psutil
psutil(python system and process utilities)是一个跨平台库,用来获取操作系统以及硬件相关的信息,比如CPU、内存、磁盘、网络等。主要用于系统监控、分析进程等。它实现了很多linux命令行工具提供的功能,如ps, top, lsof, netstat, ifconfig, who, df, kill, free
等。
使用pip安装:pip install psutil
下面是一个使用psutil查看网络流量的例子:
使用psutil查看网络流量
import time
import psutil
last_recv = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv
last_sent = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent
while True:
bytes_recv = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv
bytes_sent = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent
new_recv = bytes_recv - last_recv
new_sent = bytes_sent - last_sent
mb_new_recv = new_recv / (1024 ** 2)
mb_new_sent = new_sent / (1024 ** 2)
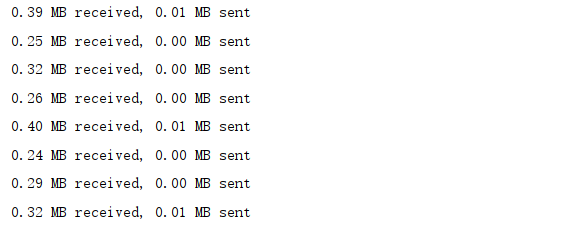
print(f"{mb_new_recv:.2f} MB received, {mb_new_sent:.2f} MB sent")
last_recv = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv
last_sent = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent
time.sleep(1)
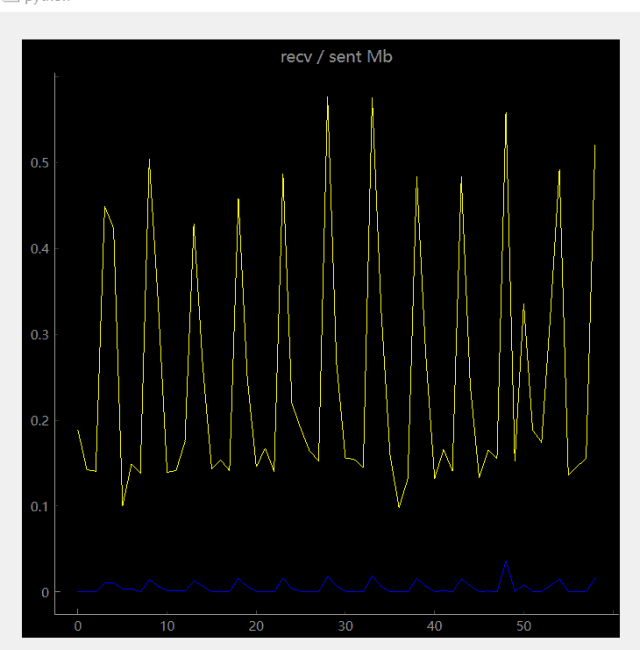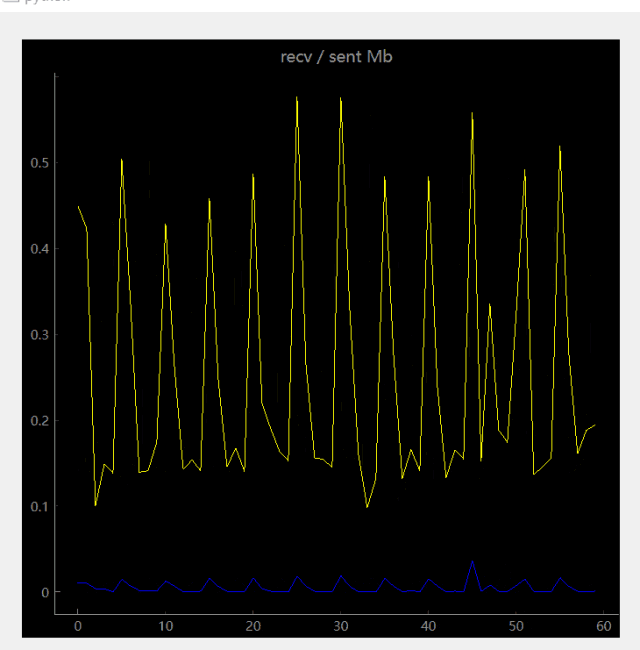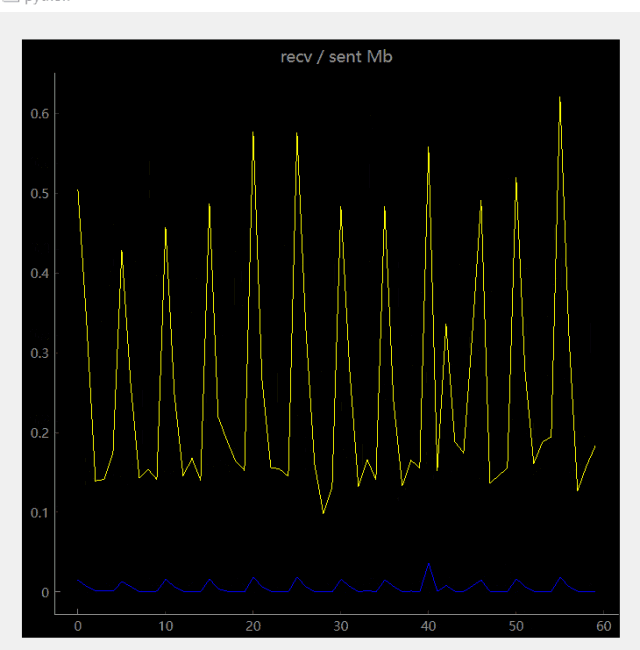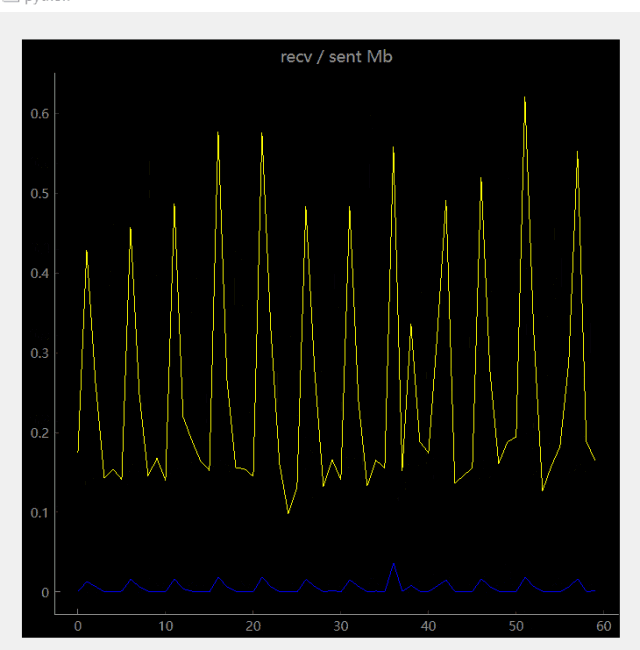
可以使用qtgraph可视化一下:
from PyQt6.QtWidgets import QWidget, QApplication
from pyqtgraph import PlotWidget
from PyQt6 import QtCore
import numpy as np
import pyqtgraph as pq
import psutil
class Window(QWidget):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# 设置下尺寸
self.resize(600, 600)
# 添加 PlotWidget 控件
self.plotWidget_ted = PlotWidget(self, title='recv / sent Mb')
# 设置该控件尺寸和相对位置
self.plotWidget_ted.setGeometry(QtCore.QRect(25, 25, 550, 550))
self.recv_lst = []
self.sent_lst = []
self.last_recv = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv
self.last_sent = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent
self.curve1 = self.plotWidget_ted.plot(self.recv_lst, name="recv_lst",pen='y')
self.curve2 = self.plotWidget_ted.plot(self.sent_lst, name="sent_lst",pen='b')
# 设定定时器
self.timer = pq.QtCore.QTimer()
# 定时器信号绑定 update_data 函数
self.timer.timeout.connect(self.update_data)
# 定时器间隔xx ms,
self.timer.start(1000)
# 数据左移
def update_data(self):
self.bytes_recv = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv
self.bytes_sent = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent
self.new_recv = self.bytes_recv - self.last_recv
self.new_sent = self.bytes_sent - self.last_sent
mb_new_recv = self.new_recv / (1024 ** 2)
mb_new_sent = self.new_sent / (1024 ** 2)
self.recv_lst.append(mb_new_recv)
self.sent_lst.append(mb_new_sent)
self.last_recv = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_recv
self.last_sent = psutil.net_io_counters().bytes_sent
if len(self.recv_lst) > 60:
self.recv_lst[:] = self.recv_lst[1:]
self.sent_lst[:] = self.sent_lst[1:]
self.curve1.setData(self.recv_lst)
self.curve2.setData(self.sent_lst)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import sys
app = QApplication(sys.argv)
window = Window()
window.show()
sys.exit(app.exec())
查看系统硬件情况(cpu、内存、硬盘)
import psutil
from pprint import pprint
def toGB(tp):
to_cvt = {'total', 'available', 'used', 'free'}
gb = []
for k, v in tp._asdict().items():
gb.append(v / (1024 ** 3) if (k in to_cvt) else v)
return tp._make(gb)
print(f"cpu核心数量:{psutil.cpu_count()}")
print(f"cpu物理核心数量:{psutil.cpu_count(logical=False)}")
print(f"cpu频率:{psutil.cpu_freq()}")
# 内存
print(f"内存:{toGB(psutil.virtual_memory())}")
print(f"交换内存:{toGB(psutil.swap_memory())}")
# 磁盘
print("硬盘分区:")
pprint(psutil.disk_partitions())
print("C盘使用情况")
print(toGB(psutil.disk_usage("C:\\"))) # C盘使用情况
pprint(psutil.disk_io_counters()) # 查看磁盘 IO 统计信息
查看进程
from pprint import pprint
import psutil
def find_procs_by_name(name):
"Return a list of processes matching 'name'."
ls = []
for p in psutil.process_iter(['name']):
if p.info['name'] == name or name in p.info['name']:
ls.append(p)
return ls
def print_process_info(p):
print("进程名称:", p.name()) # 进程名称
print("exe路径:", p.exe()) # 进程的exe路径
print("工作目录:", p.cwd()) # 进程的工作目录
print("启动的命令行", p.cmdline()) # 进程启动的命令行
print("进程id:", p.pid) # 当前进程id
print("父进程id:", p.ppid()) # 父进程id
print("父进程", p.parent()) # 父进程
print("子进程列表")
pprint(p.children()) # 子进程列表
print("状态", p.status()) # 进程状态
print("用户名:", p.username()) # 进程用户名
print("创建时间:", p.create_time()) # 进程创建时间,返回时间戳
print("使用的cpu时间:", p.cpu_times()) # 进程使用的cpu时间
print("所使用的的内存:", p.memory_info()) # 进程所使用的的内存
print("打开的文件:")
pprint(p.open_files()) # 进程打开的文件
print("相关的网络连接:")
pprint(p.connections()) # 进程相关的网络连接
print("线程数量", p.num_threads()) # 进程内的线程数量,这个进程开启了多少个线程
print("所有线程信息:")
pprint(p.threads()) # 这个进程内的所有线程信息
print("环境变量:")
pprint(p.environ()) # 进程的环境变量
if __name__ == '__main__':
ls = []
for p in psutil.process_iter(['name']):
ls.append(p)
print('ls')
pprint(ls)
# 获取进程相关的具体信息
p_lst = find_procs_by_name('python')
print('python')
pprint(p_lst)
for p in p_lst:
print(p, "=" * 80)
print_process_info(p)
参考:
[1]psutil文档:https://psutil.readthedocs.io/en/latest/#
[2]psutil中文文档:https://hellowac.github.io/psutil-doc-zh/guide/install.html
[3]psutil简介: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/380842937
[4]pyqtgraph简介:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/165998670
文章转载自一只大鸽子,如果涉嫌侵权,请发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。






