Kafka是高吞吐低延迟的高并发、高性能的消息中间件。一般来说,Kafka集群可以处理每秒几十万、甚至上百万的写入请求。Kafka是怎样做到如此高的吞吐量和性能的呢?
1 批量消息发送。
2 页缓存技术以及顺序写磁盘
3 零拷贝
批量消息发送
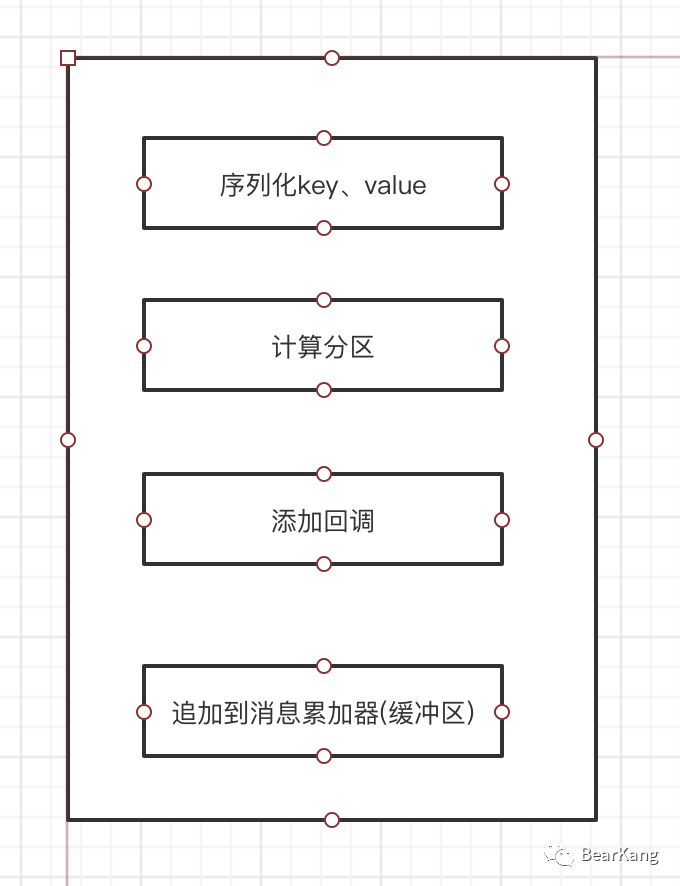
Kafka会启动一个生产者时, 启动一个叫sender的io线程,发送消息时,实际仅返回了添加进消息累加器的Future,如果ack条件为0,那么实际发送仅仅会添加到消息累加器即为结束了,发送流程大致有一下几个步骤。
this.errors = this.metrics.sensor("errors");this.sender = this.newSender(logContext, kafkClient, this.metadata);String ioThreadName = "kafka-producer-network-thread | " + this.clientId;this.ioThread = new KafkaThread(ioThreadName,this.sender, true);this.ioThread.start();config.logUnused();AppInfoParser.registerAppInfo("kafka.producer",this.clientId, this.metrics, time.milliseconds());this.log.debug("Kafka producer started");
Kafka在消息发送时,主要在代码层面做了一个批量的优化,即批量消息的发送。
public FutureRecordMetadata tryAppend(long timestamp, byte[] key, byte[] value, Header[] headers, Callback callback, long now) {if (!this.recordsBuilder.hasRoomFor(timestamp, key, value, headers)) {return null;} else {Long checksum = this.recordsBuilder.append(timestamp, key, value, headers);this.maxRecordSize = Math.max(this.maxRecordSize, AbstractRecords.estimateSizeInBytesUpperBound(this.magic(), this.recordsBuilder.compressionType(), key, value, headers));this.lastAppendTime = now;FutureRecordMetadata future = new FutureRecordMetadata(this.produceFuture, (long)this.recordCount, timestamp, checksum, key == null ? -1 : key.length, value == null ? -1 : value.length, Time.SYSTEM);this.thunks.add(new ProducerBatch.Thunk(callback, future));++this.recordCount;return future;}}
发送消息的任务则完全由sender线程完成,sender的run方法核心如下
public void run() {this.log.debug("Starting Kafka producer I/O thread.");while (this.running) {try {this.runOnce();} catch (Exception var5) {this.log.error("Uncaught error in kafka producer I/O thread: ", var5);}}}private void sendProduceRequests(Map<Integer, List<ProducerBatch>> collated, long now) {Iterator var4 = collated.entrySet().iterator();while(var4.hasNext()) {Entry<Integer, List<ProducerBatch>> entry =(Entry)var4.next();this.sendProduceRequest(now, (Integer)entry.getKey(), this.acks, this.requestTimeoutMs,(List)entry.getValue());}}
sender线程在running情况下,不停轮询就绪的的分区和批次,然后将消息按批次发送到Broker,这个过程如下图所示:
Broker页缓存和磁盘顺序写
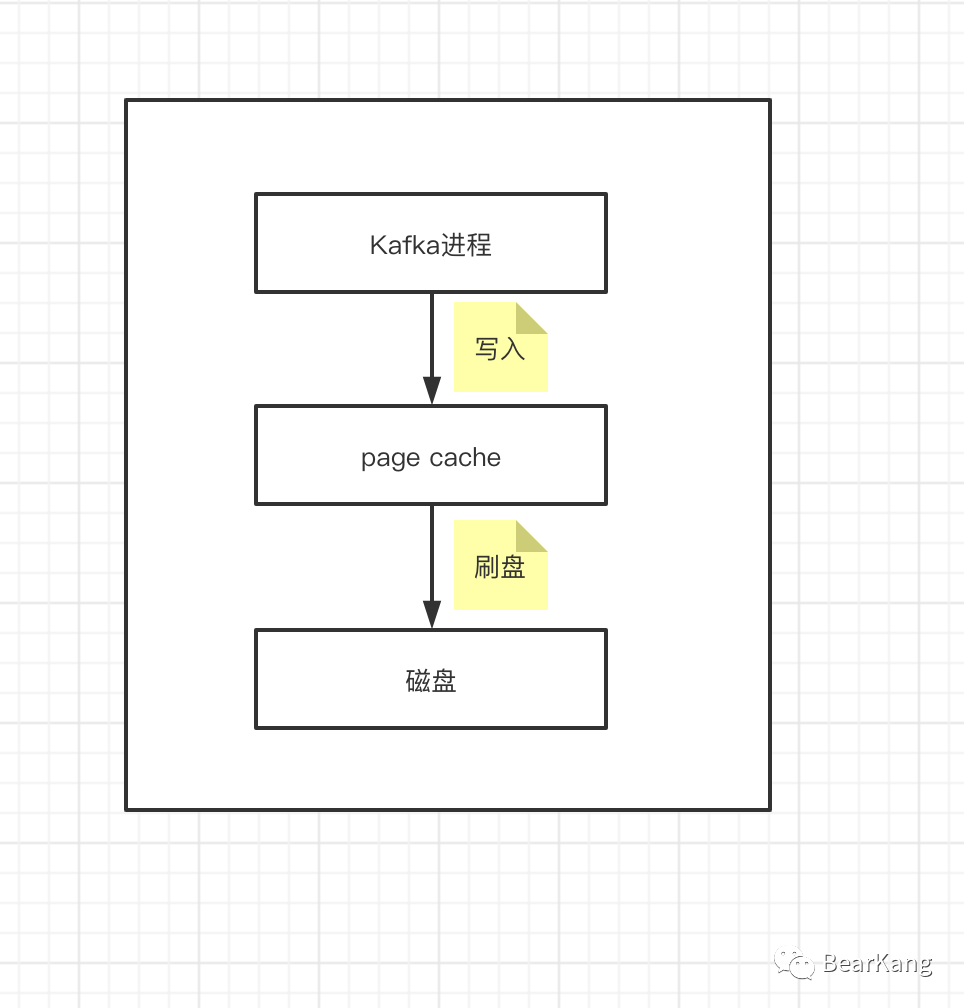
Kafka消息是持久化在磁盘上的,因此Kafka才有了持久化保证。但是我们知道磁盘io是比较耗时的操作,因此大多数中间件都会尽量避免直接和磁盘打交道,Kafka也是如此,在写入数据的时候,Kafka会先写入page cache里,也就是仅仅写入内存中,接下来由操作系统自己决定什么时候把page cache里的数据真的刷入磁盘文件中(刷盘策略),另一方面,就是kafka写数据的时候,它是以磁盘顺序写的方式来写的。也就是说,仅仅将数据追加到文件的末尾,而不是在文件的随机位置来修改数据。这种追加写的方式在性能上要比随机写效率高很多,因此Broker端的写入实际上基本可以认为是写内存。
Broker零拷贝
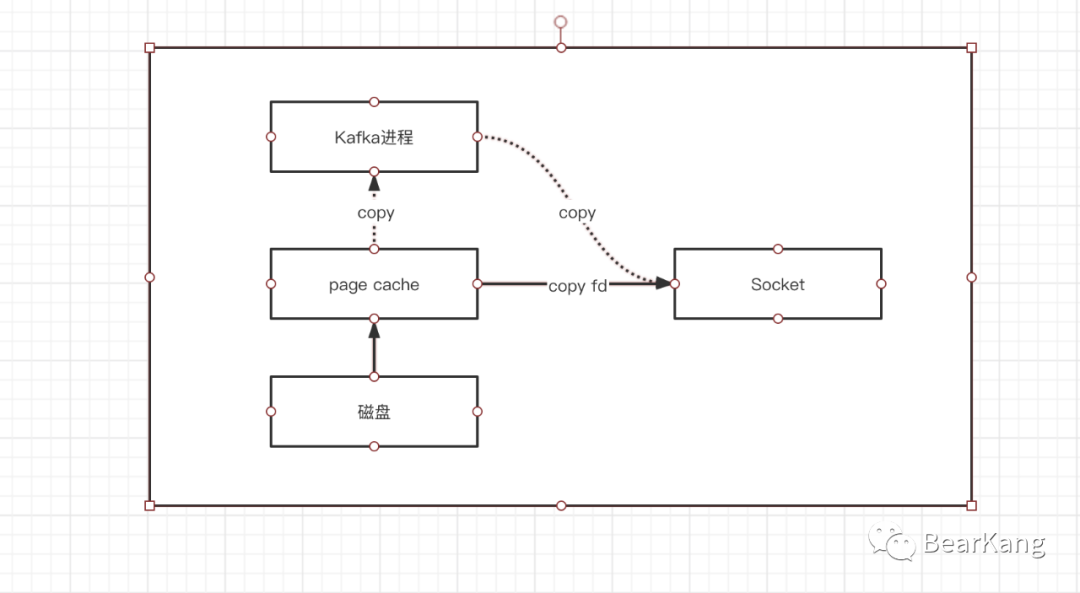
传统发送磁盘数据,数据需要经过磁盘->page cache->用户进程->Socket,经过三次拷贝,而大名鼎鼎的零拷贝只需要将数据文件从磁盘->page cache->Socket,而且从page cache拷贝到socket缓冲区只需要拷贝文件fd即可,因此可以减少两次文件的拷贝和内核到用户态的切换,因此性能得到大幅度提升。
总结
Kafka实现高吞吐量的原因是有很多方面原因的,其中包括消息的批量发送(批次大小和间隔可配置),页缓存技术和磁盘顺序写(Broker适当调大内存给更多的页缓存使用是有帮助的),消费时的零拷贝技术等。







