innodb_flush_method
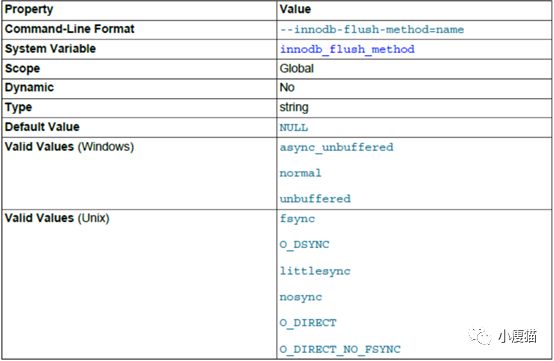
设置刷新数据到InnoDB数据文件和日志文件的方式,影响I/O吞吐量。
默认值为null时,在累Unix平台使用的是fsysc,在Windows平台使用的是async_unbuffered。
类Unix选项:
• fsync:使用fsync()来刷新数据和日志文件
• O_DSYNC:使用O_SYNC来打开和刷新日志文件,使用fsync()来刷新数据文件
• Littlesync,nosync:内部新能测试用,目前不支持
• O_DIRECT:使用O_DIRECT来打开数据文件,使用fsync()来刷新数据文件和日志文件
• O_DIRECT_NO_FSYNC:
How each setting affects performancedepends on hardware configuration and workload. Benchmark your particularconfiguration to decide which setting to use, or whether to keep the defaultsetting. Examine the InnoDB_data_fsyncs status variable to see the overallnumber of fsync() calls for each setting. The mix of read and write operationsin your workload can affect how a setting performs. For example, on a systemwith a hardware RAID controller and battery-backed write cache, O_DIRECT canhelp to avoid double buffering between the InnoDB buffer pool and the operatingsystem file system cache. On some systems where InnoDB data and log files arelocated on a SAN, the default value or O_DSYNC might be faster for a read-heavyworkload with mostly SELECT statements. Always test this parameter withhardware and workload that reflect your production environment.
innodb_buffer_pool_instances
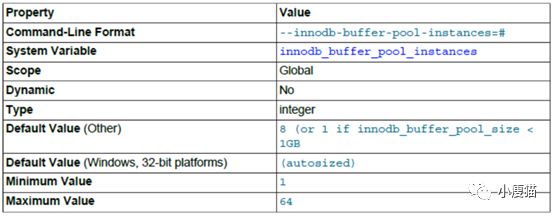
InnoDB缓冲池实例个数,即将缓冲池平分为指定的个数。可以提高并发性能。该设置不会影响单个查询响应时间,只有在高并发负载的情况下才会有用。
该配置只有在innodb_buffer_pool_size大于1G的时候才会生效。为了得到更好的效率,设置合理的个数使每个缓冲池实例大小大于1G。
innodb_thread_concurrency
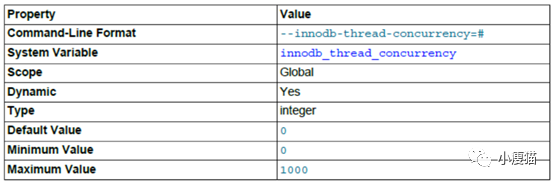
该参数用来控制并发执行的线程数。默认为0,即关闭并发控制,此时InnoDB会尽可能多的创建所需要的线程。当系统CPU或者IO出现饱和时,可以使用该参数来提高查询性能。
InnoDB会保持操作系统并发线程数在InnoDB内小于或等于该变量指定值。一旦达到上限,剩余的线程将会放在一个FIFO的队列里面等待执行。
以下是关于该值的几点参考:
• If the number of concurrentuser threads for a workload is less than 64, set innodb_thread_concurrency=0.
• If your workload isconsistently heavy or occasionally spikes, start by settinginnodb_thread_concurrency=128 and then lowering the value to 96, 80, 64, and soon, until you find the number of threads that provides the best performance.For example, suppose your system typically has 40 to 50 users, but periodicallythe number increases to 60, 70, or even 200. You find that performance isstable at 80 concurrent users but starts to show a regression above thisnumber. In this case, you would set innodb_thread_concurrency=80 to avoidimpacting performance.
• If you do not want InnoDB touse more than a certain number of virtual CPUs for user threads (20 virtualCPUs, for example), set innodb_thread_concurrency to this number (or possiblylower, depending on performance results). If your goal is to isolate MySQL fromother applications, you may consider binding the mysqld process exclusively tothe virtual CPUs. Be aware, however, that exclusive binding could result innon-optimal hardware usage if the mysqld process is not consistently busy. Inthis case, you might bind the mysqld process to the virtual CPUs but also allowother applications to use some or all of the virtual CPUs. innodb_thread_concurrencyvalues that are too high can cause performance regression due to increasedcontention on system internals and resources.
• In some cases, the optimalinnodb_thread_concurrency setting can be smaller than the number of virtualCPUs.
• Monitor and analyze your systemregularly. Changes to workload, number of users, or computing environment mayrequire that you adjust the innodb_thread_concurrency setting.
skip_name_resolve
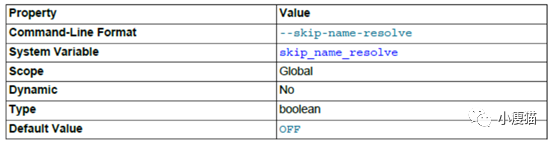
该参数用来配置连接时DNS解析,正常情况下DNS解析非常快,但是当DNS解析失败时服务为会出现“unauthenticated connections”导致所有请求都慢下来。因此,打开此开关,避免基于主机名的授权。直接使用IP地址。
innodb_io_capacity

用来当刷新脏数据时,控制MySQL每秒执行的写IO量。innodb_io_capacity限制的是所有缓冲池实例的总量,当刷新脏页时,这个量会平分到每个实例。
innodb_io_capacity可设置为接近操作系统能处理的最大IO数。对于低端的SSD,默认值200就可以了,对于高端以及总线连接的SSD可以将值设为1000,而5400RPM或者是7200RPM的硬盘,则将值设为100。
innodb_io_capacity可以设置为任何低于innodb_io_capacity_max的值。虽然可以设置为较大的值,但实际中,较大的值并不会带来多少好处。通常不推荐设置为20000及以上的值,除非对于当前的负载该配置不满足。
innodb_io_capacity_max
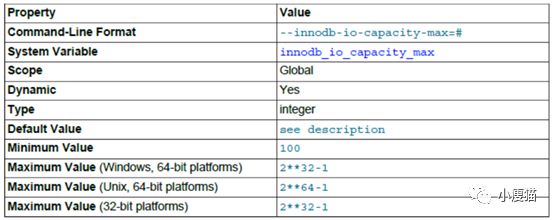
在紧急情况下,控制当刷新脏数据时MySQL每秒执行的写IO量。
在启动时指定了innodb_io_capacity而未指定innodb_io_capacity_max,则为innodb_io_capacity的两倍或者最小值2000。
一般情况innodb_io_capacity_max为innodb_io_capacity的两倍。
在写密集型系统中,可以测量设备存储设置的随机吞吐量,然后innodb_io_capacity_max设置为设备所能达到的最大IOPS。innodb_io_capacity设置为innodb_io_capacity_max的50%~75%。
When configuring innodb_io_capacity_max,twice the innodb_io_capacity is often a good starting point. The default valueof 2000 is intended for workloads that use a solid-state disk (SSD) or morethan one regular disk drive. A setting of 2000 is likely too high for workloadsthat do not use SSD or multiple disk drives, and could allow too much flushing.For a single regular disk drive, a setting between 200 and 400 is recommended.For a high-end, bus-attached SSD, consider a higher setting such as 2500. Aswith the innodb_io_capacity setting, keep the setting as low as practical, butnot so low that InnoDB cannot sufficiently extend beyond the innodb_io_capacitylimit, if necessary.






