
本文首发于Ressmix个人站点:https://www.tpvlog.com
本章,我来讲讲Broker是如何定时发送心跳到NameServer,让NameServer感知到Broker一直都存活着的。如果Broker一段时间内没有发送心跳到NameServer,那么NameServer是如何感知到Broker已经挂掉了呢?
一、心跳原理
首先,我们来回顾下BrokerController的启动,BrokerController启动的时候,其实并不是仅仅发送一次注册请求,而是启动了一个定时任务,会每隔一段时间就发送一次注册请求。
1public void start() throws Exception {
2 //...忽略无关代码
3
4 // 启动一个定时调度任务,每隔一段时间进行一次注册,默认30s
5 this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
6 @Override
7 public void run() {
8 try {
9 BrokerController.this.registerBrokerAll(true, false, brokerConfig.isForceRegister());
10 } catch (Throwable e) {
11 log.error("registerBrokerAll Exception", e);
12 }
13 }
14 }, 1000 * 10, Math.max(10000, Math.min(brokerConfig.getRegisterNameServerPeriod(), 60000)), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
15
16 //...忽略无关代码
17}
我们通过上一章已经知道,第一次发送注册请求就是把Broker路由数据放入到NameServer的RouteInfoManager的路由数据表里去。
但是后续每隔30秒Broker都会发送一次注册请求,这些后续定时发送的注册请求本质就是Broker发送的心跳,那么,NameServer是如何处理这些后续重复发送过来的注册请求(心跳)呢?
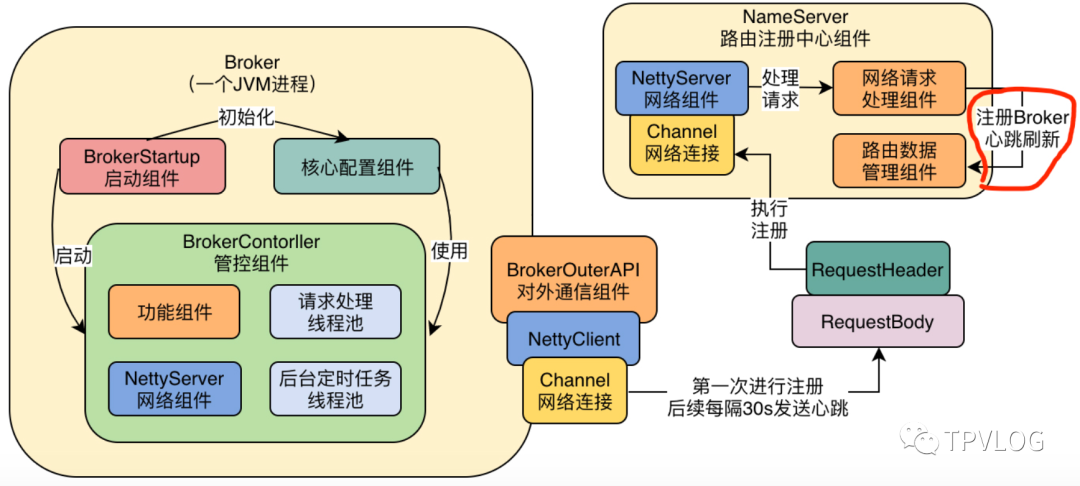
1.1 RouteInfoManager
我们来看下RouteInfoManager
的注册方法registerBroker
的逻辑。下面的代码,有几个核心要点:
Broker的路由信息全部维护在brokerAddrTable这个Map里面,然后Broker会以集群为维度被管理;
心跳机制的关键是用了一个brokerLiveTable管理Broker的最新心跳,它的key就是Broker,Value是BrokerLiveInfo对象。Broker每上送一次心跳,就会创建一个BrokerLiveInfo对象覆盖掉brokerLiveTable里面老的,BrokerLiveInfo里面有当前时间戳,表示最近一次心跳的时间。
1public RegisterBrokerResult registerBroker(
2 final String clusterName,
3 final String brokerAddr,
4 final String brokerName,
5 final long brokerId,
6 final String haServerAddr,
7 final TopicConfigSerializeWrapper topicConfigWrapper,
8 final List<String> filterServerList,
9 final Channel channel) {
10 RegisterBrokerResult result = new RegisterBrokerResult();
11 try {
12 try {
13 // 加写锁,保证同一时刻只有一个线程能进行修改
14 this.lock.writeLock().lockInterruptibly();
15
16 // 根据clusterName获取这个集群下的Broker集合
17 Set<String> brokerNames = this.clusterAddrTable.get(clusterName);
18 if (null == brokerNames) {
19 brokerNames = new HashSet<String>();
20 this.clusterAddrTable.put(clusterName, brokerNames);
21 }
22 // 添加到集群
23 brokerNames.add(brokerName);
24
25 boolean registerFirst = false;
26
27 // Broker相关数据放在brokerAddrTable这个Map里,路由信息都在里面
28 BrokerData brokerData = this.brokerAddrTable.get(brokerName);
29 // 这里首次注册的情况
30 if (null == brokerData) {
31 registerFirst = true;
32 brokerData = new BrokerData(clusterName, brokerName, new HashMap<Long, String>());
33 this.brokerAddrTable.put(brokerName, brokerData);
34 }
35
36 // 对路由数据做处理,忽略
37 Map<Long, String> brokerAddrsMap = brokerData.getBrokerAddrs();
38 //Switch slave to master: first remove <1, IP:PORT> in namesrv, then add <0, IP:PORT>
39 //The same IP:PORT must only have one record in brokerAddrTable
40 Iterator<Entry<Long, String>> it = brokerAddrsMap.entrySet().iterator();
41 while (it.hasNext()) {
42 Entry<Long, String> item = it.next();
43 if (null != brokerAddr && brokerAddr.equals(item.getValue()) && brokerId != item.getKey()) {
44 it.remove();
45 }
46 }
47
48 String oldAddr = brokerData.getBrokerAddrs().put(brokerId, brokerAddr);
49 registerFirst = registerFirst || (null == oldAddr);
50
51 if (null != topicConfigWrapper
52 && MixAll.MASTER_ID == brokerId) {
53 if (this.isBrokerTopicConfigChanged(brokerAddr, topicConfigWrapper.getDataVersion())
54 || registerFirst) {
55 ConcurrentMap<String, TopicConfig> tcTable =
56 topicConfigWrapper.getTopicConfigTable();
57 if (tcTable != null) {
58 for (Map.Entry<String, TopicConfig> entry : tcTable.entrySet()) {
59 this.createAndUpdateQueueData(brokerName, entry.getValue());
60 }
61 }
62 }
63 }
64
65 // 这里是关键,Broker心跳管理:每次接受到心跳请求后,这里会封装一个BrokerLiveInfo,放到brokerLiveTable中,替换掉老的
66 // 这个BrokerLiveInfo里面,有一个当前时间戳,代表最近一次心跳的时间
67 BrokerLiveInfo prevBrokerLiveInfo = this.brokerLiveTable.put(brokerAddr,
68 new BrokerLiveInfo(
69 System.currentTimeMillis(),
70 topicConfigWrapper.getDataVersion(),
71 channel,
72 haServerAddr));
73 if (null == prevBrokerLiveInfo) {
74 log.info("new broker registered, {} HAServer: {}", brokerAddr, haServerAddr);
75 }
76
77 // 下面的代码忽略
78 if (filterServerList != null) {
79 if (filterServerList.isEmpty()) {
80 this.filterServerTable.remove(brokerAddr);
81 } else {
82 this.filterServerTable.put(brokerAddr, filterServerList);
83 }
84 }
85
86 if (MixAll.MASTER_ID != brokerId) {
87 String masterAddr = brokerData.getBrokerAddrs().get(MixAll.MASTER_ID);
88 if (masterAddr != null) {
89 BrokerLiveInfo brokerLiveInfo = this.brokerLiveTable.get(masterAddr);
90 if (brokerLiveInfo != null) {
91 result.setHaServerAddr(brokerLiveInfo.getHaServerAddr());
92 result.setMasterAddr(masterAddr);
93 }
94 }
95 }
96 } finally {
97 this.lock.writeLock().unlock();
98 }
99 } catch (Exception e) {
100 log.error("registerBroker Exception", e);
101 }
102
103 return result;
104}
二、故障感知
了解了Broker的心跳机制,我们再来思考一个问题,如果当前的Broker挂掉了,NameServer是如何检测到的?
我们重新回到NamesrvController的initialize()
方法里去,里面启动了一个定时调度任务,调用RouteInfoManager的scanNotActiveBroker
方法去定时扫描不活跃的Broker。
1public boolean initialize() {
2 this.kvConfigManager.load();
3
4 this.remotingServer = new NettyRemotingServer(this.nettyServerConfig, this.brokerHousekeepingService);
5
6 this.remotingExecutor =
7 Executors.newFixedThreadPool(nettyServerConfig.getServerWorkerThreads(), new ThreadFactoryImpl("RemotingExecutorThread_"));
8
9 this.registerProcessor();
10
11 // 后台定时任务,扫码不活跃的Broker
12 this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
13 @Override
14 public void run() {
15 NamesrvController.this.routeInfoManager.scanNotActiveBroker();
16 }
17 }, 5, 10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
18
19 this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
20 @Override
21 public void run() {
22 NamesrvController.this.kvConfigManager.printAllPeriodically();
23 }
24 }, 1, 10, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
25
26 //...忽略无关代码
27
28 return true;
29}
2.1 RouteInfoManager
我们来看下RouteInfoManager的scanNotActiveBroker方法:
1public void scanNotActiveBroker() {
2 // 遍历brokerLiveTable
3 Iterator<Entry<String, BrokerLiveInfo>> it = this.brokerLiveTable.entrySet().iterator();
4 while (it.hasNext()) {
5 Entry<String, BrokerLiveInfo> next = it.next();
6 // 查看每个Broker的BrokerLiveInfo,也就是Broker的最新心跳时间
7 long last = next.getValue().getLastUpdateTimestamp();
8 // 如果心跳超时,就移除掉,默认120s
9 if ((last + BROKER_CHANNEL_EXPIRED_TIME) < System.currentTimeMillis()) {
10 // 断开与该超时Broker的连接
11 RemotingUtil.closeChannel(next.getValue().getChannel());
12 it.remove();
13 log.warn("The broker channel expired, {} {}ms", next.getKey(), BROKER_CHANNEL_EXPIRED_TIME);
14 this.onChannelDestroy(next.getKey(), next.getValue().getChannel());
15 }
16 }
17}
该方法很简单,就是遍历brokerLiveTable,找到那些超过120s(默认)还没发送心跳的Broker,将它们移除,同时断开连接。这就是Broker心跳机制的原理。
三、总结
本章,我讲解了Broker的心跳机制,本质就是NameServer中的RouteInfoManager组件对其中的Broker路由信息的管理,每隔一段时间扫描保存的Broker信息,检测是否活跃。






