一、 单向链表
单向链表节点结构(可以实现成范型)
public class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data) {value = data;}}复制
二、双向链表
双向链表节点结构
public class DoubleNode {public int value;public DoubleNode last;public DoubleNode next;public DoubleNode(int data) {value = data;}}复制
public class Code01_ReverseList {//单向链表public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data) {value = data;}}//双向链表public static class DoubleNode {public int value;public DoubleNode last;public DoubleNode next;public DoubleNode(int data) {value = data;}}public static Node reverseLinkedList(Node head) {Node pre = null;Node next = null;while (head != null) {next = head.next;head.next = pre;pre = head;head = next;}return pre;}public static DoubleNode reverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head) {DoubleNode pre = null;DoubleNode next = null;while (head != null) {next = head.next;head.next = pre;head.last = next;pre = head;head = next;}return pre;}public static Node testReverseLinkedList(Node head) {if (head == null) {return null;}ArrayList<Node> list = new ArrayList<>();while (head != null) {list.add(head);head = head.next;}list.get(0).next = null;int N = list.size();for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {list.get(i).next = list.get(i - 1);}return list.get(N - 1);}public static DoubleNode testReverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head) {if (head == null) {return null;}ArrayList<DoubleNode> list = new ArrayList<>();while (head != null) {list.add(head);head = head.next;}list.get(0).next = null;DoubleNode pre = list.get(0);int N = list.size();for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {DoubleNode cur = list.get(i);cur.last = null;cur.next = pre;pre.last = cur;pre = cur;}return list.get(N - 1);}public static Node generateRandomLinkedList(int len, int value) {int size = (int) (Math.random() * (len + 1));if (size == 0) {return null;}size--;Node head = new Node((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));Node pre = head;while (size != 0) {Node cur = new Node((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));pre.next = cur;pre = cur;size--;}return head;}public static DoubleNode generateRandomDoubleList(int len, int value) {int size = (int) (Math.random() * (len + 1));if (size == 0) {return null;}size--;DoubleNode head = new DoubleNode((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));DoubleNode pre = head;while (size != 0) {DoubleNode cur = new DoubleNode((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1)));pre.next = cur;cur.last = pre;pre = cur;size--;}return head;}// 要求无环,有环别用这个函数public static boolean checkLinkedListEqual(Node head1, Node head2) {while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {if (head1.value != head2.value) {return false;}head1 = head1.next;head2 = head2.next;}return head1 == null && head2 == null;}// 要求无环,有环别用这个函数public static boolean checkDoubleListEqual(DoubleNode head1, DoubleNode head2) {boolean null1 = head1 == null;boolean null2 = head2 == null;if (null1 && null2) {return true;}if (null1 ^ null2) {return false;}if (head1.last != null || head2.last != null) {return false;}DoubleNode end1 = null;DoubleNode end2 = null;while (head1 != null && head2 != null) {if (head1.value != head2.value) {return false;}end1 = head1;end2 = head2;head1 = head1.next;head2 = head2.next;}if (head1 != null || head2 != null) {return false;}while (end1 != null && end2 != null) {if (end1.value != end2.value) {return false;}end1 = end1.last;end2 = end2.last;}return end1 == null && end2 == null;}public static void main(String[] args) {int len = 50;int value = 100;int testTime = 100000;for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) {Node node1 = generateRandomLinkedList(len, value);Node reverse1 = reverseLinkedList(node1);Node back1 = testReverseLinkedList(reverse1);if (!checkLinkedListEqual(node1, back1)) {System.out.println("oops!");break;}DoubleNode node2 = generateRandomDoubleList(len, value);DoubleNode reverse2 = reverseDoubleList(node2);DoubleNode back2 = testReverseDoubleList(reverse2);if (!checkDoubleListEqual(node2, back2)) {System.out.println("oops!");break;}}System.out.println("finish!");}}复制
单向链表和双向链表最简单的练习
链表相关的问题几乎都是coding问题
1)单链表和双链表如何反转
2)把给定值都删除
public class Code02_DeleteGivenValue {public static class Node {public int value;public Node next;public Node(int data) {this.value = data;}}public static Node removeValue(Node head, int num) {while (head != null) {if (head.value != num) {break;}head = head.next;}//head来到第一个不需要删的位置Node pre = head;Node cur = head;while (cur != null) {if (cur.value == num) {pre.next = cur.next;} else {pre = cur;}cur = cur.next;}return head;}}复制
这里就是熟悉结构。链表还有哪些常见面试题,后续有专门一节来系统学习。
三、栈和队列
逻辑概念
栈:数据先进后出,犹如弹匣
队列:数据先进先出,好似排队
public class Code03_DoubleEndsQueueToStackAndQueue {public static class Node<T> {public T value;public Node<T> last;public Node<T> next;public Node(T data) {value = data;}}public static class DoubleEndsQueue<T> {public Node<T> head;public Node<T> tail;public void addFromHead(T value) {Node<T> cur = new Node<T>(value);if (head == null) {head = cur;tail = cur;} else {cur.next = head;head.last = cur;head = cur;}}public void addFromBottom(T value) {Node<T> cur = new Node<T>(value);if (head == null) {head = cur;tail = cur;} else {cur.last = tail;tail.next = cur;tail = cur;}}public T popFromHead() {if (head == null) {return null;}Node<T> cur = head;if (head == tail) {head = null;tail = null;} else {head = head.next;cur.next = null;head.last = null;}return cur.value;}public T popFromBottom() {if (head == null) {return null;}Node<T> cur = tail;if (head == tail) {head = null;tail = null;} else {tail = tail.last;tail.next = null;cur.last = null;}return cur.value;}public boolean isEmpty() {return head == null;}}public static class MyStack<T> {private DoubleEndsQueue<T> queue;public MyStack() {queue = new DoubleEndsQueue<T>();}public void push(T value) {queue.addFromHead(value);}public T pop() {return queue.popFromHead();}public boolean isEmpty() {return queue.isEmpty();}}public static class MyQueue<T> {private DoubleEndsQueue<T> queue;public MyQueue() {queue = new DoubleEndsQueue<T>();}public void push(T value) {queue.addFromHead(value);}public T poll() {return queue.popFromBottom();}public boolean isEmpty() {return queue.isEmpty();}}public static boolean isEqual(Integer o1, Integer o2) {if (o1 == null && o2 != null) {return false;}if (o1 != null && o2 == null) {return false;}if (o1 == null && o2 == null) {return true;}return o1.equals(o2);}public static void main(String[] args) {int oneTestDataNum = 100;int value = 10000;int testTimes = 100000;for (int i = 0; i < testTimes; i++) {MyStack<Integer> myStack = new MyStack<>();MyQueue<Integer> myQueue = new MyQueue<>();Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();for (int j = 0; j < oneTestDataNum; j++) {int nums = (int) (Math.random() * value);if (stack.isEmpty()) {myStack.push(nums);stack.push(nums);} else {if (Math.random() < 0.5) {myStack.push(nums);stack.push(nums);} else {if (!isEqual(myStack.pop(), stack.pop())) {System.out.println("oops!");}}}int numq = (int) (Math.random() * value);if (stack.isEmpty()) {myQueue.push(numq);queue.offer(numq);} else {if (Math.random() < 0.5) {myQueue.push(numq);queue.offer(numq);} else {if (!isEqual(myQueue.poll(), queue.poll())) {System.out.println("oops!");}}}}}System.out.println("finish!");}}
四、栈和队列的实际实现
双向链表实现
数组实现
public class Code04_RingArray {public static class MyQueue {private int[] arr;private int pushi;private int polli;private int size;private final int limit;public MyQueue(int l) {arr = new int[l];pushi = 0;polli = 0;size = 0;limit = l;}public void push(int value) {if (size == limit) {throw new RuntimeException("栈满了,不能再加了");}size++;arr[pushi] = value;pushi = nextIndex(pushi);}public int pop() {if (size == 0) {throw new RuntimeException("栈空了,不能再拿了");}size--;int ans = arr[polli];polli = nextIndex(pushi);return ans;}public boolean isEmpty() {return size == 0;}//如果现在的下标是i ; 返回下一个位置private int nextIndex(int i) {return i < limit - 1 ? i + 1 : 0;}}}
五、既然语言都有这些结构和api,为什么还需要手撸练习?
1)算法问题无关语言
2)语言提供的api是有限的,当有新的功能是api不提供的,就需要改写
3)任何软件工具的底层都是最基本的算法和数据结构,这是绕不过去的
public class Code07_TwoQueueImplementStack {public static class TwoQueueStack<T> {public Queue<T> queue;public Queue<T> help;public TwoQueueStack() {queue = new LinkedList<>();help = new LinkedList<>();}public void push(T value) {queue.offer(value);}public T poll() {while (queue.size() > 1) {help.offer(queue.poll());}T ans = queue.poll();Queue<T> tmp = queue;queue = help;help = tmp;return ans;}public T peek() {while (queue.size() > 1) {help.offer(queue.poll());}T ans = queue.peek();Queue<T> tmp = queue;queue = help;help = tmp;help.offer(ans);return ans;}public boolean isEmpty() {return queue.isEmpty();}}}
六、栈和队列的常见面试题
1、怎么用数组实现不超过固定大小的队列和栈?
栈:正常使用
队列:环形数组
2、实现一个特殊的栈,在基本功能的基础上,再实现返回栈中最小元素的功能
1)pop、push、getMin操作的时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
2)设计的栈类型可以使用现成的栈结构。
public class Code05_GetMinStack {public static class MyStack1 {private Stack<Integer> stackData;private Stack<Integer> stackMin;public MyStack1() {this.stackData = new Stack<Integer>();this.stackMin = new Stack<Integer>();}public void push(int newNum) {if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {this.stackMin.push(newNum);} else if (newNum <= this.getmin()) {this.stackMin.push(newNum);}this.stackData.push(newNum);}public int pop() {if (this.stackData.isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");}int value = this.stackData.pop();if (value == this.getmin()) {this.stackMin.pop();}return value;}public int getmin() {if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");}return this.stackMin.peek();}}public static class MyStack2 {private Stack<Integer> stackData;private Stack<Integer> stackMin;public MyStack2() {this.stackData = new Stack<Integer>();this.stackMin = new Stack<Integer>();}public void push(int newNum) {if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {this.stackMin.push(newNum);} else if (newNum < this.getmin()) {this.stackMin.push(newNum);} else {int newMin = this.stackMin.peek();this.stackMin.push(newMin);}this.stackData.push(newNum);}public int pop() {if (this.stackData.isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");}this.stackMin.pop();return this.stackData.pop();}public int getmin() {if (this.stackMin.isEmpty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Your stack is empty.");}return this.stackMin.peek();}}public static void main(String[] args) {MyStack1 stack1 = new MyStack1();stack1.push(3);System.out.println(stack1.getmin());stack1.push(4);System.out.println(stack1.getmin());stack1.push(1);System.out.println(stack1.getmin());System.out.println(stack1.pop());System.out.println(stack1.getmin());System.out.println("=============");MyStack1 stack2 = new MyStack1();stack2.push(3);System.out.println(stack2.getmin());stack2.push(4);System.out.println(stack2.getmin());stack2.push(1);System.out.println(stack2.getmin());System.out.println(stack2.pop());System.out.println(stack2.getmin());}}
3、
1)如何用栈结构实现队列结构
2)如何用队列结构实现栈结构
这两种结构的应用实在是太多了,在刷题时我们会大量见到
public class Code06_TwoStacksImplementQueue {public static class TwoStacksQueue {public Stack<Integer> stackPush;public Stack<Integer> stackPop;public TwoStacksQueue() {stackPush = new Stack<Integer>();stackPop = new Stack<Integer>();}// push栈向pop栈倒入数据private void pushToPop() {if (stackPop.empty()) {while (!stackPush.empty()) {stackPop.push(stackPush.pop());}}}public void add(int pushInt) {stackPush.push(pushInt);pushToPop();}public int poll() {if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");}pushToPop();return stackPop.pop();}public int peek() {if (stackPop.empty() && stackPush.empty()) {throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");}pushToPop();return stackPop.peek();}}public static void main(String[] args) {TwoStacksQueue test = new TwoStacksQueue();test.add(1);test.add(2);test.add(3);System.out.println(test.peek());System.out.println(test.poll());System.out.println(test.peek());System.out.println(test.poll());System.out.println(test.peek());System.out.println(test.poll());}}
七、递归?这东西是什么啊?
怎么从思想上理解递归
怎么从实际实现的角度出发理解递归
例子
求数组arr[L..R]中的最大值,怎么用递归方法实现。
1)将[L..R]范围分成左右两半。左:[L..Mid] 右[Mid+1..R]
2)左部分求最大值,右部分求最大值
3) [L..R]范围上的最大值,是max{左部分最大值,右部分最大值}
注意:2)是个递归过程,当范围上只有一个数,就可以不用再递归了
//递归public class Code08_GetMax {// 求arr中的最大值public static int getMax(int[] arr) {return process(arr, 0, arr.length - 1);}// arr[L..R]范围上求最大值public static int process(int[] arr, int L, int R) {if (L == R) { // arr[L..R]范围上只有一个数,直接返回,base casereturn arr[L];}// L..mid mid+1...R// int mid = (L+R)/2int mid = L + ((R - L) >> 1); // 中点int leftMax = process(arr, L, mid);int rightMax = process(arr, mid + 1, R);return Math.max(leftMax, rightMax);}}复制
1.7 递归的脑图和实际实现
对于新手来说,把调用的过程画出结构图是必须的,这有利于分析递归
递归并不是玄学,递归底层是利用系统栈来实现的
任何递归函数都一定可以改成非递归
八、 Master公式
形如
T(N) = a * T(N/b) + O(N^d)(其中的a、b、d都是常数)
的递归函数,可以直接通过Master公式来确定时间复杂度
如果 log(b,a) < d,复杂度为O(N^d)
如果 log(b,a) > d,复杂度为O(N^log(b,a))
如果 log(b,a) == d,复杂度为O(N^d * logN)
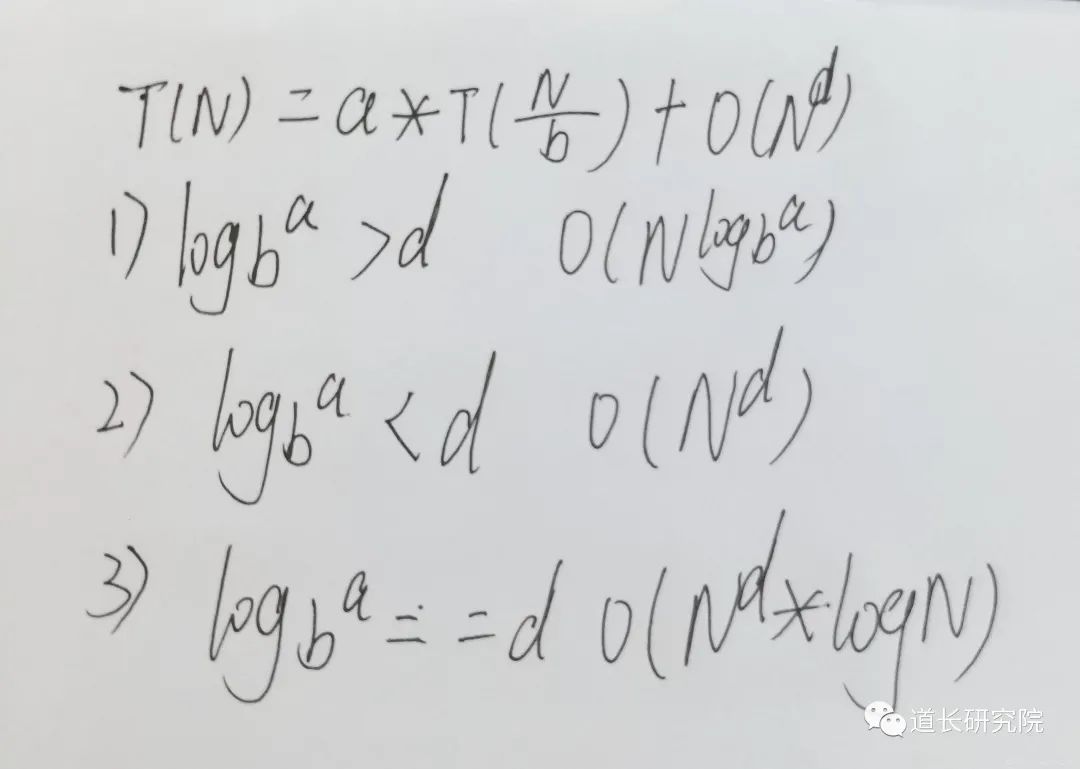
九、哈希表
1)哈希表在使用层面上可以理解为一种集合结构
2)如果只有key,没有伴随数据value,可以使用HashSet结构
3)如果既有key,又有伴随数据value,可以使用HashMap结构
4)有无伴随数据,是HashMap和HashSet唯一的区别,实际结构是一回事
5)使用哈希表增(put)、删(remove)、改(put)和查(get)的操作,可以认为时间复杂度为 O(1),但是常数时间比较大
6)放入哈希表的东西,如果是基础类型,内部按值传递,内存占用是这个东西的大小
7)放入哈希表的东西,如果不是基础类型,内部按引用传递,内存占用是8字节
十、 有序表
1)有序表在使用层面上可以理解为一种集合结构
2)如果只有key,没有伴随数据value,可以使用TreeSet结构
3)如果既有key,又有伴随数据value,可以使用TreeMap结构
4)有无伴随数据,是TreeSet和TreeMap唯一的区别,底层的实际结构是一回事
5)有序表把key按照顺序组织起来,而哈希表完全不组织
6)红黑树、AVL树、size-balance-tree和跳表等都属于有序表结构,只是底层具体实现不同
7)放入如果是基础类型,内部按值传递,内存占用就是这个东西的大小
8)放入如果不是基础类型,内部按引用传递,内存占用是8字节
9)不管是什么底层具体实现,只要是有序表,都有以下固定的基本功能和固定的时间复杂度
十、 有序表
1)void put(K key, V value)
将一个(key,value)记录加入到表中,或者将key的记录 更新成value。
2)V get(K key)
根据给定的key,查询value并返回。
3)void remove(K key)
移除key的记录。
4)boolean containsKey(K key)
询问是否有关于key的记录。
5)K firstKey()
返回所有键值的排序结果中,最小的那个。
6)K lastKey()
返回所有键值的排序结果中,最大的那个。
7)K floorKey(K key)
返回<= key 离key最近的那个
8)K ceilingKey(K key)
返回>= key 离key最近的那个
十一、 哈希表和有序表的原理
以后讲!现在的你可能会听不懂,只需要记住:
哈希表在使用时,增删改查时间复杂度都是O(1)
有序表在使用时,比哈希表功能多,时间复杂度都是O(logN)






