions(time, location, temperature, humidity)
SELECT now(), to_char(i, 'FM0000'), random()*i, random()*i FROM generate_series(1,10000) i;
4.针对过去3小时的数据,每15分钟采集度量一次,按照时间和温度降序排序
SELECT time_bucket('15 minutes', time) AS fifteen_min,
location, COUNT(*),
MAX(temperature) AS max_temp,
MAX(humidity) AS max_hum
FROM conditions
WHERE time > NOW() - interval '3 hours'
GROUP BY fifteen_min, location
ORDER BY fifteen_min DESC, max_temp DESC;
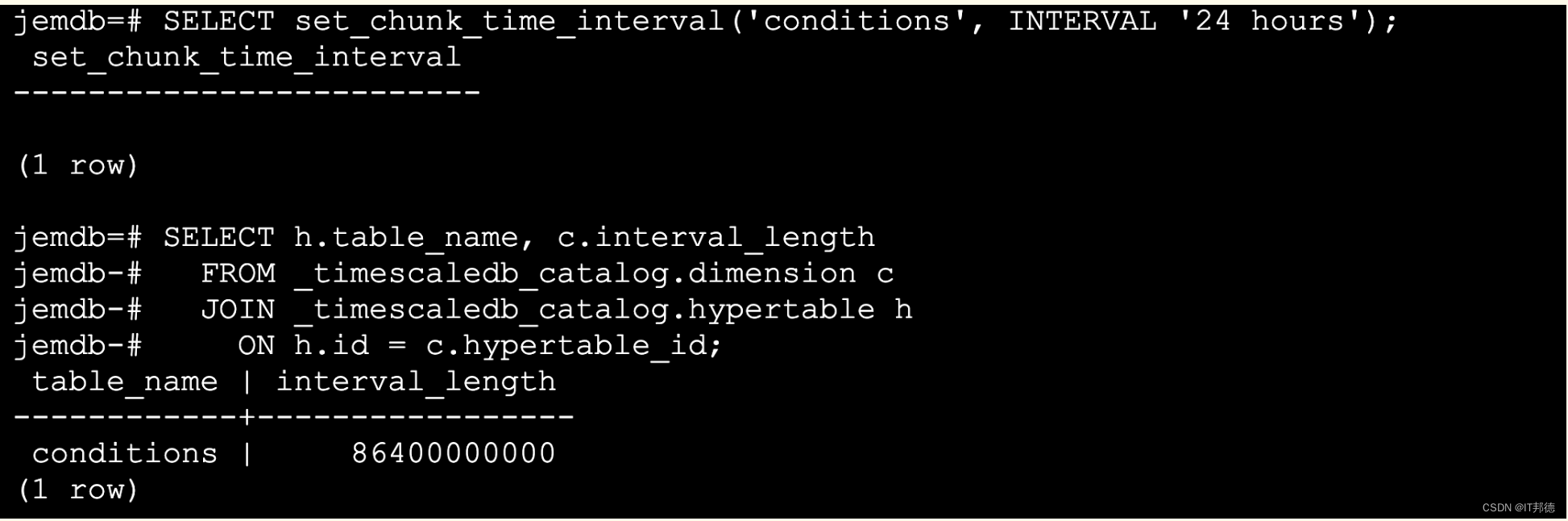
5.更改现有超表上的块间隔长度
SELECT set_chunk_time_interval('conditions', INTERVAL '24 hours');
SELECT h.table_name, c.interval_length
FROM _timescaledb_catalog.dimension c
JOIN _timescaledb_catalog.hypertable h
ON h.id = c.hypertable_id;
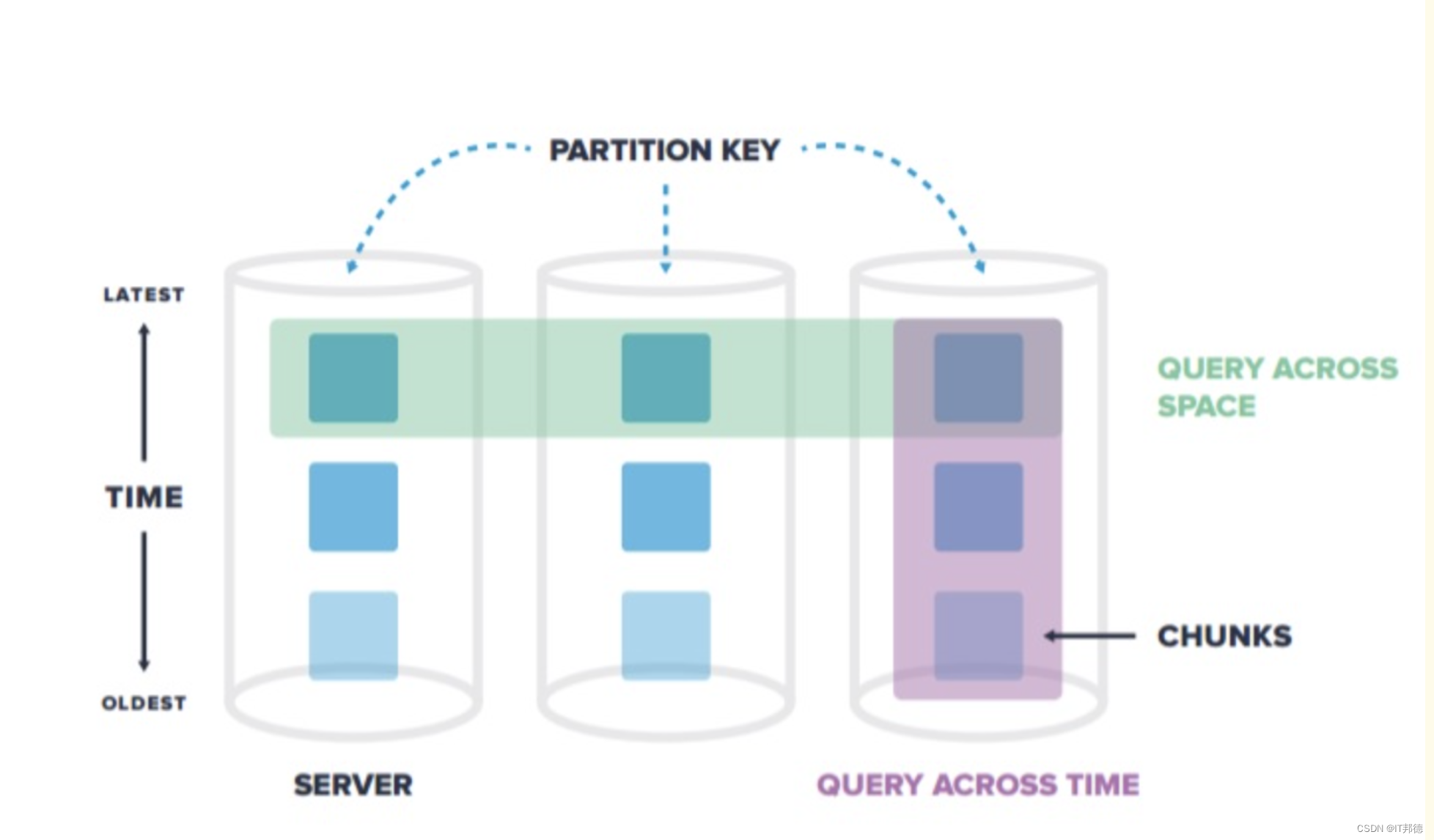
超表(hypertable)是具有特殊功能的PostgreSQL表,可以很容易地处理时间序列数据。与它们交互就像与普通PostgreSQL表交互一样,但在幕后,超表会自动按时间将数据划分为块。在TimescaleDB中,超表与普通PostgreSQL表可以一起存在。超表用来存储时序数据,这样可以提高插入和查询的性能,而且可以访问一些有用的时间序列特性。普通PostgreSQL表用来存储其它关系型数据。
📣 6 总结
随着物联网的发展,时序数据库的需求越来越多,比如水文监控、工厂的设备监控、国家安全相关的数据监控、通讯监控、金融行业指标数据、传感器数据等。
在互联网行业中,也有着非常多的时序数据,例如用户访问网站的行为轨迹,应用程序产生的日志数据等等。
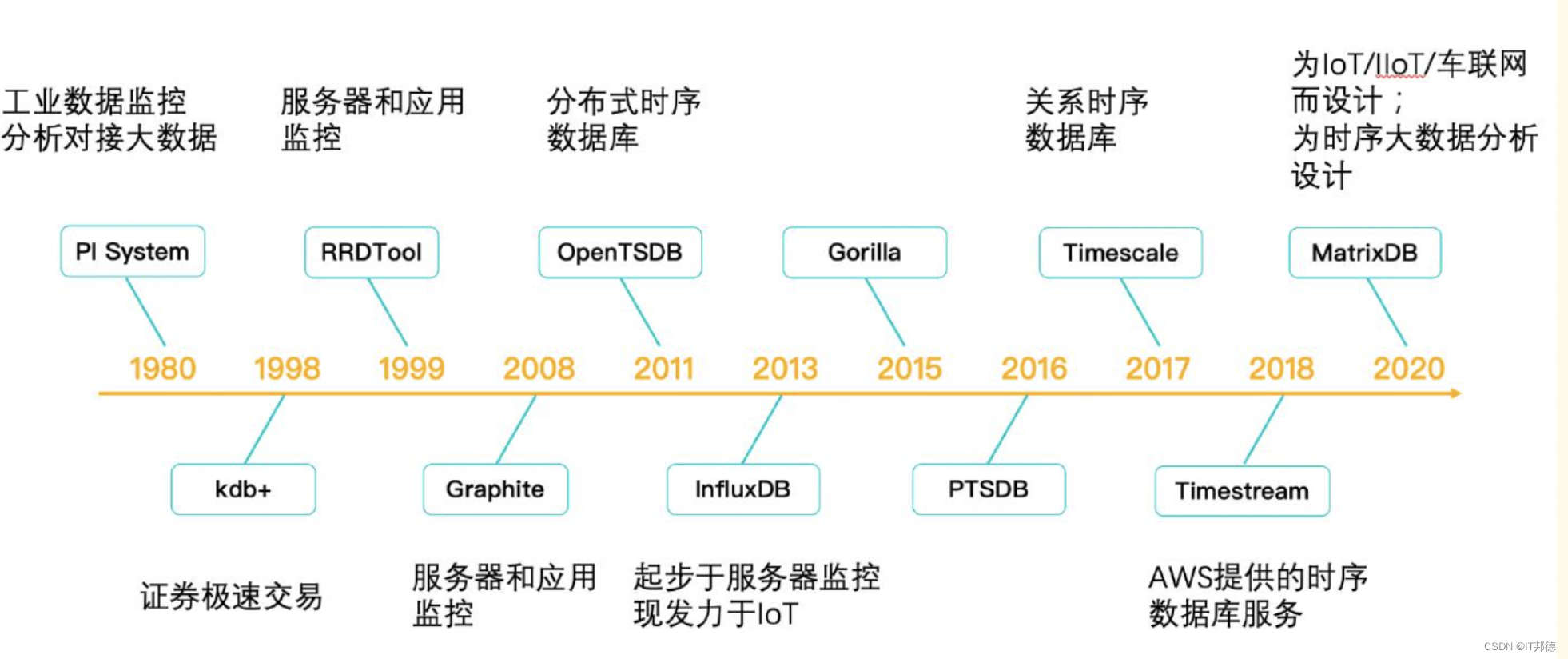
以下是时序数据库的发展史推荐给大家,一起交流学习