上一节中我们讲述了,StandardContext关联了很多的组件,这些组件都可以在Context元素下面进行配置,也可以在其他的容器组件中配置,关于这些见我们后续的分析;
我们来讲讲Context元素下独有的子元素配置;
1.Context Param
应用的参数,实际就是在web.xml中配置的context-param:
<Context> ... <Parameter name="companyName" value="My Company, Incorporated" override="false"/> ... </Context>
This is equivalent to the inclusion of the following element in the web application deployment descriptor (/WEB-INF/web.xml
):
<context-param> <param-name>companyName</param-name> <param-value>My Company, Incorporated</param-value> </context-param>
but does not require modification of the deployment descriptor to customize this value.
该属性实际设置到ServletContext中去,通过ServletContext可以获取到该属性信息;
我们在StandardContext类中看到两个属性,注意区分,parameters属性是由web.xml中进行初始化的,而applicationParameter是由Digest初始化server.xml中的Context的Parameter参数的:
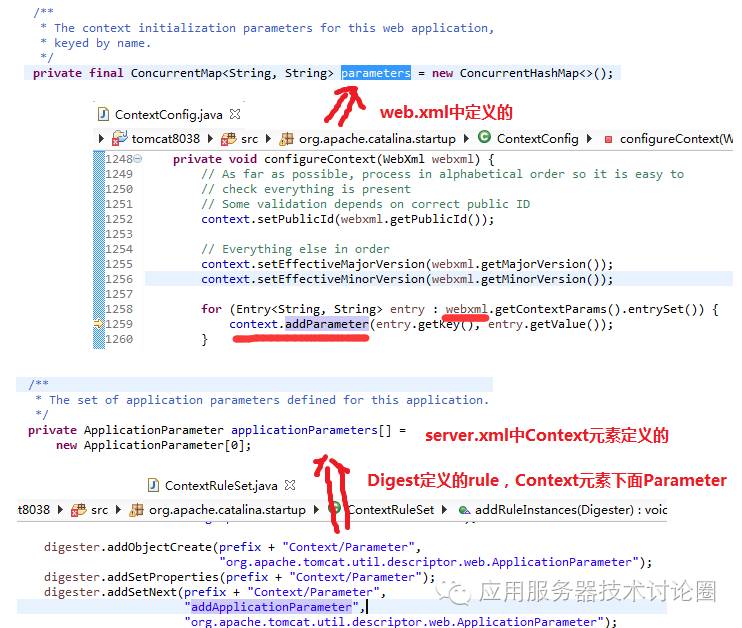
但实际上,虽然是2个属性,但最后都合二为一,都设置到了ServletContext中去了:

至于<Parameter>参数,对应的是ApplicationParameter对象:
The valid attributes for a <Parameter>
element are as follows:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
description | Optional, human-readable description of this context initialization parameter. |
name | The name of the context initialization parameter to be created. |
override | Set this to |
value | The parameter value that will be presented to the application when requested by calling |
别的属性没什么可说的,其中的override属性的做法在前面程序中可以看到,当设置了override的话,applicationParamter参数直接会覆盖掉web.xml中的属性;
后续这些属性其实都是这个路子,server.xml中配置的Context的子元素会覆盖web.xml中的配置,从优先级的角度来看,server.xml中的优先级更高;
2.JNDI绑定
对于StandardContext元素对象还有一些属性,如下面的Enviroment,这些属性是于JNDI系统有关系的,如下:
You can configure named values that will be made visible to the web application as environment entry resources, by nesting <Environment>
entries inside this element. For example, you can create an environment entry like this:
<Context> ... <Environment name="maxExemptions" value="10" type="java.lang.Integer" override="false"/> ... </Context>
This is equivalent to the inclusion of the following element in the web application deployment descriptor (/WEB-INF/web.xml
):
<env-entry> <env-entry-name>maxExemptions</env-entry-name> <env-entry-value>10</env-entry-value> <env-entry-type>java.lang.Integer</env-entry-type> </env-entry>
but does not require modification of the deployment descriptor to customize this value.
The valid attributes for an <Environment>
element are as follows:
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
description | Optional, human-readable description of this environment entry. |
name | The name of the environment entry to be created, relative to the |
override | Set this to |
type | The fully qualified Java class name expected by the web application for this environment entry. Must be a legal value for |
value | The parameter value that will be presented to the application when requested from the JNDI context. This value must be convertable to the Java type defined by the |
关于这些属性实际最后都在NamingResourceImpl中进行实现:

这些属性不仅仅包含环境信息,还包括一些ejb引用,资源引用,resource定义,resource-ref,事务ref等等;
关于这块的解析,我们在JNDI系统详细分析之后,再回过头来进行详解,尽情期待!






