PG菜鸟入门学习中,欢迎各位大佬留言技术指导。
BG
工作中接到一个需求,客户在使用 postgres 时,只想看到当前的用户所拥有的数据库。
在 mysql 中,当用户登陆时,默认只能看到自己有权限的 database,例如
$ mysql -usbtest
Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g.
Your MariaDB connection id is 39022
Server version: 10.6.12-MariaDB-log Source distribution
Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others.
Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement.
(sbtest@localhost) [(none)] 11:19:07> show databases;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| information_schema |
| sbtest |
+--------------------+
2 rows in set (0.001 sec)
(sbtest@localhost) [(none)] 11:19:08> show grants;
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| Grants for sbtest@localhost |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
| GRANT USAGE ON *.* TO `sbtest`@`localhost` |
| GRANT SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE ON `sbtest`.* TO `sbtest`@`localhost` |
+----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set (0.000 sec)
(sbtest@localhost) [(none)] 11:19:11>
但是在postgresql中,用户登陆后可以看到所有的database,例如
(sbtest@[local]) [sbtest] 11:21:56> \l
List of databases
+-----------+----------+-----------+---------+-------+------------------------------+
| Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges |
+-----------+----------+-----------+---------+-------+------------------------------+
| mydb | pguser | UTF8 | C | C | =Tc/pguser +|
| | | | | | pguser=C*T*c*/pguser |
| postgres | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =Tc/postgres +|
| | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres +|
| | | | | | postgres_connect=c/postgres |
| sbtest | sbtest | SQL_ASCII | C | C | | -- just want to see this one
| template0 | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/postgres +|
| | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres |
| template1 | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C | =c/postgres +|
| | | | | | postgres=CTc/postgres |
| yandb | postgres | SQL_ASCII | C | C | |
+-----------+----------+-----------+---------+-------+------------------------------+
(6 rows)
psql 是?
psql 是 PostgreSQL 中的一个命令行交互式客户端工具,它允许你交互地键入 SQL 命令,然后把它们发送给 PostgreSQL 服务器,再显示 SQL 或命令的结果。输入的内容允许来自一个文件,此外它还提供了一些元命令和多种类似 shell 的特性来实现书写脚本,以及对大量任务的自动化工作。具有方便快捷、没有图形化工具使用上的一些限制等特性。
list all databases
更深一步地说,\l 这条元命令真的只是这么简单一条SQL么,有没有其他判断条件。
答案都在源码里,
https://gitee.com/shawnyan/postgres/blob/master/src/bin/psql/describe.c#L916
printfPQExpBuffer(&buf,
"SELECT d.datname as \"%s\",\n"
" pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(d.datdba) as \"%s\",\n"
" pg_catalog.pg_encoding_to_char(d.encoding) as \"%s\",\n"
" d.datcollate as \"%s\",\n"
" d.datctype as \"%s\",\n",
gettext_noop("Name"),
gettext_noop("Owner"),
gettext_noop("Encoding"),
gettext_noop("Collate"),
gettext_noop("Ctype"));
if (pset.sversion >= 150000)
appendPQExpBuffer(&buf,
" d.daticulocale as \"%s\",\n"
" CASE d.datlocprovider WHEN 'c' THEN 'libc' WHEN 'i' THEN 'icu' END AS \"%s\",\n",
gettext_noop("ICU Locale"),
gettext_noop("Locale Provider"));
else
appendPQExpBuffer(&buf,
" NULL as \"%s\",\n"
" 'libc' AS \"%s\",\n",
gettext_noop("ICU Locale"),
gettext_noop("Locale Provider"));
appendPQExpBufferStr(&buf, " ");
printACLColumn(&buf, "d.datacl");
if (verbose)
appendPQExpBuffer(&buf,
",\n CASE WHEN pg_catalog.has_database_privilege(d.datname, 'CONNECT')\n"
" THEN pg_catalog.pg_size_pretty(pg_catalog.pg_database_size(d.datname))\n"
" ELSE 'No Access'\n"
" END as \"%s\""
",\n t.spcname as \"%s\""
",\n pg_catalog.shobj_description(d.oid, 'pg_database') as \"%s\"",
gettext_noop("Size"),
gettext_noop("Tablespace"),
gettext_noop("Description"));
appendPQExpBufferStr(&buf,
"\nFROM pg_catalog.pg_database d\n");
if (verbose)
appendPQExpBufferStr(&buf,
" JOIN pg_catalog.pg_tablespace t on d.dattablespace = t.oid\n");
if (pattern)
{
if (!validateSQLNamePattern(&buf, pattern, false, false,
NULL, "d.datname", NULL, NULL,
NULL, 1))
{
termPQExpBuffer(&buf);
return false;
}
}
appendPQExpBufferStr(&buf, "ORDER BY 1;");
可以看到,对于 PG15 以上版本,增加了字段 pg_catalog.pg_database.daticulocale
- code
" d.daticulocale as \"%s\",\n"
" CASE d.datlocprovider WHEN 'c' THEN 'libc' WHEN 'i' THEN 'icu' END AS \"%s\",\n",
- table
postgres=# SELECT * FROM pg_database WHERE datname='postgres'\x\g\x
Expanded display is on.
-[ RECORD 1 ]--+-----------
oid | 5
datname | postgres
datdba | 10
encoding | 6
datlocprovider | c
datistemplate | f
datallowconn | t
datconnlimit | -1
datfrozenxid | 717
datminmxid | 1
dattablespace | 1663
datcollate | en_US.utf8
datctype | en_US.utf8
daticulocale |
datcollversion | 2.31
datacl |
这个字段的作用是,作为全局变量,存放 ICU locale ID。
是 PG 15.0 新增特性。
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/release/15.0/
Allow ICU collations to be set as the default for clusters and databases (Peter Eisentraut)
Previously, only libc-based collations could be selected at the cluster and database levels. ICU collations could only be used via explicit COLLATE clauses.
关于这个feature的更多讨论,可以参阅这里
https://www.postgresql.org/message-id/flat/5e756dd6-0e91-d778-96fd-b1bcb06c161a%402ndquadrant.com
echo_hidden 是个好同志
在 PG 技术交流群中,有位老师指点迷津道,可以使用 ECHO_HIDDEN 来查看元命令的“内涵” SQL。
于是,我便从元命令 \l 入手,先查看该元命令具体调用的是哪个sql,这里就用到了 echo_hidden, 使用它来研究 psql 的内部操作, 来显示的查看当前元命令所具体代表、执行了那条 SQL 语句, 示例如下:
(sbtest@[local]) [sbtest] 11:21:59> \set ECHO_HIDDEN on
(sbtest@[local]) [sbtest] 11:34:19> \l
********* QUERY **********
SELECT d.datname as "Name",
pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(d.datdba) as "Owner",
pg_catalog.pg_encoding_to_char(d.encoding) as "Encoding",
d.datcollate as "Collate",
d.datctype as "Ctype",
pg_catalog.array_to_string(d.datacl, E'\n') AS "Access privileges"
FROM pg_catalog.pg_database d
ORDER BY 1;
**************************
将这条语句加个简单的过滤,将owner指向为当前用户,那么就可以只查看当前用户的database列表, 效果如下:
(sbtest@[local]) [sbtest] 11:34:23> SELECT d.datname as "Name",
sbtest-> pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(d.datdba) as "Owner",
sbtest-> pg_catalog.pg_encoding_to_char(d.encoding) as "Encoding",
sbtest-> d.datcollate as "Collate",
sbtest-> d.datctype as "Ctype",
sbtest-> pg_catalog.array_to_string(d.datacl, E'\n') AS "Access privileges"
sbtest-> FROM pg_catalog.pg_database d
sbtest-> where pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(d.datdba) in (select user)
sbtest-> ORDER BY 1;
+--------+--------+-----------+---------+-------+-------------------+
| Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges |
+--------+--------+-----------+---------+-------+-------------------+
| sbtest | sbtest | SQL_ASCII | C | C | |
+--------+--------+-----------+---------+-------+-------------------+
(1 row)
那么问题来了,每次都复制这么长一段sql很繁杂,有没有巧妙的方式来调用。
psqlrc 登场
此时,psqlrc 登场,将上面这大段sql写到 ~/.psqlrc 文件中。
vi ~/.psqlrc
\set l 'SELECT d.datname as "Name",pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(d.datdba) as "Owner",pg_catalog.pg_encoding_to_char(d.encoding) as "Encoding",d.datcollate as "Collate",d.datctype as "Ctype",pg_catalog.array_to_string(d.datacl, E\'\\n\') AS "Access privileges" FROM pg_catalog.pg_database d where pg_catalog.pg_get_userbyid(d.datdba) in (select user) ORDER BY 1;'
再次登录 psql 并查看 database 列表,可以看到下面的结果:
$ psql -Usbtest
(sbtest@[local]) [sbtest] 11:39:41> :l
+--------+--------+-----------+---------+-------+-------------------+
| Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges |
+--------+--------+-----------+---------+-------+-------------------+
| sbtest | sbtest | SQL_ASCII | C | C | |
+--------+--------+-----------+---------+-------+-------------------+
(1 row)
目标达成,显示结果很简单直接。
psqlrc 其他实用玩法
彩色显示
进入原生psql客户端后,略显单调,加点色彩可以使DBA工作添点乐趣,比如下图,
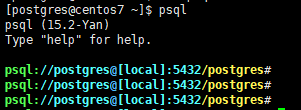
通过 prompt 加入颜色元素,便可实现这种效果。
\set PROMPT1 '%[%033[1;31m%]%[%033[32m%]psql:%[%033[36m%]//%n%[%033[34m%]@%[%033[36m%]%M:%>%[%033[33m%]/%/%[%033[K%]%[%033[0m%]%# '
启动时间
在linux中,可以使用 uptime 命令查看系统运行时间,
$ uptime
11:52:12 up 706 days, 1:50, 3 users, load average: 0.04, 0.04, 0.05
在mysql中,可以使用元命令 \s 查看数据库运行时间,
(root@localhost) [(none)] 11:52:39> \s
--------------
Uptime: 15 days 20 hours 35 min 2 sec
那么在 pg 中,则可以自定义一个 :uptime 方法。
\set uptime 'select date_trunc(\'second\',current_timestamp - pg_postmaster_start_time()) as uptime;'
(sbtest@[local]) [sbtest] 11:50:57> :uptime
+-----------------+
| uptime |
+-----------------+
| 5 days 00:52:58 |
+-----------------+
(1 row)
登陆提示语
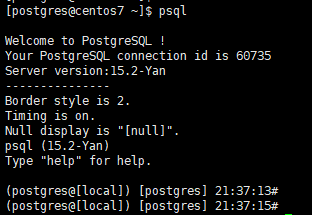
结合上述知识点,增加了登陆提示语,每次登陆 psql 时,都可以看到欢迎提示。 Welcome~~~ 🥳
[postgres@centos7 ~]$ psql
Welcome to PostgreSQL !
Your PostgreSQL connection id is 60735
Server version: 15.2-Yan
---------------
Border style is 2.
Timing is on.
Null display is "[null]".
psql (15.2-Yan)
Type "help" for help.
(postgres@[local]) [postgres] 21:37:13#
(postgres@[local]) [postgres] 21:37:15#
参考
官档和源码永远是最好的参考资料。
善于查阅原始资料才能摆脱 baidu/google/new bing/chatgpt DBA 的束缚,学习阅读源码,调试pg源码,才是走向【掌握】PostgreSQL 的唯一途径。
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/15/app-psql.html
https://github.com/postgres/postgres/blob/master/src/bin/psql/prompt.c
总结
实际使用时,可按需设定,以便于常规工作需要,psqlrc 相当于增加了快捷键或者说是增加了自定义元命令,将大段的常用sql设定为简短的缩写,省去了查阅相关sql又少敲了N多字,可以成倍节约时间用在其他更有意义的事情上,也可以延长机械键盘使用寿命。








