让我们从一些关于 MySQL Document Store 如何处理 JSON 文档的信息开始。
文档存储和 CRUD
我们知道 MySQL 8.0 Document Store 使用 CRUD 操作处理 JSON 文档。我们可以非常轻松地添加、删除和修改这些文档:
JS > db.mycollection.find()
{
"_id": "0000624d3e890000000000000001",
"name": "my_iot1",
"type": "sensor",
"capabilities": "{'temperature':'true','humidity':'true'}"
}
{
"_id": "0000624d3e890000000000000002",
"name": "my_iot2",
"type": "sensor",
"capabilities": "{'temperature':'true'}"
}
2 documents in set (0.0007 sec)
要修改文档,modify可以以不同的方式使用该方法:
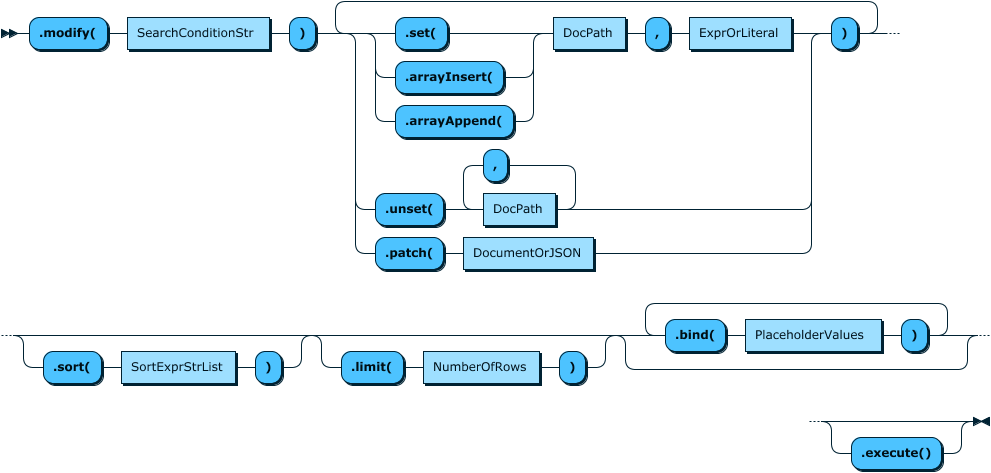
如上图所示,我们有:
- set()
- unset()
- patch()
- 和数组相关的方法
让我们看看如何使用它们:
set
JS > db.mycollection.modify("_id = '0000624d3e890000000000000002'").set("version", "0.1")
Query OK, 1 item affected (0.0031 sec)
JS > db.mycollection.find("_id = '0000624d3e890000000000000002'")
{
"_id": "0000624d3e890000000000000002",
"name": "my_iot2",
"type": "sensor",
"version": "0.1",
"capabilities": "{'temperature':'true'}"
}
1 document in set (0.0008 sec)
unset
JS > db.mycollection.modify("_id = '0000624d3e890000000000000002'").unset("version")
Query OK, 1 item affected (0.0030 sec)
JS > db.mycollection.find("_id = '0000624d3e890000000000000002'")
{
"_id": "0000624d3e890000000000000002",
"name": "my_iot2",
"type": "sensor",
"capabilities": "{'temperature':'true'}"
}
1 document in set (0.0005 sec)
patch
JS > db.mycollection.modify("_id = '0000624d3e890000000000000002'").patch({"version": "0.2", "name": "my_iot3"})
Query OK, 1 item affected (0.0033 sec)
JS > db.mycollection.find("_id = '0000624d3e890000000000000002'")
{
"_id": "0000624d3e890000000000000002",
"name": "my_iot3",
"type": "sensor",
"version": "0.2",
"capabilities": "{'temperature':'true'}"
}
1 document in set (0.0007 sec)
该patch()方法是我最喜欢的方法,因为它需要一个 JSON 条目并进行合并。
数组
allowed_users让我们添加一个包含数组的新属性 ( ):
JS > db.mycollection.modify("_id = '0000624d3e890000000000000002'").patch({"allowed_users": ["fred"]})
Query OK, 1 item affected (0.0032 sec)
JS > db.mycollection.find("_id = '0000624d3e890000000000000002'")
{
"_id": "0000624d3e890000000000000002",
"name": "my_iot3",
"type": "sensor",
"version": "0.2",
"allowed_users": [
"fred"
],
"capabilities": "{'temperature':'true'}"
}
1 document in set (0.0005 sec)
现在让我们添加一个条目:
JS > db.mycollection.modify("_id = '0000624d3e890000000000000002'").arrayAppend("allowed_users", "miguel")
Query OK, 1 item affected (0.0030 sec)
JS > db.mycollection.find("_id = '0000624d3e890000000000000002'")
{
"_id": "0000624d3e890000000000000002",
"name": "my_iot3",
"type": "sensor",
"version": "0.2",
"allowed_user": [
"fred",
"miguel"
],
"capabilities": "{'temperature':'true'}"
}
1 document in set (0.0007 sec)
现在要从数组中删除一个元素,我们需要提供它的索引:
JS > db.mycollection.modify("_id = '0000624d3e890000000000000002'").arrayDelete("allowed_user[1]")
Query OK, 1 item affected (0.0027 sec)
JS > db.mycollection.find("_id = '0000624d3e890000000000000002'")
{
"_id": "0000624d3e890000000000000002",
"name": "my_iot3",
"type": "sensor",
"version": "0.2",
"allowed_user": [
"fred"
],
"capabilities": "{'temperature':'true'}"
}
1 document in set (0.0006 sec)
我们可以看到数组的第一个元素是0。
SQL 中的 JSON
现在我们回顾了如何通过 X Dev API 使用 CRUD 操作处理 JSON,让我们看看如何在 SQL 中修改 JSON 列。
让我们使用下表:
CREATE TABLE `mytable` (
`id` int NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`inserted` timestamp NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`modified` timestamp NULL DEFAULT NULL ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
`attributes` json DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
我们有 2 条记录:
SQL > select * from mytable;
+----+---------+---------------------+----------+--------------------+
| id | name | inserted | modified | attributes |
+----+---------+---------------------+----------+--------------------+
| 1 | my_iot1 | 2022-04-06 09:48:54 | NULL | {"type": "sensor"} |
| 2 | my_iot2 | 2022-04-06 09:49:06 | NULL | {"type": "sensor"} |
+----+---------+---------------------+----------+--------------------+
要修改 SQL 中的 JSON 字段,我们需要使用专用函数:
- JSON_SET()
- JSON_INSERT()
- JSON_REPLACE()
- JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE()
- JSON_MERGE_PATCH()
- JSON_REMOVE()
- JSON_ARRAY_APPEND()和JSON_ARRAY_INSERT()
让我们看一些示例,首先将capabilities属性添加到表中所有记录的 JSON 列中:
JSON_SET
SQL > update mytable set attributes=JSON_SET(attributes, "$.version", "0.1") ;
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.0029 sec)
与 CRUD 操作相比,我们需要提供 JSON 字段的名称和路径 ( $.version)。
SQL > select id, name, attributes from mytable;
+----+---------+--------------------------------------+
| id | name | attributes |
+----+---------+--------------------------------------+
| 1 | my_iot1 | {"type": "sensor", "version": "0.1"} |
| 2 | my_iot2 | {"type": "sensor", "version": "0.1"} |
+----+---------+--------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.0007 sec)
JSON_INSERT and JSON_REPLACE
这些功能几乎相同,但是如果属性已经存在,JSON_INSERT()则不会修改它:
SQL > update mytable set attributes=JSON_INSERT(attributes, "$.type", "new sensor") where id=2;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.0012 sec)
SQL > select id, name, JSON_PRETTY(attributes) from mytable where id=2\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 2
name: my_iot2
JSON_PRETTY(attributes): {
"type": "sensor",
"version": "0.1"
}
1 row in set (0.0007 sec)
SQL > update mytable set attributes=JSON_REPLACE(attributes, "$.type", "new sensor") where id=2;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.0030 sec)
SQL > select id, name, JSON_PRETTY(attributes) from mytable where id=2\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 2
name: my_iot2
JSON_PRETTY(attributes): {
"type": "new sensor",
"version": "0.1"
}
1 row in set (0.0006 sec)
JSON_MERGE_PATCH
如果我们想像为 , 那样添加嵌入式 JSON 条目capabilities,JSON_SET在 SQL 中将无法轻松工作,并且主要将其作为字符串处理……所以再次推荐补丁版本:
SQL > update mytable set attributes=JSON_MERGE_PATCH(attributes, '{"capabilities": {"humidity": "true", "temperature": "true"}}');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.0028 sec)
SQL > select id, name, json_pretty(attributes) attributes from mytable\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
name: my_iot1
attributes: {
"type": "sensor",
"version": "0.1",
"capabilities": {
"humidity": "true",
"temperature": "true"
}
}
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 2
name: my_iot2
attributes: {
"type": "sensor",
"version": "0.1",
"capabilities": {
"humidity": "true",
"temperature": "true"
}
}
2 rows in set (0.0010 sec)
现在如果我们想去除湿度能力,我们该怎么做呢?
我们只需要再次使用json_merge_patch()并将值设置为null
SQL > update mytable set attributes=JSON_MERGE_PATCH(attributes, '{"capabilities": {"humidity": null}}');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.0033 sec)
SQL > select id, name, json_pretty(attributes) attributes from mytable\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
name: my_iot1
attributes: {
"type": "sensor",
"version": "0.1",
"capabilities": {
"temperature": "true"
}
}
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 2
name: my_iot2
attributes: {
"type": "sensor",
"version": "0.1",
"capabilities": {
"temperature": "true"
}
}
2 rows in set (0.0007 sec)
JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE
此函数允许保留属性已存在的内容并创建值数组:
SQL > update mytable set attributes=JSON_MERGE_PRESERVE(attributes, '{"version": "0.2"}');
Query OK, 2 rows affected (0.0029 sec)
SQL > select id, name, json_pretty(attributes) attributes from mytable\G
*************************** 1. row ***************************
id: 1
name: my_iot1
attributes: {
"type": "sensor",
"version": [
"0.1",
"0.2"
],
"capabilities": {
"temperature": "true"
}
}
*************************** 2. row ***************************
id: 2
name: my_iot2
attributes: {
"type": "sensor",
"version": [
"0.1",
"0.2"
],
"capabilities": {
"temperature": "true"
}
}
2 rows in set (0.0013 sec)
最后一个示例说明了我们如何通过检索最后一个值来处理此类条目:
SQL > select id, name, attributes->>"$.version[last]" version from mytable;
+----+---------+---------+
| id | name | version |
+----+---------+---------+
| 1 | my_iot1 | 0.2 |
| 2 | my_iot2 | 0.2 |
+----+---------+---------+
2 rows in set (0.0008 sec)
现在您知道了更多如何在 MySQL 中通过 CRUD 操作或在 SQL 中使用 JSON 数据类型。
不要忘记在 MySQL 数据库服务中默认启用了 X Dev API(X 协议,用于执行 CRUD 操作)!
像往常一样,享受 MySQL !
原文标题:How to modify a JSON field in SQL ?
原文作者:LEFRED
原文地址:https://lefred.be/content/how-to-modify-a-json-field-in-sql/






