
本章会继续讲解Metrics的第二个工具:Counters。
1. Counters的使用
在account内部使用Counters检测接口发生异常的次数,一段时间内如果超过阀值,会触发报警。
下面的一段代码是account用来检测用户登录失败发生的次数。
public class MetricsCounterTest extendsTest0Abstract {
private List<String> users;
private String password;
@Autowired
@Qualifier("officialCustomerService")
private LoginService loginService;
@Before
public void before() {
password = "RIYU3ZOsYAThlfqfazyEbT+qe5ACN";
users = new ArrayList<>();
users.add("bingxin.li@tendcloud.com">bingxin.li@tendcloud.com");
users.add("bingxin.li001@tendcloud.com">bingxin.li001@tendcloud.com");
users.add("bingxin.li002@tendcloud.com">bingxin.li002@tendcloud.com");
users.add("bingxin.li003@tendcloud.com">bingxin.li003@tendcloud.com");
users.add("bingxin.li004@tendcloud.com">bingxin.li004@tendcloud.com");
users.add("bingxin.li005@tendcloud.com">bingxin.li005@tendcloud.com");
users.add("libingxin2013@outlook.com">libingxin2013@outlook.com");
}
@Test
public void login() throws Exception {
MetricRegistry metrics = new MetricRegistry();
ConsoleReporter reporter = ConsoleReporter.forRegistry(metrics).build();
reporter.start(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
Counter counter = metrics.counter(
MetricRegistry.name(MetricsCounterTest.class, "failed","size"));
for (String user : users) {
try {
loginService.login(Base64.getEncoder().encodeToString(user.getBytes()),password);
} catch (HttpUnauthorizedException e) {
counter.inc();
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
Assert.assertTrue(counter.getCount() < 3);
}
}
}
}
运行后输出:
17-11-28 17:35:30=============================================================
-- Counters --------------------------------------------------------------------
metrics.MetricsCounterTest.failed.size
count = 3
java.lang.AssertionError
atorg.junit.Assert.fail(Assert.java:86)
atorg.junit.Assert.assertTrue(Assert.java:41)
atorg.junit.Assert.assertTrue(Assert.java:52)
atmetrics.MetricsCounterTest.login(MetricsCounterTest.java:66)
atsun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0(Native Method)
atsun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(NativeMethodAccessorImpl.java:62)
atsun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke(DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.java:43)
atjava.lang.reflect.Method.invoke(Method.java:498)
atorg.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod$1.runReflectiveCall(FrameworkMethod.java:50)
atorg.junit.internal.runners.model.ReflectiveCallable.run(ReflectiveCallable.java:12)
atorg.junit.runners.model.FrameworkMethod.invokeExplosively(FrameworkMethod.java:47)
atorg.junit.internal.runners.statements.InvokeMethod.evaluate(InvokeMethod.java:17)
atorg.junit.internal.runners.statements.RunBefores.evaluate(RunBefores.java:26)
从输出结果可以看出,ConsoleReporter每秒输出异常次数,当异常次数达到阀值3时,断言失败。
2. Counter 层级结构
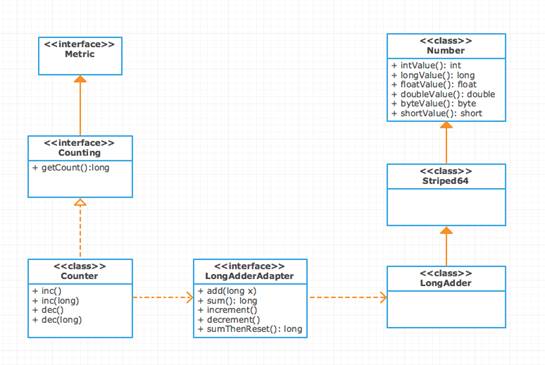
Counter内部通过持有LongAdderAdapter的实例来实现Counting接口,而LongAdderAdapter内部依赖的是JDK1.8并发原子操作的LongAdder。
那么Counter是如何获取到LongAdderAdapter的实例呢?

3. LongAdder 工作原理
通过上面的创建和适配过程,并发原子操作最终交由LongAdder类完成,下面让我们来研究下LongAdder类的工作流程。
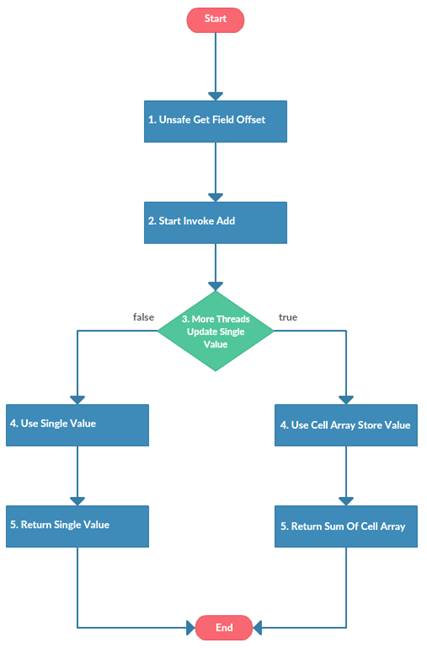
工作流程说明:
1. LongAdder继承Striped64类,Striped64使用不安全的Unsafe类来进行原子操作。为了防止不可预测的情况发生,建议不要在代码中直接使用,除非你有Doug Lea的实力。
2. LongAdder最核心的就是 add(long x) 方法,不管自增和自减都会调用此方法。
3. add方法基于base的CAS操作返回值来验证是否发生并发。
4. 未发生并发:后续的原子操作、返回值都是基于base。
5. 发生并发:通过Cell数组将原子操作分散到子项中进行,Cell是Striped64的内部类,里面有存储long值的value字段。
6. Cell数组的索引:依赖与当前线程的threadLocalRandomProbe。
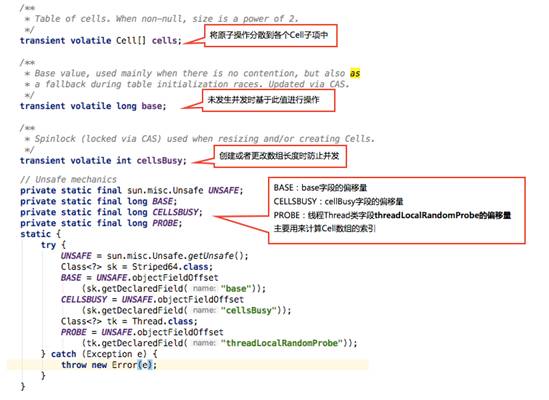
获取偏移量的代码解析:
是否发生了并发操作:
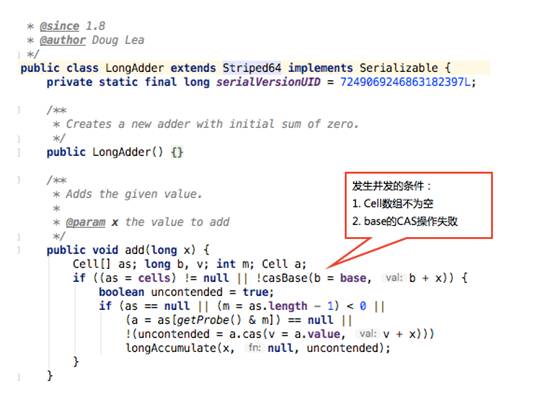
实际的并发操作:

4. 结束语
Java除了并发包,还有很多集合类等都是Doug Lea编写的,他的个人主页:http://g.oswego.edu/
通过本章对Counters的讲解,相信你一定会有所收获。







