列存索引(IMCI)
背景
虽然PolarDB有行存的并行执行,但一些客户场景,行存的执行性能无法满足其场景需求。这些查询往往有更大的数据分析量,有更高的查询返回时间要求。
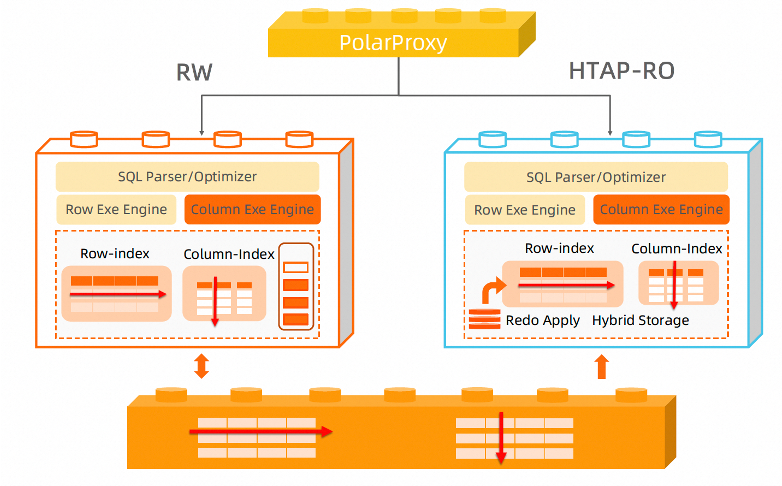
PolarDB MySQL通过列存索引(In-Memory Column Index,简称IMCI)实现了一体化处理实时事务和实时数据分析能力。客户可以通过一套数据库同时满足业务TP和AP需求。其使用完全兼容MySQL,客户业务SQL不需要做任何修改。
实现
PolarDB IMCI支持了事务级别一致性的行列混合存储;向量化执行引擎,核心算子SIMD加速,充分利用硬件能力;完全兼容MySQL。
创建列存索引后,表上的数据修改、DDL都会应用到列存存储。客户查询语句可以通过指定连接地址发给列存执行,也可以直接通过集群地址由行列优化器基于代价自动选择执行引擎。对于AP查询,优化器能够自动识别,并转给AP的RO生成列存的执行计划执行。
效果
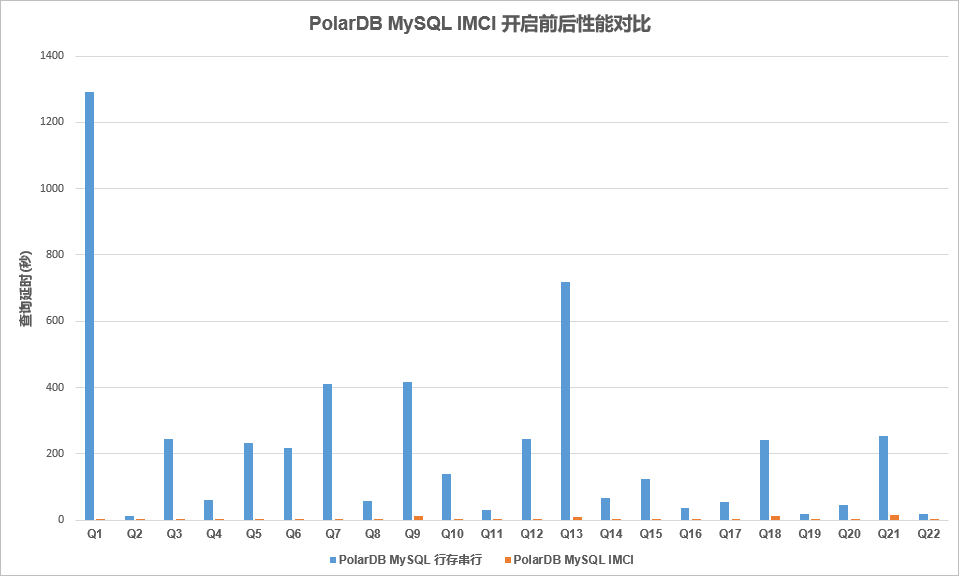
对TPCH 100G数据做性能对比测试。列存开启前后加速效果明显,部分语句可以达到百倍提升。
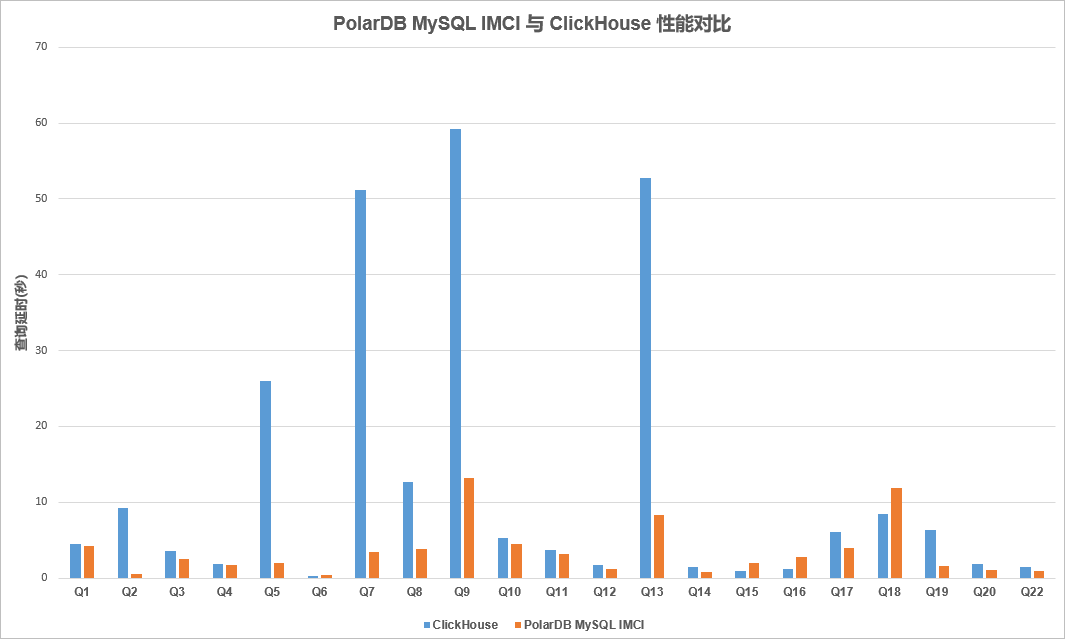
与ClickHouse对比,也有非常明显的性能优势,在Scan\Agg\Join上表现突出。
使用
在使用时,客户可以添加列存只读节点。

对需要创建列存索引的库、表添加列存索引。
-- 创建表COMMENT添加
CREATE TABLE t2(
col1 INT,
col2 DATETIME,
col3 VARCHAR(200)
) ENGINE InnoDB COMMENT 'COLUMNAR=1';
-- ALTER TABLE添加
ALTER TABLE t11 COMMENT 'COLUMNAR=1';
-- 表级添加
CREATE COLUMNAR INDEX ON <db_name>.<table_name>;
CREATE COLUMNAR INDEX ON <table_name>;
-- 库级别添加
CREATE COLUMNAR INDEX FOR TABLES IN <db_name>;
CREATE COLUMNAR INDEX FOR TABLES FROM <db_name>;
对于自动分流,参数loose_imci_ap_threshold是考虑列存执行的查询代价阈值,默认值是50000。
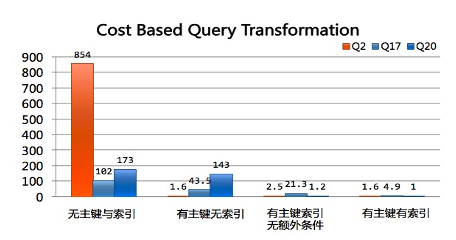
复杂查询变换
查询变换是将查询语句改写成关系代数等价的形式,是数据库优化中的一个非常重要的部分。合适的查询变换能够大幅提升查询效率,例如谓词下推可以提前过滤数据,子查询展开可以减少嵌套执行代价、生成更优Join Order。
PolarDB MySQL的客户来自各个行业,一些客户有着很复杂的SQL形式,一些SAAS场景的终端可以有大量选项自由选择。这些SQL很难被业务开发人员手动优化,而合适的等价变换往往可以获取十倍、百倍、千倍的性能提升。因此PolarDB开发了大量复杂查询变换,支持了基于代价的查询变换选择,包括但不限于:子查询解关联、LeftJoin消除、Join条件下推、IN转JOIN、子查询折叠、各类条件下推、谓词推导等等。
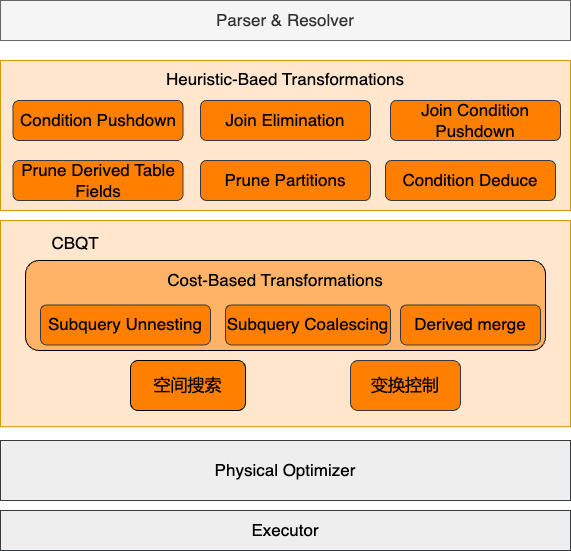
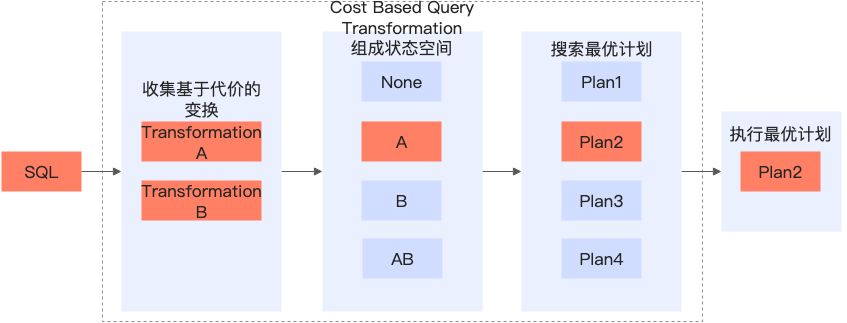
对这些查询变换我们仅对Join消除、谓词下推、子查询解关联做一个基本介绍。具体可以查看PolarDB MySQL的官网文档-查询改写。
- LeftJoin消除
对于一些报表业务,业务界面有各种不同的过滤选项可以填。对应的报表查询就是将不同选项对应的维度表用LeftJoin关联起来,叠加各类过滤条件。如果没有过滤条件,这些右表用唯一键关联,且查询除了关联条件没有使用右表相关列的场景,就可以把右表删除。例如下面的语句中,sales_fact是销售记录,product_dim和customer_dim分别是商品和顾客的维度表。当查询语句没有做product_dim和customer_dim其他过滤选项的时候,就可以把LEFT JOIN都消除,大幅提升查询性能。
-- 当开启join elimination
mysql> set @@join_elimination_mode=on;
-- 三张表的LEFT JOIN,优化后仅需要扫描一张表
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT COUNT(*) FROM sales_fact s LEFT JOIN product_dim p ON s.productkey = p.productkey LEFT JOIN customer_dim c ON c.customerkey = s.customerkey\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: s
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: NULL
-- 当关闭join elimination
mysql> set @@join_elimination_mode=off;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)
-- 需要对三张表做JOIN操作
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT COUNT(*) FROM sales_fact s LEFT JOIN product_dim p ON s.productkey = p.productkey LEFT JOIN customer_dim c ON c.customerkey = s.customerkey\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: s
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: NULL
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: p
partitions: NULL
type: eq_ref
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 8
ref: test.s.productkey
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using index
*************************** 3. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: SIMPLE
table: c
partitions: NULL
type: eq_ref
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 8
ref: test.s.customerkey
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using index
3 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
-- 表结构
CREATE TABLE `sales_fact` (
`id` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`productkey` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`customerkey` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`create_time` timestamp NOT NULL,
`update_time` timestamp NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE `product_dim` (
`productkey` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`productname` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`productclass` bigint(20) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`productkey`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
CREATE TABLE `customer_dim` (
`customerkey` bigint(20) NOT NULL,
`customer_name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`customer_address` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`customerkey`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB;
- 谓词下推
上面语句中,我们如果分析一些商品的销售量,写成如下语句。可以看到如果打开谓词下推,由于谓词条件列在group by列中,那么可以把外层的谓词条件下推到derived table中,从而提前过滤数据。
-- 打开derived condition pushdown功能
mysql> set derived_cond_pushdown_mode=on;
--可以看到谓词下推到derived table中
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT p.productkey, p.productname, s.sale_count from product_dim p, (SELECT productkey, COUNT(*) sale_count FROM sales_fact GROUP BY productkey) s WHERE p.productkey = s.productkey AND p.productkey > 1 AND p.productkey < 10\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: PRIMARY
table: p
partitions: NULL
type: range
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 8
ref: NULL
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using where
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: PRIMARY
table: <derived2>
partitions: NULL
type: ref
possible_keys: <auto_key0>
key: <auto_key0>
key_len: 9
ref: test.p.productkey
rows: 2
filtered: 100.00
Extra: NULL
*************************** 3. row ***************************
id: 2
select_type: DERIVED
table: sales_fact
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using where; Using temporary
mysql> SHOW WARNINGS\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Level: Note
Code: 1003
Message: /* select#1 */ select `test`.`p`.`productkey` AS `productkey`,`test`.`p`.`productname` AS `productname`,`s`.`sale_count` AS `sale_count` from `test`.`product_dim` `p` join (/* select#2 */ select `test`.`sales_fact`.`productkey` AS `productkey`,count(0) AS `sale_count` from `test`.`sales_fact` where ((`test`.`sales_fact`.`productkey` > 1) and (`test`.`sales_fact`.`productkey` < 10)) group by `test`.`sales_fact`.`productkey`) `s` where ((`s`.`productkey` = `test`.`p`.`productkey`) and (`test`.`p`.`productkey` > 1) and (`test`.`p`.`productkey` < 10))
-- 关闭derived condition pushdown功能
mysql> set derived_cond_pushdown_mode=off;
-- 可以看到谓词没有下推
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT p.productkey, p.productname, s.sale_count from product_dim p, (SELECT productkey, COUNT(*) sale_count FROM sales_fact GROUP BY productkey) s WHERE p.productkey = s.productkey AND p.productkey > 1 AND p.productkey < 10\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: PRIMARY
table: p
partitions: NULL
type: range
possible_keys: PRIMARY
key: PRIMARY
key_len: 8
ref: NULL
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using where
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 1
select_type: PRIMARY
table: <derived2>
partitions: NULL
type: ref
possible_keys: <auto_key0>
key: <auto_key0>
key_len: 9
ref: test.p.productkey
rows: 2
filtered: 100.00
Extra: NULL
*************************** 3. row ***************************
id: 2
select_type: DERIVED
table: sales_fact
partitions: NULL
type: ALL
possible_keys: NULL
key: NULL
key_len: NULL
ref: NULL
rows: 1
filtered: 100.00
Extra: Using temporary
mysql> SHOW WARNINGS\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
Level: Note
Code: 1003
Message: /* select#1 */ select `test`.`p`.`productkey` AS `productkey`,`test`.`p`.`productname` AS `productname`,`s`.`sale_count` AS `sale_count` from `test`.`product_dim` `p` join (/* select#2 */ select `test`.`sales_fact`.`productkey` AS `productkey`,count(0) AS `sale_count` from `test`.`sales_fact` group by `test`.`sales_fact`.`productkey`) `s` where ((`s`.`productkey` = `test`.`p`.`productkey`) and (`test`.`p`.`productkey` > 1) and (`test`.`p`.`productkey` < 10))
- 子查询解关联
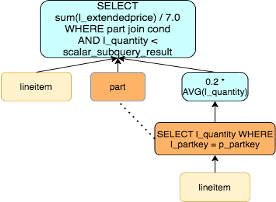
子查询解关联以TPCH的Q17为例,该查询是获得比平均供货量20%还要低的小订单量。在没有解关联的情况下,该语句的执行对于外层查询的每一行都要执行关联子查询计算聚合结果。
SELECT SUM(l_extendedprice) / 7.0 AS avg_yearly
FROM lineitem, part
WHERE p_partkey = l_partkey
AND p_brand = 'Brand#43'
AND p_container = 'WRAP PKG'
AND l_quantity < (
SELECT 0.2 * AVG(l_quantity) -- aggregate function
FROM lineitem
WHERE l_partkey = p_partkey -- correlated
);
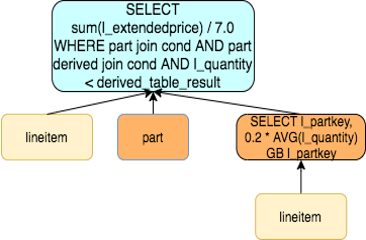
我们可以先分组聚合,再和外层做JOIN,即改写成如下语句。对于子查询没有关联索引的场景,这样可以大幅减少扫描行数,子查询中的表仅需要扫描一次。
select
sum(l_extendedprice) / 7.0 as avg_yearly
from
lineitem,
part,
(select
l_partkey as avg_lpartkey,
(0.2 * avg(l_quantity)) as avg_20ratio
from
lineitem
group by
l_partkey) as avg_lineitem
where
p_partkey = l_partkey
and p_brand = 'Brand#44'
and p_container = 'WRAP PKG'
and p_partkey = avg_lineitem.avg_lpartkey
and l_quantity < avg_20ratio;
当有唯一键关联,我们可以通过Window Function改写成如下形式,即在JOIN的同时,对要分析的数据做分组聚合。
SELECT Sum(V.avg_extprice) / 7.0 AS avg_yearly
FROM part,
(SELECT (CASE WHEN l_quantity < 0.2 * Avg(l_quantity) OVER (PARTITION BY l_partkey)
THEN l_extendedprice
ELSE NULL
END) avg_extprice,
l_partkey
FROM lineitem) V
WHERE p_partkey = V.l_partkey
AND p_brand = 'Brand#44'
AND p_container = 'WRAP PKG'
AND V.avg_extprice IS NOT NULL;
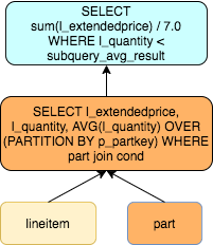
在PolarDB中通过基于代价的查询变换,会自动根据查询场景选择合适的变换方式。对TPCH的多个关联子查询都可以有不错的性能提升。