在实际工作中,你是否遇到过这些问题?
SQL执行慢但EXPLAIN看不出端倪?
死锁日志复杂,无法复现问题场景?
存储引擎行为诡异,官方文档也束手无策?
这些答案及解题灵感都藏于源码中! 本系列就准备通过案例结合源码调试来进行学习、解惑。其中源码安装可以参考历史文章MySQL8.0.40编译安装,如有问题可关注我进行交流。
2. 常用命令
使用GDB调试MySQL时 常用命令如下
break [file:line] | break sql/handler.cc:1234break ha_innobase::update_row | |
run [args] | run --defaults-file=/etc/mysql/my.cnf | |
nextn | n | |
steps | s | |
backtracebt | bt | |
print [expr] | print row->dataprint query_string | |
continuec | c | |
watch [expr] | watch table->rows_modified | |
listl | l 10l ha_innobase::index_read | |
finish | finish | |
delete [breakpoint_num] | delete 3delete删除所有断点 | |
disable [breakpoint_num] | disable 2disable禁用所有断点 | |
enable [breakpoint_num] | enable 4enable启用所有断点 | |
framef | f 2f打印当前栈帧信息 |
/usr/local/mysql-8.0.40/runtime_output_directory/mysqld --defaults-group-suffix=.1 --defaults-file=/usr/local/mysql-8.0.40/mysql-test/var/my.cnf --user=root --log-output=file --explain-format=TRADITIONAL_STRICT --loose-debug-sync-timeout=600 --core-file
root@Ubuntu22045:~# usr/local/mysql-8.0.40/runtime_output_directory/mysql -uroot -P 13000 -h 127.0.0.1
root@Ubuntu22045:~# ps -ef|grep mysqldroot 3656 2986 0 3月25 pts/0 00:01:56 usr/local/mysql-8.0.40/runtime_output_directory/mysqld --defaults-group-suffix=.1 --defaults-file=/usr/local/mysql-8.0.40/mysql-test/var/my.cnf --user=root --log-output=file --explain-format=TRADITIONAL_STRICT --loose-debug-sync-timeout=600 --core-fileroot 29180 29138 0 17:11 pts/4 00:00:00 grep --color=auto mysqldroot@Ubuntu22045:~# gdb -p 3656GNU gdb (Ubuntu 12.1-0ubuntu1~22.04.2) 12.1Copyright (C) 2022 Free Software Foundation, Inc.License GPLv3+: GNU GPL version 3 or later <http://gnu.org/licenses/gpl.html>This is free software: you are free to change and redistribute it.There is NO WARRANTY, to the extent permitted by law.Type "show copying" and "show warranty" for details.This GDB was configured as "x86_64-linux-gnu".Type "show configuration" for configuration details.For bug reporting instructions, please see:<https://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/bugs/>.Find the GDB manual and other documentation resources online at:<http://www.gnu.org/software/gdb/documentation/>.For help, type "help".Type "apropos word" to search for commands related to "word".Attaching to process 3656[New LWP 3669][New LWP 3670][New LWP 3671]
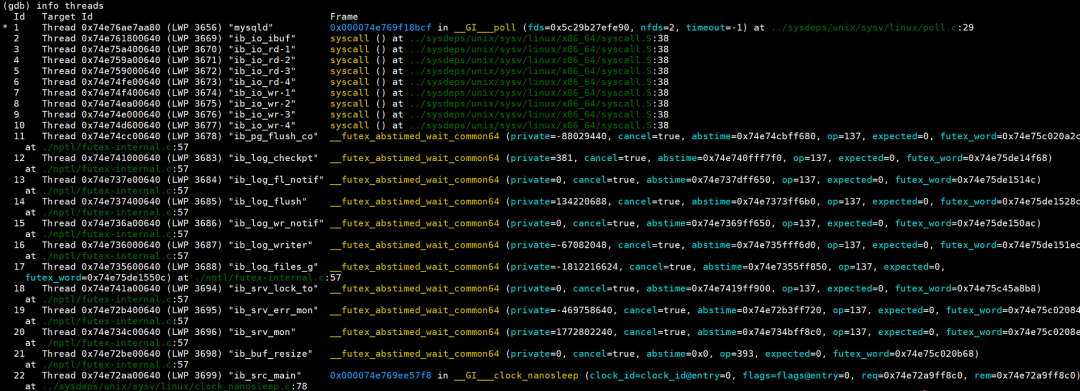
在 GDB 调试 MySQL 源码时,最常设置的断点通常集中在核心函数和关键流程节点上。以下列举几个常用断点以供参考设置:
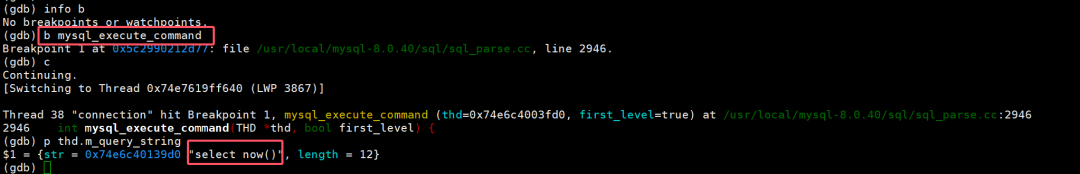
mysql_execute_command: SQL 语句执行的入口函数,几乎所有 SQL 都会经过此处。设置断点可跟踪具体 SQL 的执行路径,例如分析语法解析、权限校验等逻辑。
(gdb) b mysql_execute_commandBreakpoint 1 at 0x5c2990212d77: file usr/local/mysql-8.0.40/sql/sql_parse.cc, line 2946.(gdb) cContinuing.[Switching to Thread 0x74e7619ff640 (LWP 3867)]Thread 38 "connection" hit Breakpoint 1, mysql_execute_command (thd=0x74e6c4003fd0, first_level=true) at usr/local/mysql-8.0.40/sql/sql_parse.cc:29462946 int mysql_execute_command(THD *thd, bool first_level) {(gdb) p thd.m_query_string$1 = {str = 0x74e6c40139d0 "select now()", length = 12}(gdb)
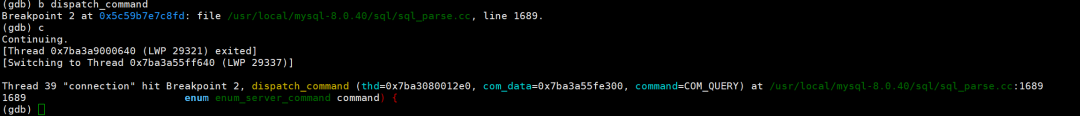
dispatch_command:负责分发客户端请求(如查询、预处理语句等)。在此处断点可观察客户端请求的处理流程,常用于调试网络交互或协议解析问题。
(gdb) b dispatch_commandBreakpoint 2 at 0x5c59b7e7c8fd: file usr/local/mysql-8.0.40/sql/sql_parse.cc, line 1689.(gdb) cContinuing.[Thread 0x7ba3a9000640 (LWP 29321) exited][Switching to Thread 0x7ba3a55ff640 (LWP 29337)]Thread 39 "connection" hit Breakpoint 2, dispatch_command (thd=0x7ba3080012e0, com_data=0x7ba3a55fe300, command=COM_QUERY) at usr/local/mysql-8.0.40/sql/sql_parse.cc:16891689 enum enum_server_command command) {(gdb)
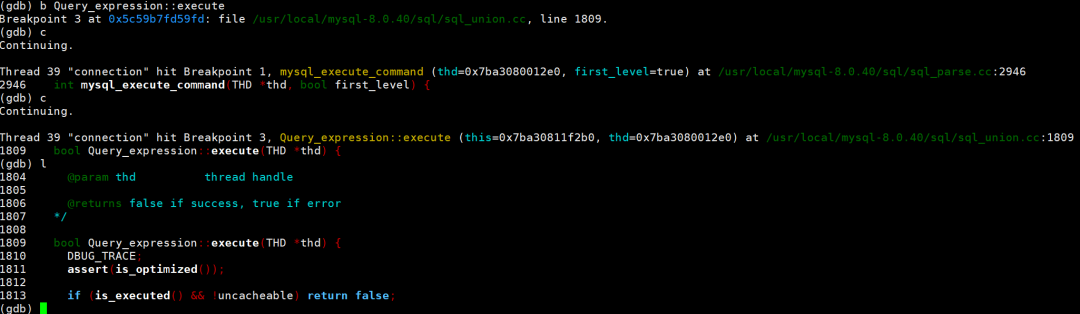
Query_expression::execute:用于跟踪查询执行计划的实际运行过程,尤其适用于分析复杂查询(如子查询、联合查询)的执行逻辑。
(gdb) b Query_expression::executeBreakpoint 3 at 0x5c59b7fd59fd: file /usr/local/mysql-8.0.40/sql/sql_union.cc, line 1809.(gdb) cContinuing.Thread 39 "connection" hit Breakpoint 1, mysql_execute_command (thd=0x7ba3080012e0, first_level=true) at /usr/local/mysql-8.0.40/sql/sql_parse.cc:29462946 int mysql_execute_command(THD *thd, bool first_level) {(gdb) cContinuing.Thread 39 "connection" hit Breakpoint 3, Query_expression::execute (this=0x7ba30811f2b0, thd=0x7ba3080012e0) at /usr/local/mysql-8.0.40/sql/sql_union.cc:18091809 bool Query_expression::execute(THD *thd) {(gdb) l1804 @param thd thread handle18051806 @returns false if success, true if error1807 */18081809 bool Query_expression::execute(THD *thd) {1810 DBUG_TRACE;1811 assert(is_optimized());18121813 if (is_executed() && !uncacheable) return false;(gdb)
其他比较常用的断点如下:
send_result_set_row:数据返回给客户端的核心函数。在此断点可分析查询结果的生成过程,例如字段序列化、数据编码等
my_net_read:客户端请求的读取函数,在此断点可观察客户端发送的原始数据包内容,常用于调试网络协议或客户端连接异常
handler::ha_write_row / handler::ha_update_row:记录存储引擎层的数据写入和更新操作,适用于调试 InnoDB/MyISAM 引擎的存储逻辑或事务一致性相关问题
innobase_commit / innobase_rollback:InnoDB 事务提交和回滚的关键函数,用于分析事务锁、MVCC 机制或死锁问题
handle_connection:处理新客户端连接的入口函数,设置断点可观察线程池分配、连接建立及认证过程
5. 总结
掌握GDB调试,等于拥有了MySQL的“显微镜”——无论是性能优化、死锁排查,还是学习源码设计,都能游刃有余!
但是也有如下避坑点(血泪经验!):
生产环境慎用GDB:调试会阻塞服务,推荐用测试实例复现问题。
多线程调试:善用info threads和thread <ID>切换上下文。
日志留存:调试前开启MySQL慢查询日志和general_log,交叉分析更高效。
代码版本对齐:确保调试的MySQL版本与源码完全一致,避免符号表错乱!






