模型需求描述
模型主要是计算中小学缓冲区与居住用地的面积比率;模型的主要逻辑如下:在POI数据中筛选出中小学,利用中小学点数据创建1000米缓冲区;接着在土地利用现状图斑中筛选出居民用地数据,然后利用居民用地数据裁剪学校缓冲区;利用行政区对分别居民用地和裁剪后的学校缓冲区数据进行标识,标识完成后,使用行政区名称字段对标识结果进行融合,最后计算学校缓冲区面积和居民用地面积的比例。
数据说明
使用的数据为某市的测试数据,图层数据的简单说明如下:数据坐标系:国家2000坐标系 POI数据 行政区划面数据 土地利用现状图斑数据
数据入库使用PostGIS 2.0 Shapefile and DBF Loader Exporter工具把shapefile数据入库到PostgreSql中;入库的步骤如下;打开PostGIS 2.0 Shapefile and DBF Loader Exporter工具,点击【View connection details】按钮,在弹出的数据库连接信息窗口中填写连接信息;填写完毕点击【ok】按钮开始连接;如连接成功,可以在【log Window】中看到连接成功的信息;如下图1,2所示。
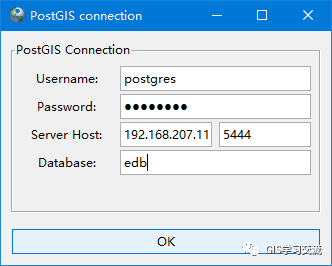
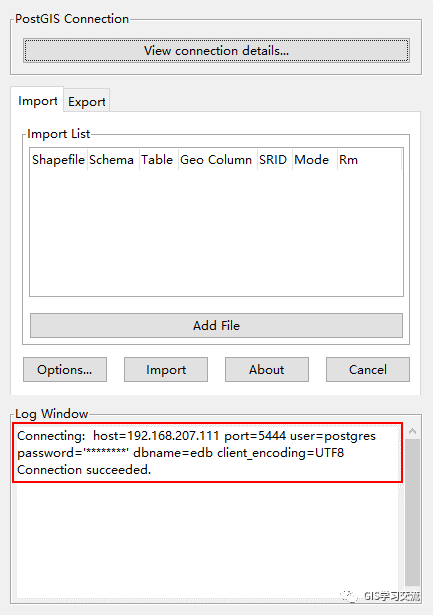
点击【Add File】按钮,选择需要入库的Shapefile数据,选择完毕后点击【Open】按钮,把数据加载到Import页面中;如下图3所示;
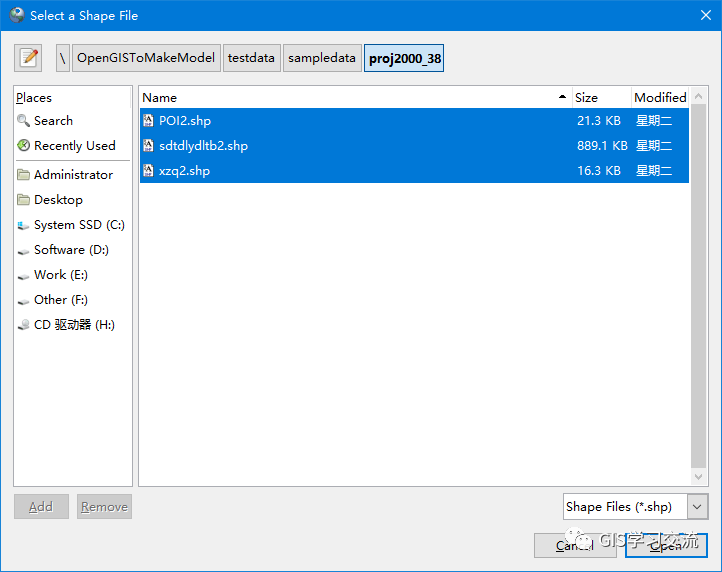
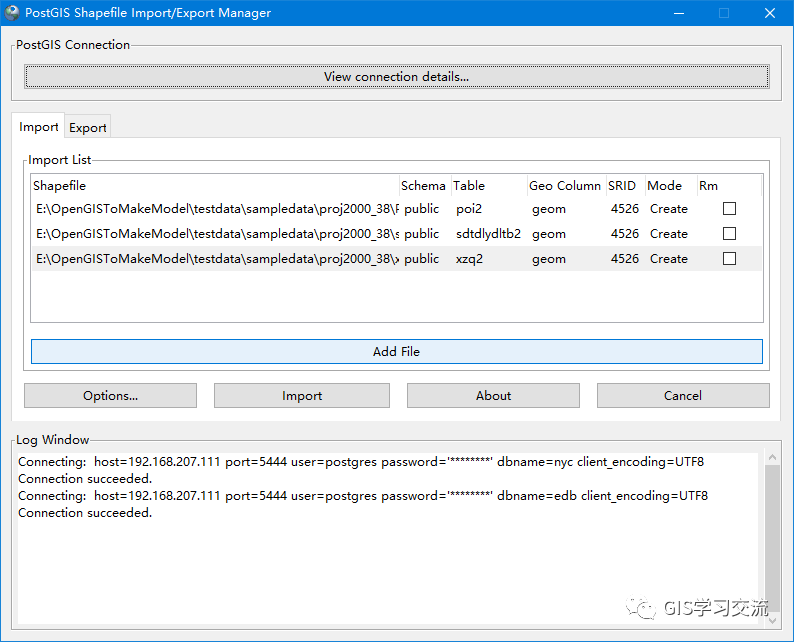
在Import页面中填写数据的空间参考标识符信息(SRID),例如这里入库的数据空间参考为CGCS2000_3_Degree_GK_Zone_38,SRID值为4526;填写完毕后点击【Import】按钮开始导入数据;如导入完成后可以在【Log Window】中查看数据入库的信息;如下图4所示。
测试环境
两台配置一样的CentOS7虚拟机上分别安装PostgreSQL9.6(Postgis2.4)和阿里云POLARDB数据库。单台虚拟机的配置如下:内存:2 GB 磁盘:40 GB CPU:2核 使用pgAdmin4客户端连接管理PostgreSQL9.6和阿里云POLARDB数据库;通过Python3.6脚本,利用Python第三方库psycopg2连接操作PostgreSQL9.6和阿里云POLARDB数据库。使用PostGIS的处理逻辑如下
在POI中筛选出中小学构建1000米的缓冲区得到图层schoolbuffer;
create table IF NOT EXISTS SchoolBuffer as select ST_Buffer(geom,1000)::geometry(Polygon,4526)as geom from (select ST_Transform(geom,4526)as geom from public.poi2 where CLASID = '110501' OR CLASID = '110502') as geotran
2.在土地利用现状数据中筛选出居住用地("DLBM" = '0701' OR "DLBM" = '0702');
create table IF NOT EXISTS juminarea as select ST_Transform(geom,4526)as geom
from public.sdtdlydltb2 where DLBM = '0701' OR DLBM = '0702'
3.使用居住用地图层裁剪schoolbuffer图层,获得schoolbuffer_clip图层;
先把居住用地数据的所有面融合为一个几何图形
--居民用地融合为一个图形Create table cliptable as (SELECT st_Union(ST_Accum(ST_SnapToGrid(geom,0.0001))) as geom from juminarea where 1=1)--居民用地裁剪学校缓冲区
create table schoolbuffer_clip as (select st_intersection(geom,(select geom from cliptable)
::geometry(MultiPolygon,4526)) as geom from SchoolBuffer where 1=1)
4.用行政区划数据分别对居住用地和schoolbuffer_clip图层进行标识;
GIS中的标识功能的描述如下图5所示。
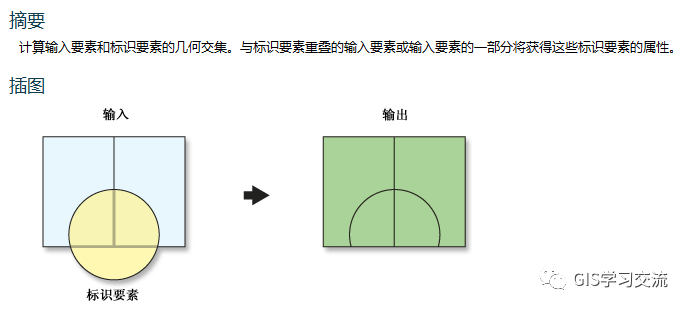
在PostGIS中找不到标识函数,所以根据标识功能,使用PostGIS的函数st_intersection()获得几何图形,再结合Update获得相交图形部分的属性信息。
5.对标识后的居住用地和schoolbuffer_clip图层分别按照行政区名称字段进行融合;
--学校融合create table schoolbuffer_Union as select xzqmc,st_union(ST_Accum(ST_SnapToGrid(geom,0.0001)))
as geom from schoolbuffer_identify where 1=1 group by xzqmc
--居民用地融合create table juminarea_Union as select xzqmc,st_union(ST_Accum(ST_SnapToGrid(geom,0.0001)))
as geom from juminarea_identify where 1=1 group by xzqmc
6.计算学校缓冲区面积,居民用地面积,计算覆盖率(学校缓冲区面积/居住用地面积);
--计算学校面积update schoolbuffer_Union set schoolArea = st_area(geom)--计算居民用地面积update schoolbuffer_Union set jumin_area=(select st_area(geom)
from juminarea_Union where juminarea_Union.xzqmc=schoolbuffer_Union.xzqmc)--计算覆盖率update schoolbuffer_Union set fugailv=schoolArea/jumin_area
Python脚本操作数据库代码
根据模型的处理逻辑,结合PostGIS的SQL语句,在Python脚本中操作数据库; PostgresqlExexute.py文件主要用于实现数据库增删查改;MakeModel.py文件用于实现模型的逻辑,主要代码如下:PostgresqlExexute.py文件
import psycopg2
class DBExcute():
def __init__(self):
#虚拟机上的polardb
self.Conn = psycopg2.connect(database='edb', user='postgres',
password="postgres", host='192.168.207.111',
port="5444")
self.Cur = self.Conn.cursor()
def ExecuteSql(self,sql):
'''
执行SQL语句并提交;一般为更新,修改,创建,删除等操作
:param sql: SQL语句
:return: 执行SQL是否成功
'''
try:
self.Cur.execute(sql)
self.Conn.commit()
return True
except Exception as err:
print("执行SQL语句发生错误{0}".format(err ))
return False
def Check_Exist(self, sql):
self.Cur.execute(sql)
count = None
for cu in self.Cur:
count = cu[0]
if count == 0:
return False
else:
return True
def GetRowstExecute(self,sql):
'''
执行查询sql,返回查询结果的行
:param sql: SQL语句
:return: 返回rows
'''
self.Cur.execute(sql)
rows=self.Cur.fetchall()
return rows
def GetExecuteSql(self,sql):
'''
执行SQL查询,返回几何图形的text
:param sql: SQL语句
:return: 只返回第一个图形的text
'''
self.Cur.execute(sql)
rows=self.Cur.fetchall()
for row in rows:
return row[0]
def dbClose(self):
self.Conn.close()#postgresql数据库操作类实例化
dbexecute=DBExcute()
MakeModel.py文件
from PostgresqlExexute import dbexecute
import time
def Union2(tableName,saveTableName):
'''
把表tableName的所有图形融合为一个图形,保存到表saveTableName中
:param tableName: 需要融合的表名称
:param saveTableName: 融合后的表名称
:return: 融合后的表名称
'''
# 判断表是否存在,存在则删除
deltablesql = "drop table if exists {0}".format(saveTableName)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(deltablesql)
sql="Create table {0} as (SELECT ST_Union(geom) as geom from {1} where 1=1)"
.format(saveTableName,tableName)
successful=dbexecute.ExecuteSql(sql)
if(successful):
print("裁剪图层融合完成!")
return saveTableName
else:
return Nonedef clip(tableName,Cliptable,saveTableName):
'''
用ClipGeoText裁剪图层tableName,并新建一个裁剪后图层
:param tableName: 图层名称
:param ClipGeoText: 裁剪图形的几何text
:return: 返回裁剪后的图层名称
'''
#判断表是否存在,存在则删除
deltablesql="drop table if exists {0}".format(saveTableName)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(deltablesql)
#判断图形是否可用
makevalid = "update {0} set geom=st_makevalid(geom) where not st_isvalid(geom)".format(Cliptable)
print("正在修复图形……")
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(makevalid)
print("裁剪图层修复完毕!")
getGeo="select st_astext(geom) from {0}".format(Cliptable)
geotext=dbexecute.GetExecuteSql(getGeo)
ClipAndCreatesql = "create table {0} as (select st_intersection(geom,(select geom from {1})
::geometry(MultiPolygon,4526)) as geom from {2} where 1=1)".format(saveTableName,Cliptable,tableName)
print("正在进行裁剪操作……")
successful=dbexecute.ExecuteSql(ClipAndCreatesql)
if successful:
return saveTableName
else:
return Nonedef identify(savetableName,intable,selGeotext,xzqmc):
'''
实现标识功能;利用相交获得与标识图形相交部分的几何图形,
然后把行政区名称,相交几何图形保存到表savetableName中
:param savetableName: 保存结果的表
:param intable: 需要标识的表
:param selGeotext: 标识几何图形的text
:param xzqmc: 标识字段
:return:
'''
#通过Geotext获得相交的部分图形,带入行政区名称,保存到savetableName中
selsql="select st_astext(st_intersection(geom,(st_geomfromtext('{0}',4526))))
from {1} where 1=1".format(selGeotext,intable)
rows=dbexecute.GetRowstExecute(selsql)
for row in rows:
geoinfo=row[0]
insertSql="insert into {0} (geom,xzqmc)values(ST_GeomFromText('{1}',4526),'{2}')"
.format(savetableName,geoinfo,xzqmc)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(insertSql)def UnionByField(intable,newTable,FieldName):
'''
按照字段FieldName把字段值相同的图形融合为一个
:param intable: 需要融合的表
:param newTable: 融合后的表
:param FieldName: 融合字段名称
:return: 融合后的表名称
'''
delsql="drop table if exists {0}".format(newTable)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(delsql)
# 判断图形是否可用
makevalid = "update {0} set geom=st_makevalid(geom) where not st_isvalid(geom)"
.format(intable)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(makevalid)#正在修复图形
union = "create table {0} as select xzqmc,st_union(geom) as geom from {1} where 1=1 group by {2}"
.format(newTable, intable, FieldName)
successful=dbexecute.ExecuteSql(union)
if successful:
return newTable
else:
return Nonedef mainFunction(POItable,sdtdlyxztable,xzqtable):
'''
社区中小学步行15分钟覆盖率模型的逻辑函数
:param POItable: POI数据表
:param sdtdlyxztable: 土地利用现状图斑表
:param xzqtable: 行政区划表
:return:
'''
#从POI中选择学校点并进行投影,缓冲
schoolbuffer="schoolbuffer" #学校poi点缓冲区
delsql="drop table if exists {0}".format(schoolbuffer)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(delsql)
bufferSql="create table IF NOT EXISTS {0} as select ST_Buffer(geom,1000)::geometry(Polygon,4526) " \
"as geom from (select ST_Transform(geom,4526)as geom from {1} where CLASID = '110501' OR" \
" CLASID = '110502') as geotran".format(schoolbuffer,POItable)
successful=dbexecute.ExecuteSql(bufferSql)
if successful==False:
print("选择学校并进行缓冲失败!")
return
#从土地利用现状图斑中选择居民用地并进行投影
juminarea="juminarea"
delsql="drop table if exists {0}".format(juminarea)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(delsql)
selSQL="create table IF NOT EXISTS {0} as select ST_Transform(geom,4526) " \
"as geom from {1} where DLBM = '0701' OR DLBM = '0702'".format(juminarea,sdtdlyxztable)
successful=dbexecute.ExecuteSql(selSQL)
if successful==False:
print("选择居民地并进行投影失败!")
return
# 居民用地融合,用于裁剪学校缓冲区
UniontableName = "uniontb"
UniontableName=Union2(juminarea,UniontableName)
#用居民用地裁剪学校缓冲区
ClipTableName = "cliptb"
if UniontableName!=None:
clip(schoolbuffer,UniontableName,ClipTableName)
else:
print("获得的裁剪图层名称为空!")
return
# 进行标识
scidentifyTb="scidentifytb";jmidentifytb="jmidentifytb"
# 创建保存标识数据的表
delsql = "drop table if exists {0}".format(scidentifyTb)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(delsql)
createSql = "create table {0} (xzqmc text,geom geometry)".format(scidentifyTb)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(createSql)
delsql = "drop table if exists {0} ".format(jmidentifytb)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(delsql)
createSql = "create table {0} (xzqmc text,geom geometry)".format(jmidentifytb)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(createSql)
selsql = "select st_astext(st_transform(geom,4526)),xzqmc from {0}".format(xzqtable)
xzqrows = dbexecute.GetRowstExecute(selsql)
for row in xzqrows:
identify(scidentifyTb, ClipTableName, row[0], row[1]) # 学校缓冲区
identify(jmidentifytb, juminarea, row[0], row[1]) #居民居住区标识
# 按行政区进行融合
schoolbufferUnion="schoolbufferUnion"
schoolbufferUnion = UnionByField(scidentifyTb, schoolbufferUnion, "xzqmc")
if schoolbufferUnion == None:
print("学校缓冲图层融合失败!")
return
juminareaUnion = "juminareaUnio"
juminareaUnion = UnionByField(jmidentifytb, juminareaUnion, "xzqmc")
if juminareaUnion == None:
print("居民用地图层融合失败!")
return
# 分别添加学校面积,居民居住用地面积,覆盖率字段
schoolarea = "schoolarea";juminareaField="juminarea"; fglfield="xxfgl"
addsql = "alter table {0} add COLUMN {1} decimal,add COLUMN {2} decimal,add COLUMN {3} decimal".format(
schoolbufferUnion, schoolarea,juminareaField,fglfield)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(addsql)
# 计算学校面积,居民用地面积
update = "update {0} set {1} = st_area(geom)".format(schoolbufferUnion, schoolarea)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(update)
#通过计算表juminareaUnion几何图形面积,并保存到表schoolbufferUnion的juminarea字段中
update="update {0} set {1}=(select st_area(geom) from {2} where {3}.xzqmc={4}.xzqmc)".format(
schoolbufferUnion,juminareaField,juminareaUnion,juminareaUnion,schoolbufferUnion
)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(update)
#计算覆盖率xxfgl字段值;schoolarea/juminareaField
update="update {0} set {1}={2}.{3}/{4}.{5}".format(schoolbufferUnion,fglfield,schoolbufferUnion,
schoolarea,schoolbufferUnion,juminareaField)
dbexecute.ExecuteSql(update)
dbexecute.dbClose()
print("All Execute Successfully!")if __name__=="__main__":
start=time.clock()
poi="poi"
tuban="sdtdlydltb"
xzq="xzq"
mainFunction(poi,tuban,xzq) #执行模型
end=time.clock()print("Running time:%s Seconds"%(end-start)) #获得模型运行时间
运行效率对比
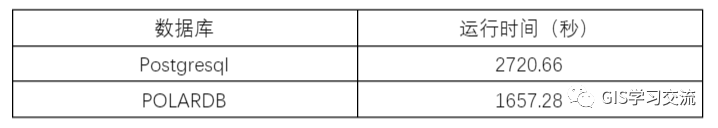
运行效率对比 使用同一份数据和相同的SQL语句在虚拟机环境相同的Postgresql和POLARDB数据库上运行,两者的运行时间对比如下表1所示。
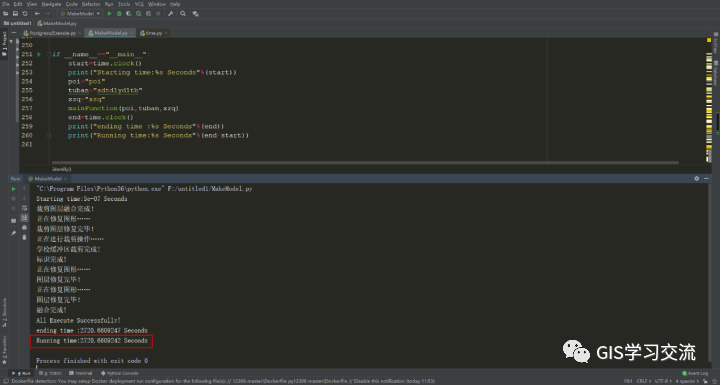
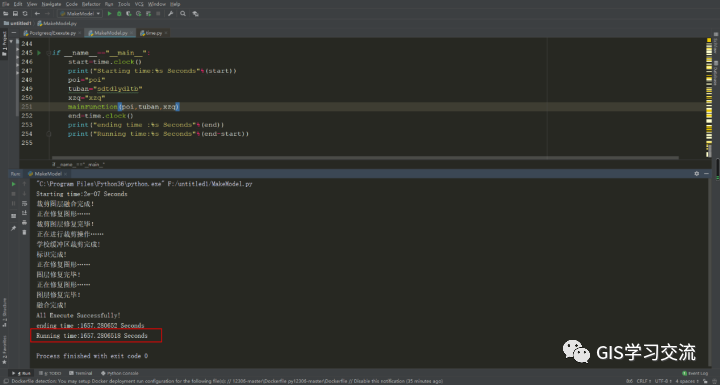
Postgresql和POLARDB数据库运行时间截图如下图6,7所示。
运行结果对比
使用同一份数据,通过ArcMap的模型构建器实现社区中小学步行15分钟覆盖率模型,模型的结构图如下图8,9所示(图8,图9为同一个模型);使用ArcMap模型构建器运行的结果作为标准,对比验证Postgresql和Polardb数据库执行模型的准确度。
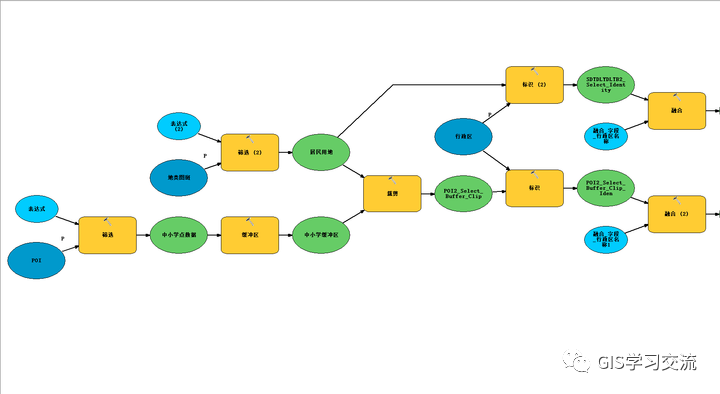
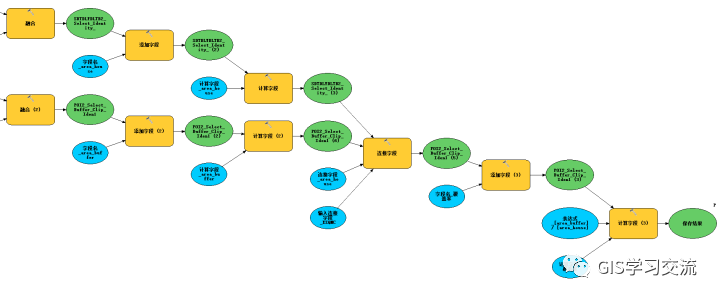
在ArcMap,polardb和postgresql数据库中运行模型的结果如下图所示。
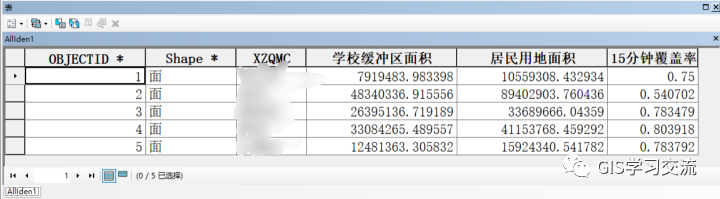
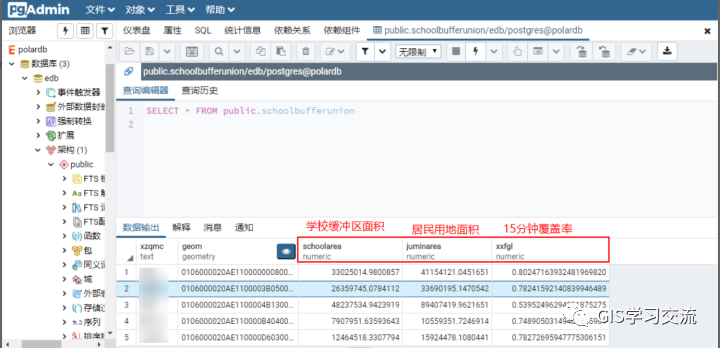
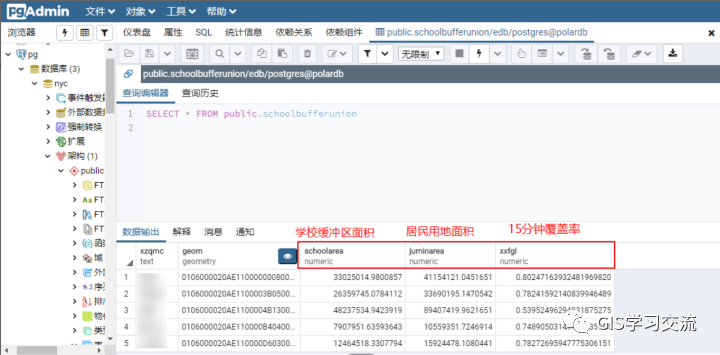
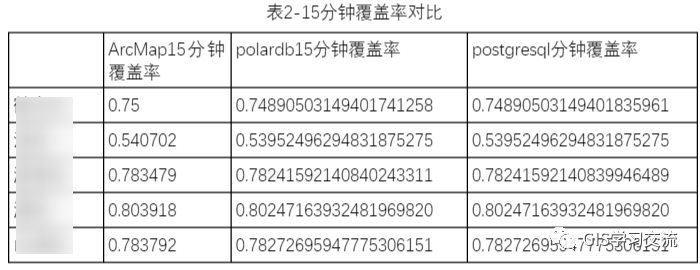
Polardb、postgresql和ArcMap的15分钟覆盖率字段值对比如下表2所示;通过对比三者的运行结果发现,polardb与postgresql的15分钟覆盖率字段值几乎完全一样;polardb(或postgresql)数据库与ArcMap的15分钟覆盖率相差0.001左右。
欢迎关注微信公众号【GIS学习交流】进行学习交流







