疑惑
这个文件%s/global/pg_control
什么时候更新呢?它更新会有原子的保证吗?这个我们想过吗
网上找的说明文档
pg_control是一个8KB大小的二进制文件,该文件中记录了PostgreSQL服务器内部信息状态的各方面信息,比如最新检查点(checkpoint)、系统状态、当前运行的postgres服务版本、CRC校验,以及initdb初始化PostgreSQL数据库蔟时设置的某些基本参数。它是在PostgreSQL的7.1版本中新引入的。实际上,该文件中的有效字段值内容仅有几百字节,即sizeof(ControlFileData)
更新源代码
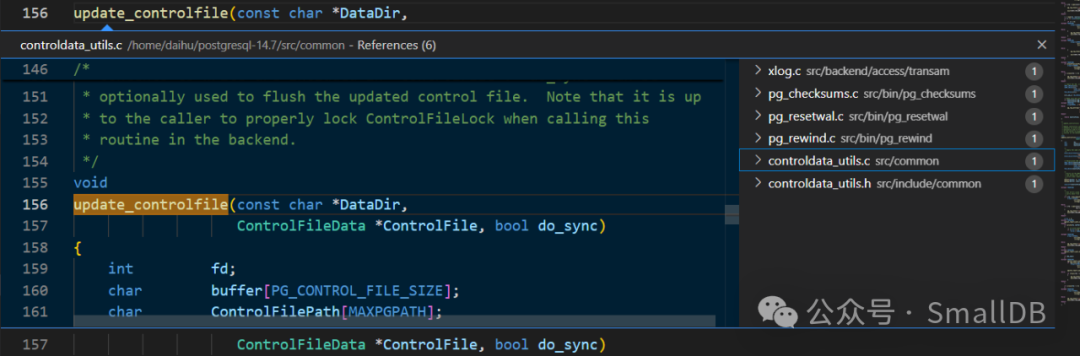
/*
* update_controlfile()
*
* Update controlfile values with the contents given by caller. The
* contents to write are included in "ControlFile". "do_sync" can be
* optionally used to flush the updated control file. Note that it is up
* to the caller to properly lock ControlFileLock when calling this
* routine in the backend.
*/
void
update_controlfile(const char *DataDir,
ControlFileData *ControlFile, bool do_sync)
{
int fd;
char buffer[PG_CONTROL_FILE_SIZE];
char ControlFilePath[MAXPGPATH];
/*
* Apply the same static assertions as in backend's WriteControlFile().
*/
StaticAssertStmt(sizeof(ControlFileData) <= PG_CONTROL_MAX_SAFE_SIZE,
"pg_control is too large for atomic disk writes");
StaticAssertStmt(sizeof(ControlFileData) <= PG_CONTROL_FILE_SIZE,
"sizeof(ControlFileData) exceeds PG_CONTROL_FILE_SIZE");
/* Recalculate CRC of control file */
INIT_CRC32C(ControlFile->crc);
COMP_CRC32C(ControlFile->crc,
(char *) ControlFile,
offsetof(ControlFileData, crc));
FIN_CRC32C(ControlFile->crc);
/*
* Write out PG_CONTROL_FILE_SIZE bytes into pg_control by zero-padding
* the excess over sizeof(ControlFileData), to avoid premature EOF related
* errors when reading it.
*/
memset(buffer, 0, PG_CONTROL_FILE_SIZE);
memcpy(buffer, ControlFile, sizeof(ControlFileData));
snprintf(ControlFilePath, sizeof(ControlFilePath), "%s/%s", DataDir, XLOG_CONTROL_FILE);
#ifndef FRONTEND
/*
* All errors issue a PANIC, so no need to use OpenTransientFile() and to
* worry about file descriptor leaks.
*/
if ((fd = BasicOpenFile(ControlFilePath, O_RDWR | PG_BINARY)) < 0)
ereport(PANIC,
(errcode_for_file_access(),
errmsg("could not open file \"%s\": %m",
ControlFilePath)));
#else
if ((fd = open(ControlFilePath, O_WRONLY | PG_BINARY,
pg_file_create_mode)) == -1)
{
pg_log_fatal("could not open file \"%s\": %m", ControlFilePath);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
#endif
errno = 0;
#ifndef FRONTEND
pgstat_report_wait_start(WAIT_EVENT_CONTROL_FILE_WRITE_UPDATE);
#endif
if (write(fd, buffer, PG_CONTROL_FILE_SIZE) != PG_CONTROL_FILE_SIZE)
{
/* if write didn't set errno, assume problem is no disk space */
if (errno == 0)
errno = ENOSPC;
#ifndef FRONTEND
ereport(PANIC,
(errcode_for_file_access(),
errmsg("could not write file \"%s\": %m",
ControlFilePath)));
#else
pg_log_fatal("could not write file \"%s\": %m", ControlFilePath);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
#endif
}
#ifndef FRONTEND
pgstat_report_wait_end();
#endif
if (do_sync)
{
#ifndef FRONTEND
pgstat_report_wait_start(WAIT_EVENT_CONTROL_FILE_SYNC_UPDATE);
if (pg_fsync(fd) != 0)
ereport(PANIC,
(errcode_for_file_access(),
errmsg("could not fsync file \"%s\": %m",
ControlFilePath)));
pgstat_report_wait_end();
#else
if (fsync(fd) != 0)
{
pg_log_fatal("could not fsync file \"%s\": %m", ControlFilePath);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
#endif
}
if (close(fd) != 0)
{
#ifndef FRONTEND
ereport(PANIC,
(errcode_for_file_access(),
errmsg("could not close file \"%s\": %m",
ControlFilePath)));
#else
pg_log_fatal("could not close file \"%s\": %m", ControlFilePath);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
#endif
}
}
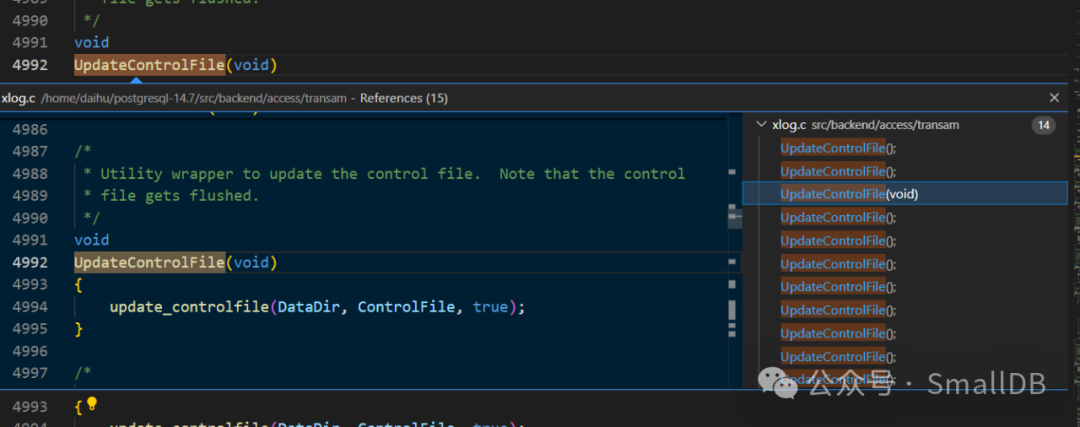
调用函数截图
重点关注第一个,其它的几个全是手动去更新,这个频率少
xlog 源代码只关注update_controlfile调用情况
src/backend/access/transam/xlog.c
14处之多调用地方
调用函数
static void
UpdateMinRecoveryPoint(XLogRecPtr lsn, bool force)
static XLogRecord *
ReadRecord(XLogReaderState *xlogreader, int emode,
bool fetching_ckpt)
staticvoid
CheckRecoveryConsistency(void)
void
CreateCheckPoint(int flags)
CreateEndOfRecoveryRecord(void)
staticvoid
CreateEndOfRecoveryRecord(void)
{
bool
CreateRestartPoint(int flags)
staticvoid
XLogReportParameters(void)
xlog_redo(XLogReaderState *record)
总结
pg_control 在如下大部分在如下四种情况下会更新里面的信息
Checkpoint Processing
Database Recovery
Point-in-Time Recovery
Base Backup
文章转载自SmallDB,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






