walsender阻止停库现象
生产停库日志输出如下:
2024-12-06 17:00:02.036 CST,,,447560,,65693cde.6d448,1320,,2023-12-01 09:54:38 CST,,0,LOG,00000,"received fast shutdown request",,,,,,,,,"","postmaster" 2024-12-06 17:00:02.295 CST,,,447560,,65693cde.6d448,1322,,2023-12-01 09:54:38 CST,,0,LOG,00000,"background worker ""logical replication launcher"" (PID 448996) exited with exit code 1",,,,,,,,,"","postmaster" 2024-12-06 17:00:10.627 CST,,,448990,,65693ce0.6d9de,213833,,2023-12-01 09:54:40 CST,,0,LOG,00000,"checkpoint complete: wrote 426844 buffers (5.1%); 0 WAL file(s) added, 0 removed, 5 recycled; write=91.427 s, sync=0.055 s, total=91.508 s; sync files=761, longest=0.028 s, average=0.001 s; distance=2197531 kB, estimate=2680783 kB",,,,,,,,,"","checkpointer" 2024-12-06 17:00:10.628 CST,,,448990,,65693ce0.6d9de,213834,,2023-12-01 09:54:40 CST,,0,LOG,00000,"shutting down",,,,,,,,,"","checkpointer" ... --checkpointer做完checkpoint,并处于shutting down状态,pm没有退出 --160s后pm接收到immediate shutdown,由探活脚本触发 2024-12-06 17:02:43.348 CST,,,447560,,65693cde.6d448,1323,,2023-12-01 09:54:38 CST,,0,LOG,00000,"received immediate shutdown request",,,,,,,,,"","postmaster" 2024-12-06 17:02:43.370 CST,"logicaluser","lzldb",283840,"10.33.77.159:39865",6751a2dc.454c0,7,"idle",2024-12-05 20:55:56 CST,89/847309655,0,WARNING,57P02,"terminating connection because of crash of another server process","The postmaster has commanded this server process to roll back the current transaction and exit, because another server process exited abnormally and possibly corrupted shared memory.","In a moment you should be able to reconnect to the database and repeat your command.",,,,,,,"Debezium Streaming","walsender" 2024-12-06 17:02:43.370 CST,"logicaluser","lzldb",157641,"10.33.77.159:39407",67408354.267c9,7,"idle",2024-11-22 21:12:52 CST,9/3193590104,0,WARNING,57P02,"terminating connection because of crash of another server process","The postmaster has commanded this server process to roll back the current transaction and exit, because another server process exited abnormally and possibly corrupted shared memory.","In a moment you should be able to reconnect to the database and repeat your command.",,,,,,,"Debezium Streaming","walsender" 2024-12-06 17:02:43.370 CST,"logicaluser","lzldb",157916,"10.33.77.159:57038",67408356.268dc,7,"idle",2024-11-22 21:12:54 CST,115/3293293502,0,WARNING,57P02,"terminating connection because of crash of another server process","The postmaster has commanded this server process to roll back the current transaction and exit, because another server process exited abnormally and possibly corrupted shared memory.","In a moment you should be able to reconnect to the database and repeat your command.",,,,,,,"Debezium Streaming","walsender" 2024-12-06 17:02:43.370 CST,"repuser","",164392,"30.151.40.19:41641",66b25869.28228,3,"streaming 42D3B/1732C5F0",2024-08-07 01:07:53 CST,296/0,0,WARNING,57P02,"terminating connection because of crash of another server process","The postmaster has commanded this server process to roll back the current transaction and exit, because another server process exited abnormally and possibly corrupted shared memory.","In a moment you should be able to reconnect to the database and repeat your command.",,,,,,,"standby_6666","walsender" 2024-12-06 17:02:43.371 CST,,,447560,,65693cde.6d448,1324,,2023-12-01 09:54:38 CST,,0,LOG,00000,"archiver process (PID 448994) exited with exit code 2",,,,,,,,,"","postmaster" 2024-12-06 17:02:43.371 CST,"logicaluser","lzldb",57755,"10.33.77.159:38918",67125534.e19b,7,"idle",2024-10-18 20:31:48 CST,243/902018192,0,WARNING,57P02,"terminating connection because of crash of another server process","The postmaster has commanded this server process to roll back the current transaction and exit, because another server process exited abnormally and possibly corrupted shared memory.","In a moment you should be able to reconnect to the database and repeat your command.",,,,,,,"Debezium Streaming","walsender" 2024-12-06 17:02:43.372 CST,"logicaluser","lzldb",157915,"10.33.77.159:43433",67408356.268db,7,"idle",2024-11-22 21:12:54 CST,60/3248014863,0,WARNING,57P02,"terminating connection because of crash of another server process","The postmaster has commanded this server process to roll back the current transaction and exit, because another server process exited abnormally and possibly corrupted shared memory.","In a moment you should be able to reconnect to the database and repeat your command.",,,,,,,"Debezium Streaming","walsender" --pm停完 2024-12-06 17:02:57.534 CST,,,447560,,65693cde.6d448,1325,,2023-12-01 09:54:38 CST,,0,LOG,00000,"database system is shut down",,,,,,,,,"","postmaster" 2024-12-06 17:03:49.536 CST,,,211844,,6752bdf3.33b84,1,,2024-12-06 17:03:47 CST,,0,LOG,00000,"ending log output to stderr",,"Future log output will go to log destination ""csvlog"".",,,,,,,"","postmaster"
17:00:02 postmaster接到fast停库
17:00:10 checkpoint做完,checkpointer停了
17:02:43 postmaster接到immediate停库
17:02:43 1个物理链路和5个逻辑链路walsender停了
17:02:57 postmaster停了
17:03:49 postmaster接到启动任务
从以上信息可以看出,实际上还是walsender阻止了停库
停库和信号
在撸源码前需要先了解信号和pg中的信号注册
pg中的常用信号
操作系统信号:
$ kill -l
1) SIGHUP 2) SIGINT 3) SIGQUIT 4) SIGILL 5) SIGTRAP
6) SIGABRT 7) SIGBUS 8) SIGFPE 9) SIGKILL 10) SIGUSR1
11) SIGSEGV 12) SIGUSR2 13) SIGPIPE 14) SIGALRM 15) SIGTERM
16) SIGSTKFLT 17) SIGCHLD 18) SIGCONT 19) SIGSTOP 20) SIGTSTP
...
PG常用的信号:
-1或-SIGHUP:挂起信号,在PG中通常是通知进程重新加载配置。-2或-SIGINT:中断信号(通常是Ctrl+C),在pg中同城对应取消命令。-3或-SIGQUIT:pg中通常是强制退出die-9或-SIGKILL:无条件终止信号。-15或-SIGTERM:终止信号,pg_terminate_backend使用的信号,pg中通常是合理退出-10或-SIGUSR1:自定义信号-12或-SIGUSR2:自定义信号-17或SIGCHLD:pm进程使用的信号,一般是子进程退出后pm接受该信号触发回收子进程任务
PG中具体哪种类型的进程注册的信号含义,看各自进程源码基本都能找到。
pg_ctl 定义的停库
有几种方法可以关闭pg库。在底层,它们都归结为向postmaster进程发送一个信号。
| signal | pg_ctl | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
SIGTERM |
Smart Shutdown | 不允许新的连接,但允许现有会话正常结束其工作。只有在所有会话终止后,它才会关闭 |
SIGINT |
Fast Shutdown | 服务器不允许新的连接,并向所有现有的子进程发送SIGTERM,中止当前的事务并迅速退出。等待几乎所有子进程(有几个子进程不需要)退出,最后关闭 |
SIGQUIT |
Immediate Shutdown | 将向所有子进程发送SIGQUIT,并等待它们终止。如果在5秒内有子进程没有终止,它们将被发送SIGKILL |
注意,pg_ctl没有发送SIGKILL(kill -9)的参数,但其实是可以直接对pm发送SIGKILL的,但肯定不推荐这么做,SIGKILL pm时pm不会对子进程、共享内存、信号量做任何处理。因为SIGQUIT pm有兜底逻辑做子进程的SIGKILL,所以SIGQUIT pm基本能保证pm能停下来。
在源码中,停库状态总共只有3种,跟停库方式相对应:
/* Startup/shutdown state */
#define NoShutdown 0
#define SmartShutdown 1
#define FastShutdown 2
#define ImmediateShutdown 3
这些状态会在停库routine源码中常见,一般通过变量Shutdown来判断当前停库状态,如:
Shutdown >= FastShutdown
pm信号
当pm收到对应信号时做相应的处理:
void
PostmasterMain(int argc, char *argv[])
{...
pqsignal_pm(SIGHUP, SIGHUP_handler); /* reread config file and have
* children do same */
pqsignal_pm(SIGINT, pmdie); /* send SIGTERM and shut down */
pqsignal_pm(SIGQUIT, pmdie); /* send SIGQUIT and die */
pqsignal_pm(SIGTERM, pmdie); /* wait for children and shut down */
pqsignal_pm(SIGALRM, SIG_IGN); /* ignored */
pqsignal_pm(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN); /* ignored */
pqsignal_pm(SIGUSR1, sigusr1_handler); /* message from child process */
pqsignal_pm(SIGUSR2, dummy_handler); /* unused, reserve for children */
pqsignal_pm(SIGCHLD, reaper); /* handle child termination */
pmdie:停库的三种信号会调用pmdie函数,pmdie是停库的关键函数,下面会重点分析。reaper:停库时会处理子进程退出清理,所以在停库的逻辑中。子进程退出会给pm发生SIGCHLD信号,然后进入reaper清理子进程,每种子进程的清理也有自己的逻辑,比如checkpointer进程的正常退出会判断archiver和walsender是否完成了各自的任务。sigusr1、sigusr2:sigusr1_handler是SIGUSER1的标准routine,每种子进程对于SIGUSR1的处理行为各不同;SIGUSR2完全是子进程自定义行为了,有些子进程没有注册这个信号。
walsender的信号
子进程fork出来时,首先就要注册信号。
WalSndSignals注册walsender进程的信号:
/* Set up signal handlers */
void
WalSndSignals(void)
{
/* Set up signal handlers */
pqsignal(SIGHUP, SignalHandlerForConfigReload);
pqsignal(SIGINT, StatementCancelHandler); /* query cancel */
pqsignal(SIGTERM, die); /* request shutdown */
pqsignal(SIGQUIT, quickdie); /* hard crash time */
InitializeTimeouts(); /* establishes SIGALRM handler */
pqsignal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
pqsignal(SIGUSR1, procsignal_sigusr1_handler);
pqsignal(SIGUSR2, WalSndLastCycleHandler); /* request a last cycle and
* shutdown */
}
要注意SIGUSR1和SIGUSR2
checkpointer的信号
CheckpointerMain注册checkpointer的信号:
void
CheckpointerMain(void)
{
...
//checkpointer会屏蔽SIGTERM,真正的停止是SIGUSR2
pqsignal(SIGHUP, SignalHandlerForConfigReload);
pqsignal(SIGINT, ReqCheckpointHandler); /* request checkpoint */
pqsignal(SIGTERM, SIG_IGN); /* ignore SIGTERM */
pqsignal(SIGQUIT, SignalHandlerForCrashExit);
pqsignal(SIGALRM, SIG_IGN);
pqsignal(SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN);
pqsignal(SIGUSR1, procsignal_sigusr1_handler);
pqsignal(SIGUSR2, SignalHandlerForShutdownRequest);
要注意SIGUSR1和SIGUSR2,同时要注意checkpointer是没有注册SIGTERM的
停库源码分析
pm信号处理和状态机
pmdie函数用于处理不同的postmaster signals,包括子进程给pm发送的SIGCHILD和pg_ctl发送的停库信号。pm信号处理主体逻辑是根据signal转换pmState状态机状态,并进入状态机PostmasterStateMachine处理。
pmdie:
/*
* pmdie -- signal handler for processing various postmaster signals.
*/
static void
pmdie(SIGNAL_ARGS)
{
int save_errno = errno;
...
switch (postgres_signal_arg)
{
case SIGTERM://Smart Shutdown
...
if (pmState == PM_RUN)
connsAllowed = ALLOW_SUPERUSER_CONNS;
...
//smart shutdown没有处理pmstate,直接交给状态机处理
//此时正常情况pmState = PM_RUN
PostmasterStateMachine();
break;
case SIGINT://Fast Shutdown
...
else if (pmState == PM_RUN ||
pmState == PM_HOT_STANDBY)
{
/* Report that we're about to zap live client sessions */
ereport(LOG,
(errmsg("aborting any active transactions")));
pmState = PM_STOP_BACKENDS;
}
//Fast Shutdown将pmstate转换为PM_STOP_BACKENDS
//然后交给状态机处理
PostmasterStateMachine();
break;
case SIGQUIT://Immediate Shutdown
...
TerminateChildren(SIGQUIT);//abort all children with SIGQUIT, wait for them to exit
pmState = PM_WAIT_BACKENDS;
/* set stopwatch for them to die */
AbortStartTime = time(NULL);
//Immediate Shutdown将pmstate转换为PM_WAIT_BACKENDS
//进入状态机前处理也会children
//先用SIGQUIT中断children,等待他们退出
//然后用SIGKILL处理还在的children
//最后非一致性退出
PostmasterStateMachine();
break;
}
...
}
在进入状态机处理函数前先看下postmaster的状态有哪些:
typedef enum
{
PM_INIT, /* postmaster starting */
PM_STARTUP, /* waiting for startup subprocess */
PM_RECOVERY, /* in archive recovery mode */
PM_HOT_STANDBY, /* in hot standby mode */
PM_RUN, /* normal "database is alive" state */
PM_STOP_BACKENDS, /* need to stop remaining backends */
PM_WAIT_BACKENDS, /* waiting for live backends to exit */
PM_SHUTDOWN, /* waiting for checkpointer to do shutdown
* ckpt */
PM_SHUTDOWN_2, /* waiting for archiver and walsenders to
* finish */
PM_WAIT_DEAD_END, /* waiting for dead_end children to exit */
PM_NO_CHILDREN /* all important children have exited */
} PMState;
由于正常都是running态关库,这里只需要关注PM_RUN以下的状态即可。
PostmasterStateMachine的执行函数实际上有顺序逻辑:
/*
* Advance the postmaster's state machine and take actions as appropriate
*
* This is common code for pmdie(), reaper() and sigusr1_handler(), which
* receive the signals that might mean we need to change state.
*/
static void
PostmasterStateMachine(void)
{
//smart shutdown,此时的pmState应是PM_RUN
if (pmState == PM_RUN || pmState == PM_HOT_STANDBY)
{
...
if (connsAllowed == ALLOW_NO_CONNS)
{
//当所有normal backend都退出后,pmState转换PM_STOP_BACKENDS
if (CountChildren(BACKEND_TYPE_NORMAL) == 0)
pmState = PM_STOP_BACKENDS;
}
}
//PM_STOP_BACKENDS会中止一些比较核心的子进程,有些子进程会继续运行
//autovacuum,bgwriter,walwriter,startup,walreiver会停止
//walsender,checkpointer, archiver, stats, and syslogger会继续跑
//smart shutdown后段会进入此逻辑,fast shutdown直接进入此逻辑
if (pmState == PM_STOP_BACKENDS)
{
...
//注意walsender这句话!
/* Signal all backend children except walsenders */
SignalSomeChildren(SIGTERM,
BACKEND_TYPE_ALL - BACKEND_TYPE_WALSND);
/* and the autovac launcher too */
if (AutoVacPID != 0)
signal_child(AutoVacPID, SIGTERM);
/* and the bgwriter too */
if (BgWriterPID != 0)
signal_child(BgWriterPID, SIGTERM);
/* and the walwriter too */
if (WalWriterPID != 0)
signal_child(WalWriterPID, SIGTERM);
/* If we're in recovery, also stop startup and walreceiver procs */
if (StartupPID != 0)
signal_child(StartupPID, SIGTERM);
if (WalReceiverPID != 0)
signal_child(WalReceiverPID, SIGTERM);
/* checkpointer, archiver, stats, and syslogger may continue for now */
//将pmState从PM_STOP_BACKENDS转换为PM_WAIT_BACKEND
//PM_WAIT_BACKEND表示等待backend退出
pmState = PM_WAIT_BACKENDS;
}
/*
* If we are in a state-machine state that implies waiting for backends to
* exit, see if they're all gone, and change state if so.
*/
//
//smart shutdown,fast shutdown后段会进入此逻辑
//immediate shutdown进入状态机处理时,直接进入此逻辑
if (pmState == PM_WAIT_BACKENDS)
{
//crash recovery和immediate shutdown时,checkpointer需要妥善退出
//archiver, stats, and syslogger不需要处理,因为他们没有连到shared memory
//Walsenders也不需要处理,它将在checkpoint记录写入之后退出,就像archiver进程一样
if (CountChildren(BACKEND_TYPE_ALL - BACKEND_TYPE_WALSND) == 0 &&
StartupPID == 0 &&
WalReceiverPID == 0 &&
BgWriterPID == 0 &&
(CheckpointerPID == 0 ||
(!FatalError && Shutdown < ImmediateShutdown)) &&
WalWriterPID == 0 &&
AutoVacPID == 0)
{
if (Shutdown >= ImmediateShutdown || FatalError)
{
//ImmediateShutdown会等待dead end进程结束
pmState = PM_WAIT_DEAD_END;
/*
* We already SIGQUIT'd the archiver and stats processes, if
* any, when we started immediate shutdown or entered
* FatalError state.
*/
}
else
{
//smart,fast shutdown走此逻辑
//常规子进程都退出了,此时该通知checkpointer做shutdown checkpoint
Assert(Shutdown > NoShutdown);
//如果checkpointer进程没有,就启动
if (CheckpointerPID == 0)
CheckpointerPID = StartCheckpointer();
/* And tell it to shut down */
if (CheckpointerPID != 0)
{
//向Checkpointer发送SIGUSR2
//pmState = PM_SHUTDOWN
signal_child(CheckpointerPID, SIGUSR2);
pmState = PM_SHUTDOWN;
}
else
{
//没有启动起来Checkpointer是一个比较严重的问题
FatalError = true;
pmState = PM_WAIT_DEAD_END;
/* Kill the walsenders, archiver and stats collector too */
//注释说kill walsender,实际上根本没有;至少不是SIGQUIT去停的
SignalChildren(SIGQUIT);
if (PgArchPID != 0)
signal_child(PgArchPID, SIGQUIT);
if (PgStatPID != 0)
signal_child(PgStatPID, SIGQUIT);
}
}
}
}
//pmdie函数和状态机函数不会制造PM_SHUTDOWN_2这个状态,但是reaper会
//reaper在处理checkpointer的退出时,会设置pmState = PM_SHUTDOWN_2;当然在reaper函数最后会进入状态机函数,也就是这里
if (pmState == PM_SHUTDOWN_2)
{
/*
* PM_SHUTDOWN_2 state ends when there's no other children than
* dead_end children left. There shouldn't be any regular backends
* left by now anyway; what we're really waiting for is walsenders and
* archiver.
*/
//PM_SHUTDOWN_2本质上是等待walsender和archiver
//只是更改了pmState状态
if (PgArchPID == 0 && CountChildren(BACKEND_TYPE_ALL) == 0)
{
pmState = PM_WAIT_DEAD_END;
}
}
if (pmState == PM_WAIT_DEAD_END)
{
//PM_WAIT_DEAD_END表示BackendList已经完全清空
if (dlist_is_empty(&BackendList) &&
PgArchPID == 0 && PgStatPID == 0)
{
/* These other guys should be dead already */
Assert(StartupPID == 0);
Assert(WalReceiverPID == 0);
Assert(BgWriterPID == 0);
Assert(CheckpointerPID == 0);
Assert(WalWriterPID == 0);
Assert(AutoVacPID == 0);
/* syslogger is not considered here */
pmState = PM_NO_CHILDREN;
}
}
//PM_NO_CHILDREN是停库的最后一个状态,表示可以正常停库了
if (Shutdown > NoShutdown && pmState == PM_NO_CHILDREN)
{
if (FatalError)
{
ereport(LOG, (errmsg("abnormal database system shutdown")));
//异常退出pm
ExitPostmaster(1);
}
...
//正常退出pm
ExitPostmaster(0);
}
}
...
}
reaper是进程回收函数,子进程退出后会发送pm SIGCHLD信号,pm通过reaper函数清理进程。 如backend、startup、checkpointer等进程都有自己的清理流程。
这里只看checkpointer的清理,另外reaper中没有关于walsender的清理逻辑:
if (pid == CheckpointerPID)
{
CheckpointerPID = 0;
//Checkpointer进程是正常退出,且pmState为PM_SHUTDOWN:等待checkpoint完成态
if (EXIT_STATUS_0(exitstatus) && pmState == PM_SHUTDOWN)
{
/*
* OK, we saw normal exit of the checkpointer after it's been
* told to shut down. We expect that it wrote a shutdown
* checkpoint. (If for some reason it didn't, recovery will
* occur on next postmaster start.)
*
* At this point we should have no normal backend children
* left (else we'd not be in PM_SHUTDOWN state) but we might
* have dead_end children to wait for.
*
* If we have an archiver subprocess, tell it to do a last
* archive cycle and quit. Likewise, if we have walsender
* processes, tell them to send any remaining WAL and quit.
*/
Assert(Shutdown > NoShutdown);
//最后一次唤醒pgarch
if (PgArchPID != 0)
signal_child(PgArchPID, SIGUSR2); //pgarch SIGUSR2=pgarch_waken_stop
//最后一次唤醒walsender
SignalChildren(SIGUSR2);//walsender SIGUSR2=WalSndLastCycleHandler
//这里设置了PM_SHUTDOWN_2
//此时Checkpointer正常退出完成了,这里应该等pgarch和walsender最后一个任务完成
//即PM_SHUTDOWN_2态
pmState = PM_SHUTDOWN_2;
...
}
else
{
//checkpointer进程异常退出都认为是crash
HandleChildCrash(pid, exitstatus,
_("checkpointer process"));
}
continue;
}
...
//最后reaper还是会进入状态机函数
PostmasterStateMachine();
...
}
checkpointer和walsender进程的退出
checkpointer主循环处理请求和关闭进程:
void
CheckpointerMain(void)
{
/*
* Loop forever
*/
for (;;)
{
bool do_checkpoint = false;
int flags = 0;
pg_time_t now;
int elapsed_secs;
int cur_timeout;
/* Clear any already-pending wakeups */
ResetLatch(MyLatch);
/*
* Process any requests or signals received recently.
*/
//处理近期的同步请求和信号
AbsorbSyncRequests();
HandleCheckpointerInterrupts();
checkpointer关闭函数:
/*
* Process any new interrupts.
*/
static void
HandleCheckpointerInterrupts(void)
{
...
if (ShutdownRequestPending)
{
/*
* From here on, elog(ERROR) should end with exit(1), not send control
* back to the sigsetjmp block above
*/
ExitOnAnyError = true;
ShutdownXLOG(0, 0);//这里会写shutdown checkpoint
proc_exit(0);//正常退出态为0
}
}
checkpointer的退出需要等待ShutdownXLOG完成。
ShutdownXLOG:
/*
* This must be called ONCE during postmaster or standalone-backend shutdown
*/
void
ShutdownXLOG(int code, Datum arg)
{
...
//这里有个checkpointer的shutting down的日志,这个日志一般都会看到
ereport(IsPostmasterEnvironment ? LOG : NOTICE,
(errmsg("shutting down")));
/*
* Signal walsenders to move to stopping state.
*/
//walsender初始化stopping
WalSndInitStopping();
//等待所有walsender处于stopping状态
WalSndWaitStopping();
if (RecoveryInProgress())
CreateRestartPoint(CHECKPOINT_IS_SHUTDOWN | CHECKPOINT_IMMEDIATE);
else
{
/*
* If archiving is enabled, rotate the last XLOG file so that all the
* remaining records are archived (postmaster wakes up the archiver
* process one more time at the end of shutdown). The checkpoint
* record will go to the next XLOG file and won't be archived (yet).
*/
if (XLogArchivingActive() && XLogArchiveCommandSet())
RequestXLogSwitch(false);
//这里就是shutdown checkpoint的创建函数
CreateCheckPoint(CHECKPOINT_IS_SHUTDOWN | CHECKPOINT_IMMEDIATE);
}
ShutdownCLOG();
ShutdownCommitTs();
ShutdownSUBTRANS();
ShutdownMultiXact();
}
checkpointer通知所有walsender开始stopping:
/*
* Signal all walsenders to move to stopping state.
*
* This will trigger walsenders to move to a state where no further WAL can be
* generated. See this file's header for details.
*/
void
WalSndInitStopping(void)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < max_wal_senders; i++)
{
WalSnd *walsnd = &WalSndCtl->walsnds[i];
pid_t pid;
SpinLockAcquire(&walsnd->mutex);
pid = walsnd->pid;
SpinLockRelease(&walsnd->mutex);
if (pid == 0)
continue;
SendProcSignal(pid, PROCSIG_WALSND_INIT_STOPPING, InvalidBackendId);
}
}
walsender通过SendProcSignal函数收到信号,信号为SIGUSR1
/*
* SendProcSignal
* Send a signal to a Postgres process
*
* Providing backendId is optional, but it will speed up the operation.
*
* On success (a signal was sent), zero is returned.
* On error, -1 is returned, and errno is set (typically to ESRCH or EPERM).
*
* Not to be confused with ProcSendSignal
*/
int
SendProcSignal(pid_t pid, ProcSignalReason reason, BackendId backendId)
{
else
{
/*
* BackendId not provided, so search the array using pid. We search
* the array back to front so as to reduce search overhead. Passing
* InvalidBackendId means that the target is most likely an auxiliary
* process, which will have a slot near the end of the array.
*/
int i;
for (i = NumProcSignalSlots - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
slot = &ProcSignal->psh_slot[i];
if (slot->pss_pid == pid)
{
/* the above note about race conditions applies here too */
/* Atomically set the proper flag */
slot->pss_signalFlags[reason] = true;
/* Send signal */
return kill(pid, SIGUSR1);
}
}
}
errno = ESRCH;
return -1;
}
walsender中SIGUSR1的注册为如下:
pqsignal(SIGUSR1, procsignal_sigusr1_handler);
pqsignal(SIGUSR2, WalSndLastCycleHandler); /* request a last cycle and
* shutdown */
sigusr1根据信号的reason来分类处理
/*
* procsignal_sigusr1_handler - handle SIGUSR1 signal.
*/
void
procsignal_sigusr1_handler(SIGNAL_ARGS)
{
...
if (CheckProcSignal(PROCSIG_WALSND_INIT_STOPPING))
HandleWalSndInitStopping();
...
}
处理PROCSIG_WALSND_INIT_STOPPING的函数为HandleWalSndInitStopping
/*
* Handle PROCSIG_WALSND_INIT_STOPPING signal.
*/
void
HandleWalSndInitStopping(void)
{
Assert(am_walsender);
/*
* If replication has not yet started, die like with SIGTERM. If
* replication is active, only set a flag and wake up the main loop. It
* will send any outstanding WAL, wait for it to be replicated to the
* standby, and then exit gracefully.
*/
if (!replication_active)
kill(MyProcPid, SIGTERM);
else
got_STOPPING = true;//如果walsender是active的,initstopping函数只会设置状态,让主循环去处理
}
这个注释中的main loop有点意义不明,walsender有主循环ServerLoop,但实际上只有WalSndWaitForWal中的循环才有关于got_STOPPING的判断。
WalSndWaitForWal函数是walsender等待新的wal日志的主循环函数。由于wal record生成之初还在内存中,walwriter会根据一定的条件flush,不是随时都flush。WalSndWaitForWal函数通过对比当前sent的LSN和flushed的LSN,以判断是否需要send新的wal日志。换句话说,没有flush的wal不会传递,flush过的wal才会传给下游。
WalSndWaitForWal关于stopping的代码段:
/*
* Wait till WAL < loc is flushed to disk so it can be safely sent to client.
*
* Returns end LSN of flushed WAL. Normally this will be >= loc, but
* if we detect a shutdown request (either from postmaster or client)
* we will return early, so caller must always check.
*/
static XLogRecPtr
WalSndWaitForWal(XLogRecPtr loc)
{
...
for (;;)
{
...
//收到got_STOPPING信息后,做一次flush wal操作
//这是必须的!因为walwriter进程在此时可能已经关闭了,可能还有wal没有刷盘
if (got_STOPPING)
XLogBackgroundFlush();
/* Update our idea of the currently flushed position. */
if (!RecoveryInProgress())
RecentFlushPtr = GetFlushRecPtr();
else
RecentFlushPtr = GetXLogReplayRecPtr(NULL);
//跳出for循环
//有了新的RecentFlushPtr位置后,还需要send
if (got_STOPPING)
break;
...
}
/* reactivate latch so WalSndLoop knows to continue */
SetLatch(MyLatch);
return RecentFlushPtr;
}
回到walsender主循环:WalSndLoop(XLogSendLogical);
/* Main loop of walsender process that streams the WAL over Copy messages. */
static void
WalSndLoop(WalSndSendDataCallback send_data)
{
...
for (;;)
{
/* Clear any already-pending wakeups */
ResetLatch(MyLatch);
...
//处理下游返回的信息
ProcessRepliesIfAny();
/*
* If we have received CopyDone from the client, sent CopyDone
* ourselves, and the output buffer is empty, it's time to exit
* streaming.
*/
//streaming做完就退出循环
if (streamingDoneReceiving && streamingDoneSending &&
!pq_is_send_pending())
break;
//output buffer是否还有pending的data,有就send
if (!pq_is_send_pending())
send_data();
else
WalSndCaughtUp = false;
/* Try to flush pending output to the client */
if (pq_flush_if_writable() != 0)
WalSndShutdown();//下游不可写入,下游端关闭了,正常关闭walsender,退出码0
/* If nothing remains to be sent right now ... */
if (WalSndCaughtUp && !pq_is_send_pending())
{
/*
* If we're in catchup state, move to streaming. This is an
* important state change for users to know about, since before
* this point data loss might occur if the primary dies and we
* need to failover to the standby. The state change is also
* important for synchronous replication, since commits that
* started to wait at that point might wait for some time.
*/
//数据已经传完了,但是仍然要发送提交信息
if (MyWalSnd->state == WALSNDSTATE_CATCHUP)
{
ereport(DEBUG1,
(errmsg("\"%s\" has now caught up with upstream server",
application_name)));
WalSndSetState(WALSNDSTATE_STREAMING);
}
//收到SIGUSR2,表示shutdown checkpoint做完了。
//把shutdown checkpoint record发出去,等待完成再退出
if (got_SIGUSR2)
WalSndDone(send_data);//退出码0
}
...
}
}
走远了,回到checkpointer的ShutdownXLOG逻辑,以上只是在分析WalSndInitStopping()。这个信号发送给walsender后,会执行WalSndWaitStopping以等待walsender。
只要有walsender没有退出,这里就是一个死循环不会return:
/*
* Wait that all the WAL senders have quit or reached the stopping state. This
* is used by the checkpointer to control when the shutdown checkpoint can
* safely be performed.
*/
void
WalSndWaitStopping(void)
{
for (;;)
{
int i;
bool all_stopped = true;
for (i = 0; i < max_wal_senders; i++)
{
WalSnd *walsnd = &WalSndCtl->walsnds[i];
SpinLockAcquire(&walsnd->mutex);
if (walsnd->pid == 0)
{
SpinLockRelease(&walsnd->mutex);
continue;
}
if (walsnd->state != WALSNDSTATE_STOPPING)
{
all_stopped = false;
SpinLockRelease(&walsnd->mutex);
break;
}
SpinLockRelease(&walsnd->mutex);
}
/* safe to leave if confirmation is done for all WAL senders */
if (all_stopped)
return;
pg_usleep(10000L); /* wait for 10 msec */
}
}
最后结合walsender.c的注释:
* If the server is shut down, checkpointer sends us
* PROCSIG_WALSND_INIT_STOPPING after all regular backends have exited. If
* the backend is idle or runs an SQL query this causes the backend to
* shutdown, if logical replication is in progress all existing WAL records
* are processed followed by a shutdown. Otherwise this causes the walsender
* to switch to the "stopping" state. In this state, the walsender will reject
* any further replication commands. The checkpointer begins the shutdown
* checkpoint once all walsenders are confirmed as stopping. When the shutdown
* checkpoint finishes, the postmaster sends us SIGUSR2. This instructs
* walsender to send any outstanding WAL, including the shutdown checkpoint
* record, wait for it to be replicated to the standby, and then exit.
- 当所有的常规backend都退出后,checkpointer会发送
PROCSIG_WALSND_INIT_STOPPING给walsender - walsender可能进入stopping状态
- 当所有walsender都进入stopping状态后,checkpointer才会做shutdown checkpoint
- 当shutdown checkpoint完成后,pm发送
SIGUSR2给walsender,walsender会发送额外的wal,包括shutdown checkpoint记录本身,并等待standby完成再退出
停库流程图
撸完源码好像懂了又好像没懂,需要一个停库流程图来理清思路。
汇总fast shutdown停库流程图:
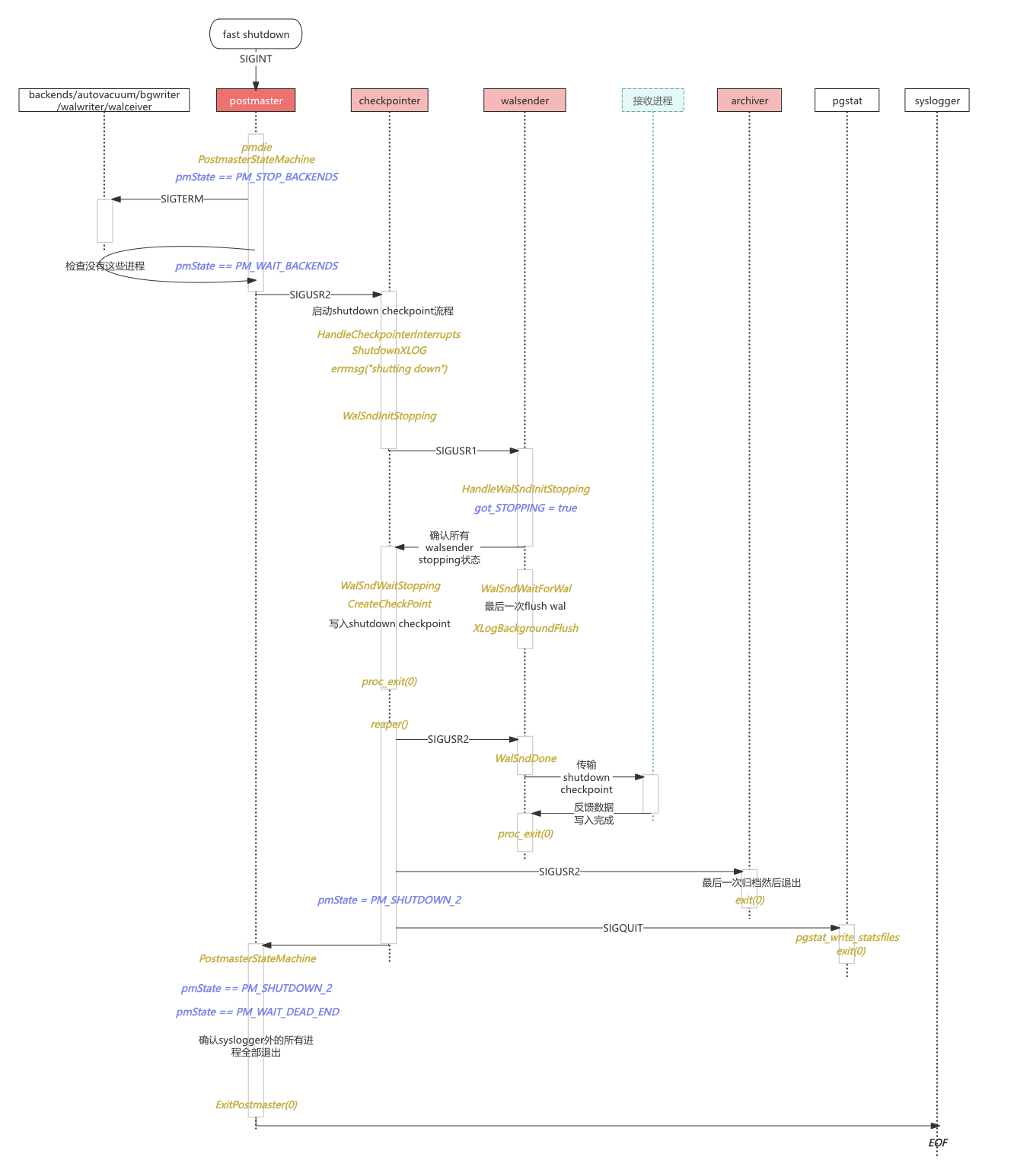
(高清大图:https://www.processon.com/view/link/6778a73a04a8344b9502637a)
- PG通过信号、各进程主循环、PM状态机、pmdie进程回收函数来共同管理停库逻辑
- 还需注意:信号本身是异步的。如果需要等待目标进程处理信号的结果,通常需要通过其他同步机制(如管道、信号量、共享内存等)来实现。PG主要通过进程依赖和进程是否正常退出来判断信号是否被正确处理。
- pgarch、walsender被认为是同一类进程,与其他进程(walwriter、bgwriter)等处理不同。pgarch、walsender需要额外做“最后一个任务”这件事。“最后一个任务”的信号通常定义为SIGUSR2
- checkpointer的正常退出依赖pgarch、walsender的正常退出
- pgarch的最后一个任务是最后一次归档。所以归档会影响停库
- walsender的倒数第二个任务是传递最后的wal,最后一个任务是传递checkpoint shutdown信息。且这些任务需要下游回复消息,所以walsender会影响停库。
测试复现
测试:复现walsender阻止停库
在fast stop停库后,walsender可能阻止停库。
测试了各自场景去复现walsender阻止停库,目前来看以下条件同时满足比较容易触发停库异常:
- 发布订阅一个walsender
- dts一个walsender
- 大量子事务导致复制槽spill中
这个三合一场景不代表唯一场景,只是测试了很多场景这个好复现一点。
--复现命令(不是特别稳定的复现)
1.建表
--pg
create table lzlpg(id bigserial primary key,a char(2000),b char(2000),c char(2000));
--oracle
create table lzl.lzloracle(id number primary key ,a char(2000),b char(2000),c char(2000)) tablespace FADATA;
2.搭建2条逻辑链路(1条发布订阅,一条dts到oracle)
3.改小logical_decoding_work_mem
logical_decoding_work_mem=1MB
4.写入大量数据(推荐子事务spill)
--一次insert一行,每个insert一个子事务
echo "begin;">subtx.sql
for i in {1..500000}
do
echo "savepoint p$i;">>subtx.sql
echo "insert into lzlpg(column1,column2,column3) select 'a','b','c';">>subtx.sql
done
nohup psql -d lzl -f subtx.sql &
5.没写入完就停库
pg_ctl stop -D $PGDATA -m fast
此时fast停库,数据库处于一个非完整停库状态,如下:
~/lzl/slot]$ ps -axjf|grep 110402 150696 64964 64961 146782 pts/42 64961 S+ 6001 0:00 \_ grep --color=auto 110402 1 110402 110402 110402 ? -1 Ss 6001 0:00 /myhost/postgres/base/rasesql1.5.6/bin/postgres -D /myhost/pg8094/data 110402 110599 110599 110599 ? -1 Ss 6001 0:00 \_ postgres: lzlpg: logger 110402 117803 117803 117803 ? -1 Ss 6001 0:00 \_ postgres: lzlpg: checkpointer 110402 117807 117807 117807 ? -1 Ss 6001 0:00 \_ postgres: lzlpg: stats collector 110402 118563 118563 118563 ? -1 Rs 6001 3:29 \_ postgres: lzlpg: walsender lzl 127.0.0.1(62971) idle 110402 222918 222918 222918 ? -1 Rs 6001 2:59 \_ postgres: lzlpg: walsender dtssync 30.181.46.203(57218) idle
walsender、checkpointer、postmaster都在,logger、stats也没有退出。
控制文件的状态为in production:生产运行中,说明checkpoint做的本地shutdown checkpoint没有做完:
~/lzl/slot]$ pg_controldata|grep -i state Database cluster state: in production
checkpointer堆栈:
pstack 117803
#0 0x00002b879fe0b983 in __select_nocancel () from /lib64/libc.so.6
#1 0x00000000008fd04a in pg_usleep (microsec=microsec@entry=10000) at pgsleep.c:56
#2 0x00000000007610c8 in WalSndWaitStopping () at walsender.c:3209
#3 0x000000000051fa86 in ShutdownXLOG (code=code@entry=0, arg=arg@entry=0) at xlog.c:8596
#4 0x00000000007215ff in HandleCheckpointerInterrupts () at checkpointer.c:566
#5 CheckpointerMain () at checkpointer.c:343
...
此时的checkpointer堵在WalSndWaitStopping函数,代表checkpointer在等待walsender进程进入stopping状态。
此时的walsender堆栈:
#0 0x00000000007484fb in ReorderBufferLargestTXN (rb=<optimized out>) at reorderbuffer.c:2345
#1 ReorderBufferCheckMemoryLimit (rb=0x2b8808b94118) at reorderbuffer.c:2390
#2 ReorderBufferQueueChange (rb=0x2b8808b94118, xid=<optimized out>, lsn=1676456602544, change=change@entry=0x2b87a229f408) at reorderbuffer.c:649
#3 0x000000000073ec99 in DecodeTruncate (buf=<optimized out>, buf=<optimized out>, ctx=<optimized out>) at decode.c:872
#4 DecodeHeapOp (buf=0x7ffda7d35180, ctx=0x2b87a224b118) at decode.c:455
#5 LogicalDecodingProcessRecord (ctx=0x2b87a224b118, record=<optimized out>) at decode.c:126
#6 0x000000000075f502 in XLogSendLogical () at walsender.c:2886
#7 0x0000000000761822 in WalSndLoop (send_data=send_data@entry=0x75f4c0 <XLogSendLogical>) at walsender.c:2287
...
walsender堵在事务溢出函数。(为什么堵还没有搞清楚!!!)
checkpointer进程阻塞在WalSndWaitStopping函数:
/*
* Wait that all the WAL senders have quit or reached the stopping state. This
* is used by the checkpointer to control when the shutdown checkpoint can
* safely be performed.
*/
void
WalSndWaitStopping(void)
{
for (;;)
{
int i;
bool all_stopped = true;
for (i = 0; i < max_wal_senders; i++)
{
WalSnd *walsnd = &WalSndCtl->walsnds[i];
SpinLockAcquire(&walsnd->mutex);
if (walsnd->pid == 0)
{
SpinLockRelease(&walsnd->mutex);
continue;
}
if (walsnd->state != WALSNDSTATE_STOPPING)
{
all_stopped = false;
SpinLockRelease(&walsnd->mutex);
break;
}
SpinLockRelease(&walsnd->mutex);
}
/* safe to leave if confirmation is done for all WAL senders */
if (all_stopped)
return;
pg_usleep(10000L); /* wait for 10 msec */
}
}
从代码和堆栈来看肯定是进入了条件walsnd->state != WALSNDSTATE_STOPPIN才会出现跳不出死循环。
测试:停库中间态的处理方案
以上是个尴尬的停库停一半的状态,除了kill -9 外,实际上还有其他好办法可以一致性停库。
- 方案1:关闭下游进程
- 方案2:发送
SIGTERM给walsender
方案1测试:
由于下游退出后,walsender也会跟随退出:
static void
ProcessRepliesIfAny(void)
{...
/*
* 'X' means that the standby is closing down the socket.
*/
case 'X':
proc_exit(0);
如果是发布订阅,在订阅端执行以下命令即可,即使是上游处于停库中间态也会将walsender退出。
\c lzldb
alter SUBSCRIPTION sub_lzl disable;
不过这依赖下游自身的处理,我们也不能快速地关闭dts等同步工具的下游接收进程。
方案2测试:
由于walsender注册了SIGTERM信号,库运行时跑的select pg_terminate_backend($walsender_pid)命令也是发送SIGTERM给walsender,所以理论上只要发送SIGTERM给walsender应该可以处理这个问题,而不必发送kill -9。
命令如下:
kill -SIGTERM 62834
#同 kill -15 62834
#同 kill 62834
正常kill后pm等进程全部退出。
查看控制文件和wal日志信息以确认是否是一致性停库:
1.pg_controldata的数据库state从in production转换为shut down一致性停库:
$ pg_controldata|grep -i state
Database cluster state: shut down
2.wal日志的最后一个record是CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN:
pg_waldump 000000010000018600000012|tail -1 pg_waldump: fatal: error in WAL record at 186/915D7920: invalid record length at 186/915D7998: wanted 24, got 0 rmgr: XLOG len (rec/tot): 114/ 114, tx: 0, lsn: 186/915D7920, prev 186/915D78A8, desc: CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN redo 186/915D7920; tli 1; prev tli 1; fpw true; xid 0:13431045; oid 3808147; multi 3; offset 6; oldest xid 485 in DB 1; oldest multi 1 in DB 1; oldest/newest commit timestamp xid: 494/13431044; oldest running xid 0; shutdown
测试:复现只有主库有CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN
生产现场有个现象是,本地wal有shutdown checkpoint但是从库没有。生产是在半停库状态时做的immediate stop,随后启动库没有启动起来。
当时主从的wal日志最后2条record类似如下:
#主库wal:
CHECKPOINT_ONLINE
CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN
#从库wal:
CHECKPOINT_ONLINE
复现命令:
# 1. 先复现walsender阻止停库
略
# 2. 查看最后一条wal record
rmgr: Standby len (rec/tot): 50/ 50, tx: 0, lsn: 188/307ABE00, prev 188/307ABDC8, desc: RUNNING_XACTS nextXid 13432445 latestCompletedXid 13432444 oldestRunningXid 13432445
# 3. pg_ctl stop -D $PGDATA -m i
# 4. 查看最后一条wal record
不变,同2
# 5. pg_ctl start -D $PGDATA
# 6. 查看最后两条wal record
rmgr: Standby len (rec/tot): 50/ 50, tx: 0, lsn: 188/307ABE00, prev 188/307ABDC8, desc: RUNNING_XACTS nextXid 13432445 latestCompletedXid 13432444 oldestRunningXid 13432445 #同2
rmgr: XLOG len (rec/tot): 114/ 114, tx: 0, lsn: 188/307ABE38, prev 188/307ABE00, desc: CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN redo 188/307ABE38; tli 1; prev tli 1; fpw true; xid 0:13432445; oid 3832732; multi 3; offset 6; oldest xid 485 in DB 1; oldest multi 1 in DB 1; oldest/newest commit timestamp xid: 494/13432444; oldest running xid 0; shutdown #出现CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN
从该复现来看,CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN其实是起库的时候做!
这与现场的动作一致:1.fast停库没停下来 2.immediate停库 3.起库没启起来。
疑问1:起库什么时候做的CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN?
疑问2:CHECKPOINT_ONLINE的触发时机?复现表象来看,偶现fast shutdown出现最后一个wal record为CHECKPOINT_ONLINE
疑问1分析:
起库做shutdown checkpoint,这很容易联想到是startup进程做的。由于之前分析过startup进程的起库流程,我们可以直接定位到函数StartupXLOG:
/*
* This must be called ONCE during postmaster or standalone-backend startup
*/
void
StartupXLOG(void)
{...
if (InRecovery) //因为是shutdown停库所以会做实例恢复
{
/*
* Perform a checkpoint to update all our recovery activity to disk.
*
* Note that we write a shutdown checkpoint rather than an on-line
* one. This is not particularly critical, but since we may be
* assigning a new TLI, using a shutdown checkpoint allows us to have
* the rule that TLI only changes in shutdown checkpoints, which
* allows some extra error checking in xlog_redo.
*
* In fast promotion, only create a lightweight end-of-recovery record
* instead of a full checkpoint. A checkpoint is requested later,
* after we're fully out of recovery mode and already accepting
* queries.
*/
if (bgwriterLaunched) //这个if明显是从库流复制用的逻辑
{...
}
else //主库的startup会走到这里
CreateCheckPoint(CHECKPOINT_END_OF_RECOVERY | CHECKPOINT_IMMEDIATE);
}
- 做shutdown checkpoint是故意的,主要是为了TLI逻辑的代码健壮性
- 只要是非一致性停库,起库的时候就会做shutdown checkpoint
所以,直接-m i暴力停库再起库,也会出现CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN,自测。
疑问2分析:
多次测试,偶现,推测是刚好停库前满足checkpoint条件触发了一次online checkpoint,纯属巧合。
联想数据库停库失败后,无论是脚本、HA还是人工介入都有可能做暴力停库,所以停库前推荐至少做一次checkpoint。
测试:归档对停库的影响
在分析停库代码的时候,还发现checkpointer进程退出后,reaper checkpointer会发送SIGUSR2给pgarch让其最后一次归档并退出:
static void
reaper(SIGNAL_ARGS)
{...
if (pid == CheckpointerPID)
{
CheckpointerPID = 0;
if (EXIT_STATUS_0(exitstatus) && pmState == PM_SHUTDOWN)
{...
/* Waken archiver for the last time */
if (PgArchPID != 0)
signal_child(PgArchPID, SIGUSR2);
...
}
...
而pm的退出依赖除syslogger外所有进程的退出:
if (pmState == PM_WAIT_DEAD_END)
{
if (dlist_is_empty(&BackendList) &&
PgArchPID == 0 && PgStatPID == 0)
{
/* These other guys should be dead already */
Assert(StartupPID == 0);
Assert(WalReceiverPID == 0);
Assert(BgWriterPID == 0);
Assert(CheckpointerPID == 0);
Assert(WalWriterPID == 0);
Assert(AutoVacPID == 0);
/* syslogger is not considered here */
pmState = PM_NO_CHILDREN;
}
}
所以在生产环境中还发现了归档慢对停库有影响。
复现命令:
#配置归档
archive_mode = on
archive_command = '/bin/false ;sleep 1000'#配置归档永远为false且设置sleep以绕过NUM_ARCHIVE_RETRIES逻辑
#停库
pg_ctl stop -D $PGDATA -m fast
停库后进程如下:
$ ps -axjf|grep 61470
72200 88406 88405 68705 pts/48 88405 S+ 6001 0:00 \_ grep --color=auto 61470
1 61470 61470 61470 ? -1 Ss 6001 0:00 /myhost/postgres/base/rasesql1.5.6/bin/postgres -D /myhost/pg8094/data
61470 61772 61772 61772 ? -1 Ss 6001 0:00 \_ postgres: lzlpg: logger
61470 63880 63880 63880 ? -1 Ss 6001 0:00 \_ postgres: lzlpg: archiver archiving 000000010000018800000007
因为这里的checkpointer已经完整停下来了,数据库是一致状态,所以archiver直接kill -9也没有关系
一句话总结
问题1.为什么停库没有停下来?
walsender阻止了停库。checkpointer给walsender发送SIGUSR1,并无限等待所有walsender进程stopping状态,checkpointer卡在这一步。
后面停库停下来是因为-m i暴力停库
问题2.walsender阻止停库中间态是否有其他方案优雅停库?
有。给所有walsender发送SIGTERM信号,既kill(or kill -15、kill -SIGTERM)。随后checkpointer、postmaster会完整停库。
walsender启动时注册过SIGTERM信号,测试来看没有处理不了的情况。
SIGTERM也是pg_terminate_backend(pid)所发送的信号,也是标准停库时应该执行的命令以停止walsender。
问题3.为什么主从库只差一条shutdown checkpoint?
3.1主从库都有CHECKPOINT_ONLINE 的解释:
- 主库触发
CHECKPOINT_ONLINE纯属巧合 - 由于物理walsender还在,这条wal record传输到了从库
3.2只有主库有CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN的解释:
- 这条
CHECKPOINT_SHUTDOWN是主库起库的时候做的 - 由于主库没有起完,这条wal record没有传到从库
问题4.archiver为什么会阻止停库?
在reaper checkpointer进程时,pm会让archiver做最后一次归档,而pm依赖除syslogger之外的所有进程退出,所以最后一次归档如果够慢或者其他问题,会阻止停库。归档失败不会,归档进程会很快退出。
问题5.哪些进程会阻止停库?
其实任意进程不退出都会阻止停库,问题在于哪些比较容易搞出事。从停库代码流程来看archiver、walsender会常阻止停库,因为他们在停库阶段会做最后一次归档or日志传递。
references
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/server-shutdown.html
https://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/Signals
postgres.c
postmaster.c
walsender.c
xlog.c
checkpointer.c
startup.c
pgarch.c






