
max_locks_per_transaction * (max_connections + max_prepared_transactions)
bill@bill=>show max_locks_per_transaction ; max_locks_per_transaction--------------------------- 10(1 row)bill@bill=>show max_connections ; max_connections----------------- 50(1 row)bill@bill=>show max_prepared_transactions; max_prepared_transactions--------------------------- 0(1 row)
bill@bill=>do language plpgsql $$bill$# declarebill$# beginbill$# for i in 1..20000 loopbill$# execute 'create table tbl_'||i||'(id int)';bill$# end loop;bill$# end;bill$# $$;ERROR: out of shared memoryHINT: You might need to increase max_locks_per_transaction.CONTEXT: SQL statement 'create table tbl_1889(id int)'PL/pgSQL function inline_code_block line 5 at EXECUTE
Spinlocks:自旋锁,其保护的对象一般是数据库内部的一些数据结构,是一种轻量级的锁。
LWLocks:轻量锁,也是主要用于保护数据库内部的一些数据结构,支持独占和共享两种模式。
SIReadLock predicate locks:谓词锁,主要是用来表示数据库对象和事务间的一个特定关系。
Regular locks:又叫heavyweight locks,也就是我们常说的表锁、行锁这些。也是我们接下来要详细讨论的。
typedef struct LockMethodData{ int numLockModes; const LOCKMASK *conflictTab; const char *const * lockModeNames; const bool *trace_flag;} LockMethodData;
numLockModes:锁模式数量,读/写等。
conflictTab:不同锁模式间的冲突关系。
lockModeNames:LockMethod名。
trace_flag:用户debug信息输出。
DEFAULT_LOCKMETHOD:系统默认锁方法,例如表锁、行锁。
USER_LOCKMETHOD:用户定义的锁方法,例如advisory lock。
RESOURCE_LOCKMETHOD:资源锁。
typedef struct LOCK{ /* hash key */ LOCKTAG tag; /* unique identifier of lockable object */ /* data */ LOCKMASK grantMask; /* bitmask for lock types already granted */ LOCKMASK waitMask; /* bitmask for lock types awaited */ SHM_QUEUE procLocks; /* list of PROCLOCK objects assoc. with lock */ PROC_QUEUE waitProcs; /* list of PGPROC objects waiting on lock */ int requested[MAX_LOCKMODES]; /* counts of requested locks */ int nRequested; /* total of requested[] array */ int granted[MAX_LOCKMODES]; /* counts of granted locks */ int nGranted; /* total of granted[] array */ bool holdTillEndXact; /* flag for global deadlock detector */} LOCK;
typedef enum LockTagType{ LOCKTAG_RELATION, /* whole relation */ /* ID info for a relation is DB OID + REL OID; DB OID = 0 if shared */ LOCKTAG_RELATION_EXTEND, /* the right to extend a relation */ /* same ID info as RELATION */ LOCKTAG_PAGE, /* one page of a relation */ /* ID info for a page is RELATION info + BlockNumber */ LOCKTAG_TUPLE, /* one physical tuple */ /* ID info for a tuple is PAGE info + OffsetNumber */ LOCKTAG_TRANSACTION, /* transaction (for waiting for xact done) */ /* ID info for a transaction is its TransactionId */ LOCKTAG_VIRTUALTRANSACTION, /* virtual transaction (ditto) */ /* ID info for a virtual transaction is its VirtualTransactionId */ LOCKTAG_RELATION_APPENDONLY_SEGMENT_FILE, /* Segment file within an Append-Only relation */ /* ID info for a relation is DB OID + REL OID + (LOGICAL) SEGMENT FILE # */ LOCKTAG_OBJECT, /* non-relation database object */ /* ID info for an object is DB OID + CLASS OID + OBJECT OID + SUBID */ /* * Note: object ID has same representation as in pg_depend and * pg_description, but notice that we are constraining SUBID to 16 bits. * Also, we use DB OID = 0 for shared objects such as tablespaces. */ LOCKTAG_RESOURCE_QUEUE, /* ID info for resource queue is QUEUE ID */ LOCKTAG_DISTRIB_TRANSACTION,/* CDB: distributed transaction (for waiting for distributed xact done) */ LOCKTAG_USERLOCK, /* reserved for old contrib/userlock code */ LOCKTAG_ADVISORY /* advisory user locks */} LockTagType;
typedef struct PROCLOCK{ /* tag */ PROCLOCKTAG tag; /* unique identifier of proclock object */ /* data */ LOCKMASK holdMask; /* bitmask for lock types currently held */ LOCKMASK releaseMask; /* bitmask for lock types to be released */ SHM_QUEUE lockLink; /* list link in LOCK's list of proclocks */ SHM_QUEUE procLink; /* list link in PGPROC's list of proclocks */ int nLocks; /* total number of times lock is held by this process, used by resource scheduler */ SHM_QUEUE portalLinks; /* list of ResPortalIncrements for this proclock, used by resource scheduler */} PROCLOCK;typedef struct PROCLOCKTAG{ /* NB: we assume this struct contains no padding! */ LOCK *myLock; /* link to per-lockable-object information */ PGPROC *myProc; /* link to PGPROC of owning backend */} PROCLOCKTAG;
typedef struct LOCALLOCKTAG{ LOCKTAG lock; /* identifies the lockable object */ LOCKMODE mode; /* lock mode for this table entry */} LOCALLOCKTAG;typedef struct LOCALLOCKOWNER{ /* * Note: if owner is NULL then the lock is held on behalf of the session; * otherwise it is held on behalf of my current transaction. * * Must use a forward struct reference to avoid circularity. */ struct ResourceOwnerData *owner; int64 nLocks; /* # of times held by this owner */} LOCALLOCKOWNER;typedef struct LOCALLOCK{ /* tag */ LOCALLOCKTAG tag; /* unique identifier of locallock entry */ /* data */ LOCK *lock; /* associated LOCK object, if any */ PROCLOCK *proclock; /* associated PROCLOCK object, if any */ uint32 hashcode; /* copy of LOCKTAG's hash value */ bool istemptable; /* MPP: During prepare we set this if the lock is on a temp table, to avoid MPP-1094 */ int64 nLocks; /* total number of times lock is held */ int numLockOwners; /* # of relevant ResourceOwners */ int maxLockOwners; /* allocated size of array */ bool holdsStrongLockCount; /* bumped FastPathStrongRelationLocks */ bool lockCleared; /* we read all sinval msgs for lock */ LOCALLOCKOWNER *lockOwners; /* dynamically resizable array */} LOCALLOCK;
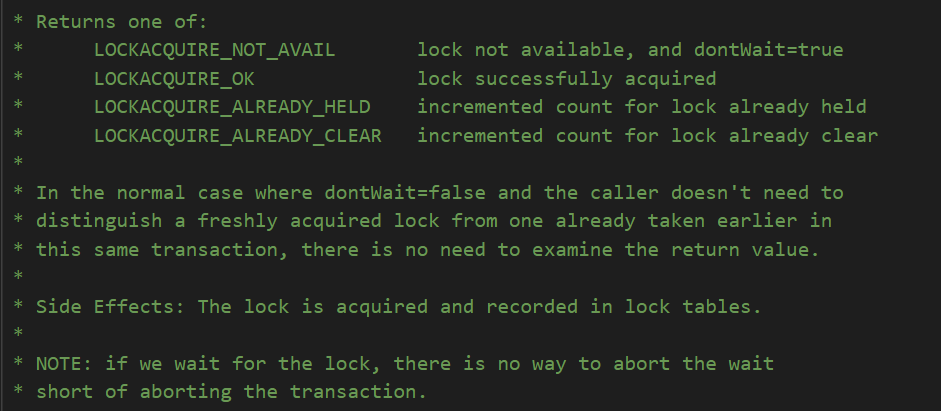
LockAcquireResultLockAcquire(const LOCKTAG *locktag, LOCKMODE lockmode, bool sessionLock, bool dontWait){ return LockAcquireExtended(locktag, lockmode, sessionLock, dontWait, true, NULL);}
static boolFastPathTransferRelationLocks(LockMethod lockMethodTable, const LOCKTAG *locktag, uint32 hashcode){ LWLock *partitionLock = LockHashPartitionLock(hashcode); Oid relid = locktag->locktag_field2; uint32 i; for (i = 0; i < ProcGlobal->allProcCount; i++) { PGPROC *proc = &ProcGlobal->allProcs[i]; uint32 f; LWLockAcquire(proc->backendLock, LW_EXCLUSIVE); if (proc->databaseId != locktag->locktag_field1) { LWLockRelease(proc->backendLock); continue; } for (f = 0; f < FP_LOCK_SLOTS_PER_BACKEND; f++) { uint32 lockmode; /* Look for an allocated slot matching the given relid. */ if (relid != proc->fpRelId[f] || FAST_PATH_GET_BITS(proc, f) == 0) continue; /* Find or create lock object. */ LWLockAcquire(partitionLock, LW_EXCLUSIVE); for (lockmode = FAST_PATH_LOCKNUMBER_OFFSET; lockmode < FAST_PATH_LOCKNUMBER_OFFSET + FAST_PATH_BITS_PER_SLOT; ++lockmode) { PROCLOCK *proclock; if (!FAST_PATH_CHECK_LOCKMODE(proc, f, lockmode)) continue; proclock = SetupLockInTable(lockMethodTable, proc, locktag, hashcode, lockmode); if (!proclock) { LWLockRelease(partitionLock); LWLockRelease(proc->backendLock); return false; } /* Set holdTillEndXact of proclock */ proclock->tag.myLock->holdTillEndXact = \ FAST_PATH_GET_HOLD_TILL_END_XACT_BITS(proc, f) > 0; GrantLock(proclock->tag.myLock, proclock, lockmode); FAST_PATH_CLEAR_LOCKMODE(proc, f, lockmode); } LWLockRelease(partitionLock); /* No need to examine remaining slots. */ break; } LWLockRelease(proc->backendLock); } return true;}
查找backend本地的LOCALLOCK,如果存在该lock,并且当前backend已经持有了该锁,将对应ResourceOwner的锁计数减1,如果减到了0,则ResourceOwner需要释放该锁。另外,将总的granted数量-1。
如果释放的锁的锁模式小于ShareUpdateExclusiveLock,从fastpath中查找该锁,如果找到,释放对应模式的锁。
如果locallock中的lock为空,那么从shared hash table中查找该锁,因为有可能该锁被其它backend从fastpath放入到了shared hash table中(加锁逻辑中)。
释放该锁,如果有等待的锁请求,那么唤醒其它等待的进程。
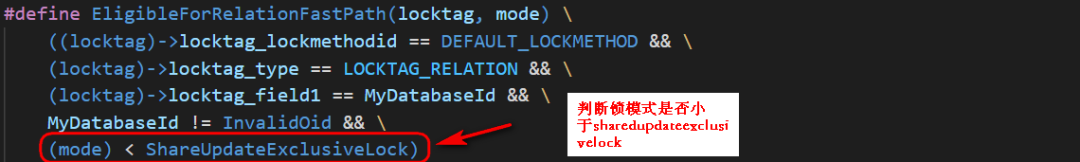
加锁的LockMethod为default方法;
加锁的对象为relation;
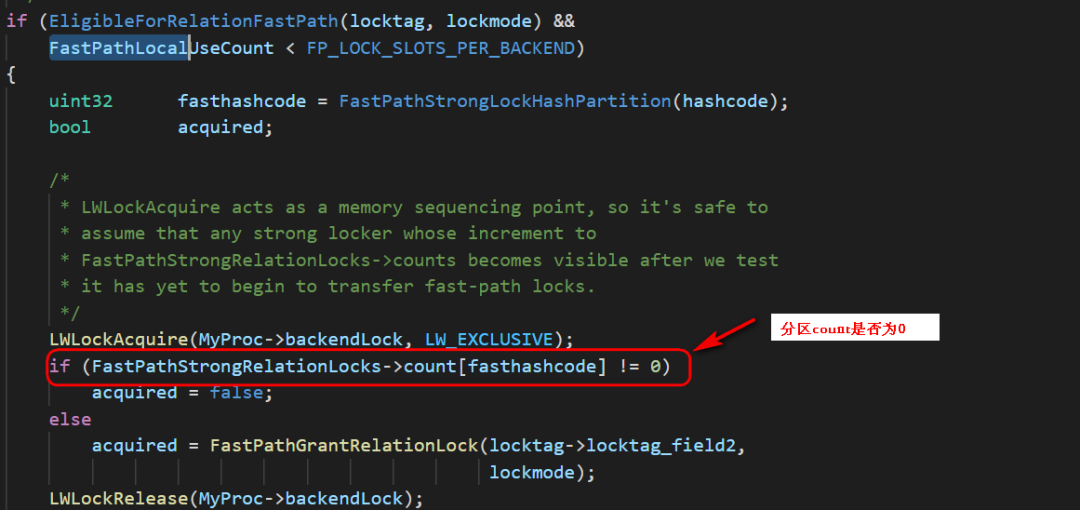
加锁的模式必须小于ShareUpdateExclusiveLock;
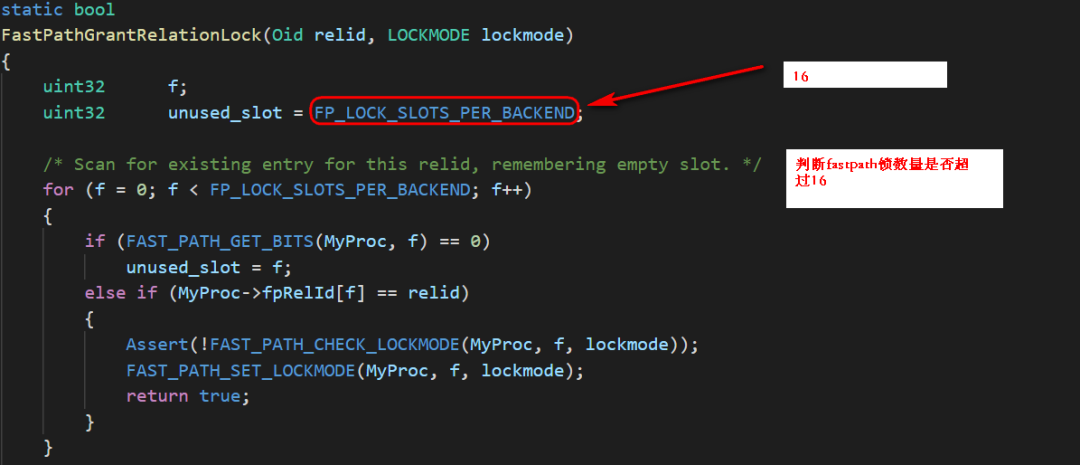
每个backend,最多只能有16把锁通过fastpath获取得到,如果超过这个值则不能;
当前请求的锁对象上没有被加上大于ShareUpdateExclusiveLock模式的锁。





新闻|Babelfish使PostgreSQL直接兼容SQL Server应用程序

更多新闻资讯,行业动态,技术热点,请关注中国PostgreSQL分会官方网站
https://www.postgresqlchina.com
中国PostgreSQL分会生态产品
https://www.pgfans.cn
中国PostgreSQL分会资源下载站
https://www.postgreshub.cn








