为什么需要动态路由?
之前说过 Gateway 的路由配置,常用的有两种方式:
这两者之间因为配置文件的方式修改起来比较灵活,然后通过 Stream+Bus 的方式刷新路由配置,所以大家使用的比较多。
但是如果我们在网关层需要类似于 Canary Release(金丝雀发布,也称灰度发布)这样的能力的话,那么以上两种配置路由的方式就都显得太笨拙了。
矿井中的金丝雀
17 世纪,英国矿井工人发现,金丝雀对瓦斯这种气体十分敏感。空气中哪怕有极其微量的瓦斯,金丝雀也会停止歌唱;而当瓦斯含量超过一定限度时,虽然鲁钝的人类毫无察觉,金丝雀却早已毒发身亡。当时在采矿设备相对简陋的条件下,工人们每次下井都会带上一只金丝雀作为 “瓦斯检测指标”,以便在危险状况下紧急撤离。
Spring Cloud Gateway 中虽然已经提供了关于权重的断言,我们在配置文件中可以直接这样配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
复制 | spring:
application:
name: cloud-gateway
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: service1_prod
uri: http://localhost:8081
predicates:
- Path=/test
- Weight=service1, 90
- id: service1_canary
uri: http://localhost:8082
predicates:
- Path=/test
- Weight=service1, 10
复制 |
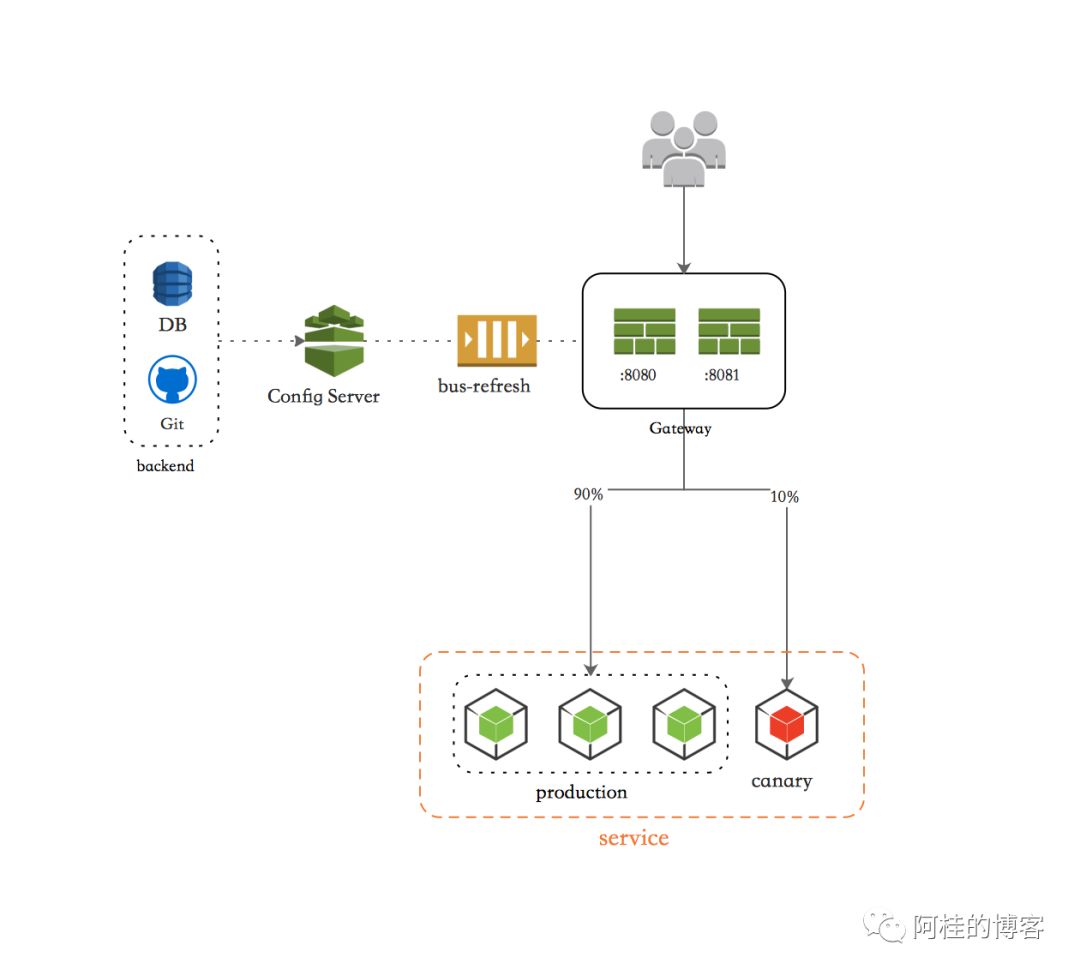
以实现 Canary Release 的能力,但是每次发布都配置一遍未免太过麻烦了。
出于 “懒” 的本性,我们当然希望在发布脚本里能在运行时直接动态修改service1_prod
、service1_canary
的权重,这样我们就不用手动修改还提心吊胆的担心改错了。
这其实就是 “动态路由” 了。
Spring Cloud Gateway 默认动态路由实现
Spring Cloud Gateway 在去年 6 月份发布了 2.0 第一个 release 版本,其实已经自带动态路由了, 但是官方文档并没有讲如何动态配置。
不过我们翻看 Spring Cloud Gateway 源码,会发现类 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.actuate.GatewayControllerEndpoint
中提供了网关配置的 RESTful 接口,默认是没有启用的。
在配置类 org.springframework.cloud.gateway.config.GatewayAutoConfiguration
中配置了 GatewayControllerEndpoint
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
复制 | @Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(Health.class)
protected static class GatewayActuatorConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnEnabledEndpoint
public GatewayControllerEndpoint gatewayControllerEndpoint(RouteDefinitionLocator routeDefinitionLocator, List<GlobalFilter> globalFilters,
List<GatewayFilterFactory> GatewayFilters, RouteDefinitionWriter routeDefinitionWriter,
RouteLocator routeLocator) {
return new GatewayControllerEndpoint(routeDefinitionLocator, globalFilters, GatewayFilters, routeDefinitionWriter, routeLocator);
}
}
复制 |
也就是说在存在org.springframework.boot.actuate.health.Health
时启用,我们想用自带的接口就需要添加 actuator 依赖
1
2
3
4
复制 | <dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
复制 |
并且还要将 actuator 的端点暴露出来
1
2
3
4
5
复制 | management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
复制 |
然后我们就能通过自带的GatewayControllerEndpoint
的 RESTful API 修改运行时的路由了
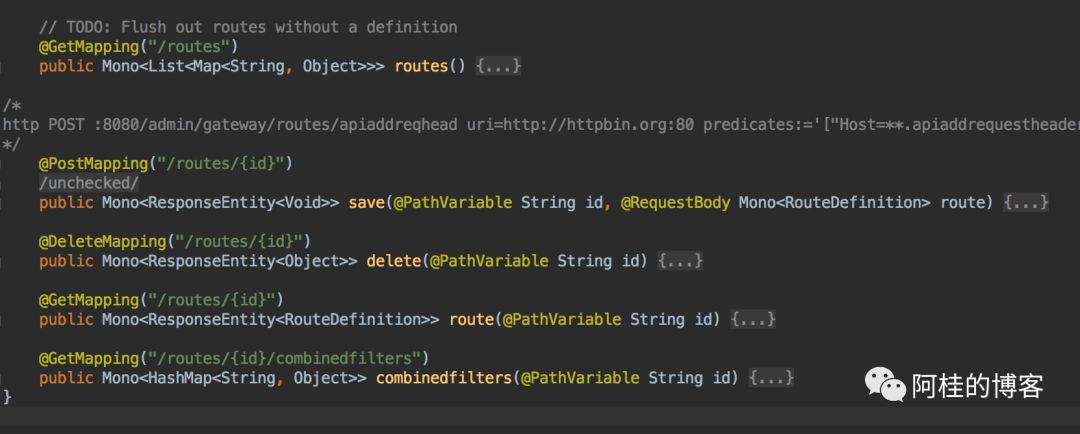
此时我们已经能实现之前的目标了
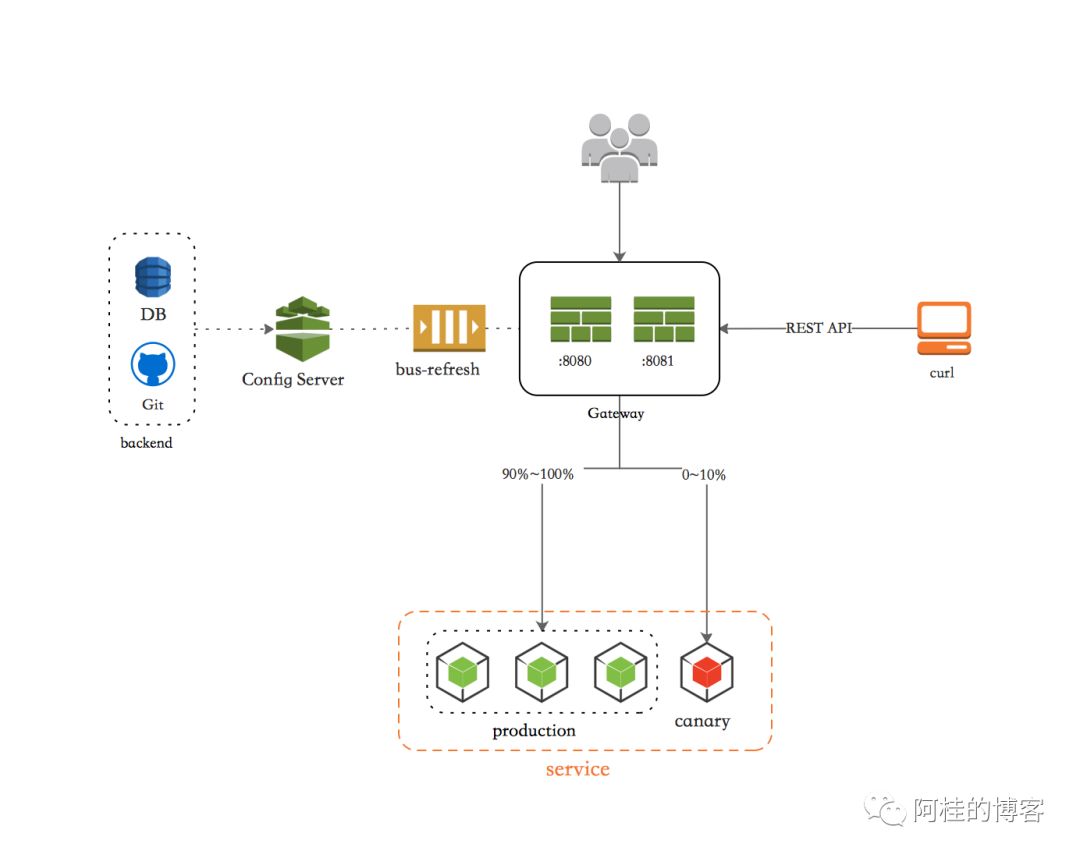
但是 Gateway 自带的这套是仅仅支持了 JVM 级别的动态路由,不能序列化存储的。
默认的实现:
1
2
3
4
5
6
复制 | // GatewayAutoConfiguration
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(RouteDefinitionRepository.class)
public InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository inMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository() {
return new InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository();
}
复制 |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
复制 | // InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository
public class InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository implements RouteDefinitionRepository {
private final Map<String, RouteDefinition> routes = synchronizedMap(new LinkedHashMap<String, RouteDefinition>());
@Override
public Mono<Void> save(Mono<RouteDefinition> route) {
return route.flatMap( r -> {
routes.put(r.getId(), r);
return Mono.empty();
});
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> delete(Mono<String> routeId) {
return routeId.flatMap(id -> {
if (routes.containsKey(id)) {
routes.remove(id);
return Mono.empty();
}
return Mono.defer(() -> Mono.error(new NotFoundException("RouteDefinition not found: "+routeId)));
});
}
@Override
public Flux<RouteDefinition> getRouteDefinitions() {
return Flux.fromIterable(routes.values());
}
}
复制 |
这样就导致我们的路由配置要分散存储在两个地方:Config Server 和 内存中,非常不利于管理。
另外在生产环境使用的话,Gateway 一定是一个集群,一个个去调用每个实例的 refresh 端口并不利于扩展。
Spring Cloud Gateway 路由加载过程
看了上面的源码后,是不是感觉其实我们完全可以替换掉InMemoryRouteDefinitionRepository
来用 DB 或 Redis 做持久化存储,来实现持久化的动态路由。
不过在动手之前,我们还是要先看一下 Gateway 的路由加载过程,这样才更好的实现我们的需求。
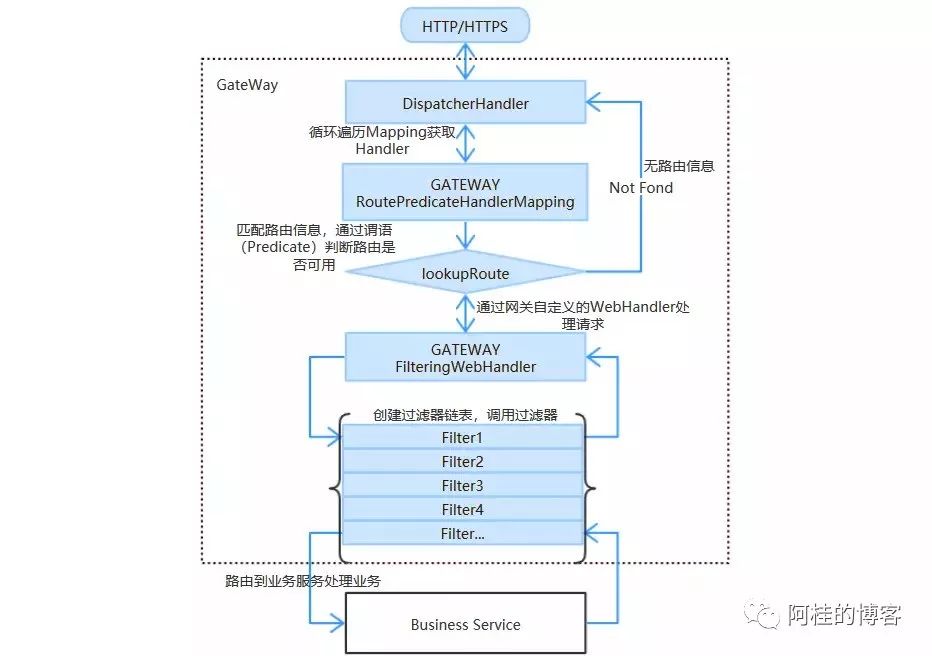
DispatcherHandler
接管用户请求
RoutePredicateHandlerMapping
路由匹配
根据 RouteLocator
获取 RouteDefinitionLocator
返回多个 RouteDefinitionLocator.getRouteDefinitions()
的路由定义信息
FilteringWebHandler
执行路由定义中的 filter 最后路由到具体的业务服务中
从加载流程上可以看出,我们要扩展动态路由的话,最核心的是要从RouteDefinitionLocator
上入手。
持久化的分布式动态路由组件
我们现在可以对 Gateway 做一些扩展来改善上述的问题。
扩展思路
增加一个路由管理模块
参考GatewayControllerEndpoint
实现
路由配置全部存储在 MySQL 中(Config Server 还需要,但不再存储路由配置了)
启动时将路由配置加载到 Redis 中,运行时双写
提供 RESTful API 以便脚本调用
前端页面可以配合 JSON Viewer 或类似插件,便于修改展示
网关模块扩展

注:用 Redis 一方面是为了支持 WebFlux(Reactor) 的背压(Backpressure),另一方面是为了刷新 Gateway 集群。
具体实现
路由管理模块
数据库的表结
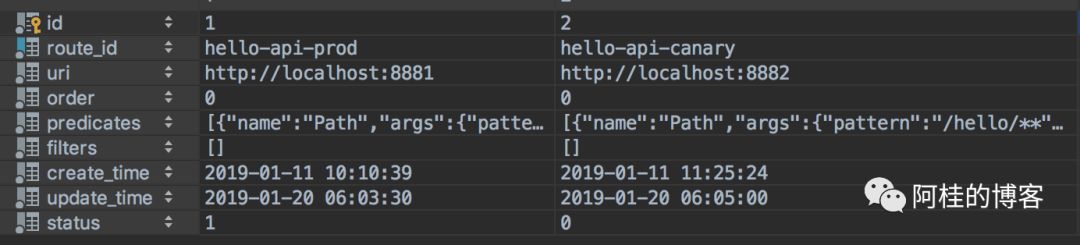
定义相关实体,这里参考 Gateway 源码的相关定义,涉及到三个类:
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteDefinition
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.handler.predicate.PredicateDefinition
org.springframework.cloud.gateway.filter.FilterDefinition
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
复制 | public class GatewayRoute {
private String routeId;
private String uri;
private Integer order;
private List<GatewayPredicateDefinition> predicates;
private List<GatewayFilterDefinition> filters;
private Long id;
private LocalDateTime createTime;
private LocalDateTime updateTime;
private EntityStatus status;
}
public class GatewayPredicateDefinition {
private String name;
private Map<String, String> args = new LinkedHashMap<>();
}
public class GatewayFilterDefinition {
private String name;
private Map<String, String> args = new LinkedHashMap<>();
}
复制 |
Controller 参考GatewayControllerEndpoint
实现即可。因为我的实现是软删除,所以对创建 / 更新做了明确区分。
注意里边有个refresh()
方法,并不是像GatewayControllerEndpoint
一样发RefreshRoutesEvent
,而是往 Redis publish 了一条消息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
复制 | @Slf4j
@RestController
@RequestMapping("")
public class GatewayDynamicRouteController {
@Autowired
private GatewayRouteService gatewayRouteService;
/**
* 创建路由
*
* @param model
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/routes")
public Mono<ResponseEntity<Map>> create(@RequestBody Mono<GatewayRoute> model) {
return model.flatMap(r -> {
String routeId = r.getRouteId();
return gatewayRouteService.findOneByRouteId(routeId)
.defaultIfEmpty(new GatewayRoute())
.flatMap(old -> {
if (old.getId() != null) {
return Mono.defer(() -> Mono.just(ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN).body(buildRetBody(403, "routeId " + routeId + " 已存在", null))));
}
log.info("[ROUTE] <biz> creating. {}", defer(() -> JsonUtils.toJSON(r)));
return gatewayRouteService.insert(Mono.just(r))
.flatMap(id -> {
return Mono.just((ResponseEntity.created(URI.create("/routes/" + id))
.body(buildRetBody(0, "success", ImmutableMap.of("id", id)))));
});
});
});
}
/**
* 修改路由
*
* @param id
* @param model
* @return
*/
@PutMapping("/routes/{id}")
public Mono<ResponseEntity<Map>> update(@PathVariable Long id, @RequestBody Mono<GatewayRoute> model) {
return model.flatMap(r -> {
String routeId = r.getRouteId();
return gatewayRouteService.findOneById(id)
.flatMap(old -> {
if (old == null) {
return Mono.defer(() -> Mono.just(ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.FORBIDDEN).body(buildRetBody(403, "routeId " + routeId + " 还未创建", null))));
}
log.info("[ROUTE] <biz> updating. id:{}\n before:{}\n after:{}",
id, defer(() -> JsonUtils.toJSON(old)), defer(() -> JsonUtils.toJSON(r)));
return gatewayRouteService.update(Mono.just(r))
.then(Mono.defer(() -> Mono.just((ResponseEntity.ok(buildRetBody(0, "success", null))))));
});
});
}
/**
* @param id
* @param status 0 正常,1 删除
* @return
*/
@PutMapping("/routes/{id}/{status}")
public Mono<ResponseEntity<Object>> updateStatus(@PathVariable Long id, @PathVariable Integer status) {
EntityStatus entityStatus = EntityStatus.fromValue(status);
if (entityStatus == null) {
return Mono.defer(() -> Mono.just(ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST).build()));
}
return gatewayRouteService.updateStatus(id, entityStatus)
.then(Mono.defer(() -> Mono.just(ResponseEntity.ok().build())))
.onErrorResume(t -> t instanceof NotFoundException, t -> Mono.just(ResponseEntity.notFound().build()));
}
/**
* 获取单个路由信息
*
* @param id
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/routes/{id}")
public Mono<ResponseEntity<GatewayRoute>> route(@PathVariable Long id) {
return gatewayRouteService.findOneById(id)
.map(ResponseEntity::ok)
.switchIfEmpty(Mono.just(ResponseEntity.notFound().build()));
}
/**
* 刷新路由
*
* @return
*/
@PostMapping("/routes/refresh")
public Mono<ResponseEntity<Object>> refresh() {
return gatewayRouteService.refresh()
.map(aLong -> {
if (aLong > 0) {
return ResponseEntity.ok().build();
} else {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.SERVICE_UNAVAILABLE).build();
}
});
}
private Map<String, Object> buildRetBody(int code, String msg, Object data) {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("code", code);
map.put("message", msg);
map.put("data", data);
return map;
}
}
复制 |
网关模块
重写一个新的RouteDefinitionRepository
,主要是要实现getRouteDefinitions()
方法。
对于save
和delete
这两个方法,我是故意不处理的,因为路由的管理均在上边的路由管理模块实现了,网关模块只关注路由的获取。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
复制 | @Slf4j
@Component
public class DynamicRouteDefinitionRepository implements RouteDefinitionRepository {
@Autowired
private ReactiveRedisTemplate<String, String> redisTemplate;
@Override
public Flux<RouteDefinition> getRouteDefinitions() {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash()
.values(GATEWAY_ROUTES)
.map(json -> JsonUtils.fromJson(json.toString(), RouteDefinition.class));
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> save(Mono<RouteDefinition> route) {
return Mono.empty();
}
@Override
public Mono<Void> delete(Mono<String> routeId) {
return Mono.empty();
}
}
复制 |
除此之外,为了配合路由管理模块实现网关集群的刷新路由配置,网关模块里还需要加一个 Redis 的配置以订阅刷新消息。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
复制 | @Slf4j
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
ReactiveRedisMessageListenerContainer container(GatewayRouteService routeService, ReactiveRedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
ReactiveRedisMessageListenerContainer container = new ReactiveRedisMessageListenerContainer(connectionFactory);
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(() -> {
container.destroyLater().subscribe();
}));
container.receive(topic())
.map(p -> p.getMessage())
.subscribe(message -> {
log.info("Received <{}>", message);
routeService.publishRefreshEvent();
});
return container;
}
@Bean
public ChannelTopic topic() {
return new ChannelTopic("gateway-route-refresh-topic");
}
}
复制 |
自此也就大功告成了~
配置格式
这样的动态路由,是用 JSON 格式来配置的,如果格式不对,可是要报 500 错误的!
这里简单举个栗子:
如果我们在配置文件里要配的路由是这样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
复制 | spring:
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: user-api
uri: http://user-api:8080
order: 0
predicates:
- Path=/user/**
- Weight=user-service, 90
filters:
- StripPrefix=1
复制 |
那么翻译成 JSON 格式就是要这样(其中 status 是我自己加的,可以忽略)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
复制 | {
"routeId": "user-api",
"uri": "http://user-api:8080",
"order": 0,
"predicates": [
{
"name": "Path",
"args": {
"pattern": "/user/**"
}
},
{
"name": "Weight",
"args": {
"weight.group": "user-service",
"weight.weight": "90"
}
}
],
"filters": [
{
"name": "StripPrefix",
"args": {
"parts": "1"
}
}
],
"status": 0
}
复制 |
至于其中predicate
和filter
的name
字段都还好理解,即使是 yaml 格式的我们也是要写的。这个有相关的文档,目前的规则就是RoutePredicateFactory
和GatewayFilterFactory
这两个接口下所有的实现类去掉这两个后缀后的名字(见org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support.NameUtils
)。
那么args
里边的 key 的名字又是哪来的呢?
这个没有文档,翻看源码发现此处的 key 有两种配置方式:
用_genkey_0
、_genkey_1
…_genkey_n
这种形式,比较方便但是可读性比较差,还得注意顺序。(这个的源码也在 NameUtils 里)
另一种就是像我上边例子中写的,这需要去各个RoutePredicateFactory
和GatewayFilterFactory
的源码找对应的命名规则。(还需要参考org.springframework.cloud.gateway.support.ShortcutConfigurable
)














