Function
以下只列出每个函数的部分内容,详细信息请参考 orafce 的文档: https://github.com/orafce/orafce/blob/master/doc/orafce_documentation/Orafce_Documentation_05.md
数学函数
BITAND
BITAND,返回两个数值型数值在按位进行 AND 运算后的结果。
PostgreSQL 也自带了这个函数,orafce 对这个函数做了改进。
-- 未安装 orafce
postgres=# \df BITAND
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+--------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | bitand | bit | bit, bit | func
(1 row)
-- 安装 orafce
postgres=# \df BITAND
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+--------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | bitand | bit | bit, bit | func
public | bitand | bigint | bigint, bigint | func
(2 rows)
postgres=# SELECT BITAND(5,3) FROM DUAL;
bitand
--------
1
(1 row)
双曲函数
从 PostgreSQL 12 版本就已经支持以下三个双曲函数(Hyperbolic Functions),双曲正弦(SINH),双曲余弦(COSH),双曲正切(TANH)
详情参考 PostgreSQL 的官方文档:https://www.postgresql.org/docs/12/functions-math.html
postgres=# SELECT SINH(1.414) FROM DUAL;
sinh
--------------------
1.9346016882495571
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT COSH(2.236) FROM DUAL;
cosh
-------------------
4.731359100024696
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT TANH(3) FROM DUAL;
tanh
--------------------
0.9950547536867306
(1 row)
字符串函数
BTRIM
BTRIM,从字符串的开头和结尾删除指定的字符。Oracle 数据库不存在 BTRIM。
PostgreSQL 也自带了这个函数,orafce 对这个函数做了改进,orafce 对 BTRIM 函数的更改对比:
-- 未安装 orafce
postgres=# \df BTRIM
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+-------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | btrim | bytea | bytea, bytea | func
pg_catalog | btrim | text | text | func
pg_catalog | btrim | text | text, text | func
(3 rows)
-- 安装 orafce
postgres=# \df BTRIM
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+-------+------------------+----------------------+------
oracle | btrim | text | character | func
oracle | btrim | text | character, character | func
oracle | btrim | text | character, nvarchar2 | func
oracle | btrim | text | character, text | func
oracle | btrim | text | character, varchar2 | func
oracle | btrim | text | nvarchar2 | func
oracle | btrim | text | nvarchar2, character | func
oracle | btrim | text | nvarchar2, nvarchar2 | func
oracle | btrim | text | nvarchar2, text | func
oracle | btrim | text | nvarchar2, varchar2 | func
oracle | btrim | text | text | func
oracle | btrim | text | text, character | func
oracle | btrim | text | text, nvarchar2 | func
oracle | btrim | text | text, text | func
oracle | btrim | text | text, varchar2 | func
oracle | btrim | text | varchar2 | func
oracle | btrim | text | varchar2, character | func
oracle | btrim | text | varchar2, nvarchar2 | func
oracle | btrim | text | varchar2, text | func
oracle | btrim | text | varchar2, varchar2 | func
pg_catalog | btrim | bytea | bytea, bytea | func
(21 rows)
使用 PostgreSQL 自带的 BTRIM 函数处理的字符串如果是 CHAR 类型,则会删除行尾空格,然后删除修剪字符。
在以下示例中,将返回从 “aabcaba” 两端删除 “a” 的字符串。
-- 使用 PostgreSQL 自带的 BTRIM 函数,先删除行尾空格,然后删除修剪字符
postgres=# create table tt (id int,name char(10));
postgres=# insert into tt values (3,'aabcaba');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# SELECT name, BTRIM(name,'a') from tt where id=3;
name | btrim
------------+-------
aabcaba | bcab
(1 row)
-- 使用 orafce 的 LENGTH 函数,不会删除行尾空格
postgres=# SELECT name, BTRIM(name,'a') from tt where id=3;
name | btrim
------------+----------
aabcaba | bcaba
(1 row)
INSTR
INSTR,返回字符串中子字符串的位置。
postgres=# \df INSTR
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+-------+------------------+-------------------------------------------------+------
pg_catalog | instr | integer | str text, patt text | func
pg_catalog | instr | integer | str text, patt text, start integer | func
pg_catalog | instr | integer | str text, patt text, start integer, nth integer | func
(3 rows)
在以下示例中,在字符串 “ABCACBCAAC” 中找到字符 “BC” ,并返回这些字符的位置。
postgres=# SELECT INSTR('ABCACBCAAC','BC') FROM DUAL;
instr
-------
2
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT INSTR('ABCACBCAAC','BC',-1,2) FROM DUAL;
instr
-------
2
(1 row)
LENGTH
LENGTH,以字符个数返回字符串的长度。
PostgreSQL 也自带了这个函数,但是使用 PostgreSQL 自带的 LENGTH 函数处理的字符串是 CHAR 类型,则长度中不包含行尾空格。
-- 未安装 orafce
postgres=# \df LENGTH
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+--------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | length | integer | bit | func
pg_catalog | length | integer | bytea | func
pg_catalog | length | integer | bytea, name | func
pg_catalog | length | integer | character | func
pg_catalog | length | double precision | lseg | func
pg_catalog | length | double precision | path | func
pg_catalog | length | integer | text | func
pg_catalog | length | integer | tsvector | func
(8 rows)
-- 安装 orafce
postgres=# \df LENGTH
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+--------+------------------+---------------------+------
oracle | length | integer | character | func
pg_catalog | length | integer | bit | func
pg_catalog | length | integer | bytea | func
pg_catalog | length | integer | bytea, name | func
pg_catalog | length | double precision | lseg | func
pg_catalog | length | double precision | path | func
pg_catalog | length | integer | text | func
pg_catalog | length | integer | tsvector | func
(8 rows)
在以下示例中,将返回表 tt 中 name 列(使用 CHAR(10) 定义)中的字符数。
-- 使用 PostgreSQL 自带的 LENGTH 函数,char(10) 返回 4 ,不包含行尾空格
postgres=# create table tt (id int,name char(10));
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# insert into tt values (1,'AAAA');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# select name, LENGTH(name) from tt where id=1;
name | length
------------+--------
AAAA | 4
(1 row)
-- 在 Oracle 中的 LENGTH 函数,char(10) 返回 10 ,包含行尾空格
SQL> create table tt (id int,name char(10));
SQL> insert into tt values (1,'AAAA');
SQL> select name, LENGTH(name) from tt where id=1;
NAME LENGTH(NAME)
---------- ------------
AAAA 10
-- 使用 orafce 的 LENGTH 函数,char(10) 返回 10 ,包含行尾空格,与 Oracle 相符合
postgres=# create table tt (id int,name char(10));
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# insert into tt values (1,'AAAA');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=# select name, LENGTH(name) from tt where id=1;
name | length
------------+--------
AAAA | 10
(1 row)
LENGTHB
LENGTHB,以字节数返回字符串的长度。
LENGTHB 函数处理的字符串是 CHAR 类型,则长度中会包含行尾空格。
postgres=# \df LENGTHB
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+---------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | lengthb | integer | varchar2 | func
(1 row)
在以下示例中,将返回表 tt 中列 name(使用 CHAR(10) 定义)中的字节数。注意,在第二个 SELECT 语句中,每个汉字的长度为 3 个字节,两个汉字总共 6 个字节,其中 8 个行尾空格增加了 8 个字节,这给出了 14 个字节的结果。
drop table tt;
create table tt (id int,name char(10));
insert into tt values (1,'AAAAA');
insert into tt values (3,'中国');
postgres=# SELECT name, LENGTHB(name) FROM tt WHERE id = 1;
name | lengthb
------------+---------
AAAAA | 10
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT name, LENGTHB(name) FROM tt WHERE id = 3;
name | lengthb
--------------+---------
中国 | 14
(1 row)
--但是 Oracle 统计中文还是 10 个字节
SQL> SELECT name, LENGTHB(name) FROM tt WHERE id = 3;
NAME LENGTHB(NAME)
---------- -------------
中国 10
SQL> SELECT LENGTHB('中国') from dual;
LENGTHB('??????')
-----------------
6
对于中文的字节数统计有点迷糊,如果应用程序代码中存在 LENGTHB ,需要额外关注一下。
LPAD
LPAD,在字符串的左边填充指定长度的字符串
PostgreSQL 也自带了这个函数,但是使用 PostgreSQL 自带的 LPAD 函数处理的字符串如果是 CHAR 类型,则删除行尾空格,然后将填充字符添加到字符串中。
-- 未安装 orafce
postgres=# \df LPAD
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | lpad | text | text, integer | func
pg_catalog | lpad | text | text, integer, text | func
(2 rows)
-- 安装 orafce
postgres=# \df LPAD
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+------+------------------+-------------------------------+------
oracle | lpad | text | bigint, integer, integer | func
oracle | lpad | text | character, integer | func
oracle | lpad | text | character, integer, character | func
oracle | lpad | text | character, integer, nvarchar2 | func
oracle | lpad | text | character, integer, text | func
oracle | lpad | text | character, integer, varchar2 | func
oracle | lpad | text | integer, integer, integer | func
oracle | lpad | text | numeric, integer, integer | func
oracle | lpad | text | nvarchar2, integer | func
oracle | lpad | text | nvarchar2, integer, character | func
oracle | lpad | text | nvarchar2, integer, nvarchar2 | func
oracle | lpad | text | nvarchar2, integer, text | func
oracle | lpad | text | nvarchar2, integer, varchar2 | func
oracle | lpad | text | smallint, integer, integer | func
oracle | lpad | text | text, integer | func
oracle | lpad | text | text, integer, character | func
oracle | lpad | text | text, integer, nvarchar2 | func
oracle | lpad | text | text, integer, text | func
oracle | lpad | text | text, integer, varchar2 | func
oracle | lpad | text | varchar2, integer | func
oracle | lpad | text | varchar2, integer, character | func
oracle | lpad | text | varchar2, integer, nvarchar2 | func
oracle | lpad | text | varchar2, integer, text | func
oracle | lpad | text | varchar2, integer, varchar2 | func
(24 rows)
在下面的示例中,返回一个 20 个字符的字符串,该字符串是通过在 ‘abc’ 的左边填充 ‘a’ 而形成的。
drop table tt;
create table tt (id int,name char(10));
insert into tt values (1,'abc');
-- 使用 PostgreSQL 自带的 LPAD 函数,会先删除行尾空格,再填充字符
postgres=# SELECT name, LPAD(name,20,'a') FROM tt;
name | lpad
------------+----------------------
abc | aaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaaabc
(1 row)
-- 在 Oracle 中的 LPAD 函数,不会删除行尾空格
SQL> SELECT name, LPAD(name,20,'a') FROM tt;
NAME LPAD(NAME,20,'A')
---------- ----------------------------------------
abc aaaaaaaaaaabc
-- 使用 orafce 的 LPAD 函数,也不会删除行尾空格,与 Oracle 相符合
postgres=# SELECT name, LPAD(name,20,'a') FROM tt;
name | lpad
------------+----------------------
abc | aaaaaaaaaaabc
(1 row)
RPAD
RPAD,在字符串的右边填充指定长度的字符串,与 LPAD 类似
LTRIM
LTRIM,从字符串的开头删除指定的字符。
PostgreSQL 也自带了这个函数,但是使用 PostgreSQL 自带的 LTRIM 函数处理的字符串如果是 CHAR 类型,则先删除行尾空格,然后删除修剪字符。
-- 未安装 orafce
postgres=# \df LTRIM
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+-------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | ltrim | text | text | func
pg_catalog | ltrim | text | text, text | func
(2 rows)
-- 安装 orafce
postgres=# \df LTRIM
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+-------+------------------+----------------------+------
oracle | ltrim | text | character | func
oracle | ltrim | text | character, character | func
oracle | ltrim | text | character, nvarchar2 | func
oracle | ltrim | text | character, text | func
oracle | ltrim | text | character, varchar2 | func
oracle | ltrim | text | nvarchar2 | func
oracle | ltrim | text | nvarchar2, character | func
oracle | ltrim | text | nvarchar2, nvarchar2 | func
oracle | ltrim | text | nvarchar2, text | func
oracle | ltrim | text | nvarchar2, varchar2 | func
oracle | ltrim | text | text | func
oracle | ltrim | text | text, character | func
oracle | ltrim | text | text, nvarchar2 | func
oracle | ltrim | text | text, text | func
oracle | ltrim | text | text, varchar2 | func
oracle | ltrim | text | varchar2 | func
oracle | ltrim | text | varchar2, character | func
oracle | ltrim | text | varchar2, nvarchar2 | func
oracle | ltrim | text | varchar2, text | func
oracle | ltrim | text | varchar2, varchar2 | func
(20 rows)
在下面的示例中,将返回从 “aabcab” 开头删除 “ab” 的字符串。
drop table tt;
create table tt (id int,name char(10));
insert into tt values (1,'aabcab');
-- 使用 PostgreSQL 自带的 LTRIM 函数,会先删除行尾空格,再删除修剪字符
postgres=# SELECT name, LTRIM(name,'ab'), LENGTH(LTRIM(name,'ab')) FROM tt;
name | ltrim | length
------------+-------+--------
aabcab | cab | 3
(1 row)
-- 在 Oracle 中的 LTRIM 函数,不会删除行尾空格
SQL> SELECT name, LTRIM(name,'ab'), LENGTH(LTRIM(name,'ab')) FROM tt;
NAME LTRIM(NAME LENGTH(LTRIM(NAME,'AB'))
---------- ---------- ------------------------
aabcab cab 7
-- 使用 orafce 的 LTRIM 函数,也不会删除行尾空格,与 Oracle 相符合
postgres=# SELECT name, LTRIM(name,'ab'), LENGTH(LTRIM(name,'ab')) FROM tt;
name | ltrim | length
------------+---------+--------
aabcab | cab | 7
(1 row)
RTRIM
RTRIM,从字符串的末尾删除指定的字符,与 LTRIM 类似
NLSSORT
NLSSORT,用于在与默认语言环境不同的语言环境 (COLLATE) 的整理顺序中进行比较和排序。
postgres=# \df NLSSORT
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+---------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | nlssort | bytea | text | func
pg_catalog | nlssort | bytea | text, text | func
(2 rows)
示例:
drop table tt;
create table tt (id int,name varchar2(10));
insert into tt values (1001,'aabcabbc'),(2001,'abcdef'),(3001,'aacbaab');
postgres=# SELECT id, name FROM tt ORDER BY NLSSORT(name,'da_DK.UTF8');
id | name
------+----------
2001 | abcdef
1001 | aabcabbc
3001 | aacbaab
(3 rows)
postgres=# SELECT id, name FROM tt ORDER BY NLSSORT(name,'en_US.UTF8');
id | name
------+----------
1001 | aabcabbc
3001 | aacbaab
2001 | abcdef
(3 rows)
-- 可以使用 SELECT 语句设置 set_nls_sort 语言环境
postgres=# SELECT set_nls_sort('da_DK.UTF8');
postgres=# SELECT id, name FROM tt ORDER BY NLSSORT(name);
id | name
------+----------
2001 | abcdef
1001 | aabcabbc
3001 | aacbaab
(3 rows)
postgres=# SELECT set_nls_sort('en_US.UTF8');
postgres=# SELECT id, name FROM tt ORDER BY NLSSORT(name);
id | name
------+----------
1001 | aabcabbc
3001 | aacbaab
2001 | abcdef
(3 rows)
REGEXP_COUNT
REGEXP_COUNT,在字符串中搜索正则表达式,并返回匹配的个数。
postgres=# \df REGEXP_COUNT
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+--------------+------------------+---------------------------+------
oracle | regexp_count | integer | text, text | func
oracle | regexp_count | integer | text, text, integer | func
oracle | regexp_count | integer | text, text, integer, text | func
(3 rows)
示例:
postgres=# SELECT REGEXP_COUNT('a'||CHR(10)||'d', 'a.d') FROM DUAL;
regexp_count
--------------
0
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT REGEXP_COUNT('a'||CHR(10)||'d', 'a.d', 1, 'm') FROM DUAL;
regexp_count
--------------
0
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT REGEXP_COUNT('a'||CHR(10)||'d', 'a.d', 1, 'n') FROM DUAL;
regexp_count
--------------
1
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT REGEXP_COUNT('a'||CHR(10)||'d', '^d$', 1, 'm') FROM DUAL;
regexp_count
--------------
1
(1 row)
REGEXP_INSTR
REGEXP_INSTR,返回模式匹配所在的字符串中的开始或结束位置。
postgres=# \df REGEXP_INSTR
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+--------------+------------------+------------------------------------------------------+------
oracle | regexp_instr | integer | text, text | func
oracle | regexp_instr | integer | text, text, integer | func
oracle | regexp_instr | integer | text, text, integer, integer | func
oracle | regexp_instr | integer | text, text, integer, integer, integer | func
oracle | regexp_instr | integer | text, text, integer, integer, integer, text | func
oracle | regexp_instr | integer | text, text, integer, integer, integer, text, integer | func
(6 rows)
示例:
postgres=# SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('1234567890', '(123)(4(56)(78))') FROM DUAL;
regexp_instr
--------------
1
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('1234567890', '(4(56)(78))', 3) FROM DUAL;
regexp_instr
--------------
4
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('199 Oretax Prayers, Riffles Stream, CA', '[S|R|P][[:alpha:]]{6}', 3, 2, 1) FROM DUAL;
regexp_instr
--------------
28
(1 row)
-- 以下这个返回的结果是错误的,版本 orafce 3.18
postgres=# SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('123 123456 1234567, 1234567 1234567 12', '[^ ]+', 1, 6) FROM DUAL;
regexp_instr
--------------
1
(1 row)
SQL> SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('123 123456 1234567, 1234567 1234567 12', '[^ ]+', 1, 6) FROM DUAL;
REGEXP_INSTR('1231234561234567,1234567123456712','[^]+',1,6)
------------------------------------------------------------
37
此问题已解决,详见:https://github.com/orafce/orafce/issues/171
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.regexp_instr(text, text, integer, integer)
RETURNS integer
LANGUAGE plpgsql
STRICT
AS $function$
DECLARE
v_pos integer;
v_pattern text;
r record;
start_pos integer DEFAULT 1;
new_start integer;
BEGIN
IF $3 < 1 THEN
RAISE EXCEPTION 'argument ''position'' must be a number greater than 0';
END IF;
IF $4 < 1 THEN
RAISE EXCEPTION 'argument ''occurence'' must be a number greater than 0';
END IF;
-- Without subexpression specified, assume 0 which mean that the first
-- position for the substring matching the whole pattern is returned.
-- We need to enclose the pattern between parentheses.
v_pattern := '(' || $2 || ')';
-- Oracle default behavior is newline-sensitive,
-- PostgreSQL not, so force 'p' modifier to affect
-- newline-sensitivity but not ^ and $ search.
$1 := substr($1, $3);
start_pos := $3;
FOR r IN SELECT (regexp_matches($1, v_pattern, 'pg'))[1]
LOOP
v_pos := position(r.regexp_matches IN $1);
IF $4 = 1 THEN
RETURN v_pos + start_pos - 1;
ELSE
$4 := $4 - 1;
END IF;
new_start := v_pos + length(r.regexp_matches);
$1 := substr($1, new_start);
start_pos := start_pos + new_start - 1;
END LOOP;
RETURN 0;
END;
$function$
;
postgres=# SELECT REGEXP_INSTR('123 123456 1234567, 1234567 1234567 12', '[^ ]+', 1, 6) FROM DUAL;
regexp_instr
--------------
37
(1 row)
REGEXP_LIKE
REGEXP_LIKE,返回一个布尔值,用于确定字符串是否匹配正则表达式
postgres=# \df REGEXP_LIKE
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+-------------+------------------+---------------------+------
oracle | regexp_like | boolean | text, text | func
oracle | regexp_like | boolean | text, text, text | func
(2 rows)
示例:
postgres=# SELECT REGEXP_LIKE('a'||CHR(10)||'d', 'a.d', 'm') FROM DUAL;
regexp_like
-------------
f
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT REGEXP_LIKE('a'||CHR(10)||'d', 'a.d', 'n') FROM DUAL;
regexp_like
-------------
t
(1 row)
REGEXP_SUBSTR
REGEXP_SUBSTR,返回与函数调用中指定的模式匹配的字符串。
postgres=# \df REGEXP_SUBSTR
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+---------------+------------------+---------------------------------------------+------
oracle | regexp_substr | text | text, text | func
oracle | regexp_substr | text | text, text, integer | func
oracle | regexp_substr | text | text, text, integer, integer | func
oracle | regexp_substr | text | text, text, integer, integer, text | func
oracle | regexp_substr | text | text, text, integer, integer, text, integer | func
(5 rows)
示例:
postgres=# SELECT REGEXP_SUBSTR('number of your street, zipcode town, FR', ',[^,]+') FROM DUAL;
regexp_substr
----------------
, zipcode town
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT regexp_substr('number of your street, zipcode town, FR', ',[^,]+', 24) FROM DUAL;
regexp_substr
---------------
, FR
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT regexp_substr('number of your street, zipcode town, FR', ',[^,]+', 1, 2) FROM DUAL;
regexp_substr
---------------
, FR
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT regexp_substr('1234567890 1234567890', '(123)(4(56)(78))', 1, 1, 'i', 0) FROM DUAL;
regexp_substr
---------------
12345678
(1 row)
REGEXP_REPLACE
REGEXP_REPLACE,返回与函数调用中指定的模式匹配的字符串。
PostgreSQL 也自带了这个函数,orafce 对这个函数做个改进。
-- 未安装 orafce
postgres=# \df REGEXP_REPLACE
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+----------------+------------------+------------------------+------
pg_catalog | regexp_replace | text | text, text, text | func
pg_catalog | regexp_replace | text | text, text, text, text | func
(2 rows)
-- 安装 orafce
postgres=# \df REGEXP_REPLACE
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+----------------+------------------+------------------------------------------+------
oracle | regexp_replace | text | text, text, text | func
oracle | regexp_replace | text | text, text, text, integer | func
oracle | regexp_replace | text | text, text, text, integer, integer | func
oracle | regexp_replace | text | text, text, text, integer, integer, text | func
pg_catalog | regexp_replace | text | text, text, text, text | func
(5 rows)
示例:
postgres=# SELECT regexp_replace('512.123.4567 612.123.4567', '([[:digit:]]{3})\.([[:digit:]]{3})\.([[:digit:]]{4})', '(\1) \2-\3') FROM DUAL;
regexp_replace
-------------------------------
(512) 123-4567 (612) 123-4567
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT oracle.REGEXP_REPLACE('number your street, zipcode town, FR', '( ){2,}', ' ', 9);
regexp_replace
----------------------------------------
number your street, zipcode town, FR
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT oracle.REGEXP_REPLACE('number your street, zipcode town, FR', '( ){2,}', ' ', 9, 2);
regexp_replace
---------------------------------------------
number your street, zipcode town, FR
(1 row)
SUBSTR
SUBSTR,在字符串的提取指定位置和长度的一部分字符。
PostgreSQL 也自带了这个函数,orafce 对这个函数做个改进。
-- 未安装 orafce
postgres=# \df SUBSTR
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+--------+------------------+-------------------------+------
pg_catalog | substr | bytea | bytea, integer | func
pg_catalog | substr | bytea | bytea, integer, integer | func
pg_catalog | substr | text | text, integer | func
pg_catalog | substr | text | text, integer, integer | func
(4 rows)
-- 安装 orafce
postgres=# \df SUBSTR
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+--------+------------------+--------------------------------------+------
oracle | substr | text | character varying, numeric | func
oracle | substr | text | character varying, numeric, numeric | func
oracle | substr | text | numeric, numeric | func
oracle | substr | text | numeric, numeric, numeric | func
oracle | substr | text | str text, start integer | func
oracle | substr | text | str text, start integer, len integer | func
pg_catalog | substr | bytea | bytea, integer | func
pg_catalog | substr | bytea | bytea, integer, integer | func
(8 rows)
示例:
postgres=# SELECT SUBSTR('ABCDEFG',3,4) "Substring" FROM DUAL;
Substring
-----------
CDEF
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT SUBSTR('ABCDEFG',-5,4) "Substring" FROM DUAL;
Substring
-----------
CDEF
(1 row)
SUBSTRB
SUBSTRB,在字符串的提取指定位置和长度的一部分字符。
postgres=# \df SUBSTRB
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+---------+------------------+----------------------------+------
pg_catalog | substrb | varchar2 | varchar2, integer | func
pg_catalog | substrb | varchar2 | varchar2, integer, integer | func
(2 rows)
示例:
postgres=# SELECT SUBSTRB('aaabbbccc',4,3) FROM DUAL;
substrb
---------
bbb
(1 row)
-- 以下这个返回的结果应该是错误的
postgres=# SELECT SUBSTRB('aaabbbccc',-2,6) FROM DUAL;
substrb
---------
aaa
(1 row)
SQL> SELECT SUBSTRB('aaabbbccc',-2,6) FROM DUAL;
SU
--
cc
问题已解决,详见:https://www.modb.pro/db/389172
Date/time 函数
ADD_MONTHS
ADD_MONTHS,返回加月份的日期
postgres=# \df ADD_MONTHS
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+------------+-----------------------------+------------------------------------+------
oracle | add_months | timestamp without time zone | timestamp with time zone, integer | func
pg_catalog | add_months | pg_catalog.date | day pg_catalog.date, value integer | func
(2 rows)
下面的示例显示了在 2016 年 5 月 1 日上加 3 个月的结果。
postgres=# SELECT ADD_MONTHS(to_date('2016/05/01','YYYY/MM/DD'),3) from dual;
add_months
---------------------
2016-08-01 00:00:00
(1 row)
DBTIMEZONE
DBTIMEZONE,返回数据库时区
postgres=# \df DBTIMEZONE
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+------------+------------------+---------------------+------
oracle | dbtimezone | text | | func
(1 row)
示例:
postgres=# SELECT DBTIMEZONE() FROM DUAL;
dbtimezone
------------
PRC
(1 row)
-- oracle,加括号会报错误,但这个函数在程序上一般用不上
SQL> SELECT DBTIMEZONE() FROM DUAL;
SELECT DBTIMEZONE() FROM DUAL
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-00923: FROM keyword not found where expected
SQL> SELECT DBTIMEZONE FROM DUAL;
DBTIME
------
+00:00
SESSIONTIMEZONE
SESSIONTIMEZONE,返回会话的时区。
postgres=# \df SESSIONTIMEZONE
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+-----------------+------------------+---------------------+------
oracle | sessiontimezone | text | | func
(1 row)
在以下示例中,将返回会话的时区。
postgres=# SELECT SESSIONTIMEZONE() FROM DUAL;
sessiontimezone
-----------------
PRC
(1 row)
-- oracle,加括号会报错误,但这个函数在程序上一般用不上
SQL> SELECT SESSIONTIMEZONE() FROM DUAL;
SELECT SESSIONTIMEZONE() FROM DUAL
*
ERROR at line 1:
ORA-00923: FROM keyword not found where expected
SQL> SELECT SESSIONTIMEZONE FROM DUAL;
SESSIONTIMEZONE
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
+08:00
LAST_DAY
LAST_DAY,返回指定日期所在月份的最后一天
postgres=# \df LAST_DAY
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+----------+-----------------------------+--------------------------+------
oracle | last_day | timestamp without time zone | timestamp with time zone | func
pg_catalog | last_day | pg_catalog.date | value pg_catalog.date | func
(2 rows)
在下面的示例中,返回 “2016 年 2 月 1 日” 的最后日期:
postgres=# SELECT LAST_DAY(to_date('2016/02/01','YYYY/MM/DD')) from dual;
last_day
---------------------
2016-02-29 00:00:00
(1 row)
MONTHS_BETWEEN
MONTHS_BETWEEN,返回两个日期之间的月数
postgres=# \df MONTHS_BETWEEN
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+----------------+------------------+----------------------------------------------------+------
oracle | months_between | numeric | timestamp with time zone, timestamp with time zone | func
pg_catalog | months_between | numeric | date1 pg_catalog.date, date2 pg_catalog.date | func
(2 rows)
在以下示例中,将返回 “2016 年 3 月 15 日” 和 “2015 年 11 月 15 日” 之间的月份差。
postgres=# SELECT MONTHS_BETWEEN(to_date('2016/03/15','YYYY/MM/DD'), to_date('2015/11/15','YYYY/MM/DD')) FROM DUAL;
months_between
----------------
4
(1 row)
NEXT_DAY
NEXT_DAY,返回指定日期之后一周内特定日期的日期。
postgres=# \df NEXT_DAY
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+----------+-----------------------------+----------------------------------------+------
oracle | next_day | timestamp without time zone | timestamp with time zone, integer | func
oracle | next_day | timestamp without time zone | timestamp with time zone, text | func
pg_catalog | next_day | pg_catalog.date | value pg_catalog.date, weekday integer | func
pg_catalog | next_day | pg_catalog.date | value pg_catalog.date, weekday text | func
(4 rows)
在下面的示例中,返回 “2016 年 5 月 1 日” 之后的第一个星期五的日期。
postgres=# SELECT NEXT_DAY(to_date('2016/05/01','YYYY/MM/DD'), 'Friday') FROM DUAL;
next_day
---------------------
2016-05-06 00:00:00
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT NEXT_DAY(to_date('2016/05/01','YYYY/MM/DD'), 6) FROM DUAL;
next_day
---------------------
2016-05-06 00:00:00
(1 row)
ROUND and TRUNC
ROUND,对日期进行四舍五入。TRUNC,截断日期,截取时不进行四舍五入。
PostgreSQL 也自带了这两个函数,但是不能操作日期类型,orafce 对这两个函数做个改进。
-- 未安装 orafce
postgres=# \df ROUND
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+-------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | round | double precision | double precision | func
pg_catalog | round | numeric | numeric | func
pg_catalog | round | numeric | numeric, integer | func
(3 rows)
postgres=# \df TRUNC
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+-------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | trunc | double precision | double precision | func
pg_catalog | trunc | macaddr | macaddr | func
pg_catalog | trunc | macaddr8 | macaddr8 | func
pg_catalog | trunc | numeric | numeric | func
pg_catalog | trunc | numeric | numeric, integer | func
(5 rows)
-- 安装 orafce
postgres=# \df ROUND
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+-------+-----------------------------+---------------------------------------------+------
oracle | round | numeric | double precision, integer | func
oracle | round | numeric | real, integer | func
pg_catalog | round | double precision | double precision | func
pg_catalog | round | numeric | numeric | func
pg_catalog | round | numeric | numeric, integer | func
pg_catalog | round | pg_catalog.date | value pg_catalog.date | func
pg_catalog | round | pg_catalog.date | value pg_catalog.date, fmt text | func
pg_catalog | round | timestamp without time zone | value timestamp without time zone | func
pg_catalog | round | timestamp without time zone | value timestamp without time zone, fmt text | func
pg_catalog | round | timestamp with time zone | value timestamp with time zone | func
pg_catalog | round | timestamp with time zone | value timestamp with time zone, fmt text | func
(11 rows)
postgres=# \df TRUNC
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+-------+-----------------------------+---------------------------------------------+------
oracle | trunc | numeric | double precision, integer | func
oracle | trunc | numeric | real, integer | func
pg_catalog | trunc | double precision | double precision | func
pg_catalog | trunc | macaddr | macaddr | func
pg_catalog | trunc | macaddr8 | macaddr8 | func
pg_catalog | trunc | numeric | numeric | func
pg_catalog | trunc | numeric | numeric, integer | func
pg_catalog | trunc | pg_catalog.date | value pg_catalog.date | func
pg_catalog | trunc | pg_catalog.date | value pg_catalog.date, fmt text | func
pg_catalog | trunc | timestamp without time zone | value timestamp without time zone | func
pg_catalog | trunc | timestamp without time zone | value timestamp without time zone, fmt text | func
pg_catalog | trunc | timestamp with time zone | value timestamp with time zone | func
pg_catalog | trunc | timestamp with time zone | value timestamp with time zone, fmt text | func
(13 rows)
在下面的示例中,返回 “2016 年 6 月 20 日 18:00:00” 按星期几进行四舍五入的结果。
postgres=# SELECT ROUND(to_date('2016/06/20 18:00:00','YYYY/MM/DD HH24:MI:SS'),'DAY') FROM DUAL;
round
---------------------
2016-06-19 00:00:00
(1 row)
在下面的示例中,返回按天截断的 “2016 年 8 月 10 日 15:30:00” 的结果。
postgres=# SELECT TRUNC(to_date('2016/08/10 15:30:00','YYYY/MM/DD HH24:MI:SS'),'DAY') FROM DUAL;
trunc
---------------------
2016-08-07 00:00:00
(1 row)
SYSDATE
SYSDATE,返回系统日期。
postgres=# \df SYSDATE
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+---------+------------------+---------------------+------
oracle | sysdate | date | | func
(1 row)
在以下示例中,将返回系统日期。
postgres=# SELECT SYSDATE() FROM DUAL;
sysdate
---------------------
2022-04-01 21:54:40
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT SYSDATE FROM DUAL;
ERROR: column "sysdate" does not exist
LINE 1: SELECT SYSDATE FROM DUAL;
-- 问题:SYSDATE需要加括号(),而 oracle 不带括号()
SQL> SELECT SYSDATE FROM DUAL;
SYSDATE
-------------------
2022-04-01 21:55:03
使用 SYSDATE 作为默认值建表
postgres=# CREATE TABLE channels (
postgres(# updateTimeStamp DATE default (SYSDATE),
postgres(# createTimeStamp DATE default (SYSDATE)
postgres(# );
ERROR: cannot use column reference in DEFAULT expression
LINE 2: updateTimeStamp DATE default (SYSDATE),
^
postgres=# CREATE TABLE channels2 (
postgres(# updateTimeStamp DATE default (SYSDATE()),
postgres(# createTimeStamp DATE default (SYSDATE())
postgres(# );
CREATE TABLE
题外话,oracle 的 sysdate 函数与 PostgreSQL 的哪个时间函数最类似
postgres=# select pg_sleep(5),clock_timestamp() from generate_series(1,2);
pg_sleep | clock_timestamp
----------+-------------------------------
| 2022-03-31 16:59:43.000442+08
| 2022-03-31 16:59:48.00597+08
(2 rows)
postgres=# select pg_sleep(5),now() from generate_series(1,2);
pg_sleep | now
----------+-------------------------------
| 2022-03-31 17:00:05.911341+08
| 2022-03-31 17:00:05.911341+08
(2 rows)
postgres=# select pg_sleep(5),transaction_timestamp() from generate_series(1,2);
pg_sleep | transaction_timestamp
----------+-------------------------------
| 2022-03-31 17:00:42.874299+08
| 2022-03-31 17:00:42.874299+08
(2 rows)
postgres=# select pg_sleep(5),current_timestamp from generate_series(1,2);
pg_sleep | current_timestamp
----------+-------------------------------
| 2022-03-31 17:01:55.394196+08
| 2022-03-31 17:01:55.394196+08
(2 rows)
postgres=# select pg_sleep(5),statement_timestamp() from generate_series(1,2);
pg_sleep | statement_timestamp
----------+-------------------------------
| 2022-03-31 17:02:24.156702+08
| 2022-03-31 17:02:24.156702+08
(2 rows)
postgres=# select pg_sleep(5),oracle.sysdate() from generate_series(1,2);
pg_sleep | sysdate
----------+---------------------
| 2022-03-31 09:15:25
| 2022-03-31 09:15:25
(2 rows)
只有 clock_timestamp()函数在单个事务中返回不同的时间信息。
oracle 中的 sysdate 不带 timezone,oracle 的 sysdate 从 sql 开始时取值,整个 SQL 执行期间不变。
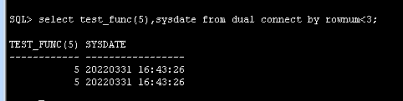
test_func 每次 sleep 5秒,在ORACLE sysdate返回相同的结果
数据类型格式化函数
TO_CHAR
TO_CHAR,将值转换为字符串。
PostgreSQL 也自带了这个函数,orafce 对这个函数做个改进。
-- 未安装 orafce
postgres=# \df TO_CHAR
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+---------+------------------+-----------------------------------+------
pg_catalog | to_char | text | bigint, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | double precision, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | integer, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | interval, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | numeric, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | real, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | timestamp without time zone, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | timestamp with time zone, text | func
(8 rows)
-- 安装 orafce
postgres=# \df TO_CHAR
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+---------+------------------+-----------------------------------+------
oracle | to_char | text | timestamp without time zone | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | bigint, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | double precision, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | integer, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | interval, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | num bigint | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | num double precision | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | numeric, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | num integer | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | num numeric | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | num real | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | num smallint | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | real, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | timestamp without time zone, text | func
pg_catalog | to_char | text | timestamp with time zone, text | func
(15 rows)
示例:
postgres=# SELECT TO_CHAR(123.45) FROM DUAL;
to_char
---------
123.45
(1 row)
-- 转换日期格式
postgres=# select * from test_range;
id | create_time
----+---------------------
1 | 2022-04-01 10:08:18
(1 row)
postgres=# select TO_CHAR(create_time,'YYYY/MM/DD HH24:MI:SS') from test_range;
to_char
---------------------
2022/04/01 10:08:18
(1 row)
-- 可以使用 orafce.nls_date_format 变量设置日期/时间格式
postgres=# SET orafce.nls_date_format = 'YYYY/MM/DD HH24:MI:SS';
SET
postgres=# select TO_CHAR(create_time) from test_range;
to_char
---------------------
2022/04/01 10:08:18
(1 row)
postgres=# SET orafce.nls_date_format = 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS';
SET
postgres=# select TO_CHAR(create_time) from test_range;
to_char
---------------------
2022-04-01 10:08:18
(1 row)
TO_DATE
TO_DATE,根据指定格式将字符串转换为日期。
PostgreSQL 也自带了这个函数,orafce 对这个函数做个改进。
-- 未安装 orafce
postgres=# \df TO_DATE
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+---------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | to_date | date | text, text | func
(1 row)
-- 安装 orafce
postgres=# \df TO_DATE
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+---------+------------------+---------------------+------
oracle | to_date | date | text | func
oracle | to_date | date | text, text | func
(2 rows)
在以下示例中,字符串 “2016/12/31” 被转换为日期并返回
postgres=# SELECT TO_DATE('2016/12/31','YYYY/MM/DD') FROM DUAL;
to_date
---------------------
2016-12-31 00:00:00
(1 row)
-- 问题:orafce.nls_date_format 似乎对 TO_DATE 不起作用
postgres=# SET orafce.nls_date_format = 'YYYY/MM/DD HH24:MI:SS';
SET
postgres=# SELECT TO_DATE('2016/12/31','YYYY/MM/DD') FROM DUAL;
to_date
---------------------
2016-12-31 00:00:00
(1 row)
TO_NUMBER
TO_NUMBER,根据指定格式将值转换为数字。
PostgreSQL 也自带了这个函数,orafce 对这个函数做个改进。
-- 未安装 orafce
postgres=# \df TO_NUMBER
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+-----------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | to_number | numeric | text, text | func
(1 row)
-- 安装 orafce
postgres=# \df TO_NUMBER
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+-----------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | to_number | numeric | numeric | func
pg_catalog | to_number | numeric | numeric, numeric | func
pg_catalog | to_number | numeric | str text | func
pg_catalog | to_number | numeric | text, text | func
(4 rows)
示例:
-- 数字文字 "-130.5" 被转换为数值并返回。
postgres=# SELECT TO_NUMBER(-130.5) FROM DUAL;
to_number
-----------
-130.5
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT TO_NUMBER('-130.5') FROM DUAL;
to_number
-----------
-130.5
(1 row)
-- 转换 varchar2
postgres=# \d tt2
Table "public.tt2"
Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default
--------+----------------+-----------+----------+---------
id | varchar2(100) | | |
name | nvarchar2(100) | | |
ctime | date | | |
postgres=# select id, TO_NUMBER(id) from tt2 where id = '3003963447';
id | to_number
------------+------------
3003963447 | 3003963447
TO_MULTI_BYTE
TO_MULTI_BYTE,将单字节字符串转换为多字节字符串,也是将半角字符转换为全角字符。
postgres=# \df TO_MULTI_BYTE
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+---------------+------------------+---------------------+------
public | to_multi_byte | text | str text | func
(1 row)
在以下示例中,“abc123” 被转换为全角字符并返回。
postgres=# SELECT TO_MULTI_BYTE('abc123') FROM DUAL;
to_multi_byte
---------------
abc123
(1 row)
TO_SINGLE_BYTE
TO_SINGLE_BYTE,将多字节字符串转换为单字节字符串,也是将全角字符转换为半角字符。
postgres=# \df TO_SINGLE_BYTE
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+----------------+------------------+---------------------+------
public | to_single_byte | text | str text | func
(1 row)
在以下示例中,“abc123” 被转换为半角字符并返回。
postgres=# SELECT TO_SINGLE_BYTE('abc123') FROM DUAL;
to_single_byte
----------------
abc123
(1 row)
条件表达式函数
DECODE
DECODE,比较值,如果它们匹配,则返回相应的值。
PostgreSQL 也自带了这个函数,orafce 对这个函数做个改进。
-- 未安装 orafce
postgres=# \df DECODE
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+--------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | decode | bytea | text, text | func
(1 row)
-- 安装 orafce
postgres=# \df DECODE
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+--------+-----------------------------+--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------
pg_catalog | decode | bytea | text, text | func
public | decode | bigint | anyelement, anyelement, bigint | func
public | decode | bigint | anyelement, anyelement, bigint, anyelement, bigint | func
public | decode | bigint | anyelement, anyelement, bigint, anyelement, bigint, anyelement, bigint | func
public | decode | bigint | anyelement, anyelement, bigint, anyelement, bigint, anyelement, bigint, bigint | func
public | decode | bigint | anyelement, anyelement, bigint, anyelement, bigint, bigint | func
public | decode | bigint | anyelement, anyelement, bigint, bigint | func
public | decode | character | anyelement, anyelement, character | func
public | decode | character | anyelement, anyelement, character, anyelement, character | func
public | decode | character | anyelement, anyelement, character, anyelement, character, anyelement, character | func
public | decode | character | anyelement, anyelement, character, anyelement, character, anyelement, character, character | func
public | decode | character | anyelement, anyelement, character, anyelement, character, character | func
public | decode | character | anyelement, anyelement, character, character | func
public | decode | integer | anyelement, anyelement, integer | func
public | decode | integer | anyelement, anyelement, integer, anyelement, integer | func
public | decode | integer | anyelement, anyelement, integer, anyelement, integer, anyelement, integer | func
public | decode | integer | anyelement, anyelement, integer, anyelement, integer, anyelement, integer, integer | func
public | decode | integer | anyelement, anyelement, integer, anyelement, integer, integer | func
public | decode | integer | anyelement, anyelement, integer, integer | func
public | decode | numeric | anyelement, anyelement, numeric | func
public | decode | numeric | anyelement, anyelement, numeric, anyelement, numeric | func
public | decode | numeric | anyelement, anyelement, numeric, anyelement, numeric, anyelement, numeric | func
public | decode | numeric | anyelement, anyelement, numeric, anyelement, numeric, anyelement, numeric, numeric | func
public | decode | numeric | anyelement, anyelement, numeric, anyelement, numeric, numeric | func
public | decode | numeric | anyelement, anyelement, numeric, numeric | func
public | decode | pg_catalog.date | anyelement, anyelement, pg_catalog.date | func
public | decode | pg_catalog.date | anyelement, anyelement, pg_catalog.date, anyelement, pg_catalog.date | func
public | decode | pg_catalog.date | anyelement, anyelement, pg_catalog.date, anyelement, pg_catalog.date, anyelement, pg_catalog.date | func
public | decode | pg_catalog.date | anyelement, anyelement, pg_catalog.date, anyelement, pg_catalog.date, anyelement, pg_catalog.date, pg_catalog.date | func
public | decode | pg_catalog.date | anyelement, anyelement, pg_catalog.date, anyelement, pg_catalog.date, pg_catalog.date | func
public | decode | pg_catalog.date | anyelement, anyelement, pg_catalog.date, pg_catalog.date | func
public | decode | text | anyelement, anyelement, text | func
public | decode | text | anyelement, anyelement, text, anyelement, text | func
public | decode | text | anyelement, anyelement, text, anyelement, text, anyelement, text | func
public | decode | text | anyelement, anyelement, text, anyelement, text, anyelement, text, text | func
public | decode | text | anyelement, anyelement, text, anyelement, text, text | func
public | decode | text | anyelement, anyelement, text, text | func
public | decode | timestamp without time zone | anyelement, anyelement, timestamp without time zone | func
public | decode | timestamp without time zone | anyelement, anyelement, timestamp without time zone, anyelement, timestamp without time zone | func
public | decode | timestamp without time zone | anyelement, anyelement, timestamp without time zone, anyelement, timestamp without time zone, anyelement, timestamp without time zone | func
public | decode | timestamp without time zone | anyelement, anyelement, timestamp without time zone, anyelement, timestamp without time zone, anyelement, timestamp without time zone, timestamp without time zone | func
public | decode | timestamp without time zone | anyelement, anyelement, timestamp without time zone, anyelement, timestamp without time zone, timestamp without time zone | func
public | decode | timestamp without time zone | anyelement, anyelement, timestamp without time zone, timestamp without time zone | func
public | decode | timestamp with time zone | anyelement, anyelement, timestamp with time zone | func
public | decode | timestamp with time zone | anyelement, anyelement, timestamp with time zone, anyelement, timestamp with time zone | func
public | decode | timestamp with time zone | anyelement, anyelement, timestamp with time zone, anyelement, timestamp with time zone, anyelement, timestamp with time zone | func
public | decode | timestamp with time zone | anyelement, anyelement, timestamp with time zone, anyelement, timestamp with time zone, anyelement, timestamp with time zone, timestamp with time zone | func
public | decode | timestamp with time zone | anyelement, anyelement, timestamp with time zone, anyelement, timestamp with time zone, timestamp with time zone | func
public | decode | timestamp with time zone | anyelement, anyelement, timestamp with time zone, timestamp with time zone | func
public | decode | time without time zone | anyelement, anyelement, time without time zone | func
public | decode | time without time zone | anyelement, anyelement, time without time zone, anyelement, time without time zone | func
public | decode | time without time zone | anyelement, anyelement, time without time zone, anyelement, time without time zone, anyelement, time without time zone | func
public | decode | time without time zone | anyelement, anyelement, time without time zone, anyelement, time without time zone, anyelement, time without time zone, time without time zone | func
public | decode | time without time zone | anyelement, anyelement, time without time zone, anyelement, time without time zone, time without time zone | func
public | decode | time without time zone | anyelement, anyelement, time without time zone, time without time zone | func
(55 rows)
- DECODE 将要转换的值与搜索值一一进行比较。如果值匹配,则返回相应的结果值。如果没有匹配的值,则返回已指定的默认值。如果未指定默认值,则返回 NULL 值。
- 如果多次指定相同的搜索值,则返回的结果值是为第一次出现的搜索值列出的值。
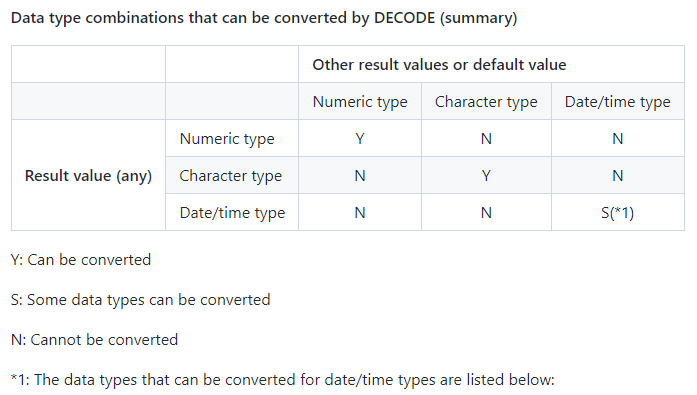
- 以下数据类型可用于结果值和默认值:
CHAR
VARCHAR
VARCHAR2
NCHAR
NCHAR VARYING
NVARCHAR2
TEXT
INTEGER
BIGINT
NUMERIC
DATE
TIME WITHOUT TIME ZONE
TIMESTAMP WITHOUT TIME ZONE
TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE - DECODE 可以转换的数据类型组合(总结)
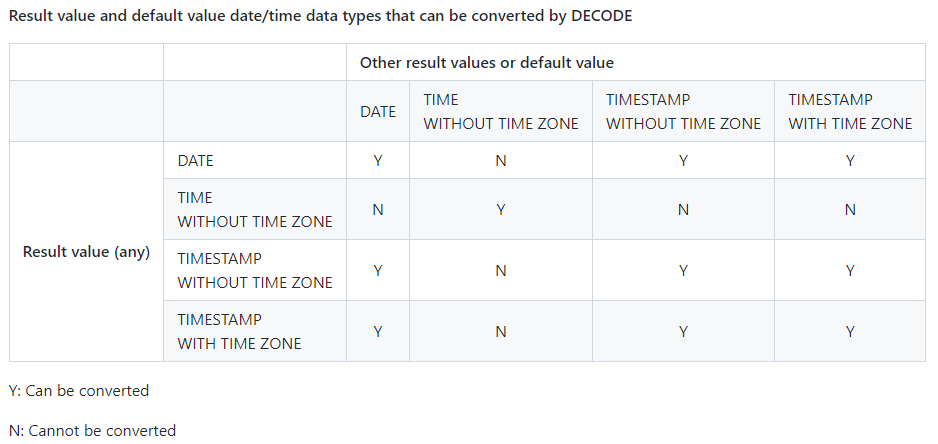
- 可通过 DECODE 转换的结果值和默认值日期/时间数据类型
在以下示例中,比较表 t1 中 col3 的值并将其转换为不同的值。如果 col3 值与搜索值 1 匹配,则返回的结果值为 “one”。如果 col3 值不匹配任何搜索值 1、2 或 3,则返回默认值 “other number”。
drop table tt;
create table tt (col1 int,col3 int);
insert into tt values (1001,1),(2001,2),(3001,3),(4001,4);
SELECT col1,
DECODE(col3, 1, 'one',
2, 'two',
3, 'three',
'other number') "num-word"
FROM tt;
col1 | num-word
------+--------------
1001 | one
2001 | two
3001 | three
4001 | other number
(4 rows)
GREATEST and LEAST
GREATEST 和 LEAST 函数从任意数量的表达式列表中选择最大值或最小值。表达式必须都可以转换为通用数据类型,这将是结果的类型
这两个函数与 PostgreSQL 自带的行为相同,只是不是仅在所有参数为 NULL 时才返回 NULL ,而是在其中一个参数为 NULL 时返回 NULL ,就像在 Oracle 中一样。
postgres=# \df GREATEST
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+----------+-----------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------
oracle | greatest | anynonarray | anynonarray, VARIADIC anyarray | func
oracle | greatest | bigint | bigint, bigint | func
oracle | greatest | bigint | bigint, bigint, bigint | func
oracle | greatest | character | character, character | func
oracle | greatest | character | character, character, character | func
oracle | greatest | integer | integer, integer | func
oracle | greatest | integer | integer, integer, integer | func
oracle | greatest | numeric | numeric, numeric | func
oracle | greatest | numeric | numeric, numeric, numeric | func
oracle | greatest | pg_catalog.date | pg_catalog.date, pg_catalog.date | func
oracle | greatest | pg_catalog.date | pg_catalog.date, pg_catalog.date, pg_catalog.date | func
oracle | greatest | smallint | smallint, smallint | func
oracle | greatest | smallint | smallint, smallint, smallint | func
oracle | greatest | text | text, text | func
oracle | greatest | text | text, text, text | func
oracle | greatest | timestamp without time zone | timestamp without time zone, timestamp without time zone | func
oracle | greatest | timestamp without time zone | timestamp without time zone, timestamp without time zone, timestamp without time zone | func
oracle | greatest | timestamp with time zone | timestamp with time zone, timestamp with time zone | func
oracle | greatest | timestamp with time zone | timestamp with time zone, timestamp with time zone, timestamp with time zone | func
oracle | greatest | time without time zone | time without time zone, time without time zone | func
oracle | greatest | time without time zone | time without time zone, time without time zone, time without time zone | func
(21 rows)
postgres=# \df LEAST
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+-------+-----------------------------+---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------+------
oracle | least | anynonarray | anynonarray, VARIADIC anyarray | func
oracle | least | bigint | bigint, bigint | func
oracle | least | bigint | bigint, bigint, bigint | func
oracle | least | character | character, character | func
oracle | least | character | character, character, character | func
oracle | least | integer | integer, integer | func
oracle | least | integer | integer, integer, integer | func
oracle | least | numeric | numeric, numeric | func
oracle | least | numeric | numeric, numeric, numeric | func
oracle | least | pg_catalog.date | pg_catalog.date, pg_catalog.date | func
oracle | least | pg_catalog.date | pg_catalog.date, pg_catalog.date, pg_catalog.date | func
oracle | least | smallint | smallint, smallint | func
oracle | least | smallint | smallint, smallint, smallint | func
oracle | least | text | text, text | func
oracle | least | text | text, text, text | func
oracle | least | timestamp without time zone | timestamp without time zone, timestamp without time zone | func
oracle | least | timestamp without time zone | timestamp without time zone, timestamp without time zone, timestamp without time zone | func
oracle | least | timestamp with time zone | timestamp with time zone, timestamp with time zone | func
oracle | least | timestamp with time zone | timestamp with time zone, timestamp with time zone, timestamp with time zone | func
oracle | least | time without time zone | time without time zone, time without time zone | func
oracle | least | time without time zone | time without time zone, time without time zone, time without time zone | func
(21 rows)
示例:
-- 返回最大值
postgres=# SELECT GREATEST ('C', 'F', 'E') from dual;
greatest
----------
F
(1 row)
-- 返回最小值,测试带 NULL 值的情况
-- PostgreSQL 自带的行为,仅在所有参数为 NULL 时才返回 NULL
postgres=# \pset null ###
postgres=# SELECT LEAST ('C', NULL, 'E');
least
-------
C
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT LEAST (NULL,NULL,NULL);
least
-------
###
(1 row)
-- Oracle,其中一个参数为 NULL 时就返回 NULL
SQL> SELECT LEAST ('C', NULL, 'E') from dual;
L
-
SQL>
-- orafce,也是其中一个参数为 NULL 时就返回 NULL ,就像在 Oracle 中一样。
postgres=# \pset null ###
postgres=# select oracle.least('C', NULL, 'E') from dual;
least
-------
###
(1 row)
LNNVL
LNNVL 确定指定条件的值是 TRUE 还是 FALSE。
如果条件的结果为 FALSE 或 NULL,则返回 TRUE。如果条件的结果为 TRUE,则返回 FALSE。
postgres=# \df LNNVL
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+-------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | lnnvl | boolean | boolean | func
(1 row)
在以下示例中,当 col3 的值小于等于 2000 或为空值时,将返回表 tt 的 col1 和 col3。
drop table tt;
create table tt (col1 int,col3 int);
insert into tt values (1001,1000),(1002,2000),(2002,null),(3001,3000);
postgres=# select * from tt;
col1 | col3
------+------
1001 | 1000
1002 | 2000
2002 |
3001 | 3000
(4 rows)
postgres=# SELECT col1,col3 FROM tt WHERE LNNVL( col3 > 2000 );
col1 | col3
------+------
1001 | 1000
1002 | 2000
2002 |
(3 rows)
NANVL
NANVL,当值不是数字 (NaN) 时返回替代值。
替代值可以是数字或可以转换为数字的字符串。
postgres=# \df NANVL
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+-------+------------------+-------------------------------------+------
public | nanvl | double precision | double precision, character varying | func
public | nanvl | double precision | double precision, double precision | func
public | nanvl | numeric | numeric, character varying | func
public | nanvl | numeric | numeric, numeric | func
public | nanvl | real | real, character varying | func
public | nanvl | real | real, real | func
(6 rows)
在以下示例中,如果表 tt 中 col3 的值为 NaN 值,则返回 “0”。
SELECT col1, NANVL(col3,0) FROM tt;
--不知道怎么插入 NaN 值,放弃本次测试
NVL
NVL,当值为 NULL 时返回替代值(必须是数值类型)。
postgres=# \df NVL
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+------+------------------+------------------------+------
oracle | nvl | bigint | bigint, integer | func
oracle | nvl | integer | integer, integer | func
oracle | nvl | numeric | numeric, integer | func
public | nvl | anyelement | anyelement, anyelement | func
(4 rows)
在以下示例中,如果表 tt 中 col3 的值为 NULL 值,则返回 “0”。
drop table tt;
create table tt (col1 int,col3 int);
insert into tt values (1001,1000),(1002,2000),(2002,null),(3001,3000);
postgres=# SELECT col1, NVL(col3,0) "nvl" FROM tt;
col1 | nvl
------+------
1001 | 1000
1002 | 2000
2002 | 0
3001 | 3000
(4 rows)
NVL2
NVL2,根据值是否为 NULL 返回替代值(不要求是数值类型)。
postgres=# \df NVL2
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+------+------------------+------------------------------------+------
public | nvl2 | anyelement | anyelement, anyelement, anyelement | func
(1 row)
在以下示例中,如果表 tt 中 col3 列的值为 NULL,则返回 “IS NULL”,如果不为 NULL,则返回 “IS NOT NULL”。
drop table tt;
create table tt (col1 int,col3 int);
insert into tt values (1001,1000),(1002,2000),(2002,null),(3001,3000);
-- oracle
SQL> SELECT col1, NVL2(col3,'IS NOT NULL','IS NULL') FROM tt;
COL1 NVL2(COL3,'
---------- -----------
1001 IS NOT NULL
1002 IS NOT NULL
2002 IS NULL
3001 IS NOT NULL
-- orafce 对这个函数似乎支持的还是有问题
postgres=# SELECT col1, NVL2(col3,0,1) FROM tt;
col1 | nvl2
------+------
1001 | 0
1002 | 0
2002 | 1
3001 | 0
(4 rows)
-- 返回数值类型的没问题,返回字符类型有问题
postgres=# SELECT col1, NVL2(col3,'IS NOT NULL','IS NULL') FROM tt;
ERROR: invalid input syntax for type integer: "IS NOT NULL"
LINE 1: SELECT col1, NVL2(col3,'IS NOT NULL','IS NULL') FROM tt;
^
问题已解决,详见:https://www.modb.pro/db/389172
聚合函数
LISTAGG
LISTAGG,连接并分隔一组字符串值并返回结果。
postgres=# \df LISTAGG
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+---------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | listagg | text | text | agg
pg_catalog | listagg | text | text, text | agg
(2 rows)
在以下示例中,将返回表 tt 中列 col1 的值由 ‘:’ 分隔的结果。
drop table tt;
create table tt (col1 int,col3 int);
insert into tt values (1001,1000),(1002,2000),(2002,null),(3001,3000);
-- oracle
SQL> SELECT LISTAGG(col1,':') WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY col1) from tt;
LISTAGG(COL1,':')WITHINGROUP(ORDERBYCOL1)
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
1001:1002:2002:3001
-- orafce,问题:不支持隐式转换
postgres=# SELECT LISTAGG(col1,':') FROM tt;
ERROR: function listagg(integer, unknown) does not exist
LINE 1: SELECT LISTAGG(col1,':') FROM tt;
^
HINT: No function matches the given name and argument types. You might need to add explicit type casts.
postgres=# SELECT LISTAGG(col1::text,':') FROM tt;
listagg
---------------------
1001:1002:2002:3001
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT LISTAGG(col3::text,':') FROM tt;
listagg
----------------
1000:2000:3000
(1 row)
-- orafce,问题:不能排序,不支持 oracle 的 WITHIN
drop table tt;
create table tt (col1 text,col3 int);
insert into tt values ('2001',1000),('1002',2000),('1002',null),('3001',3000);
postgres=# SELECT LISTAGG(col1,':') FROM tt;
listagg
---------------------
2001:1002:1002:3001
(1 row)
postgres=# SELECT LISTAGG(col1,':') WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY col1) from tt;
ERROR: function listagg(text, unknown, text) does not exist
LINE 1: SELECT LISTAGG(col1,':') WITHIN GROUP (ORDER BY col1) from t...
^
HINT: No function matches the given name and argument types. You might need to add explicit type casts.
MEDIAN
MEDIAN,计算一组数字的中位数。
postgres=# \df MEDIAN
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
------------+--------+------------------+---------------------+------
pg_catalog | median | double precision | double precision | agg
pg_catalog | median | real | real | agg
(2 rows)
在以下示例中,返回表 tt 中列 col1 的中位数。
drop table tt;
create table tt (col1 text,col3 int);
insert into tt values ('2001',1000),('1002',2000),('1002',null),('3001',3000);
-- 一样不支持隐式转换
postgres=# SELECT MEDIAN(col1) FROM tt;
ERROR: function median(text) does not exist
LINE 1: SELECT MEDIAN(col1) FROM tt;
^
HINT: No function matches the given name and argument types. You might need to add explicit type casts.
postgres=# SELECT MEDIAN(col1::double precision) FROM tt;
median
--------
1501.5
(1 row)
返回内部信息的函数
DUMP
DUMP,返回值的内部信息。
postgres=# \df DUMP
List of functions
Schema | Name | Result data type | Argument data types | Type
--------+------+-------------------+---------------------+------
public | dump | character varying | "any" | func
public | dump | character varying | "any", integer | func
public | dump | character varying | text | func
public | dump | character varying | text, integer | func
(4 rows)
在下面的示例中,返回表 tt 中列 col1 的内部信息。
drop table tt;
create table tt (col1 text,col3 int);
insert into tt values ('2001',1000),('1002',2000),('1002',null),('3001',3000);
postgres=# SELECT col1, DUMP(col1) FROM tt;
col1 | dump
------+------------------------------
2001 | Typ=25 Len=5: 11,50,48,48,49
1002 | Typ=25 Len=5: 11,49,48,48,50
1002 | Typ=25 Len=5: 11,49,48,48,50
3001 | Typ=25 Len=5: 11,51,48,48,49
(4 rows)
SQL 运算符
DATE 类型的 orafce 支持以下日期时间运算符。







