




IEEE 2017 - Batch Insertion Strategy in a Distribution Database.pdf
免费下载

Batch Insertion Strategy in a Distribution Database
Jintao Gao
School of Computer
Northwestern Polytechnical University
Xi’an 710129, China
gaojintao@mail.nwpu.edu.cn
Wenjie Liu, Hongtao Du and Xiaofang Zhang
School of Computer
Northwestern Polytechnical University
Xi’an 710129, China
{liuwenjie& zhangxiaofang & duhongtao}@nwpu.edu.cn
Abstract—History data produced by financial enterprises are
usually very large, and needed to be transmitted from one
table partly or wholly to another table, which requests flexible
and efficient insertion strategy. Distributed systems are good at
handling massive data under big data era. For the high
performance and extendibility, financial enterprises recently
tend to handle and analyze their business data with distributed
systems instead of traditional 'IOE' architecture. Distributed
systems are weak at SQL support, like HBase, which only
provides some simple program interfaces for users, not
satisfying financial enterprise's data insertion requirement. To
solve these problems, we proposes a batch insertion
strategy(BIS). The main contents of BIS include multiple
insertion strategies used to implement large data inserting,
threshold optimization technology used to decrease the
network cost and redirection technology used to reduce the
pressure of system. BIS is implemented in a distributed
database system called OceanBase which is designed by
Alibaba Group. The experiment data are from the actual
business data of some financial enterprises, and the experiment
results show that performance of BIS is basically as well as
existed value insertion in OceanBase but much better than
program insertion.
Keywords- distributed system; large data; batch insertion;
threshold optimization; redirection technology
I. INTRODUCTION
Data insertion is the basic function of traditional database,
taking very important role in processing financial business.
As the coming of big data era, financial enterprises gradually
discard 'IOE'(I represents IBM, O represents Oracle, and E
represents EMC) architecture, and tend to handle massive
data using distributed system. But SQL in distributed
systems are not friendly, not supporting flexible large data
inserting, which will block normal business process of
financial enterprise.
Large history data produced by financial enterprise are
needed to be partly exported from one table and imported to
another table. In traditional database, insertion technology is
very sophisticated. But under distributed environment, to
find out a convenient, flexible and efficient method to insert
large data are quite challenge.
Google introduced a serial distributed systems and
architectures that lead the development direction of
distributed system, such as GFS[2], MapReduce[3] and
spanner[5]. But their insertion functions in SQL level are
only limited to insert very little data or use tools to import
data which is not flexible.
To resolve these problems, we proposed a batch insertion
strategy(BIS), which can flexibly and efficiently insert large
data into a distributed system. BIS is implemented in
OceanBase[13](architecture as chapter 2). Although there is
already an insertion method in OceanBase, it only supports
inserting very few data. BIS's implementing is based on the
existed insertion method, and come up a better result. The
contributions of this paper are as follows.
1. Deeply study the existed insertion strategies, including
traditional and distributed databases, and propose the batch
insertion strategy.
2. For decreasing network cost, a threshold optimization
method is proposed.
3. To reduce the pressure of system under situation of
high concurrent insert operations, a redirection technology is
provided.
4. Using actually data from financial enterprise as
experiment data, we get the conclusion that under BIS, large
data can be inserted into OceanBase[13]
normally, and the
performance of BIS is nearly equal to existed insertion
method, but much better than program insertion method.
And BIS is also suitable for other distributed system to insert
large data.
II. R
ELATED CONCEPTS
A. Physical operator(Po)
Po is used to complete some job[15], like sort or join,
which is the node of physical operator tree. The main
operations of Po contain initializing and getting one row
from its children.
B. Physical operator tree(Pot)
Pot represents SQL's execution semantics[15], and its
node is Po. The physical plan’s execution procedure of one
SQL starts from initializing root of Pot, then depth-firstly
traverse to initialize other nodes. After initializing the whole
tree, it can get one row from leaf node to root iteratively. The
formal definition of Pot is as follows.
The whole tree is defined as pot=T(V,E). V represents
nodes of T, and E represents the relations of V in T, like
father-son.
Foundation items: National Natural Science Fo
undation of China
(61672434); National High Technology Research; Development Program
(863) of China (2015AA015307) and Natural Science Basic Research Plan
in Shaanxi Province of China (No.2017JM6104).
978-1-5-97-7/1$31.00 ©201 IEEE
Authorized licensed use limited to: Ant Financial. Downloaded on August 29,2023 at 08:45:18 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply.
The node of T is defined as V={Z,I,F,c}. Z represents the
semantics of some Po, like sort or join; I represents the
initializing operation; F represents the operation of fetching
one row; c represents the children of one V.
The edge of T is defined as E: ƪ: V –> ci, which
represents some connecting relations between nodes of T.
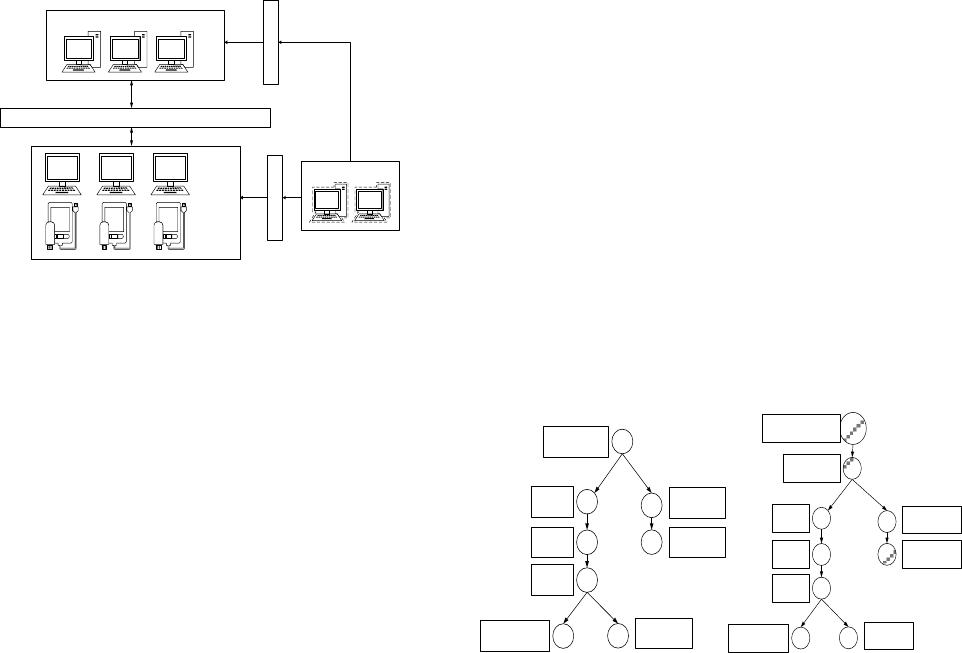
C. Implementation environment
We implement BIS in a distributed database, designed by
Alibaba, called OceanBase[13](as fig 1).
...
...
network
UdpateServer
MergeServer
ChunkServer
...
Master slaveslave
Master slave
network
network
RootServer
Figure 1. Architecture of OceanBase
Architecture of OceanBase: OceanBase contains four
components, including RootServer, UpdateServer, Merge-
Server, and ChunkServer, which are connected by network.
The network architecture is libeasy, which is built upon
libevent[12], is very suitable for transmitted little packet, but
there exists limitation about package size, which is only 2
megabytes.
RootServer(RS): RS is the controller of OceanBase,
used to provide metadata for other servers and manage the
distribution of MergeServer and ChunkServer.
UpdateServer(UPS): Master UPS is the only entrance
for insert/update/delete operation. The delta data are stored at
main memory of UPS by the structure of B+tree, and every
delta data must contain the row key used to identify this data,
and lock it.
MergeServer(MS): MS is to receive the SQL package
input by users, parse SQL, generate logical plan, physical
plan, and return the execution result to users.
ChunkServer(CS): CS is used to store baseline data,
and its architecture is distribution, easily scalable, similar
with BigTable[4] and HBase[1].
III. B
ATCH INSERTION STRATEGY
In SQL level, OceanBase uses SQL of insert-values to
complete data inserting operation. The function of insert-
values has two main problems, including: 1. The inserted
values are needed to be input by users, which is very
inflexible. 2. It is only allowed to insert few data one time
due to the network limitation of OceanBase. For these
problems existed in OceanBase, the original insertion
strategy is not able to support financial enterprise's normal
business, like large history data's insertion. To solve these
problems, this paper came up with the batch insertion
strategy(BIS), but not limited to OceanBase. Under BIS, an
insert-select SQL sentence is supported in OceanBase, used
to insert large data into one table from other tables more
flexibly than original insert-values. The central idea of BIS
is: reusing and rebuilding the original insert-values’ physical
plan, dynamically checking the size of insertion data to set
the one-batch insertion threshold, and reducing the pressure
of UPS by redirecting technology.
A. rebuilding physical plan
The physical plan of insert-values means to insert the
input fixed values into some table, while insert-select’s
physical plan is to insert multi-table's mixed data into one
table. The execution semantics of insert-select is changed
comparing with insert-values, so the corresponding physical
plan is needed to be rebuilt based on the physical plan of
insert-values. The physical plan of insert-values(P) is showed
at fig2 (a) and physical plan of insert-select(P') is showed at
fig2 (b).
Physical plans showed at fig2 are both generated at MS,
and {V
0
,V
6
,V
7
} at fig 2(a) are executed at MS, {V
1
,V
2
,V
3
,
V
4
,V
5
} at fig 2(a) are executed at UPS. Similarly, {V
0
”, V
0
’,
V
6
, V
8
} at fig 2(b) are executed at MS, {V
1
, V
2
, V
3
, V
4
, V
5
}
at fig 2(b) are executed at UPS. The following contents will
introduce the difference of P and P', and how to overcome
network limitation and reduce the pressure of UPS based on
P'.
V1
Z: insert
C: V2
V2
Z: lock
C: V3
V3
Z: merge
C: V4,V5
V4
Z: get-UPS-data
C: NULL
V5
Z: get-S
C: NULL
V6
Z: convert-S
C: V6
V7
Z: parse-S
C: NULL
V0
Z: insert-values
C: V1,V6
V6
Z: convert-S
C: V7
V8
Z: parse-select
C: NULL
V1
Z: insert
C: V2
V2
Z: lock
C: V3
V3
Z: merge
C: V4,V5
V4
Z: get-UPS-data
C: NULL
V5
Z: get-S
C: NULL
V0'
Z: insert-select
C: V1,V6
V0"
Z: insert-loop-control
C: V0'
(a) (b)
Figure 2. physical plan of insert-values(a) and insert-select(b)
At fig 2(a), V
0
is the root of insert-values, used to
control the whole procedure of inserting, including
execution of P and result returning. The whole Pot's
initialization and row's fetching are triggered by V
0
's
operations I and F. Operation V
1
is used to actually
complete the insertion operation. V
2
is the operation used to
locate insertion address and lock this address by
corresponding row key. V
3
is used to merge the insertion
data(from V
4
) and row keys of insertion data(from V
5
). V
4
is
used to get the value of operation list(at fig 2) by row key.
V
6
is used to cast S into the format of main table. V
7
is used
to parse S and judge if |vi| is equal to column size of main
table.
At fig2(b), the difference with fig2(a) including:
substituting V
7
with V
8
, substituting V
0
with V
0
', and
Authorized licensed use limited to: Ant Financial. Downloaded on August 29,2023 at 08:45:18 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply.
of 5
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论