前言
基于物品相似度开发几种方式对比
基于物品相似度开发
■ 余弦相似度
import org.apache.spark.ml.recommendation.ALS.Ratingimport org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.{CoordinateMatrix, MatrixEntry}import org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SparkSession}object CositemOpt {def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {val spark = SparkSession.builder().master("local[5]").getOrCreate()import spark.implicits._val movieRatings = spark.read.textFile("/Users/zhangjingyu/Desktop/ES/utou_main.csv").rdd.map(line => {val fields = line.split(",")Rating(fields(0).toInt,fields(1).toInt,fields(2).toFloat)}).toDF("user_id","item_id","rating")//求平均值val meanRating = movieRatings.groupBy("item_id").mean("rating").toDF("item_id","mean_rate")//关联表val joinRating = movieRatings.join(meanRating,"item_id").toDF("item_id","user_id","rating","mean_rate")// joinRating.show(false)//创建DateFrame临时表val dataFrame = joinRating.createOrReplaceTempView("ratings")//求差值val optRating = spark.sql("select user_id,item_id,(rating - mean_rate) as rating from ratings")optRating.show(false)val matrixentry = optRating.rdd.map{case Row(user_id : Int, item_id : Int , rating : Double) => {MatrixEntry(user_id.toLong,item_id.toLong,rating.toDouble)}}val coordinateMatrix = new CoordinateMatrix(matrixentry)val simItem = coordinateMatrix.toIndexedRowMatrix().columnSimilarities().entriesval simItemScore = simItem.map(line => {(line.i,line.j,line.value)}).toDF("item_id","sim_item_id","score")//simItemScore.where("item_id = 1").sort(simItemScore("score").desc).show(false)}}
■ 调整余弦相似度
import org.apache.spark.ml.recommendation.ALS.Ratingimport org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.{CoordinateMatrix, MatrixEntry}import org.apache.spark.sql.types.{StringType, StructField, _}import org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SparkSession}object CosItemOptRec {def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {val spark = SparkSession.builder().master("local[5]").getOrCreate()import spark.implicits._/*** ratings.csv* userId,movieId,rating,timestamp* 1,1,4.0,964982703*/val movieRatings = spark.read.textFile("/Users/zhangjingyu/Desktop/ES学习/ratings_test.csv").rdd.map(line => {val field = line.split(",")Rating(field(0).toInt,field(1).toInt,field(2).toFloat)}).toDF("user_id","movie_id","rating")/*** movies.scv* movieId,title,genres* 1,Toy Story (1995),Adventure|Animation|Children|Comedy|Fantasy*/val movieContent = spark.read.textFile("/Users/zhangjingyu/Desktop/ES/movies.csv").rdd.map(line => {val field = line.split(",")(field(0).toInt,field(1).toString,field(2).toString)}).toDF("movie_id","movie_title","movie_genres")val meanItemRating = movieRatings.groupBy("movie_id").mean("rating").toDF("movie_id","mean_rating")val joinItemRating = movieRatings.join(meanItemRating,"movie_id").toDF("movie_id","user_id","rating","mean_rating")joinItemRating.createOrReplaceTempView("ratings")val meanRes = spark.sql("select user_id,movie_id,(rating - mean_rating) as rating from ratings")// meanRes.show(false)val MatrixRdd = meanRes.rdd.map{case Row(user_id : Int , movie_id : Int , rating : Double) => {MatrixEntry(user_id.toLong,movie_id.toLong,rating.toDouble)}}val coordinateMatrix = new CoordinateMatrix(MatrixRdd)val simItemSco = coordinateMatrix.toIndexedRowMatrix().columnSimilarities().entries// simItemSco.foreach(println)val simItem10 = simItemSco.filter(_.i == 47).map(line => Row(line.j,line.value))// simItem10.foreach(println)val structField = Array(StructField("movie_id",LongType,true),StructField("score",DoubleType,true))val structType = new StructType(structField)val resDF = spark.createDataFrame(simItem10,structType)movieContent.join(resDF,"movie_id").sort(resDF("score").desc).toDF("sim_movie_id","movie_title","movie_genres","sim_score").show(false)}}
■ 皮尔逊相关度
Spark官方API中也提供了pearson相关度计算方法,这个计算方法就是采用的公式二的计算。公式一与公式二的基本是相似的。当计算的的i和j不是用户共同评分的时候,结果不是很好。
公式二:
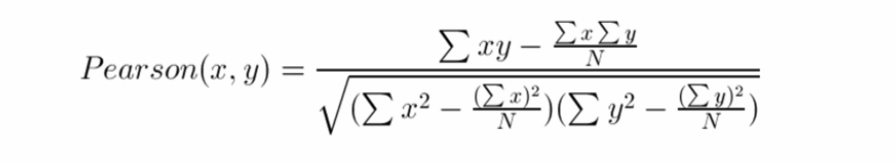
演示代码如下:
import org.apache.spark.ml.recommendation.ALS.Ratingimport org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.{CoordinateMatrix, MatrixEntry}import org.apache.spark.mllib.stat.Statisticsimport org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SparkSession}import scala.collection.mutable.ListBufferobject PearsonItem {def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {val spark = SparkSession.builder().master("local[5]").getOrCreate()import spark.implicits._val movieRating = spark.read.textFile("/Users/zhangjingyu/Desktop/ES/utou_main.csv").rdd.map(x => {val field = x.split(",")Rating(field(0).toInt,field(1).toInt,field(2).toFloat)}).toDF("user_id","movie_id","rate")val matrix = movieRating.rdd.map{case Row(user_id : Int , movie_id : Int , rate : Float) => {MatrixEntry(user_id.toLong,movie_id.toLong,rate.toDouble)}}val coordinateMatrix = new CoordinateMatrix(matrix)val indexRowMatrix = coordinateMatrix.toIndexedRowMatrix()val pearson_vector = indexRowMatrix.rows.toJavaRDD().rdd.map(x => x.vector)val pearson_sim = Statistics.corr(pearson_vector)// println(pearson_sim)/*** 1.0 NaN NaN ... (7 total)* NaN 1.0 0.8569515946486446 ...* NaN 0.8569515946486446 1.0 ...* NaN 0.3712165082817225 0.26336216566171755 ...* NaN 0.8875895031209077 0.7054762001861277 ...* NaN 0.7637626158259733 0.368160520255362 ...* NaN 0.6236095644623235 0.3006018060210759 ...*/val ma = pearson_sim.asML.toSparseval nums = pearson_sim.asML.toSparse.numColsval lst = new ListBuffer[Array[Double]]for(x <- 0 to nums - 1){lst.append(Array(1,x,ma.apply(1,x)))}/*** +----+--------+------------------+* |item|sim_item|score |* +----+--------+------------------+* |1.0 |3.0 |0.3712165082817225|* |1.0 |6.0 |0.6236095644623235|* |1.0 |5.0 |0.7637626158259733|* |1.0 |2.0 |0.8569515946486446|* |1.0 |4.0 |0.8875895031209077|* |1.0 |1.0 |1.0 |* |1.0 |0.0 |NaN |* +----+--------+------------------+*/lst.map(x => (x(0) , x(1) , x(2))).toDF("item","sim_item","score").sort("score").show(false)}}
皮尔逊相关度与调整余弦相似度的区别-代码验证(数据集)
皮尔逊相关度与调整余弦相似度的区别-代码验证(验证结果)
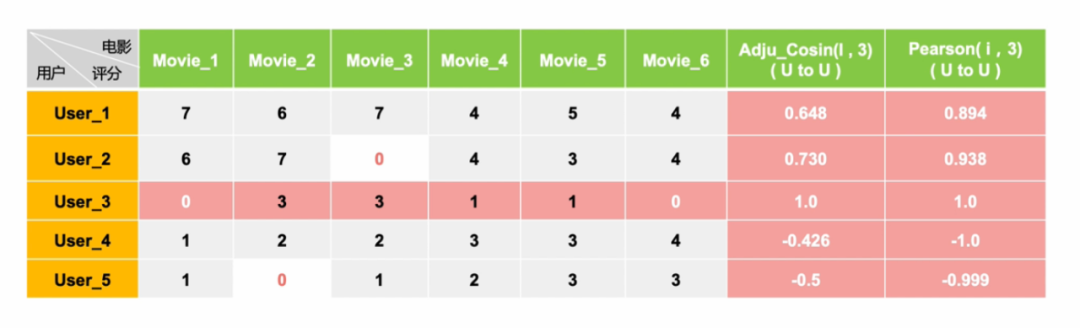
公式数据举例:

皮尔逊二次开发
1、皮尔逊二次开发(剔除非公共集)
import breeze.numerics.powimport org.apache.spark.ml.recommendation.ALS.Ratingimport org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.{CoordinateMatrix, MatrixEntry}import org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SparkSession}import scala.collection.mutable.ListBufferobject MyPearson {//皮尔逊相关度计算公式def pearsonCorrelationSimilar(vec1 : Vector[Double] , vec2 : Vector[Double]) : Double = {val sum_vec1 = vec1.sumval sum_vec2 = vec2.sum//平方和val square_sum_vec1 = vec1.map(x => x * x).sumval square_sum_vec2 = vec2.map(x => x * x).sum//向量合并val zipVec = vec1.zip(vec2)val product = zipVec.map(x => x._1 * x._2).sum//分子计算val numerator = product - (sum_vec1 * sum_vec2)/vec1.length//分母计算(这里因为是公共向量,长度一样,所以vec1.length = vec2.length)val dominato =pow((square_sum_vec1 - pow(sum_vec1 , 2) / vec1.length ) * (square_sum_vec2 - pow(sum_vec2 , 2) / vec2.length ) , 0.5)numerator / dominato}def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {val spark = SparkSession.builder().master("local[5]").getOrCreate()import spark.implicits._val movieContent = spark.read.textFile("/Users/zhangjingyu/Desktop/ES/utou_main.csv").map(line => {val field = line.split(",")Rating(field(0).toInt,field(1).toInt,field(2).toFloat)}).toDF("user","item","rate")val matrixRdd = movieContent.rdd.map{case Row(user : Int , item : Int , rate : Float) => {MatrixEntry(item.toLong,user.toLong,rate.toDouble)}}val coordinateMatrix = new CoordinateMatrix(matrixRdd)val indexRowMatrix = coordinateMatrix.toIndexedRowMatrix()/*** IndexedRow(4,(6,[1,2,3,4,5],[4.0,4.0,1.0,3.0,2.0]))* IndexedRow(1,(6,[1,2,4,5],[7.0,6.0,1.0,1.0]))* IndexedRow(6,(6,[1,2,4,5],[4.0,4.0,4.0,3.0]))* IndexedRow(3,(6,[1,3,4,5],[7.0,3.0,2.0,1.0]))* IndexedRow(5,(6,[1,2,3,4,5],[5.0,3.0,1.0,3.0,3.0]))* IndexedRow(2,(6,[1,2,3,4],[6.0,7.0,3.0,2.0]))*///找出对电影1评分的公共用户val my_vector = indexRowMatrix.rows.filter(_.index == 1).map(x => (x.index,x.vector)).first()// my_vector.foreach(println)//1,(6,[1,2,4,5],[7.0,6.0,1.0,1.0])val res_df = indexRowMatrix.rows.toJavaRDD().rdd.map(x => {//电影1向量//(6,[1,2,4,5],[7.0,6.0,1.0,1.0])val my_index_vector = my_vector._2.toSparse.indices.toVectorval my_value_vector = my_vector._2//全部向量// (6,[1,2,3,4,5],[4.0,4.0,1.0,3.0,2.0]))// (6,[1,2,4,5],[7.0,6.0,1.0,1.0]))// (6,[1,2,4,5],[4.0,4.0,4.0,3.0]))// (6,[1,3,4,5],[7.0,3.0,2.0,1.0]))// (6,[1,2,3,4,5],[5.0,3.0,1.0,3.0,3.0]))// (6,[1,2,3,4],[6.0,7.0,3.0,2.0]))val other_index_vector = x.vector.toSparse.indices.toVectorval other_value_vector = x.vector//公共向量val g_all = my_index_vector.intersect(other_index_vector)val my_list = new ListBuffer[Double]val other_list = new ListBuffer[Double]for(index <- 0 to g_all.size - 1){my_list.append(my_value_vector(g_all(index)))other_list.append(other_value_vector(g_all(index)))}val my_res_vector = my_list.toVectorval other_res_vector = other_list.toVector(my_vector._1 , x.index , pearsonCorrelationSimilar(my_res_vector , other_res_vector))}).toDF("item_id","sim_item_id","score")/*** +-------+-----------+------------------+* |item_id|sim_item_id|score |* +-------+-----------+------------------+* |1 |1 |1.0 |* |1 |3 |0.987829161147262 |* |1 |2 |0.9406341620035445|* |1 |4 |0.8971499589146108|* |1 |5 |0.6767529681839596|* |1 |6 |0.5726371269248889|* +-------+-----------+------------------+*/res_df.orderBy(res_df("score").desc).show(false)}}
2、皮尔逊调整余弦相似度开发(剔除非公共集)
import breeze.numerics.powimport org.apache.spark.ml.recommendation.ALS.Ratingimport org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.distributed.{CoordinateMatrix, MatrixEntry}import org.apache.spark.sql.{Row, SparkSession}import scala.collection.mutable.ListBufferobject MyPearsonCos {def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {val spark = SparkSession.builder().master("local[5]").getOrCreate()import spark.implicits._val context = spark.read.textFile("/Users/zhangjingyu/Desktop/ES/utou_main.csv").rdd.map(x => {val field = x.split(",")Rating(field(0).toInt,field(1).toInt,field(2).toFloat)}).toDF("user","item","rate")val matrixRdd = context.rdd.map{case Row(user : Int , item : Int , rate : Float) => {MatrixEntry(item.toLong,user.toLong,rate.toDouble)}}val coordinateMatrix = new CoordinateMatrix(matrixRdd)val indexRowMatrix = coordinateMatrix.toIndexedRowMatrix()val my_vector = indexRowMatrix.rows.filter(_.index == 1).map(x => {(x.index , x.vector)}).first()val res_df = indexRowMatrix.rows.toJavaRDD().rdd.map(x => {val my_index_vector = my_vector._2.toSparse.indices.toVectorval my_value_vector = my_vector._2val other_index_vector = x.vector.toSparse.indices.toVectorval other_value_vector = x.vectorval g_all = my_index_vector.intersect(other_index_vector)val my_list = new ListBuffer[Double]val other_list = new ListBuffer[Double]for(index <- 0 to g_all.size - 1 ){my_list.append(my_value_vector(g_all(index)))other_list.append(other_value_vector(g_all(index)))}val my_res_vector = my_list.toVectorval other_res_vector = other_list.toVector(my_vector._1 , x.index , pearsonCosSimilar(my_res_vector , other_res_vector))}).toDF("item_id","sim_item_id","score")res_df.orderBy(res_df("score").desc).show(false)/*** +-------+-----------+------------------+* |item_id|sim_item_id|score |* +-------+-----------+------------------+* |1 |1 |0.9999999999999999|* |1 |3 |0.987829161147262 |* |1 |2 |0.9406341620035447|* |1 |4 |0.8971499589146108|* |1 |5 |0.6767529681839596|* |1 |6 |0.5726371269248889|* +-------+-----------+------------------+*/}def pearsonCosSimilar(vector1: Vector[Double] , vector2: Vector[Double]) : Double = {//平均数(平均数不能在外部进行计算,要将非重叠部分剔除后再进行求均数)val mean_vec1 = vector1.sum / vector1.lengthval mean_vec2 = vector2.sum / vector2.length//平方和val square_sum_vec1 = vector1.map(x => (x - mean_vec1) * (x - mean_vec1)).sumval square_sum_vec2 = vector2.map(x => (x - mean_vec2) * (x - mean_vec2)).sum//向量合并val zipVec = vector1.zip(vector2)val product = zipVec.map(x => (x._1-mean_vec1) * (x._2 - mean_vec2)).sum//分子计算val numerator = product//分母计算val dominato =pow(square_sum_vec1 , 0.5) * pow(square_sum_vec2 , 0.5)numerator/dominato}}
3、杰卡德(Jaccard) 相似度
杰卡德相似度,是两个集合的交集元素个数在并集中所占的比例。由于集合非常适用于布尔向量表示,所以杰卡德相似度简直就是为布尔值向量私人定做的。对应的计算方式是:
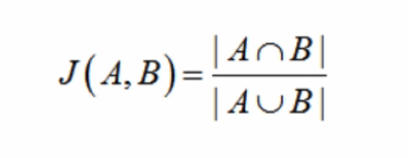
* 分子是两个布尔向量做点积计算,得到的就是交集元素个数;
* 分母是两个布尔向量做或运算,再求元素和。
余弦相似度适用于评分数据,杰卡德相似度适合用于隐式反馈数据。例如,使用用户的收藏行为,计算用户之间的相似度,杰卡德相似度就适合来承担这个任务。

扫描二维码 关注我们
微信号 : BIGDT_IN
文章转载自数据信息化,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。







