GBase 8c 学习笔记 006 —— GBase 8c 常用对象
逻辑结构
GBase 8c 基本对象
- User:用户
- Database:数据库
- Schema:模式
- Table:数据表
- Index:索引
- View:视图
- Function:函数
- Sequence:序列
GBase 8c 逻辑存储结构
- Tablespace,即表空间,是一个目录,可以存在多个,里面存储的是它所包含的数据库的各种物理文件。每个表空间可以对应多个Database。
- Database,即数据库,用于管理各类数据对象,各数据库间相互隔离。数据库管理的对象可分布在多个Tablespace上。
- Datafile Segment,即数据文件,通常每张表只对应一个数据文件。如果某张表的数据大于1GB,则会分为多个数据文件存储。
- Table,即表,每张表只能属于一个数据库,也只能对应到一个Tablespace。每张表对应的数据文件必须在同一个Tablespace中。
- Block,即数据块,是数据库管理的基本单位,默认大小为8KB。
常用对象
表空间
在 GBase 8c 中,表空间是一个目录,可以存在多个,里面存储的是它所包含的数据库的各种物理文件。
通过表空间,用户可以控制一个数据库存储的磁盘布局。使用表空间有以下优点:
- 如果数据库所在的分区或者卷空间已满,又不能逻辑上扩展更多空间,可以在不同的分区上创建和使用表空间,直到系统重新配置空间。
- 表空间允许管理员根据数据库对象的使用模式安排数据位置,从而提高性能:
- 频繁使用的索引可以放在性能稳定且运算速度较快的磁盘上,比如 SSD 固态设备。
- 存储归档的数据,很少使用或者对性能要求不高的表可以存储在一个运算速度较慢的磁盘上。
- 通过表空间,管理员可以设置其占用的磁盘空间上限,用以在和其他数据共用分区的时候,防止表空间占用相同分区上的其他空间。
管理表空间
管理表空间的语句主要包括:创建表空间、修改表空间属性,以及删除表空间。
| 功能 | 相关SQL |
|---|---|
| 创建表空间 | CREATE TABLESPACE |
| 修改表空间属性 | ALTER TABLESPACE |
| 删除表空间 | DROP TABLESPACE |
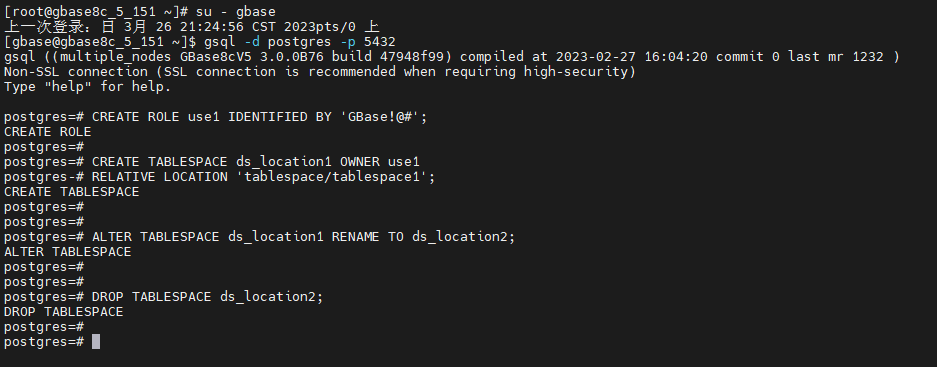
表空间管理示例
[root@gbase8c_5_151 ~]# su - gbase
上一次登录:日 3月 26 21:24:56 CST 2023pts/0 上
[gbase@gbase8c_5_151 ~]$ gsql -d postgres -p 5432
gsql ((multiple_nodes GBase8cV5 3.0.0B76 build 47948f99) compiled at 2023-02-27 16:04:20 commit 0 last mr 1232 )
Non-SSL connection (SSL connection is recommended when requiring high-security)
Type "help" for help.
-- 创建用户use1。
postgres=# CREATE ROLE use1 IDENTIFIED BY 'GBase!@#';
CREATE ROLE
gbase8c=#
-- 创建表空间,且所有者指定为用户use1。
postgres=# CREATE TABLESPACE ds_location1 OWNER use1
postgres-# RELATIVE LOCATION 'tablespace/tablespace1';
CREATE TABLESPACE
postgres=#
-- 把表空间ds_location1重命名为ds_location2。
postgres=# ALTER TABLESPACE ds_location1 RENAME TO ds_location2;
ALTER TABLESPACE
postgres=#
-- 删除表空间。
postgres=# DROP TABLESPACE ds_location2;
DROP TABLESPACE
postgres=#
自带表空间
GBase 8c 自带两个表空间:
- 默认表空间 pg_default:
用来存储非共享系统表、用户表、用户表index、临时表、临时表index、内部临时表的默认表空间。
对应存储目录为实例数据目录下的base目录。 - 共享表空间 pg_global:
用来存放共享系统表的表空间。对应存储目录为实例数据目录下的global目录。
数据库管理
数据库是组织、存储和管理数据的仓库,管理数据库的语句主要包括:创建数据库、修改数据库属性,以及删除数据库。
| 功能 | 相关SQL |
|---|---|
| 创建数据库 | CREATE DATABASE |
| 修改数据库属性 | ALTER DATABASE |
| 删除数据库 | DROP DATABASE |
数据库兼容模式
DBCOMPATIBILITY 兼容模式:
可选值:A(默认值)、B、C、PG。分别表示兼容 O、MY、TD 和 POSTGRES。
- A 兼容性下,数据库将空字符串作为NULL处理,数据类型DATE会被替换为TIMESTAMP(0) WITHOUT TIME ZONE。
- B 兼容性下,在将字符串转换成整数类型时,如果输入不合法,B兼容性会将输入转换为0,而其它兼容性则会报错。
- B、PG 兼容性下,CHAR 和 VARCHAR以字符为计数单位,其它兼容性以字节为计数单位。例如,对于UTF-8字符集,CHAR(3)在B、PG兼容性下能存放3个中文字符,而在其它兼容性下只能存放1个中文字符。
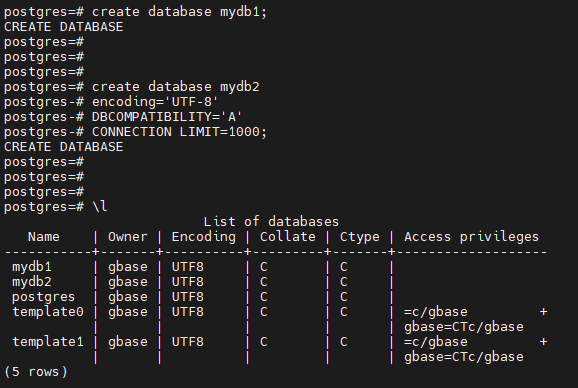
数据库管理示例
-- 创建数据库:
postgres=# create database mydb1;
CREATE DATABASE
postgres=#
postgres=# create database mydb2
postgres-# encoding='UTF-8' -- 编码集
postgres-# DBCOMPATIBILITY='A' -- 兼容模式
postgres-# CONNECTION LIMIT=1000; -- 并发连接限制
CREATE DATABASE
postgres=#
postgres=# \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+-------+----------+---------+-------+-------------------
mydb1 | gbase | UTF8 | C | C |
mydb2 | gbase | UTF8 | C | C |
postgres | gbase | UTF8 | C | C |
template0 | gbase | UTF8 | C | C | =c/gbase +
| | | | | gbase=CTc/gbase
template1 | gbase | UTF8 | C | C | =c/gbase +
| | | | | gbase=CTc/gbase
(5 rows)
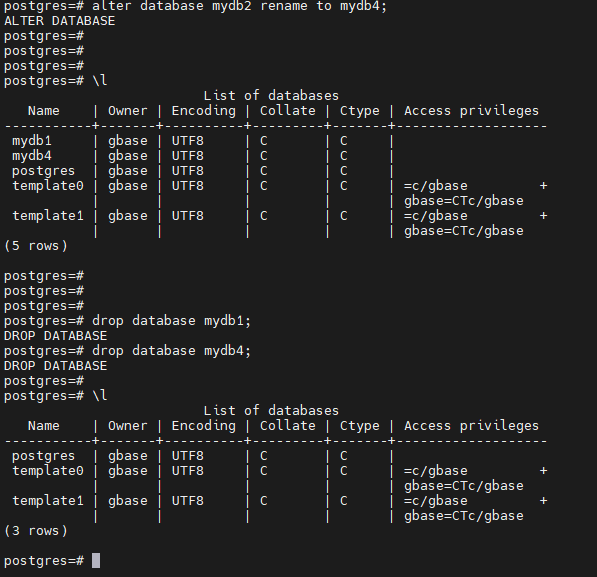
-- 修改数据库名称:
postgres=# alter database mydb2 rename to mydb4;
ALTER DATABASE
postgres=#
postgres=# \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+-------+----------+---------+-------+-------------------
mydb1 | gbase | UTF8 | C | C |
mydb4 | gbase | UTF8 | C | C |
postgres | gbase | UTF8 | C | C |
template0 | gbase | UTF8 | C | C | =c/gbase +
| | | | | gbase=CTc/gbase
template1 | gbase | UTF8 | C | C | =c/gbase +
| | | | | gbase=CTc/gbase
(5 rows)
-- 删除数据库:
postgres=# drop database mydb1;
DROP DATABASE
postgres=# drop database mydb4;
DROP DATABASE
postgres=#
postgres=# \l
List of databases
Name | Owner | Encoding | Collate | Ctype | Access privileges
-----------+-------+----------+---------+-------+-------------------
postgres | gbase | UTF8 | C | C |
template0 | gbase | UTF8 | C | C | =c/gbase +
| | | | | gbase=CTc/gbase
template1 | gbase | UTF8 | C | C | =c/gbase +
| | | | | gbase=CTc/gbase
(3 rows)
postgres=#
模式(Schema)概述
- GBase 8c 使用模式 (Schema) 对数据库(database)做逻辑分割。所有的数据库对象都建立在模式下面,用户可以根据自己拥有的权限,访问数据库中一个或多个schema的对象。这样就使得多个用户可以使用同一个数据库而不相互干扰。
- 和数据库不同,模式不是严格分离的:只要有权限,一个用户可以访问他所连接的数据库中的任意模式中的对象。
- 相同的对象名称可以被用于不同的模式中而不会发生冲突,例如同一个数据库下名为schema1和schema2的模式下都可以包含名为table1的表。
-- 搜索路径
gbase8c=# show search_path;
search_path
---------------- "$user",public
(1 row)
模式管理
模式是一组数据库对象的集合,主要用于控制对数据库对象的访问。管理模式的语句
主要包括:创建模式、修改模式属性,以及删除模式。
| 功能 | 相关SQL |
|---|---|
| 创建模式 | CREATE SCHEMA |
| 修改模式属性 | ALTER SCHEMA |
| 删除模式 | DROP SCHEMA |
模式使用示例
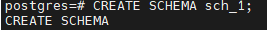
--- 创建模式
postgres=# CREATE SCHEMA sch_1;
CREATE SCHEMA
postgres=#
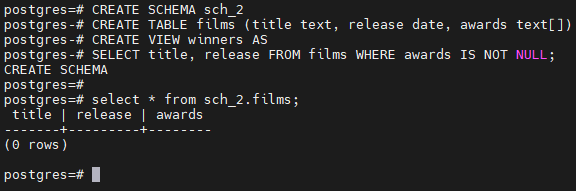
-- 创建一个schema,子命令创建表films 和视图 winners。
postgres=# CREATE SCHEMA sch_2
postgres-# CREATE TABLE films (title text, release date, awards text[])
postgres-# CREATE VIEW winners AS
postgres-# SELECT title, release FROM films WHERE awards IS NOT NULL;
CREATE SCHEMA
postgres=#
postgres=# select * from sch_2.films;
title | release | awards
-------+---------+--------
(0 rows)
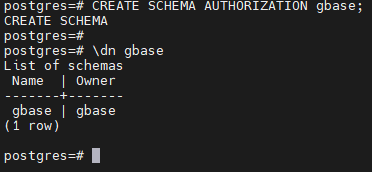
--- 创建模式(不带模式名)
postgres=# CREATE SCHEMA AUTHORIZATION gbase;
CREATE SCHEMA
postgres=#
postgres=# \dn gbase
List of schemas
Name | Owner
-------+-------
gbase | gbase
(1 row)
postgres=#
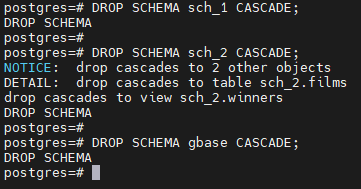
--级联删除schema。
postgres=# DROP SCHEMA sch_1 CASCADE;
DROP SCHEMA
postgres=#
postgres=# DROP SCHEMA sch_2 CASCADE;
NOTICE: drop cascades to 2 other objects
DETAIL: drop cascades to table sch_2.films
drop cascades to view sch_2.winners
DROP SCHEMA
postgres=#
postgres=# DROP SCHEMA gbase CASCADE;
DROP SCHEMA
postgres=#
使用注意事项
- 不建议创建以PG_为前缀的schema名,该类的schema是为数据库系统预留的。
- 在每次创建新用户时,系统会在当前登录的数据库中为新用户创建一个同名Schema。对于其他数据库,若需要同名Schema,则需要用户手动创建。
- 每个数据库都有名为 pg_catalog 的 schema,它包含系统表和所有内置数据类型、函数、操作符。搜索路径(search_path)始终以pg_temp和pg_catalog这两个schema作为搜索路径顺序中的前两位。
- 模式的权限: 默认情况下,用户无法访问模式中不属于他们的对象。
- 若要访问,模式的所有者必须在模式上赋予他们“USAGE”权限
- 用户要想在其他用户的模式里创建对象,需要被赋予在该模式上的“CREATE”权限
用户、角色及权限
- 用户(User):使用数据库管理系统的个体。
- 角色(Role):一组用户的集合,按照数据库系统中承担的责任划分具有不同权限的角色。
- 系统权限:又称为用户属性,包括 SYSADMIN、CREATEDB、CREATEROLE、AUDITADMIN和LOGIN等。
- 对象权限:数据库对象(表和视图、指定字段、数据库、函数、模式、表空间等)的相关权限(创建、删除、修改等)。
初始用户
GBase 8c安装过程中自动生成的帐户称为初始用户。初始用户拥有系统的最高权限,能够执行所有的操作。该帐户与进行GBase 8c安装的操作系统用户同名。在第一次登录数据库后,要及时修改初始用户的密码。
用户、角色管理
- 角色是用来管理权限的,从数据库安全的角度考虑,可以把所有的管理和操作权限划分到不同的角色上。
- 用户是用来登录数据库的,通过对用户赋予不同的权限,可以方便地管理用户对数据库的访问及操作。
| 功能 | 相关SQL |
|---|---|
| 创建角色\用户 | CREATE ROLE、CREATE USER |
| 修改角色\用户属性 | ALTER ROLE、ALTER USER |
| 删除角色\用户 | DROP ROLE、DROP USER |
用户与角色使用示例
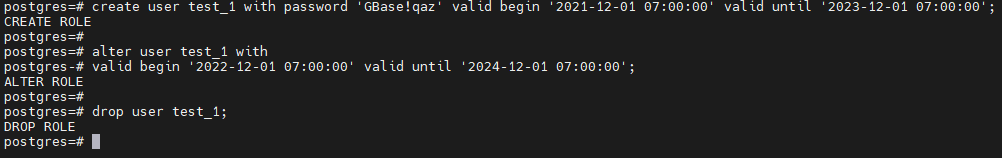
-- 使用 CREATE 语法创建用户并指定用户的有效开始时间和有效结束时间
postgres=# create user test_1 with password 'GBase!qaz' valid begin '2021-12-01 07:00:00' valid until '2023-12-01 07:00:00';
CREATE ROLE
postgres=#
-- 使用 ALTER 语法重新设置有效期
postgres=# alter user test_1 with
postgres-# valid begin '2022-12-01 07:00:00' valid until '2024-12-01 07:00:00';
ALTER ROLE
postgres=#
-- 使用 DROP 语法进行删除。
postgres=# drop user test_1;
DROP ROLE
postgres=#
管理数据表
- 数据表是建立在数据库中的,在不同的数据库中可以存放相同的表。可以通过使用模式在同一个数据库中创建相同名称的表。
- 数据表是数据库中的一种特殊数据结构,用于存储数据对象以及对象之间的关系。
| 功能 | 相关SQL |
|---|---|
| 创建表 | CREATE TABLE |
| 修改表属性 | ALTER TABLE |
| 删除表 | DROP TABLE |
数据表使用示例
-- 使用 CREATE 语法创建数据表
postgres=# CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS tab_1
postgres-# ( W_WAREHOUSE_SK INTEGER,
postgres(# W_WAREHOUSE_ID CHAR(16),
postgres(# W_GMT_OFFSET DECIMAL(5,2)
postgres(# );
CREATE TABLE
postgres=#
postgres=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage
--------+-------+-------+-------+----------------------------------
public | dual | view | gbase |
public | tab_1 | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
(2 rows)
postgres=# \d+ tab_1
Table "public.tab_1"
Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Stats target | Description
----------------+---------------+-----------+----------+--------------+-------------
w_warehouse_sk | integer | | plain | |
w_warehouse_id | character(16) | | extended | |
w_gmt_offset | numeric(5,2) | | main | |
Has OIDs: no
Distribute By: HASH(w_warehouse_sk)
Location Nodes: ALL DATANODES
Options: orientation=row, compression=no
-- 重命名表
postgres=# ALTER TABLE tab_1 RENAME TO tab_2;
ALTER TABLE
postgres=#
postgres=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage
--------+-------+-------+-------+----------------------------------
public | dual | view | gbase |
public | tab_2 | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
(2 rows)
postgres=#
-- 新增列
postgres=# ALTER TABLE tab_2 ADD W_NEW_COLUMN CHAR(2);
ALTER TABLE
postgres=#
-- 删除表
postgres=# DROP TABLE tab_2;
DROP TABLE
postgres=#

分布式模式下数据表分类
Replication 表
即复制表,各个 datanode 节点中,写入表的数据完全相同。读数据时,只需要读取任意一个 datanode 节点上的数据。一般小表或者只读表( dimension table,维度表,即描述性或静态数据表 )采用此种方式。
Distribute 表(默认创建方式)
即分布式表,基于指定列的 hash 值将数据完全切分到不同的 datanode 节点中,即与Replication 表相反,各个 datanode 节点中,表的数据完全不同。适用于 write-heavy tables,如事实表。
创建复制表示例
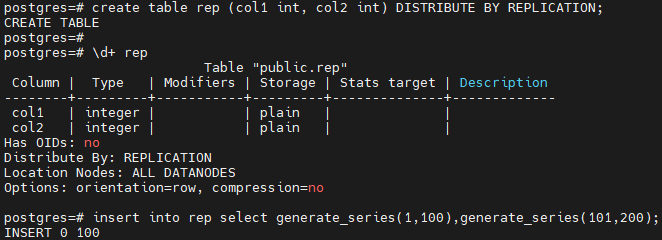
-- 创建复制表 rep
postgres=# create table rep (col1 int, col2 int) DISTRIBUTE BY REPLICATION;
CREATE TABLE
postgres=#
postgres=# \d+ rep
Table "public.rep"
Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Stats target | Description
--------+---------+-----------+---------+--------------+-------------
col1 | integer | | plain | |
col2 | integer | | plain | |
Has OIDs: no
Distribute By: REPLICATION
Location Nodes: ALL DATANODES
Options: orientation=row, compression=no
-- 插入 100 条数据
postgres=# insert into rep select generate_series(1,100),generate_series(101,200);
INSERT 0 100
postgres=#
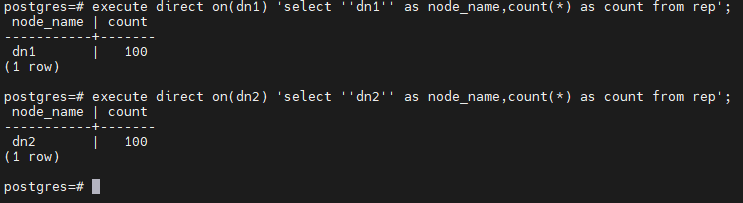
-- 在 dn1 上查询
postgres=# execute direct on(dn1) 'select ''dn1'' as node_name,count(*) as count from rep';
node_name | count
-----------+-------
dn1 | 100
(1 row)
-- 在 dn2 上查询
postgres=# execute direct on(dn2) 'select ''dn2'' as node_name,count(*) as count from rep';
node_name | count
-----------+-------
dn2 | 100
(1 row)
创建分布表示例
-- 创建分布表 dist
postgres=# create table dist (col1 int, col2 int) DISTRIBUTE BY HASH(col1);
CREATE TABLE
-- 插入 100 条数据
postgres=# insert into dist select generate_series(1,100),generate_series(101,200);
INSERT 0 100
postgres=#
postgres=# \d+ dist
Table "public.dist"
Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Stats target | Description
--------+---------+-----------+---------+--------------+-------------
col1 | integer | | plain | |
col2 | integer | | plain | |
Has OIDs: no
Distribute By: HASH(col1)
Location Nodes: ALL DATANODES
Options: orientation=row, compression=no
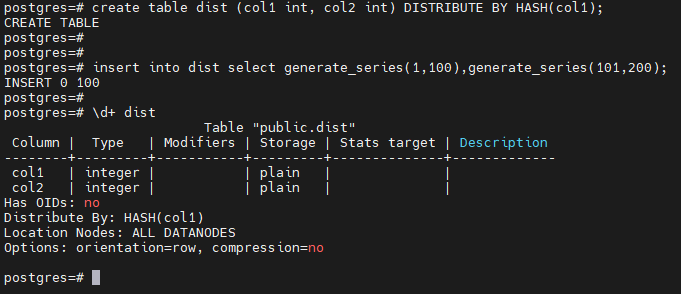
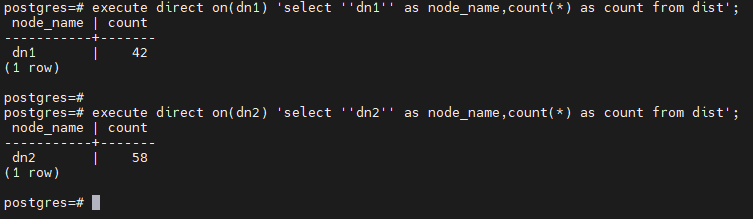
-- 在 dn1 上查询
postgres=# execute direct on(dn1) 'select ''dn1'' as node_name,count(*) as count from dist';
node_name | count
-----------+-------
dn1 | 42
(1 row)
postgres=#
-- 在 dn2 上查询
postgres=# execute direct on(dn2) 'select ''dn2'' as node_name,count(*) as count from dist';
node_name | count
-----------+-------
dn2 | 58
(1 row)
postgres=#
其它常用对象——视图(View)
当用户对数据库中的一张或者多张表的某些字段的组合感兴趣,而又不想每次键入这些查询时,用户就可以定义一个视图(View),以便解决这个问题。
视图与基本表不同,它不是物理上实际存在的。数据库中仅存放视图的定义,而不存放视图对应的数据,这些数据仍存放在原来的基本表中。若基本表中的数据发生变化,从视图中查询出的数据也随之改变。
物化视图是“物化”(Materialized)之后的视图,它将视图查询的结果实际存储在磁盘中,有效提升查询性能。
物化视图以类表的形式保存结果,但无法像普通表那样进行数据更新,需要使用REFRESH 从基表获取更新数据。
普通视图使用示例
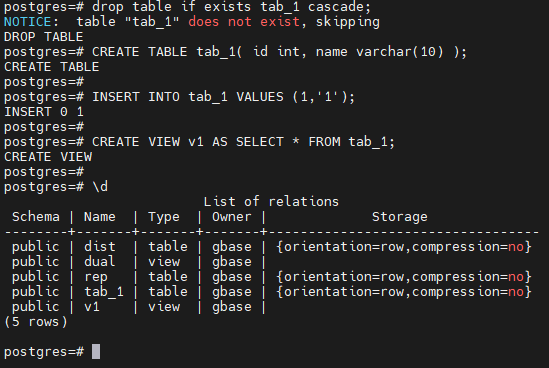
-- 创建数据表
postgres=# drop table if exists tab_1 cascade;
NOTICE: table "tab_1" does not exist, skipping
DROP TABLE
postgres=# CREATE TABLE tab_1( id int, name varchar(10) );
CREATE TABLE
postgres=# INSERT INTO tab_1 VALUES (1,'1');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=#
--创建视图
postgres=# CREATE VIEW v1 AS SELECT * FROM tab_1;
CREATE VIEW
postgres=#
postgres=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage
--------+-------+-------+-------+----------------------------------
public | dist | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | dual | view | gbase |
public | rep | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | tab_1 | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | v1 | view | gbase |
(5 rows)
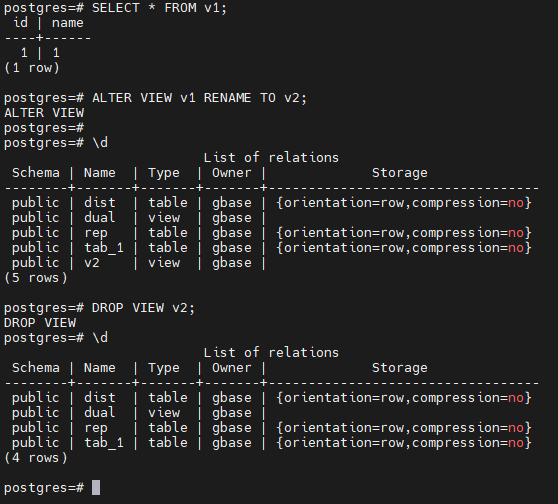
-- 查询视图数据
postgres=# SELECT * FROM v1;
id | name
----+------
1 | 1
(1 row)
-- 重命名视图
postgres=# ALTER VIEW v1 RENAME TO v2;
ALTER VIEW
postgres=#
postgres=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage
--------+-------+-------+-------+----------------------------------
public | dist | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | dual | view | gbase |
public | rep | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | tab_1 | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | v2 | view | gbase |
(5 rows)
-- 删除视图
postgres=# DROP VIEW v2;
DROP VIEW
postgres=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage
--------+-------+-------+-------+----------------------------------
public | dist | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | dual | view | gbase |
public | rep | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | tab_1 | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
(4 rows)
postgres=#
物化视图使用示例
-- 创建物化视图
postgres=# CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW mv1 AS SELECT * FROM tab_1;
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
postgres=#
postgres=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage
--------+-------+-------------------+-------+----------------------------------
public | dist | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | dual | view | gbase |
public | mv1 | materialized view | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | rep | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | tab_1 | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
(5 rows)
-- 新增数据
postgres=# INSERT INTO tab_1 VALUES (2,'2');
INSERT 0 1
postgres=#
postgres=# SELECT * FROM mv1;
id | name
----+------
1 | 1
(1 row)
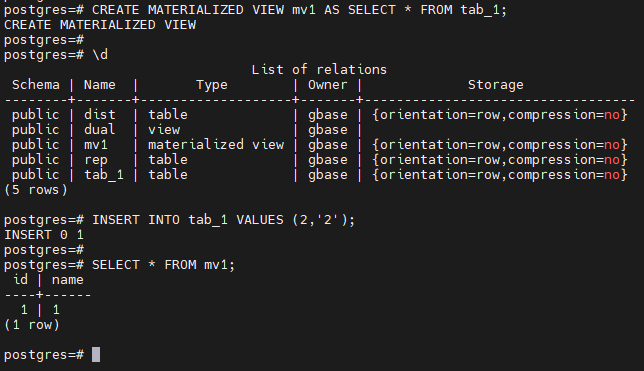
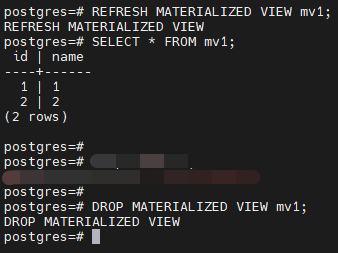
-- 刷新物化视图
postgres=# REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW mv1;
REFRESH MATERIALIZED VIEW
postgres=#
postgres=# SELECT * FROM mv1;
id | name
----+------
1 | 1
2 | 2
(2 rows)
-- 删除物化视图
postgres=# DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW mv1;
DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW
其它常用对象——序列(Sequence)
**序列(Sequence)**是用来产生唯一整数的数据库对象,序列的值是按照一定规则自增的整数,可以看作是存放等差数列的特殊表。因为自增所以不重复,因此说 Sequence 具有唯一标识性。这也是 Sequence常被用作主键的原因。
创建序列的同时如果指定相应的模式名,则该序列就在给定的模式中创建,否则会在当前模式中创建。序列名必须和同一个模式中的其他序列、表、索引、视图或外表的名称不同。
通过序列使某字段成为唯一标识符的方法有两种:
- 一种是声明字段的类型为序列整型,由数据库在后台自动创建一个对应的 Sequence。
- 一种是使用 CREATE SEQUENCE 自定义一个新的 Sequence,然后将 nextval(‘sequence_name’) 函数读取的序列值,指定为某一字段的默认值,这样该字段就可以作为唯一标识符。
示例一:声明字段类型为序列整型
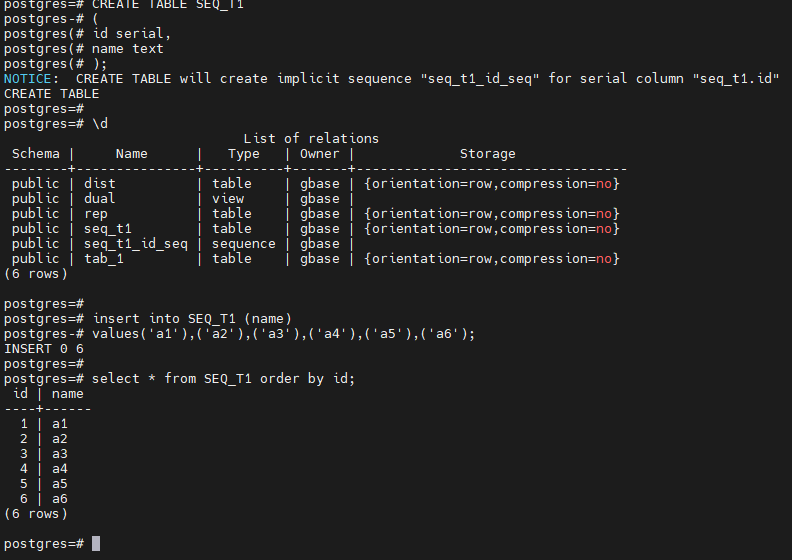
-- 创建数据表,指定 serial 类型
postgres=# CREATE TABLE SEQ_T1
postgres-# (
postgres(# id serial,
postgres(# name text
postgres(# );
NOTICE: CREATE TABLE will create implicit sequence "seq_t1_id_seq" for serial column "seq_t1.id"
CREATE TABLE
postgres=#
postgres=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage
--------+---------------+----------+-------+----------------------------------
public | dist | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | dual | view | gbase |
public | rep | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | seq_t1 | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | seq_t1_id_seq | sequence | gbase |
public | tab_1 | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
(6 rows)
postgres=#
postgres=# insert into SEQ_T1 (name)
postgres-# values('a1'),('a2'),('a3'),('a4'),('a5'),('a6');
INSERT 0 6
postgres=#
postgres=# select * from SEQ_T1 order by id;
id | name
----+------
1 | a1
2 | a2
3 | a3
4 | a4
5 | a5
6 | a6
(6 rows)
postgres=#
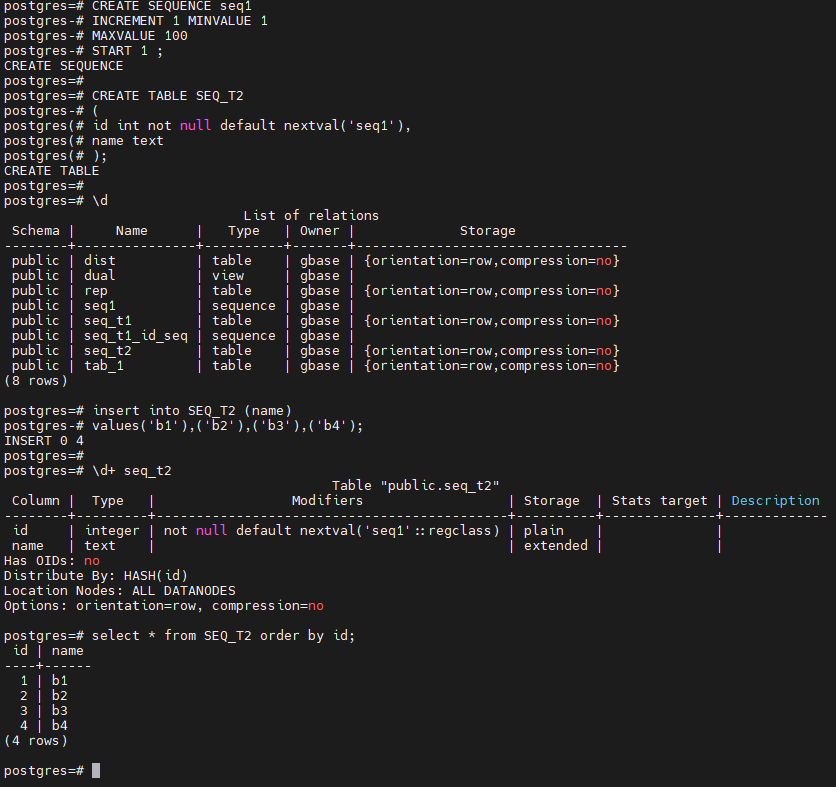
示例二:使用create sequence创建序列
-- 创建序列
postgres=# CREATE SEQUENCE seq1
postgres-# INCREMENT 1 MINVALUE 1
postgres-# MAXVALUE 100
postgres-# START 1 ;
CREATE SEQUENCE
postgres=#
-- 指定为某一字段的默认值,使该字段具有唯一标识属性。
postgres=# CREATE SEQUENCE seq1
postgres-# INCREMENT 1 MINVALUE 1
postgres-# MAXVALUE 100
postgres-# START 1 ;
CREATE SEQUENCE
postgres=#
postgres=# CREATE TABLE SEQ_T2
postgres-# (
postgres(# id int not null default nextval('seq1'),
postgres(# name text
postgres(# );
CREATE TABLE
postgres=#
postgres=# \d
List of relations
Schema | Name | Type | Owner | Storage
--------+---------------+----------+-------+----------------------------------
public | dist | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | dual | view | gbase |
public | rep | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | seq1 | sequence | gbase |
public | seq_t1 | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | seq_t1_id_seq | sequence | gbase |
public | seq_t2 | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
public | tab_1 | table | gbase | {orientation=row,compression=no}
(8 rows)
postgres=# \d+ seq_t2
Table "public.seq_t2"
Column | Type | Modifiers | Storage | Stats target | Description
--------+---------+--------------------------------------------+----------+--------------+-------------
id | integer | not null default nextval('seq1'::regclass) | plain | |
name | text | | extended | |
Has OIDs: no
Distribute By: HASH(id)
Location Nodes: ALL DATANODES
Options: orientation=row, compression=no
-- 插入数据
postgres=# insert into SEQ_T2 (name)
postgres-# values('b1'),('b2'),('b3'),('b4');
INSERT 0 4
-- 查询表
postgres=# select * from SEQ_T2 order by id;
id | name
----+------
1 | b1
2 | b2
3 | b3
4 | b4
(4 rows)
其它常用对象——同义词(synonym)
**同义词(Synonym)**是数据库对象的别名,用于记录与其他数据库对象名间的映射关系,用户可以使用同义词访问关联的数据库对象。
注意事项
- 定义同义词的用户成为其所有者。
- 若指定模式名称,则同义词在指定模式中创建。否则,在当前模式创建。
- 支持通过同义词访问的数据库对象包括:表、视图、函数和存储过程。
- 使用同义词时,用户需要具有对关联对象的相应权限。
- 支持使用同义词的DML语句包括:SELECT、INSERT、UPDATE、DELETE、EXPLAIN、CALL。
同义词创建语法:
CREATE [ OR REPLACE ] SYNONYM synonym_name
FOR object_name; -- object_name可以是不存在的对象名称
同义词使用示例
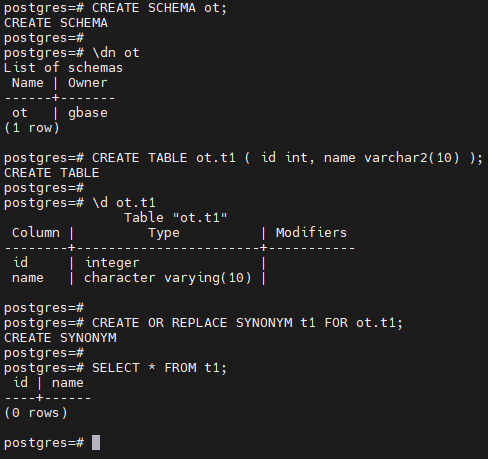
-- 创建模式 ot
gbase8c=# CREATE SCHEMA ot;
postgres=# CREATE SCHEMA ot;
CREATE SCHEMA
postgres=#
postgres=# \dn ot
List of schemas
Name | Owner
------+-------
ot | gbase
(1 row)
-- 创建表 ot.t1 及其同义词 t1
postgres=# CREATE TABLE ot.t1 ( id int, name varchar2(10) );
CREATE TABLE
postgres=#
postgres=# \d ot.t1
Table "ot.t1"
Column | Type | Modifiers
--------+-----------------------+-----------
id | integer |
name | character varying(10) |
postgres=#
postgres=# CREATE OR REPLACE SYNONYM t1 FOR ot.t1;
CREATE SYNONYM
postgres=#
-- 使用同义词 t1
postgres=# SELECT * FROM t1;
id | name
----+------
(0 rows)
postgres=#
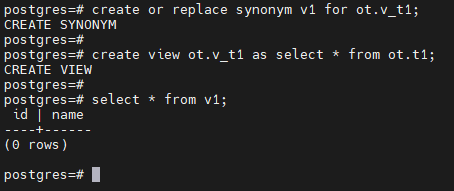
--创建同义词v1及其关联视图ot.v_t
--(注意,此时关联对象ot.v_t1不存在,但同义词可以创建成功)
postgres=# create or replace synonym v1 for ot.v_t1;
CREATE SYNONYM
postgres=#
postgres=# create view ot.v_t1 as select * from ot.t1;
CREATE VIEW
postgres=#
postgres=# select * from v1;
id | name
----+------
(0 rows)
postgres=#