




A User-space Sendfile Verb base on RDMA and Flash.pdf
免费下载
uSendfile: A User-space Sendfile Verb based on Flash and RDMA
Hongzhang Yang*, Yahui Yang*, Yaofeng Tu†, Ping Wang*
∗Peking University, China
Email: {yanghongzhang, yhyang, pwang}@pku.edu.cn
ЪZTE Corporation, China
Email: tu.yaofeng@zte.com.cn
Abstract—Flash and RDMA (Remote Direct Memory Access)
provide extremely high performance in storage and network
hardware. However, a gap between distributed system and new
hardware exists. Although RDMA speeds up memory access
between two nodes, there are many serious problems to be
solved when sending data or command from one flash to
another flash. In this paper, we propose a distributed system
on flash and RDMA, and implement a User-space Sendfile
verb based on it. Experimental results show that the RPC in
DSFR outperforms the traditional RPC mechanism by dozens
of times, and the uSendfile reduces time overhead significantly.
Keywords- Sendfile; RPC; Distributed System; Flash; RDMA
I. INTRODUCTION
With the increasing demands of cloud storage and big
data processing, it becomes a popular approach to scale the
data management from a single node to distributed
environments. The traditional distributed systems use HDD
(Hard Disk Drive) as the storage medium, and transfer data
through RPC (remote procedure call) which is based on the
TCP/IP protocol. Flash and RDMA provide extremely high
performance in storage and network hardware. Although
RDMA speeds up memory access between two nodes, there
are many serious problems to be solved when sending data
or command from one flash to another flash. The distributed
system designed for flash and RDMA is fairly needed.
RDMA is capable of improving the network transmission
delay during data processing between different nodes.
RDMA achieves zero-copy data transmission without the
involvement of the operating systems on both sides, which
can provide high bandwidth and low latency. RDMA
supports three kinds of queues, Sending Queue (SQ),
Receiving Queue (RQ), and Completion Queue (CQ). SQ
and RQ are usually created in pairs, called Queue Pairs (QP).
RDMA is widely used in distributed systems [1-2].
Flash is the core component of SSD (Solid State Drive).
Flash has some special access patterns due to its physical
features [3-4], including erasing before writing, garbage
collection, and out-of-place update. Before writing data to
flash, it is occasionally to do garbage collection firstly, and
then erase old blocks, so writing performance may be
affected seriously. All in all, because of the difference
between HDD and flash, the system design needs to be
rebuilt.
In this paper, we propose a distributed system on flash
and RDMA, and implement a User-space Sendfile verb
based on it. The goal of this paper is to solve the problem of
efficiency in the process of sending data or command from
one node to another in distributed systems, so as to take full
advantage of Flash and RDMA. In summary, we make the
following contributions:
x We design a distributed system on flash and RDMA
called DSFR, which optimizes the parallel network
topology of RDMA for data transmission, the
RDMA-based RPC to improve the performance of
the distributed system, and an efficient flash garbage
collection method.
x We also design a User-space Sendfile verb called
uSendfile, which solves the problem caused by
traditional kernel Sendfile verb. The uSendfile
combines reading file from local flash to local
memory and sending this file from local memory to
remote memory, as well as to remote flash.
x We implement and evaluate the above works.
Experimental results show that the RPC in DSFR
outperforms the traditional RPC mechanism by
dozens of times. What’s more, the uSendfile has
been reduced by an order of magnitude over Sendfile
on the exactly same flash and RDMA.
II. M
OTIVATION
A. Problem of distributed system on flash and RDMA
When transfer data or command from one node to
another, there are many problems. Firstly, a single QP may
become the bottleneck, thus failing to saturate the processing
power of the NIC (Network Interface Controller). As a result,
multiple QP connections can be created between two nodes,
and messages can be transferred in parallel to improve the
throughput. What’s more, the traditional RPC is too complex,
especially the process of the Acknowledgement, which
seems unnecessary. Additionally, current research of flash
garbage collection methods are unreasonable, resulting in
cold dirty data pages being relocated twice, the first time in
garbage collection, and the second time in cache replacement.
Therefore, the system on flash and RDMA needs to be
optimized urgently.
465
2019 IEEE 12th International Conference on Cloud Computing (CLOUD)
2159-6190/19/$31.00 ©2019 IEEE
DOI 10.1109/CLOUD.2019.00080
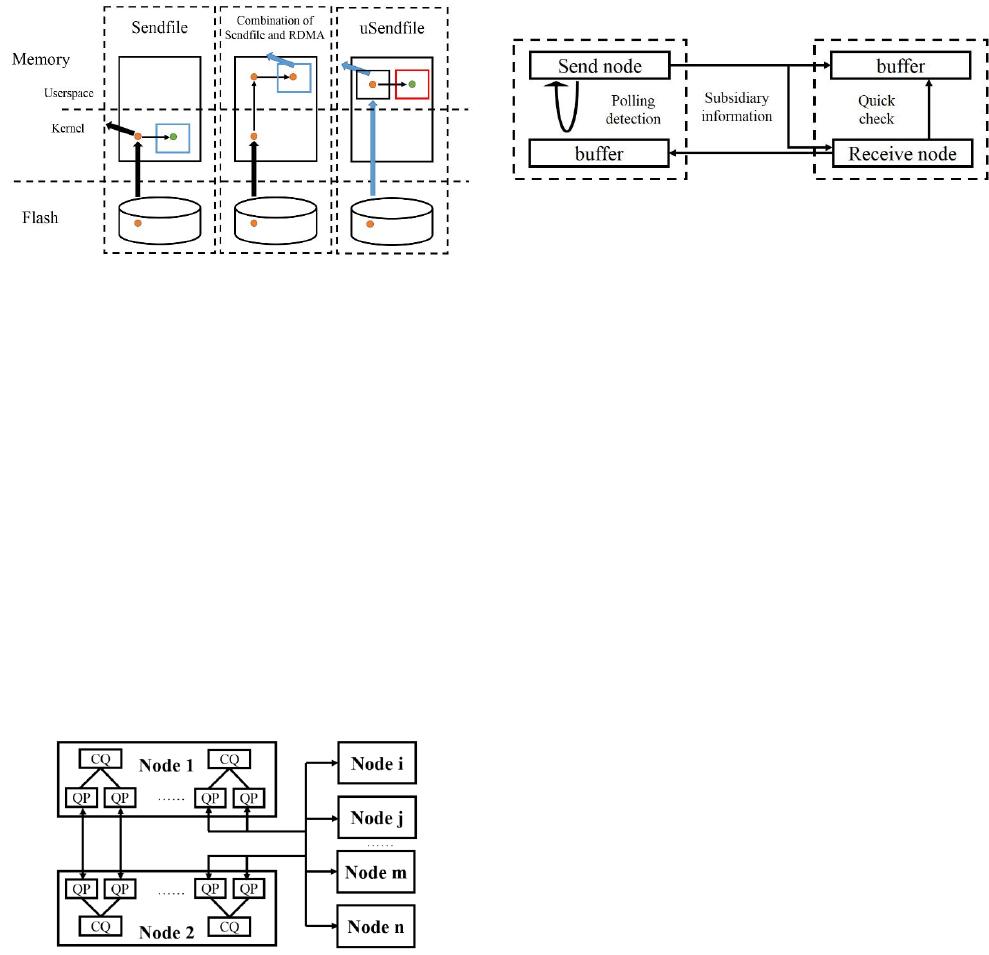
B. Problem of kernel Sendfile verb
As is known to all, remote host can read or write the data
on the local memory by RDMA. Similarly, remote host can
read or write the data on local flash by NVMeoF (NVMe
over fabric). From the data holder’s view, both RDMA and
NVMeoF authorize the remote host to access its data, nearly
to do anything the remote host wants. However, some
scenarios don’t allow such authorization, maybe for security
reason, in which case, it is fairly important that the data
holder can actively push or send its local data stored on flash,
to the remote host, as efficiently as the RDMA and NVMeoF
do. Obviously the most common method is Sendfile verb in
the Linux kernel [5].
Figure 1. Comparison between Sendfile, combination, and uSendfile.
It is regrettable that the combination of Sendfile and
RDMA simply directly, will make it had, because we have to
convert the kernel mode data read from the flash to user
mode, which indeed harms the zero copy of Sendfile. Facing
the two side of one coin, one side is user mode RDMA,
another side is kernel mode Sendfile. In order to reduce this
unnecessary copy, we design a User-space Sendfile verb,
called uSendfile, which will discuss in detail chapter 4. Fig.
1 shows the comparison between Sendfile in Linux kernel,
the current combination of Sendfile and RDMA, and the
uSendfile.
III. D
ISTRIBUTED SYSTEM ON FLASH AND RDMA
In this chapter, we propose a distributed system on flash
and RDMA, which solves the problem mention in chapter 2.
A. Parallel Network Topology of RDMA
We design a parallel network topology of RDMA to
improve the distributed system processing performance as
well as the overall DSFR system performance.
Figure 2. Parallel network topology of RDMA
Fig. 2 shows the network topology in DSFR, where the
number of QPs in each node satisfies the following equation:
1
qp
1
node
1
bw
Where: N
qp
—— the number of QPs in each node;
N
node
—— the number of nodes in the system;
N
bw
—— the number of CQs between two nodes.
In the above parallel network topology of RDMA, the
communication link between each two nodes changes from 1
(traditional) to N
bw
. Accordingly, the message processing
capability is improved, and the all-to-all interconnection
between N nodes is guaranteed.
B. RDMA-based RPC
Figure 3. RDMA-based RPC architecture
We design the RPC architecture in DSFR, as is shown in
Fig. 3. Since RDMA communication is directly based on the
registered memory, it is necessary to organize the message
receive/send buffer management module at both the sender
side and the receiver side, which has the following features:
x The send node and the receive node allocate a
contiguous area of memory when the system is
initialized and register it to the network card so that
the area can be accessed remotely.
x Before the data is sent, the send node thread chooses
a suitable memory buffer from the local buffer
management module to store the messages to be sent.
x When the message arrives at the receiver, the receive
node needs to handle the concurrent requests from
remote servers, so the buffer is divided into several
fixed areas. The memory area is used independently
by each client, so as to avoid the message
overlapping.
The send node writes data to the memory area of the
server through write_imm primitive. The threads quickly
locate the message memory address according to the
immediate field of the message, identify the message types,
and deal with them.
C. Efficient Garbage Collection on Flash
We design an efficient garbage collection method for
flash, which solves the problem of secondary relocation of
data pages. As a result, the additional overhead caused by
garbage collection and cache replacement decreases.
According to the Least Recently Used (LRU) algorithm,
all the pages in cache are in an order. So x% at the end of the
LRU queue is marked as cold, and the rest are marked as hot.
Modified data pages in the cache are marked as dirty, which
are inconsistent with data pages in flash. Dirty pages in cold
466
of 5
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论