Hi~朋友,关注置顶防止错过消息
SpringApplication在构造完以后,我们会调用run方法启动应用程序,run方法的主要逻辑有:
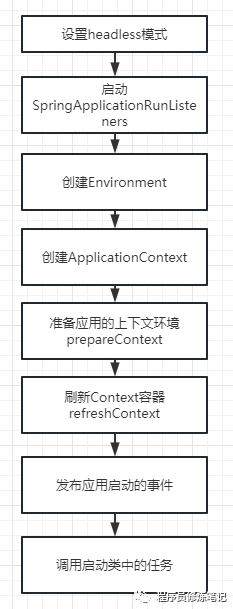
SpringApplication Run方法分析
整个Run方法的逻辑主要如上图:
• 设置headless模式
• 启动SpringApplicationRunListeners
• 创建Environment
• 创建应用上下文(ApplicationContext)
• 准备应用上下文环境
• 刷新应用上下文
• 发布应用启动的事件
• 调用启动类中的任务
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
//设置java.awt.headless系统属性为true,Headless模式是系统的一种配置模式。
//在该模式下,系统缺少了显示设备、键盘或鼠标。但是服务器生成的数据需要提供给显示设备等使用。
//因此使用headless模式,一般是在程序开始激活headless模式,告诉程序现在你要工作在Headless模式下,依靠系统的计算能力模拟出这些特性来
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 设置Environment(此处就会读取application.yaml的配置文件)
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
//创建应用上下文环境,也就是Spring的IOC容器
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
//准备应用上下文环境,会去加载配置类基于注解的bean、xml配置文件中定义的bean
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
//刷新上下文,对于servlet应用程序这个方法会去创建和启动web服务器
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
//应用运行时监听器发布应用启动事件
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
//调用启动类中的任务
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
启动SpringApplicationRunListeners
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
}
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,
getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args), this.applicationStartup);
}
void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, Class<?> mainApplicationClass) {
doWithListeners("spring.boot.application.starting", (listener) -> listener.starting(bootstrapContext),
(step) -> {
if (mainApplicationClass != null) {
step.tag("mainApplicationClass", mainApplicationClass.getName());
}
});
}
@Override
public void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(bootstrapContext, this.application, this.args));
}
• 通过getRunListeners方法找到所有的SpringApplicationRunListener(通过META-INF/spring.factories找到具体的实现类,然后利用反射生成具体的对象)
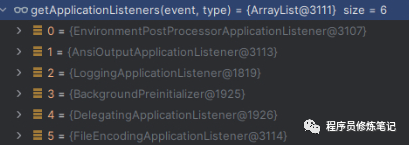
• 调用SpringApplicationRunListener的starting方法(在这里spring-boot-2.7.7中的是EventPublishingRunListener)
• EventPublishingRunListener中的starting方法就是广播一个ApplicationStartingEvent事件,此时对ApplicationStartingEvent感兴趣的Listeners就会对其进行处理(调用其onApplicationEvent方法),下图是对该事件感兴趣的Listeners
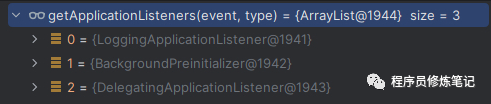
创建Environment
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
}
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
Assert.state(!environment.containsProperty("spring.main.environment-prefix"),
"Environment prefix cannot be set via properties.");
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
EnvironmentConverter environmentConverter = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader());
environment = environmentConverter.convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment, deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
if (this.addConversionService) {
environment.setConversionService(new ApplicationConversionService());
}
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
• 首先会通过getOrCreateEnvironment方法初始化Environment,这里Environment的具体类型是ApplicationServletEnvironment
• 接下来会通过configureEnvironment来初始化参数,该方法首先会在Environment中设置一个ConversionService(ApplicationConversionService),然后将命令行中的参数添加到Environment的MutablePropertySources中
• 接下来通过listeners.environmentPrepared发布ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,对此事件感兴趣的Listener将会对此事件进行处理
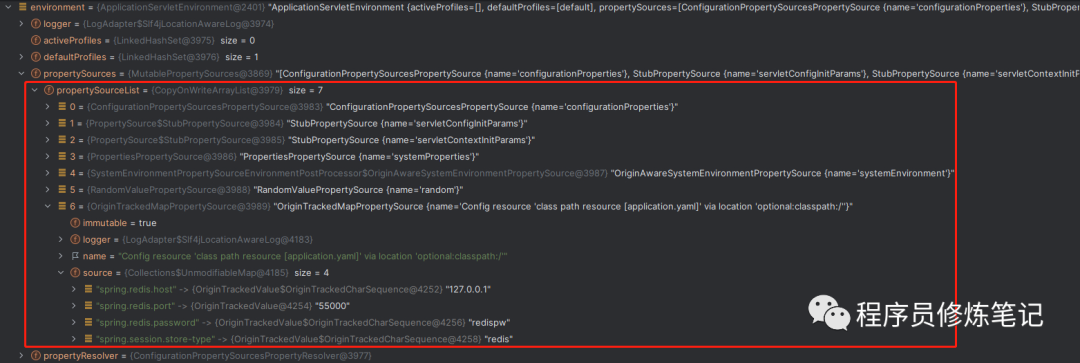
• 当prepareEnvironment方法执行完成以后,Environment中的Property也处理完成,如下图:
创建ApplicationContext
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
return this.applicationContextFactory.create(this.webApplicationType);
}
这里会默认创建一个AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext类型的ApplicationContext。
预处理应用上下文prepareContext
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
bootstrapContext.close(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) {
((AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory) beanFactory).setAllowCircularReferences(this.allowCircularReferences);
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new PropertySourceOrderingBeanFactoryPostProcessor(context));
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
• 首先通过context.setEnvironment方法将前面组装好的Environment放入上下文中
• postProcessApplicationContext后置处理Context,主要是将Environment中的ConversionService对象放入到Context中的BeanFactory(DefaultListableBeanFactory)中
• 紧接着在applyInitializers中会调用所有的ApplicationContextInitializer的initialize方法
• listeners.contextPrepared方法用来发布ApplicationContextInitializedEvent事件,对此事件感兴趣的Listeners将会对事件进行处理
• logStartupInfo和logStartupProfileInfo会打印启动详情和当前环境(profile)
• context.getBeanFactory会获取到BeanFactory
• beanFactory.registerSingleton方法会将对象注册到Bean管理容器中,这里首先会注册ApplicationArguments和Banner
• context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor会添加后置处理器
• load方法为会main方法所在的创建BeanDefinition,并注册进Spring上下文
• listeners.contextLoaded会发布ApplicationPreparedEvent事件
刷新应用上下文refreshContext
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
shutdownHook.registerApplicationContext(context);
}
refresh(context);
}
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}
refreshContext方法是比较关键的方法,该方法主要用来完成各种非延迟加载Bean的初始化以及ContextRefreshedEvent事件的发布,这个方法后续单独一篇详细讲
发布ApplicationStartedEvent
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
• listeners.started中会发布ApplicationStartedEvent事件
• callRunners方法中,通过应用上下文来获取所有ApplicationRunner以及CommandLineRunner接口实现类,接下来逐个调用其run方法
本期文章就到这,扫码关注,更多内容我们下期再见!







