二叉树存储
二叉树的存储结构分为:顺序存储结构和链式存储结构。
1.顺序存储结构
把一棵满二叉树自上而下,从左到右顺序编号,把编号依次存放在数组中,如下图所示:

设满二叉树结点在数组中索引号为i,那么有如下性质:
(1)如果i=0,此结点无双亲,为根结点;
(2)如果i>0,其双亲结点为(i-1)/2 ,这里为整除,保留整数位;
(3)结点为i 的左孩子为2i+1,右孩子为2i+2;
(4)如果i>0,当i为奇数时,它是双亲结点的左孩子,兄弟为i+1;当i为偶数时,它是双亲结点的右孩子,兄弟结点为i-1;
(5)深度为k的满二叉树需要长度为2^k -1 的数组进行存储。
2.链式存储
当k值很大时,又有很多空结点的时候,使用顺序存储结构来存储,会造成极大的浪费,这时应使用链式存储结构来存储如下:
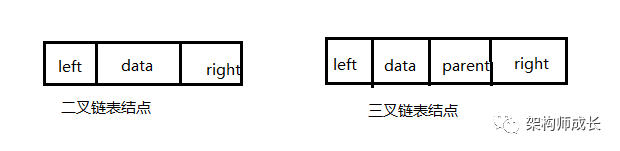
构建和遍历实现
分别实现二叉树深度优先和广度优先的先根序遍历:
import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.Stack;public class BinaryTree {public static void main(String[] args) {/** 0* / \* 1 2* / \ /\* 3 4 5 6*/int[] arr = new int[]{0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6};TreeNode root = createBinaryTree(arr, 0);getDFS(root);getBFS(root);}private static int getDeep(int index) {int deep = 1;while (index > 0) {deep += 1;index = (index-1)/2;}return deep;}//构建二叉树private static TreeNode createBinaryTree(int[] arr, int index) {TreeNode node = null;if (index < arr.length) {int value = arr[index];node = new TreeNode(value, getDeep(index));node.left = createBinaryTree(arr, index * 2 + 1);node.right = createBinaryTree(arr, index * 2 + 2);return node;}return node;}//深度优先遍历-先序遍历private static void getDFS(TreeNode root) {System.out.println("深度优先遍历-先序遍历:");if (root == null) {return;}Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<>();stack.push(root);while (!stack.isEmpty()) {TreeNode temp = stack.pop();for (int i=0; i<temp.deep; i++) {System.out.print("\t");}System.out.println(temp.value);//这里利用了堆的--先进后出的特性,所以右节点要在左节点前入堆if (temp.right != null) {stack.push(temp.right);}if (temp.left != null) {stack.push(temp.left);}}}//广度优先遍历-先序遍历private static void getBFS(TreeNode root) {System.out.println("广度优先遍历-先序遍历:");if (root == null) {return;}ArrayList<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayList<>();queue.add(root);while (queue.size() > 0) {TreeNode temp = queue.remove(0);for (int i=0; i<temp.deep; i++) {System.out.print("\t");}System.out.println(temp.value);//这里利用了队列的--先进先出的特性,所以左节点要在右节点前入堆if (temp.left != null) {queue.add(temp.left);}if (temp.right != null) {queue.add(temp.right);}}}//二叉树结构static class TreeNode {int value;int deep;TreeNode left;TreeNode right;TreeNode(int value, int deep) {this.value = value;this.deep = deep;}}}
参考:
https://blog.csdn.net/hnzmdlhc/article/details/90271032
https://blog.csdn.net/weiqiang_1989/article/details/87280801
文章转载自架构师成长,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






