-
学习目标:
学习openGauss体系结构,使用多个用户访问同一个数据库 -
实践操作学习:
创建用户joh1、joh2、joh3,验证数据库johdb可以被这三个用户访问,分别在数据库中创建一张表并插入查询数据,验证一个用户可以被多个用户访问
- 环境准备:
su - omm
gsql -r
drop database if exists johdb;
drop database if exists johdb1;
drop database if exists johdb2;
drop database if exists johdb3;
drop tablespace if exists joh_tbs;
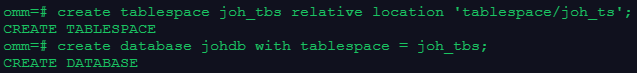
create tablespace joh_tbs relative location 'tablespace/joh_ts';
create database johdb with tablespace = joh_tbs;
- 创建用户joh1、joh2、joh3
create user joh1 identified by 'johpwd@123';
create user joh2 identified by 'johpwd@123';
create user joh3 identified by 'johpwd@123';
- 用户赋予SYSADMIN权限
alter user joh1 sysadmin;
alter user joh2 sysadmin;
alter user joh3 sysadmin;
--查看用户
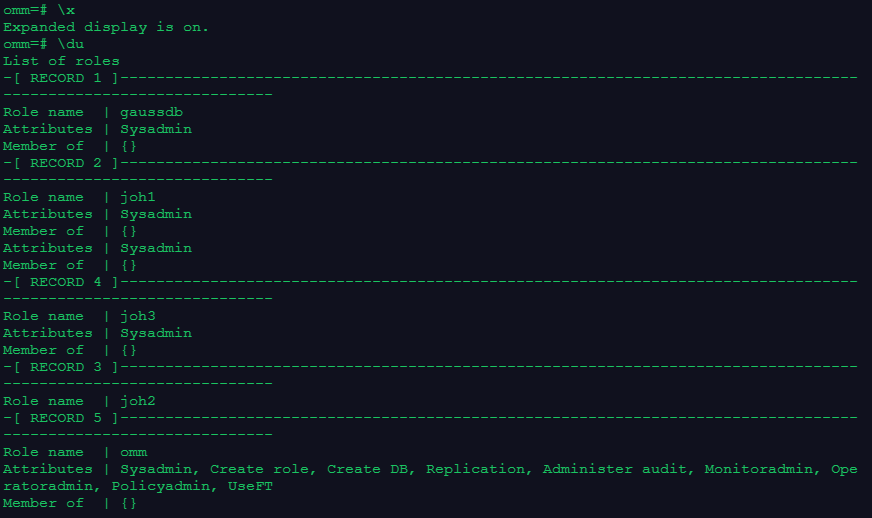
\du
- 在终端下分别使用joh1、joh2、joh3用户访问johdb数据库。
--以joh1身份在数据库joh中创建表t1
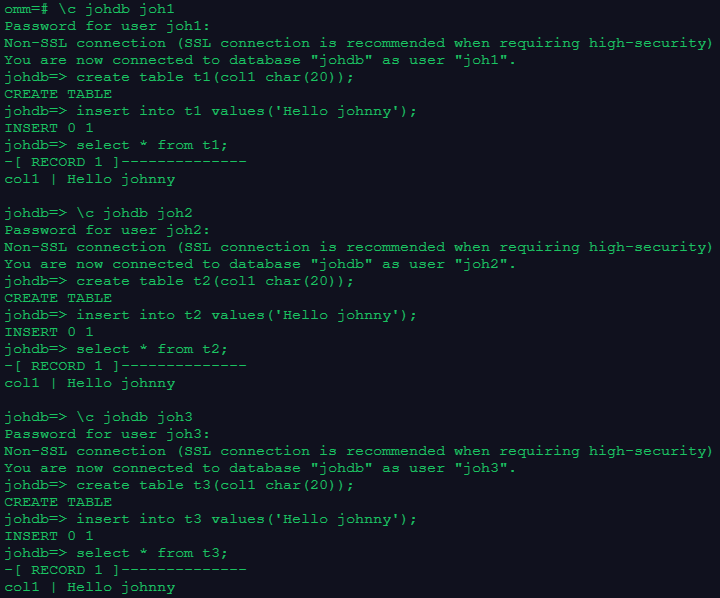
\c johdb joh1
create table t1(col1 char(20));
insert into t1 values('Hello johnny');
select * from t1;
--以joh2身份在数据库joh中创建表t2
\c johdb joh2
create table t2(col1 char(20));
insert into t2 values('Hello johnny');
select * from t2;
--以joh3身份在数据库joh中创建表t3
\c johdb joh3
create table t3(col1 char(20));
insert into t3 values('Hello johnny');
select * from t3;
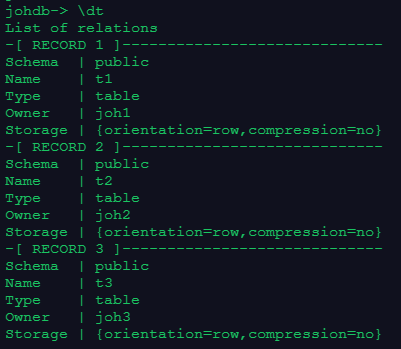
- 使用三个用户任意一个执行\dt命令,查看当前数据库johdb下有哪些表。
- 总结:
与oracle中database(schema)和user概念和一不同,opengauss与pg相同,将user与database(schema)分开管理,允许多个用户使用一个数据库并且不会互相干扰。
「喜欢这篇文章,您的关注和赞赏是给作者最好的鼓励」
关注作者
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文章的来源(墨天轮),文章链接,文章作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






