作者
digoal
日期
2017-11-26
标签
PostgreSQL , 经营分析系统 , 手机行业 , 标签 , 圈选 , 透视 , 估值 , 决策
背景
经营分析、决策支持是现代企业的一个让数据发挥有效价值的分析型系统。
在各个行业中随处可见,例如共享充电宝中,协助销售了解实时的设备租赁情况,销售业绩。在电商中,协助小二和商户发掘目标用户群体。金融行业中,协助输出国民的存款、消费、贷款的画像。
PostgreSQL, Greenplum都是非常适合于经营分析、决策支持的数据库。因为它们具备了一些特性,适合实时的分析透视。(流式计算、合并写入、阅后即焚、GIN倒排索引、varbit类型、列存储、BITMAP合并扫描、HLL估值类型、采样算法等等)。
我也写过很多实际的应用案例,可以参考本文末尾。
经营分析系统的需求大同小异,在手机行业中,以imei或imsi为KEY,每个手机根据它的用户的行为,生成一些属性,针对每个属性,划分出不同的标签,形成了手机用户的画像。再针对画像进行人群的圈选、透视,协助分析。
例如,基于PostgreSQL数组以及GIN索引的设计:
经营分析设计示例
1、目标设计
2、表结构设计
3、属性表
4、标签表
5、标签表索引设计
6、打标签(含新增、更新、删除标签)测试
7、圈选测试
8、透视测试
9、决策设计示例
流式+函数式计算
结构设计
1、手机用户属性表
create table tbl1 (
imei text primary key, -- 手机唯一标识
v1 int, -- 年龄
v2 float8, -- 收入
v3 geometry, -- 住址经纬
v4 geometry, -- 公司经纬
v5 char(1), -- 性别
v6 timestamp, -- 最后活跃时间
v7 int2, -- 每日在线时长
v8 int2, -- 星座
v9 text, -- 其他标签。。。。。
......
);
2、标签元数据表
create table tbl2 (
tagid int primary key, -- 标签名
desc text, -- 描述,例如性别,年龄分段,收入分段,区域等等,作为一个标签标识。
);
3、标签表
```
create table tbl3 (
imei text primary key, -- 手机唯一标识
tagids int[], -- 标签数组
ins_tags int[], -- 合并操作需要的中间字段
del_tags int[] -- 合并操作需要的中间字段
);
create index idx_tbl3_tagids on tbl3 using gin (tagids gin__int_ops);
或
create index idx_tbl3_tagids on tbl3 using gist (tagids gist__intbig_ops);
或
create index idx_tbl3_tagids on tbl3 using gist (tagids gist__int_ops);
```
4、标签表与属性表实际上可以合一,在透视时,可以避免一次JOIN(降低透视的耗时),但是会引入更新IO放大的问题,因为属性表可能是宽表。
根据实际的性能情况来选择是否合一。
需求与SQL设计
1、圈人
```
select imei from tbl3 where tagids @> array[标签1, 标签2]; -- 查找包含标签1,标签2的人群。
select imei from tbl3 where tagids && array[标签1, 标签2]; -- 查找包含标签1,标签2中任意一个或多个的人群。
select imei from tbl3 where tagids && array[标签1, 标签2] and tagid @> array[标签3, 标签4]; -- 查找包含标签3,标签4。同时包含标签1,标签2中任意一个或多个的人群。
```
2、针对圈出人群的精准透视
select v8,count(*) from tbl1 where
imei = any (array(
select imei from tbl3 where tagids @> array[标签1, 标签2]
) )
group by v8;
3、新增或追加标签
使用intarray插件,简化数组交、并、差操作。
create extension intarray;
insert into tbl3 (imei, tagids) values (?, ?[]) on conflict (imei) do update set tagids=tbl3.tagids|excluded.tagids;
4、删标签
update tbl3 set tagids = tagids - ?[] where imei=?;
5、更新标签
update tbl3 set tagids = ?[] where imei=?;
6、批量并行新增、追加、删除、更新标签优化
如果要一次性操作很多条记录(例如1000万条记录),并且有并行的贴标签操作(同一条用户被多个SQL更新)。需要注意两个问题:
6.1 大事务导致膨胀的问题,建议分段操作。
6.2 行锁冲突问题,建议新增(插入),然后合并到标签表。
优化方法,
实现标签最终一致性。
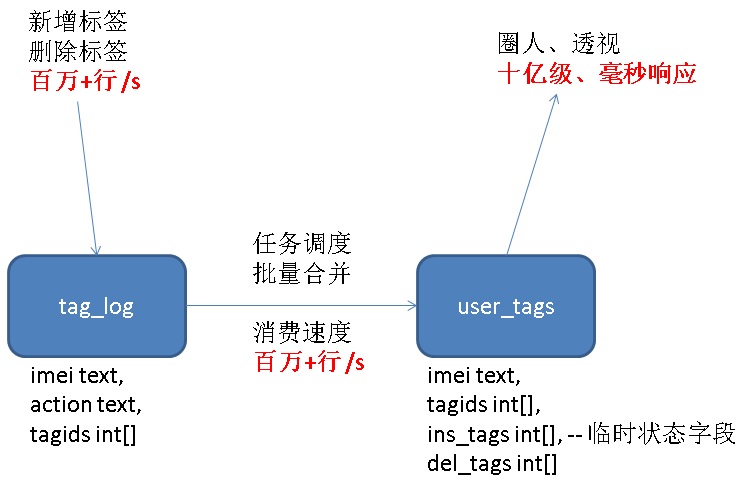
将直接增、删、改标签表,改成写行为日志tag_log,采用任务调度,批量合并到标签表:
```
create table tag_log (
imei text, -- 手机唯一标识
action text, -- insert, delete 表示增加、删除标签 (更新需求应该没有,如有,直接到标签表操作)
tagids int[], -- 标签IDs
crt_time timestamp default clock_timestamp() -- 时间
);
create index idx_tag_log_1 on tag_log (crt_time);
-- 16个分区表 do language plpgsql $$ declare begin for i in 0..15 loop execute format('create table tag_log%s (like tag_log including all) inherits(tag_log)', i); end loop; end; $$; ```
串行任务,阅后即焚(假设-99999999是一个永远不存在的TAGID)
-- CTE语法,支持阅后即焚的批量合并方法
with tmp as (delete from tag_log where ctid = any ( array (
select ctid from tag_log order by crt_time limit 10000 -- 按时序,批量取1万条
)) returning * )
, tmp1 as (select imei,
uniq(sort(array_agg(case when action='insert' then tagids else -99999999 end))) - (-99999999) AS ins_tags,
uniq(sort(array_agg(case when action='delete' then tagids else -99999999 end))) - (-99999999) AS del_tags
from (select imei, action, unnest(tagids) as tagids from tmp) t group by imei)
insert into tbl3 (imei, tagids, ins_tags, del_tags)
select imei, ins_tags-del_tags, ins_tags, del_tags from tmp1
on conflict (imei) do update set tagids=((tbl3.tagids | excluded.ins_tags) - excluded.del_tags), ins_tags=excluded.ins_tags, del_tags=excluded.del_tags;
并行任务,阅后即焚
```
例如开启16个并行
abs(mod(hashtext(imei), 16))=?
```
-- CTE语法,支持阅后即焚的批量合并方法
with tmp as (delete from tag_log where ctid = any ( array (
select ctid from tag_log where abs(mod(hashtext(imei), 16))=0 order by crt_time limit 10000 -- 按时序,批量取1万条,按HASH并行
)) returning * )
, tmp1 as (select imei,
uniq(sort(array_agg(case when action='insert' then tagids else -99999999 end))) - (-99999999) AS ins_tags,
uniq(sort(array_agg(case when action='delete' then tagids else -99999999 end))) - (-99999999) AS del_tags
from (select imei, action, unnest(tagids) as tagids from tmp) t group by imei)
insert into tbl3 (imei, tagids, ins_tags, del_tags)
select imei, ins_tags-del_tags, ins_tags, del_tags from tmp1
on conflict (imei) do update set tagids=((tbl3.tagids | excluded.ins_tags) - excluded.del_tags), ins_tags=excluded.ins_tags, del_tags=excluded.del_tags;
写成函数,方便调用
```
create or replace function consume_tag_log(mo int, mov int, lim int) returns void as $$
declare
begin
execute format($$with tmp as (delete from tag_log where ctid = any ( array (
select ctid from tag_log where abs(mod(hashtext(imei), %s))=%s order by crt_time limit %s
)) returning * )
, tmp1 as (select imei,
uniq(sort(array_agg(case when action='insert' then tagids else -99999999 end))) - (-99999999) AS ins_tags,
uniq(sort(array_agg(case when action='delete' then tagids else -99999999 end))) - (-99999999) AS del_tags
from (select imei, action, unnest(tagids) as tagids from tmp) t group by imei)
insert into tbl3 (imei, tagids, ins_tags, del_tags)
select imei, ins_tags-del_tags, ins_tags, del_tags from tmp1
on conflict (imei) do update set tagids=((tbl3.tagids | excluded.ins_tags) - excluded.del_tags), ins_tags=excluded.ins_tags, del_tags=excluded.del_tags$$,
mo, mov, lim);
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
select consume_tag_log(16,0,10000); -- 并行处理
select consume_tag_log(16,1,10000);
.....
select consume_tag_log(16,15,10000);
```
```
create or replace function consume_tag_log(lim int) returns void as $$
declare
begin
execute format($$with tmp as (delete from tag_log where ctid = any ( array (
select ctid from tag_log order by crt_time limit %s
)) returning * )
, tmp1 as (select imei,
uniq(sort(array_agg(case when action='insert' then tagids else -99999999 end))) - (-99999999) AS ins_tags,
uniq(sort(array_agg(case when action='delete' then tagids else -99999999 end))) - (-99999999) AS del_tags
from (select imei, action, unnest(tagids) as tagids from tmp) t group by imei)
insert into tbl3 (imei, tagids, ins_tags, del_tags)
select imei, ins_tags-del_tags, ins_tags, del_tags from tmp1
on conflict (imei) do update set tagids=((tbl3.tagids | excluded.ins_tags) - excluded.del_tags), ins_tags=excluded.ins_tags, del_tags=excluded.del_tags$$,
lim);
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
select consume_tag_log(10000); -- 每次处理1万条
```
创建调度任务,执行消费函数调度即可。
阅后即焚的处理速度,每秒 百万行。
《(OLTP) 高吞吐数据进出(堆存、行扫、无需索引) - 阅后即焚(读写大吞吐并测)》
性能验证
1、标签取值范围5万,正态分布

2、多表批量写入函数
create or replace function ins(
imei text,
tagids int[]
) returns void as $$
declare
suffix int := abs(mod(hashtext(imei),16));
begin
execute format($_$insert into tag_log%s values ('%s', 'insert', '%s'::int[])$_$, suffix, imei, tagids);
end;
$$ language plpgsql strict;
3、多表批量消费
标签表分表
do language plpgsql $$
declare
begin
for i in 0..15 loop
execute format('create table tbl3_%s (like tbl3 including all) inherits(tbl3)', i);
end loop;
end;
$$;
多表批量消费
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.consume_tag_log(suffix int, lim integer)
RETURNS void
LANGUAGE plpgsql
STRICT
AS $function$
declare
begin
execute format($_$with tmp as (delete from tag_log%s where ctid = any ( array (
select ctid from tag_log%s order by crt_time limit %s -- 按时序,批量取1万条,按HASH并行
)) returning * )
, tmp1 as (select imei,
uniq(sort(array_agg(case when action='insert' then tagids else -99999999 end))) - (-99999999) AS ins_tags,
uniq(sort(array_agg(case when action='delete' then tagids else -99999999 end))) - (-99999999) AS del_tags
from (select imei, action, unnest(tagids) as tagids from tmp) t group by imei)
insert into tbl3_%s (imei, tagids, ins_tags, del_tags)
select imei, ins_tags-del_tags, ins_tags, del_tags from tmp1
on conflict (imei) do update set tagids=((tbl3_%s.tagids | excluded.ins_tags) - excluded.del_tags), ins_tags=excluded.ins_tags, del_tags=excluded.del_tags$_$,
suffix, suffix, lim, suffix, suffix);
end;
$function$;
4、数据写入压测脚本
```
vi test.sql
\set tag1 random_gaussian(1, 50000, 20)
\set tag2 random_gaussian(1, 50000, 20)
\set tag3 random_gaussian(1, 50000, 20)
\set tag4 random_gaussian(1, 50000, 20)
\set tag5 random_gaussian(1, 50000, 20)
\set tag6 random_gaussian(1, 50000, 20)
\set tag7 random_gaussian(1, 50000, 20)
\set tag8 random_gaussian(1, 50000, 20)
\set imei random(1,1000000000)
select ins(:imei, (array[:tag1,:tag2,:tag3,:tag4,:tag5,:tag6,:tag7,:tag8])::int[]);
nohup pgbench -M prepared -n -r -P 1 -f ./test.sql -c 28 -j 28 -T 3000 >./tag.log 2>&1 &
```
5、数据消费,并行调度
用秒杀技术实现并行调度,避免单个HASH被重复调用。
《HTAP数据库 PostgreSQL 场景与性能测试之 30 - (OLTP) 秒杀 - 高并发单点更新》
这里直接用分区表写入的话,性能会更爽,原理请看如下:
《阿里云RDS PostgreSQL OSS 外部表 - (dblink异步调用封装)并行写提速案例》
```
vi test1.sql
\set mov random(0,15)
select consume_tag_log(:mov,10000) where pg_try_advisory_xact_lock(:mov);
nohup pgbench -M prepared -n -r -P 1 -f ./test1.sql -c 16 -j 16 -T 3000 >./consume.log 2>&1 &
```
6、压测结果
写入速度
```
单条单步写入,约 14.3万 行/s
改成多表批量写入,可以提高到100万+ 行/s
```
消费速度
```
单表并行批量消费,约 25.5万 行/s
改成多表并行批量消费,可以提高到 100万+ 行/s
```
查询速度,毫秒级
``` postgres=# explain (analyze,verbose,timing,costs,buffers) select count(imei) from tbl3 where tagids @> (array[25281,25288])::int[]; QUERY PLAN
Aggregate (cost=224.50..224.51 rows=1 width=8) (actual time=2.745..2.746 rows=1 loops=1) Output: count(imei) Buffers: shared hit=193 -> Bitmap Heap Scan on public.tbl3 (cost=218.44..224.49 rows=5 width=33) (actual time=2.716..2.738 rows=9 loops=1) Output: imei, tagids, ins_tags, del_tags Recheck Cond: (tbl3.tagids @> '{25281,25288}'::integer[]) Heap Blocks: exact=9 Buffers: shared hit=193 -> Bitmap Index Scan on idx_tbl3_tagids (cost=0.00..218.44 rows=5 width=0) (actual time=2.707..2.707 rows=9 loops=1) Index Cond: (tbl3.tagids @> '{25281,25288}'::integer[]) Buffers: shared hit=184 Planning time: 0.165 ms Execution time: 2.797 ms (13 rows) ```
除了以上基于数组、GIN索引的设计,PostgreSQL还有一些技术,可以用在经营分析系统。
技术1 实时透视 - 技术之 - 流式统计
通过insert on conflict,流式的统计固定模型的维度数据。
《PostgreSQL 流式统计 - insert on conflict 实现 流式 UV(distinct), min, max, avg, sum, count ...》
满足这类查询的实时流式统计:
select a,count(*),sum(b),avg(b),min(b),max(b) from tbl group by a;
技术2 实时透视、估算 - 技术之 - 流式统计 + HLL
通过insert on conflict,流式的统计固定模型的维度数据。这里要用到hll插件,存储count(dinstinct x)的估值
《PostgreSQL 流式统计 - insert on conflict 实现 流式 UV(distinct), min, max, avg, sum, count ...》
《PostgreSQL hll (HyperLogLog) extension for "State of The Art Cardinality Estimation Algorithm" - 3》
《PostgreSQL hll (HyperLogLog) extension for "State of The Art Cardinality Estimation Algorithm" - 2》
《PostgreSQL hll (HyperLogLog) extension for "State of The Art Cardinality Estimation Algorithm" - 1》
满足这类查询的实时流式统计:
select a, count(distinct b) from tbl group by a;
技术3 实时透视、估算 - 技术之 - 计划估算
根据执行计划得到评估行。
如果输入多个字段条件,为了提高行估算准确度,可以定义多字段统计信息,10新增的功能:
满足这类查询的估算需求:
```
select count(*) from tbl where xxxx;
SQL换算成
select * from tbl where xxxx; -- 通过explain的行估算拿结果
```
技术4 实时透视、估算 - 技术之 - 采样估算
《秒级任意维度分析1TB级大表 - 通过采样估值满足高效TOP N等统计分析需求》
采样估算,适合求TOP N。
满足这类查询的估算需求:
select a from tbl group by a order by count(*) desc limit N;
技术5 实时圈选、透视 - 技术之 - GIN倒排
倒排索引针对多值类型,例如 hstore, array, tsvector, json, jsonb。
主树的K-V分别为:
element-ctid(行号)list or tree
辅树为
ctid list or tree
从而高效的满足这类查询的需求:
```
-- 包含哪些元素
select * from tbl where arr @> array[xx,xx];
-- 包含哪些任意元素之一
select * from tbl where arr && array[xx,xx];
```
内部使用BITMAP扫描方法,过滤到少量数据块。
技术6 实时圈选、透视 - 技术之 - bitmap
这个方法非常的巧妙,将tag和imei做了倒转,以tag为key, imei为bitmap来存储。
create table tag_users (
tagid int primary key, -- 标签
imeibitmap varbit, -- 每个imei用一个BIT位表示
);
查询换算:
```
-- 包含某些标签的用户
select bitand(imeibitmap) from tag_users where tagid in (?,?,...);
-- 包含任意标签的用户
select bitor(imeibitmap) from tag_users where tagid in (?,?,...);
```
案例参考:
《阿里云RDS for PostgreSQL varbitx插件与实时画像应用场景介绍》
《基于 阿里云 RDS PostgreSQL 打造实时用户画像推荐系统(varbitx)》
技术7 实时圈选、透视 - 技术之 - 并行计算
PostgreSQL 10加入了并行计算的能力,在join , filter, seqscan, order by, agg, group等方面都支持并行。
性能指标参考:
《HTAP数据库 PostgreSQL 场景与性能测试之 23 - (OLAP) 并行计算》
技术8 实时圈选、透视 - 技术之 - MPP, 列存储, 位图索引
基于PostgreSQL的MPP 数据仓库Greenplum,支持列存储,位图索引。
用资源,暴力解决问题。
没有太多的设计技巧,堆机器就可以,但是本身的效率远比impalar, hive好很多。
Greenplum是非常值得推荐的OLAP数据库。在金融、政府、航空等大数据领域有众多案例。
决策支持技术
流式数据处理+UDF函数计算技术。可以满足实时决策的需求。
案例如下:
《HTAP数据库 PostgreSQL 场景与性能测试之 32 - (OLTP) 高吞吐数据进出(堆存、行扫、无需索引) - 阅后即焚(JSON + 函数流式计算)》
《HTAP数据库 PostgreSQL 场景与性能测试之 27 - (OLTP) 物联网 - FEED日志, 流式处理 与 阅后即焚 (CTE)》
相似案例举例
1、实时统计 count(distinct)估值,min, max, avg, sum, count精确值。
《PostgreSQL 流式统计 - insert on conflict 实现 流式 UV(distinct), min, max, avg, sum, count ...》
2、
《PostgreSQL 异步消息实践 - Feed系统实时监测与响应(如 电商主动服务) - 分钟级到毫秒级的实现》
《(OLTP) 物联网 - FEED日志, 流式处理 与 阅后即焚 (CTE)》
3、让explain产生精确的多字段输入条件行数估值(select * from table where a=? and|or b=? ....)
4、《恭迎万亿级营销(圈人)潇洒的迈入毫秒时代 - 万亿user_tags级实时推荐系统数据库设计》
《阿里云RDS for PostgreSQL varbitx插件与实时画像应用场景介绍》
《基于 阿里云 RDS PostgreSQL 打造实时用户画像推荐系统(varbitx)》
5、决策支持,流式函数计算
《(OLTP) 高吞吐数据进出(堆存、行扫、无需索引) - 阅后即焚(JSON + 函数流式计算)》
《(OLTP) 高吞吐数据进出(堆存、行扫、无需索引) - 阅后即焚(读写大吞吐并测)》
6、圈人案例
7、时间、空间、多维圈人、透视案例
《空间|时间|对象 圈人 + 透视 - 暨PostgreSQL 10与Greenplum的对比和选择》
《PostgreSQL\GPDB 毫秒级海量 时空数据透视 典型案例分享》
《PostgreSQL\GPDB 毫秒级海量 多维数据透视 案例分享》
8、视频网站透视案例
《音视图(泛内容)网站透视分析 DB设计 - 阿里云(RDS、HybridDB) for PostgreSQL最佳实践》
9、
《海量用户实时定位和圈人 - 团圆社会公益系统(位置寻人\圈人)》
《万亿级电商广告 - brin黑科技带你(最低成本)玩转毫秒级圈人(视觉挖掘姊妹篇) - 阿里云RDS PostgreSQL, HybridDB for PostgreSQL最佳实践》
《多字段,任意组合条件查询(无需建模) - 毫秒级实时圈人 最佳实践》
10、
《经营、销售分析系统DB设计之PostgreSQL, Greenplum - 共享充电宝 案例实践》
PostgreSQL 许愿链接
您的愿望将传达给PG kernel hacker、数据库厂商等, 帮助提高数据库产品质量和功能, 说不定下一个PG版本就有您提出的功能点. 针对非常好的提议,奖励限量版PG文化衫、纪念品、贴纸、PG热门书籍等,奖品丰富,快来许愿。开不开森.
9.9元购买3个月阿里云RDS PostgreSQL实例
PostgreSQL 解决方案集合
德哥 / digoal's github - 公益是一辈子的事.







