Table of Contents
Q1.combined indexes 和 multicolumn indexes的使用场景
问题描述
什么时候使用combined indexes(组合索引),什么时候使用multicolumn indexes(多列索引)?
问题解答
-
multicolumn indexes:一个索引可以定义在表的多个列上
CREATE INDEX idx_test_multi ON test (a, b); -
组合索引:查询时使用多个索引
查询规划器可以选择对查询执行多个位图索引扫描,然后通过
BitmapAnd / BitmapOr将它们组合成用于扫描堆的单个结构
合并位图扫描虽然高效,但每次额外的位图扫描都会增加总查询的成本。多列索引更有针对性,通常返回的结果也更少,这意味着更高效的对扫描效率。总的来说,多列索引适用于查询结果少,组合查询可能针对复杂查询更有效
Q2.allow_system_table_mods
问题描述
PostgreSQL 中allow_system_table_mods没有开启,是否还能修改系统表呢?
问题解答
postgres=# select name,setting,short_desc from pg_settings where name = 'allow_system_table_mods';
name | setting | short_desc
-------------------------+---------+---------------------------------------------------------
allow_system_table_mods | off | Allows modifications of the structure of system tables.
(1 row)
allow_system_table_mods是一个开发选项,允许对系统表的结构进行修改。它可以被initdb使用。这个参数只能在服务器启动时设置。默认值为off
注意:该参数是修改系统表的结构时的限制,普通表不会
普通表
postgres=# select attrelid::regclass,attname,atttypid::regtype from pg_attribute where attrelid='test'::regclass and attname = 'id' ; attrelid | attname | atttypid ----------+---------+---------- test | id | integer (1 row) postgres=# update pg_attribute set atttypid = 'int8'::regtype where attrelid='test'::regclass and attname = 'id'; UPDATE 1 postgres=# select attrelid::regclass,attname,atttypid::regtype from pg_attribute where attrelid='test'::regclass and attname = 'id' ; attrelid | attname | atttypid ----------+---------+---------- test | id | bigint (1 row)系统表:对系统表pg_class的relname列重命名
postgres=# show allow_system_table_mods ; allow_system_table_mods ------------------------- off (1 row) postgres=# alter table pg_class rename COLUMN relname to relname_test ; ERROR: permission denied: "pg_class" is a system catalog postgres=# alter system set allow_system_table_mods = on ; ALTER SYSTEM -- 重启 pg_ctl restart 后再次修改 postgres=# show allow_system_table_mods ; allow_system_table_mods ------------------------- on (1 row) postgres=# alter table pg_class rename COLUMN relname to relname_test ; ALTER TABLE postgres=# \d pg_class Table "pg_catalog.pg_class" Column | Type | Collation | Nullable | Default ---------------------+--------------+-----------+----------+--------- oid | oid | | not null | relname_test | name | | not null | ...
Q3.vacuum和analyze对表和索引的处理
问题描述
PostgreSQL中,vacuum
问题解答
vacuum的主要作用有两个,一个是清理死元组,另一个是冻结旧的txid;analyze是为了收集表的统计信息
默认的vacuum会对表和索引都进行处理,12版本引入INDEX_CLEANUP选项,可以跳过对索引的空间回收。analyze是收集表的统计信息,更新pg_statistic系统表,从而为辅助pg优化器做决策,让query执行的更好。
-
vacuum会对表和索引都进行扫描:
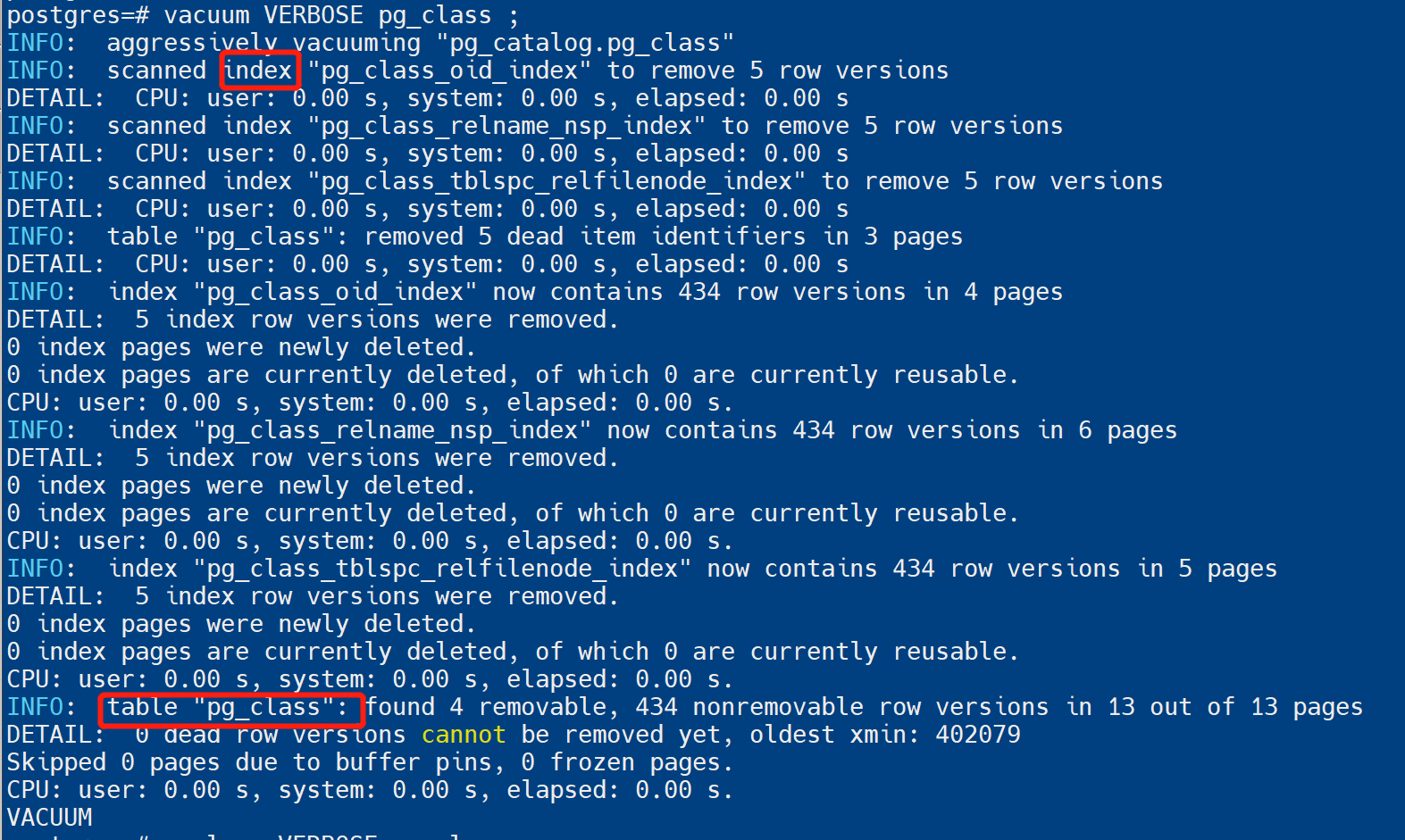
-
analyze对表进行处理:

Q4.默认权限的区别
问题描述
PostgreSQL中如何回收用户连接数据库的权限?
问题解答
有两种方式,一种是对单个数据库的connect权限回收,一种是对用户的登录权限回收
-- 创建用户
postgres=# create user utest ;
CREATE ROLE
-- 创建数据库
postgres=# create database a ;
CREATE DATABASE
postgres=# create database b ;
CREATE DATABASE
postgres=# create database c ;
CREATE DATABASE
-- 测试:用户utest 可以连接a,b,c数据库
postgres=# \connect a utest ;
You are now connected to database "a" as user "utest".
a=> \connect b utest ;
You are now connected to database "b" as user "utest".
b=> \connect c utest ;
You are now connected to database "c" as user "utest".
-- 需求:取消用户 utest 连接数据库 a,b,c 的权限
--# 法一:对于database,revoke用户的connect权限
postgres=# revoke CONNECT on DATABASE a from PUBLIC ;
REVOKE
postgres=# \connect a utest
connection to server on socket "/tmp/.s.PGSQL.6000" failed: FATAL: permission denied for database "a"
DETAIL: User does not have CONNECT privilege.
Previous connection kept
...
--# 法二:对于user,取消utest的login权限
postgres=# alter user utest NOLOGIN ;
ALTER ROLE
postgres=# \connect a utest
connection to server on socket "/tmp/.s.PGSQL.6000" failed: FATAL: role "utest" is not permitted to log in
Previous connection kept
在PostgreSQL中的权限分类:
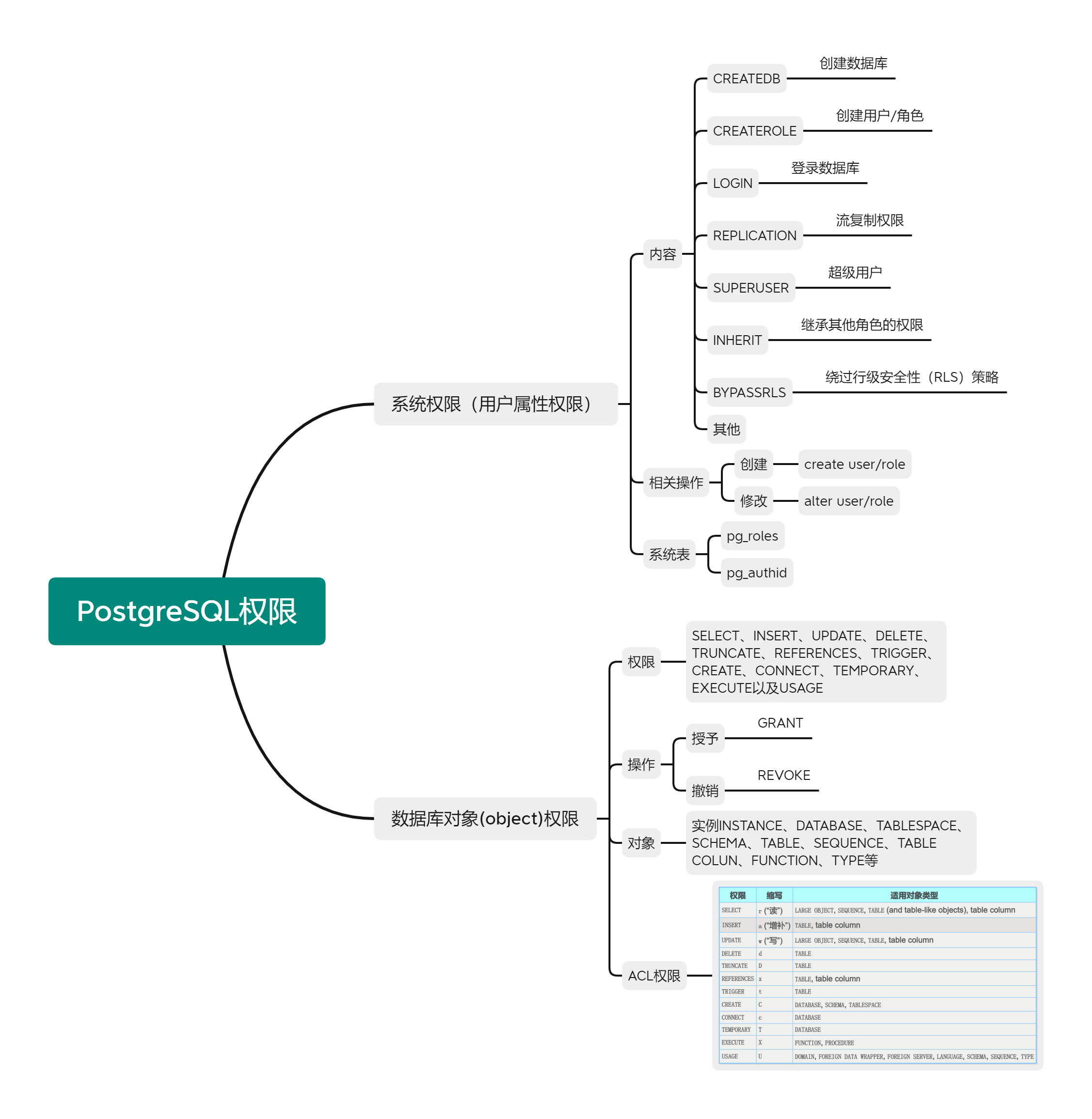
Q5.如何把linux用户跟postgreSQL数据库用户绑在一起?
问题描述
在PostgreSQL中,如何使用操作系统用户登录数据库?
问题解答
可以使用ident认证。
1)ident 认证的两种方式
- peer - 仅支持 unix 套接字
- ident - 可以支持 tcp/ip 方式连接
2)涉及到两个文件
-
pg_hba.conf (基于主机的认证文件)
-
pg_ident.conf (用户映射标识文件)
属性:
- mapname: 映射名称 (与 pg_hba.conf 中的映射名称一致[options])
- system-username: 操作系统用户名称
- pg-username: 数据库用户名称
3)作用:某个操作系统用户的应用单独跑业务
4)示例
操作系统用户 appuser 使用 ident 对等认证,使用 uident 用户登录到数据库 db_ident
-
创建操作系统用户
[root@og_node2 ~]# useradd -u 2001 appuser [root@og_node2 ~]# echo appuser | passwd --stdin appuser Changing password for user appuser. passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully. -
创建数据库 db_ident 和用户 uident
postgres=# create user uident with password 'uident' ; CREATE ROLE postgres=# create database db_ident owner uident ; CREATE DATABASE -
配置 pg_hba.conf 的用户认证名称
[lmj@og_node2 pgdata]$ cat pg_hba.conf | egrep -v "^#|^$" | grep ident host db_ident uident 192.168.183.142/32 ident map=ident_test -
配置 pg_ident.conf 文件
[lmj@og_node2 pgdata]$ cat pg_ident.conf | egrep -v "^#|^$" | grep ident ident_test appuser uident -
执行
pg_ctl reload重新加载[lmj@og_node2 pgdata]$ pg_ctl reload server signaled -
使用 appuser 操作系统用户连接数据库 - 连接失败。原因:没有启用 ident 服务
[appuser@og_node2 ~]$ /data/pgsql/bin/psql -d db_ident -U uident -h 192.168.183.142 psql: FATAL: Ident authentication failed for user "uident" -
启用 ident 服务
systemctl start oidentd.service -
再次使用 appuser 操作系统用户连接数据库 - 连接成功!
[appuser@og_node2 ~]$ /data/pgsql/bin/psql -d db_ident -U uident -h 192.168.183.142 psql (10.17) Type "help" for help. db_ident=>
5)注意:
- 在配置 pg_hba.conf 文件时的 option 为
map=MAPNAME - 使用其他操作系统用户(非初始化数据库的用户)连接数据库时需使用
psql的绝对路径,或者设置环境变量。 - 使用 ident 认证方式登录数据库需启动 oidentd 服务
- 应用场景:没有权限的操作系统用户通过 TCP/IP 网络使用 ident 认证可以跳过密码认证






