MySQL变量中的分类
MySQL中变量可分为以下四类
1、用户定义变量
2、参数变量
3、局部变量
4、系统变量
MySQL官方的介绍点 这里
1、用户定义变量
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/user-variables.html
用户变量的声明
SET @var_name = expr [, @var_name = expr] …
例如以下声明语句
set @test1 = 10;
set @test2 := 20;
select @test3 := help_topic_id from mysql.help_topic where help_topic_id = 30;
复制对于 set 语句 用 = 号或 := 号赋值是一样的
对于select 语句 只能用 := 号赋值。
用户定义变量的作用域是当前session
在后面的语句中都可以使用刚才定义的变量
select @test1,@test2,@test3
复制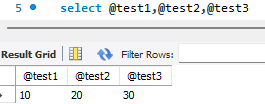
Performance Schema user_variables_by_thread table can see all user variables for all sessions
Performance_schema.user_variables_by_thread 可以看到所有用户定义的变量
select * from Performance_schema.user_variables_by_thread
复制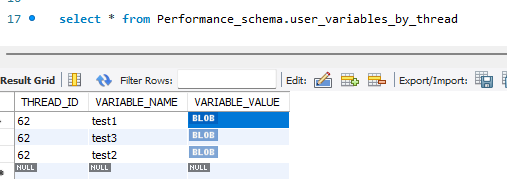
2、参数变量与局部变量
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/stored-program-variables.html
参数变量与局部变量都是存储过程或函数内部使用的变量
局部变量的声明
DECLARE var_name [, var_name] … type [DEFAULT value]
delimiter ;;
CREATE PROCEDURE sp1 (paramvar int)
BEGIN
if paramvar =1 then
begin
declare localvar1 int default 10;
declare help_topic_id int default -10;
select localvar1,help_topic_id from mysql.help_topic where mysql.help_topic.help_topic_id = 10;
end;
else
begin
select localvar1,help_topic_id from mysql.help_topic where help_topic_id = 30;
end;
end if;
END ;;
复制paramvar 就为参数变量
localvar1与 help_topic_id 就为我声明的局部变量
通过上面这个存储过程来说明局部变量存在的几个注意事项
1、当局部变量与列名重复时,优先取的是局部变量
当执行 call sp1(1); 时结果如下
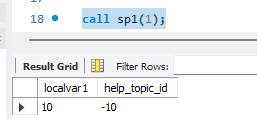
help_topic_id 局部变量为-10,而我where 条件限制的的 help_topic_id 列 值为10
但最终select 出来 help_topic_id 的值为-10;
2、局部变量的作用域就为begin end的语句块以及嵌套的子句块
当执行 call sp1(0); 时结果如下
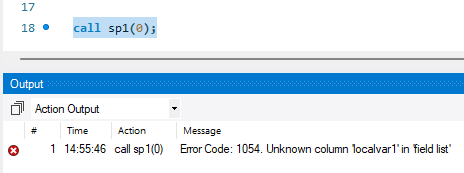
第二个begin end 块不能识别第一个begin end 块定义的局部变量
3、系统变量
session级变量赋值
SET SESSION sql_mode = 'TRADITIONAL';
SET LOCAL sql_mode = 'TRADITIONAL';
SET @@SESSION.sql_mode = 'TRADITIONAL';
SET @@LOCAL.sql_mode = 'TRADITIONAL';
SET @@sql_mode = 'TRADITIONAL';
SET sql_mode = 'TRADITIONAL';
复制session级变量赋值 可以用上面6种方式赋值。但建议还是用第1种或第3种
session变量赋值后立即生效
全局变量赋值
SET GLOBAL max_connections = 1000;
SET @@GLOBAL.max_connections = 1000;
复制全局变量赋值可以用上面两种方式
全局变量这样设置的在数据库重启后,将回到默认值或配置文件中配置的值
查看sort_buffer_size 当前session的值,全局的值、max_connections全局的值(max_connections为全局级的,不存在session的值)
select @@SESSION.sort_buffer_size, @@GLOBAL.sort_buffer_size,@@GLOBAL.max_connections;
复制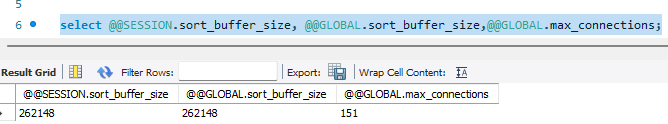
用如下语句更改sort_buffer_size,max_connections 全局的值
SET @@GLOBAL.sort_buffer_size = 16384, @@GLOBAL.max_connections = 200;
复制然后再查看
select @@sort_buffer_size,@@max_connections;
复制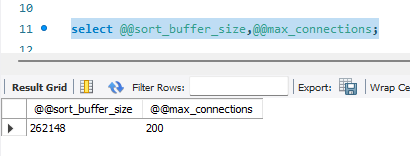
可以看到 sort_buffer_size未生效,但max_connections生效了,为什么呢?
因为全局变量设置后,只有对新的连接生效,而对当前连接是不生效的
为什么max_connections 又生效的呢?
对用select @@系统变量。 如果这个变量不存在session级,则会显示全局级的值 所以select与set 在这里有区别,官方文档专门列出来了让开发者留意。
Note
A reference to a system variable in an expression as @@var_name (with @@ rather than @@GLOBAL. or @@SESSION.) returns the session value if it exists and the global value otherwise. This differs from SET @@var_name = expr, which always refers to the session value.
设置全局变量的值 并重启后仍然有效
SET PERSIST max_connections = 1000;
SET @@PERSIST.max_connections = 1000;
复制设置全局变量的值,只在重启后才生效
SET PERSIST_ONLY max_connections = 1000;
SET @@PERSIST_ONLY.max_connections = 1000;
复制








