前文回顾
-
[实现一个简单的Database10(译文)
译注:cstack在github维护了一个简单的、类似sqlite的数据库实现,通过这个简单的项目,可以很好的理解数据库是如何运行的。本文是第十二篇,主要是实现扫描多级B-Tree
Part 12 扫描多级B-Tree
我们现在支持构建一个多级B-Tree,但是我们在程序中破坏了 select 语句。下面是一个插入15行数据并打印出来的测例。
+ it 'prints all rows in a multi-level tree' do + script = [] + (1..15).each do |i| + script << "insert #{i} user#{i} person#{i}@example.com" + end + script << "select" + script << ".exit" + result = run_script(script) + + expect(result[15...result.length]).to match_array([ + "db > (1, user1, person1@example.com)", + "(2, user2, person2@example.com)", + "(3, user3, person3@example.com)", + "(4, user4, person4@example.com)", + "(5, user5, person5@example.com)", + "(6, user6, person6@example.com)", + "(7, user7, person7@example.com)", + "(8, user8, person8@example.com)", + "(9, user9, person9@example.com)", + "(10, user10, person10@example.com)", + "(11, user11, person11@example.com)", + "(12, user12, person12@example.com)", + "(13, user13, person13@example.com)", + "(14, user14, person14@example.com)", + "(15, user15, person15@example.com)", + "Executed.", "db > ", + ]) + end复制但是现在当我们运行这个测例的时候,它实际上发生的是:
db > select (2, user1, person1@example.com) Executed.复制这很奇怪。它只打印了一行,而且数据看起来发生了损坏(注意输出的 id 和 username 不匹配)。
这个奇怪之处是因为 execute_select() 函数在表的开始位置执行,我们现在的实现 table_start() 函数返回根节点的第0个单元格。但是现在树的跟节点是一个内部节点,它并不包含任何数据行。打印出的数据是根节点当初作为叶子节点时遗留下的。execute_select() 函数应该返回的是最左侧的叶子节点的第0个单元格。
所以现在抛弃旧的实现:
-Cursor* table_start(Table* table) { - Cursor* cursor = malloc(sizeof(Cursor)); - cursor->table = table; - cursor->page_num = table->root_page_num; - cursor->cell_num = 0; - - void* root_node = get_page(table->pager, table->root_page_num); - uint32_t num_cells = *leaf_node_num_cells(root_node); - cursor->end_of_table = (num_cells == 0); - - return cursor; -}复制并且添加一个新的实现来搜索 key 0 (可能存在的最小的 key)。即使在表中 key 0不存在,这个方法也会返回最小id的位置(最左叶子节点的开始位置)。
+Cursor* table_start(Table* table) { + Cursor* cursor = table_find(table, 0); + + void* node = get_page(table->pager, cursor->page_num); + uint32_t num_cells = *leaf_node_num_cells(node); + cursor->end_of_table = (num_cells == 0); + + return cursor; +}复制有了这些修改,测例仍然只打印出一个节点的行数:
db > select (1, user1, person1@example.com) (2, user2, person2@example.com) (3, user3, person3@example.com) (4, user4, person4@example.com) (5, user5, person5@example.com) (6, user6, person6@example.com) (7, user7, person7@example.com) Executed. db >复制有15个条目,B-tree包含了一个内部节点和两个叶子节点,看起来就是下面的样子:
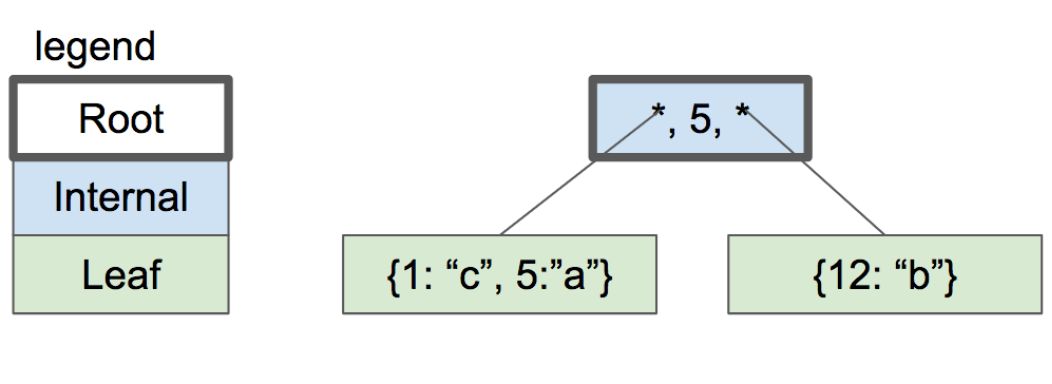
structure of our btree
为了遍历整个表,我们需要在遍历到第一个节点的结尾时跳到第二个叶子节点(继续遍历)。为了能够这样,我们需要在叶子节点的头部保存一个叫做“next_leaf”的字段,这个字段将保存右边兄弟叶子节点的 page number。而最右侧的叶子节点中next_leaf字段将保存 0 值,来表示它没有兄弟节点(无论如何,page 0 是为表的根节点保留的)。
更新叶子节点的头部格式来包含新的字段:
const uint32_t LEAF_NODE_NUM_CELLS_SIZE = sizeof(uint32_t); const uint32_t LEAF_NODE_NUM_CELLS_OFFSET = COMMON_NODE_HEADER_SIZE; -const uint32_t LEAF_NODE_HEADER_SIZE = - COMMON_NODE_HEADER_SIZE + LEAF_NODE_NUM_CELLS_SIZE; +const uint32_t LEAF_NODE_NEXT_LEAF_SIZE = sizeof(uint32_t); +const uint32_t LEAF_NODE_NEXT_LEAF_OFFSET = + LEAF_NODE_NUM_CELLS_OFFSET + LEAF_NODE_NUM_CELLS_SIZE; +const uint32_t LEAF_NODE_HEADER_SIZE = COMMON_NODE_HEADER_SIZE + + LEAF_NODE_NUM_CELLS_SIZE + + LEAF_NODE_NEXT_LEAF_SIZE;复制添加一个方法来访问这个字段:
+uint32_t* leaf_node_next_leaf(void* node) { + return node + LEAF_NODE_NEXT_LEAF_OFFSET; +}复制在初始化一个新的叶子节点的时候,设置 next_leaf 字段的默认值值为0:
@@ -322,6 +330,7 @@ void initialize_leaf_node(void* node) { set_node_type(node, NODE_LEAF); set_node_root(node, false); *leaf_node_num_cells(node) = 0; + *leaf_node_next_leaf(node) = 0; // 0 represents no sibling }复制每当分裂叶子节点时,更新同级兄弟节点的指针。老叶子节点的兄弟变成了新叶子节点,而新叶子节点的兄弟变成了旧叶子节点的兄弟。
@@ -659,6 +671,8 @@ void leaf_node_split_and_insert(Cursor* cursor, uint32_t key, Row* value) { uint32_t new_page_num = get_unused_page_num(cursor->table->pager); void* new_node = get_page(cursor->table->pager, new_page_num); initialize_leaf_node(new_node); + *leaf_node_next_leaf(new_node) = *leaf_node_next_leaf(old_node); + *leaf_node_next_leaf(old_node) = new_page_num;复制增加几个新的字段,改变几个变量:
it 'prints constants' do script = [ ".constants", @@ -199,9 +228,9 @@ describe 'database' do "db > Constants:", "ROW_SIZE: 293", "COMMON_NODE_HEADER_SIZE: 6", - "LEAF_NODE_HEADER_SIZE: 10", + "LEAF_NODE_HEADER_SIZE: 14", "LEAF_NODE_CELL_SIZE: 297", - "LEAF_NODE_SPACE_FOR_CELLS: 4086", + "LEAF_NODE_SPACE_FOR_CELLS: 4082", "LEAF_NODE_MAX_CELLS: 13", "db > ", ])复制现在,每当我们想将游标推进到叶子节点的末尾时,就可以检查叶子节点是否有兄弟节点。如果有,跳到兄弟节点。否则,我们就结束在表的末尾。
@@ -428,7 +432,15 @@ void cursor_advance(Cursor* cursor) { cursor->cell_num += 1; if (cursor->cell_num >= (*leaf_node_num_cells(node))) { - cursor->end_of_table = true; + /* Advance to next leaf node */ + uint32_t next_page_num = *leaf_node_next_leaf(node); + if (next_page_num == 0) { + /* This was rightmost leaf */ + cursor->end_of_table = true; + } else { + cursor->page_num = next_page_num; + cursor->cell_num = 0; + } } }复制有了这些更改之后,我们实际上就可以打印 15 行了…
db > select (1, user1, person1@example.com) (2, user2, person2@example.com) (3, user3, person3@example.com) (4, user4, person4@example.com) (5, user5, person5@example.com) (6, user6, person6@example.com) (7, user7, person7@example.com) (8, user8, person8@example.com) (9, user9, person9@example.com) (10, user10, person10@example.com) (11, user11, person11@example.com) (12, user12, person12@example.com) (13, user13, person13@example.com) (1919251317, 14, on14@example.com) (15, user15, person15@example.com) Executed. db >复制…但是有一行数据好像损坏了。
(1919251317, 14, on14@example.com)复制在做几次调试之后,我发现问题是因为在分裂叶子节点时的一个bug导致的:
@@ -676,7 +690,9 @@ void leaf_node_split_and_insert(Cursor* cursor, uint32_t key, Row* value) { void* destination = leaf_node_cell(destination_node, index_within_node); if (i == cursor->cell_num) { - serialize_row(value, destination); + serialize_row(value, + leaf_node_value(destination_node, index_within_node)); + *leaf_node_key(destination_node, index_within_node) = key; } else if (i > cursor->cell_num) { memcpy(destination, leaf_node_cell(old_node, i - 1), LEAF_NODE_CELL_SIZE); } else {复制请记住,叶节点中的每个单元格首先包含一个键,然后包含一个值:
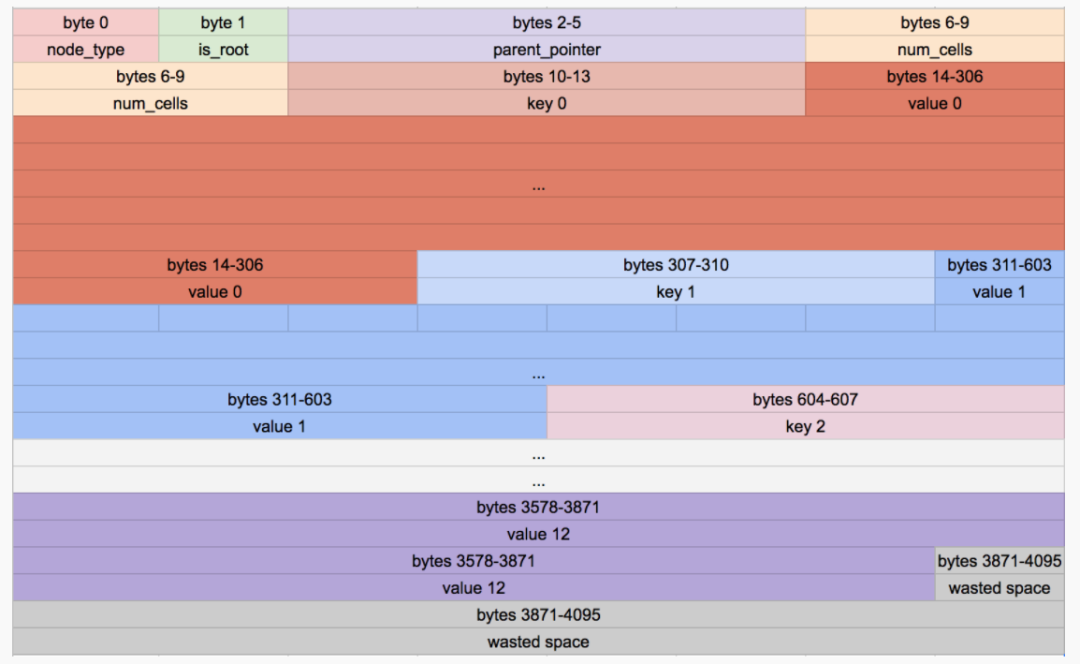
Original leaf node format
我们将新行(值)写入单元格的开头,键应该放在那里。这意味着用户名(username)的一部分进入了id部分(因为疯狂的大id)。在修改bug之后,我们终于按预期打印出了整个表格。
db > select (1, user1, person1@example.com) (2, user2, person2@example.com) (3, user3, person3@example.com) (4, user4, person4@example.com) (5, user5, person5@example.com) (6, user6, person6@example.com) (7, user7, person7@example.com) (8, user8, person8@example.com) (9, user9, person9@example.com) (10, user10, person10@example.com) (11, user11, person11@example.com) (12, user12, person12@example.com) (13, user13, person13@example.com) (14, user14, person14@example.com) (15, user15, person15@example.com) Executed. db >复制哇哦!一个又一个BUG,但我们正在取得进展。直到下次。
Enjoy GreatSQL 😃
关于 GreatSQL
GreatSQL是由万里数据库维护的MySQL分支,专注于提升MGR可靠性及性能,支持InnoDB并行查询特性,是适用于金融级应用的MySQL分支版本。
相关链接: GreatSQL社区 Gitee GitHub Bilibili
GreatSQL社区:
社区博客有奖征稿详情:https://greatsql.cn/thread-100-1-1.html

技术交流群:
微信:扫码添加
GreatSQL社区助手微信好友,发送验证信息加群。







