




Anser:Adaptive Information Sharing Framework of AnalyticDB_阿里云.pdf
免费下载
Anser: Adaptive Information Sharing Framework of AnalyticDB
Liang Lin
Alibaba Group
Hangzhou, China
yibo.ll@alibaba-inc.com
Yuhan Li
Alibaba Group
Hangzhou, China
lyh200442@alibaba-
inc.com
Bin Wu
Alibaba Group
Hangzhou, China
binwu.wb@alibaba-
inc.com
Huijun Mai
Alibaba Group
Hangzhou, China
huijun.mhj@alibaba-
inc.com
Renjie Lou
Alibaba Group
Hangzhou, China
json.lrj@alibaba-inc.com
Jian Tan
Alibaba Group
Hangzhou, China
j.tan@alibaba-inc.com
Feifei Li
Alibaba Group
Hangzhou, China
lifeifei@alibaba-inc.com
ABSTRACT
The surge in data analytics has fostered burgeoning demand for
AnalyticDB on Alibaba Cloud, which has well served thousands of
customers from various business sectors. The most notable feature
is the diversity of the workloads it handles, including batch process-
ing, real-time data analytics, and unstructured data analytics. To
improve the overall performance for such diverse workloads, one of
the major challenges is to optimize long-running complex queries
without sacricing the processing eciency of short-running inter-
active queries. While existing methods attempt to utilize runtime
dynamic statistics for adaptive quer y processing, they often focus
on specic scenarios instead of providing a holistic solution.
To address this challenge, we propose a new framework called
Anser, which enhances the design of traditional distributed data
warehouses by embedding a new information sharing mechanism.
This allows for the ecient management of the production and
consumption of various dynamic information across the system.
Building on top of Anser, we introduce a novel scheduling pol-
icy that optimizes both data and information exchanges within
the physical plan, enabling the acceleration of complex analyti-
cal queries without sacricing the performance of short-running
interactive queries. We conduct comprehensive experiments over
public and in-house workloads to demonstrate the eectiveness
and eciency of our proposed information sharing framework.
PVLDB Reference Format:
Liang Lin, Yuhan Li, Bin Wu, Huijun Mai, Renjie Lou, Jian Tan, and Feifei
Li. Anser: Adaptive Information Sharing Framework of AnalyticDB.
PVLDB, 16(12): 3636 - 3648, 2023.
doi:10.14778/3611540.3611553
1 INTRODUCTION
As modern organizations struggle with managing diverse work-
loads including batch processing, real-time data analytics, and un-
structured data analytics, they face the challenge of maintaining
optimal performance. To meet this challenge, there has been a trend
This work is licensed under the Creative Commons BY-NC-ND 4.0 International
License. Visit https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/ to view a copy of
this license. For any use beyond those covered by this license, obtain permission by
emailing info@vldb.org. Copyright is held by the owner/author(s). Publication rights
licensed to the VLDB Endowment.
Proceedings of the VLDB Endowment, Vol. 16, No. 12 ISSN 2150-8097.
doi:10.14778/3611540.3611553
(a) The distribution of diverse workloads.
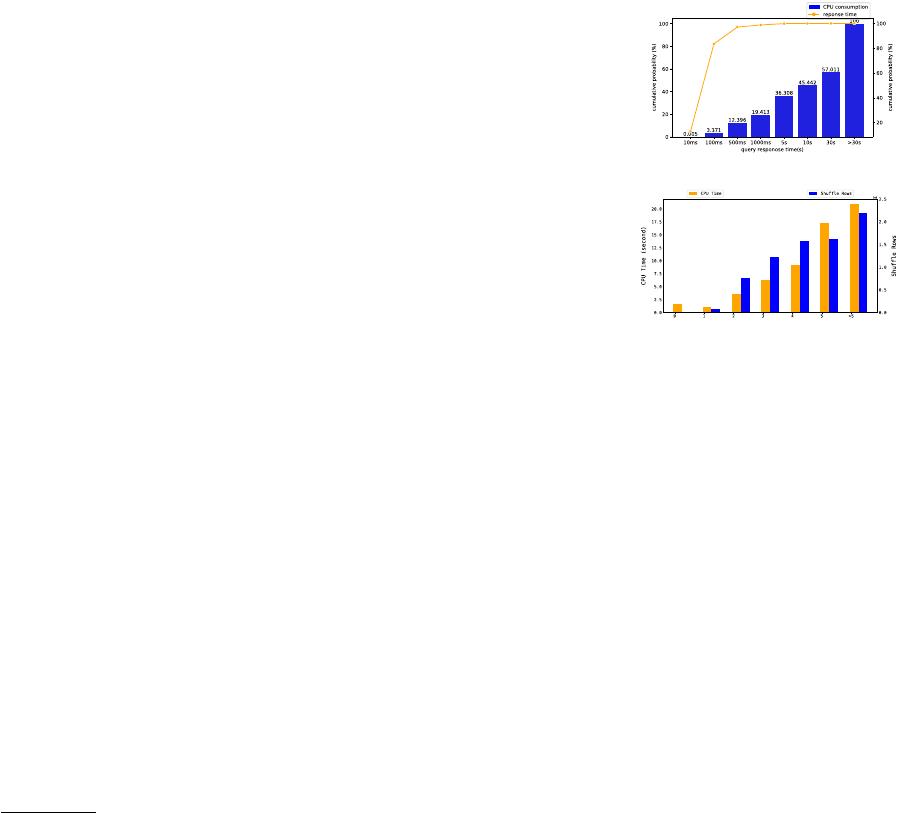
(b) Resource consumption of JOIN queries.
Figure 1: Statistics collected from AnalyticDB ’s production
workloads.
towards system convergence, with many organizations transition-
ing towards uniform systems that can handle diverse workloads.
One of the most widely adopted industry solutions is Spark [
9
,
49
],
a fast and exible data processing engine that can handle diverse
workloads. Similarly, Redshift [
10
,
26
], a cloud-based data ware-
housing solution, oers automatic tuning capabilities to handle
complex workloads more eciently.
AnalyticDB [
14
,
46
] is a high-performance data warehouse de-
veloped by Alibaba Cloud. It has been extensively adopted both
internally for Alibaba Group’s business operations and externally
across a range of industries, such as e-commerce, nance, logistics,
education, and entertainment. Within AnalyticDB , we have noticed
a trend of increasing diversity in terms of query response times.
As shown in Figure 1a, many simple and short queries, such as
business-critical intelligence queries issued from dashboards, can
be processed in milliseconds. These queries account for up to 80% of
the customers’ workloads in our production environments. To sat-
isfy the quality of service requirements, it is essential to ensure that
these interactive short queries have sucient resources. Meanwhile,
it is also common to have complex analytical queries that exceed
hundreds of KB in size, involving aggregations, multi-way joins,
and nested subqueries. Statistics show that long queries with re-
sponse times (RT) more than 10 seconds account for over 10% of the
3636

workloads, which yet consume more than 50% of the computation
resources. To evaluate the resource consumption of the complex
analytical queries, we collect related statistics of JOIN queries from
AnalyticDB ’s production workloads (as shown in Figure 1b), in-
cluding the query CPU time and the number of shued rows. As
the number of join operators increases, the required resources also
grow dramatically.
As evidenced by the statistics above, optimization techniques
for expensive batch computing tasks and ETL jobs play a vital role
in improving the overall performance of modern data warehous-
ing systems. As the number of concurrent queries increases, the
competition for resources (e.g., CPU, memory and network) be-
tween queries has b ecome very serious. In some cases, long queries
may exhaust resources in a database instance and subsequent short
queries belonging to the same instance will not be processed. We
summarize several key challenges that remain unsolved:
Challenge 1: Scenario customization for adaptive query processing.
As workloads become increasingly diverse and statistics become
less available, it has become clear that traditional "optimize-then-
execute" strategies [
24
,
31
,
41
] are no longer sucient. This realiza-
tion has led to a broad range of studies in the eld of adaptive query
processing [
20
]. Many commercial databases have implemented
various adaptive techniques, but the current approaches tend to
build scenario-customized solutions for each technique, which can
introduce unnecessary complexity into the system [
7
,
34
,
44
,
50
].
For example, Spark’s adaptive query execution [
50
] supports four
features: mid-query re-optimization, dynamically coalescing shue
partitions, dynamically switching join strategies, and dynamically
optimizing skew joins. Each feature individually collects dynamic
statistics and makes adjustments. A general-purpose information
framework that can t into these dierent scenarios would signif-
icantly reduce costs. By developing a framework that can share
information across dierent adaptive techniques, it would be pos-
sible to eliminate redundant eorts and minimize the complexity
of the system. Such a framework would enable data warehousing
systems to optimize their performance without having to build
scenario-customized solutions for each individual technique. Fur-
thermore, the same statistics could be used by dierent cases (for
example, all of the four features that Spark supports require shue
le statistics), yet implementing each case individually deprives the
opportunity for the same information to be used multiple times. In
particular, when statistics collection is resource-consuming (such
as with a bloom lter), sharing information among multiple cases
could potentially signicantly reduce costs.
Challenge 2: Eective and ecient management of dynamic statis-
tics. To potentially identify and share common dynamic statistics,
the information collection and utilization need to be decoupled
from existing modules of query engine, and a holistic management
of the information lifecycle is required to register, collect, store,
disperse, and destroy the information. None of the previous studies
have clearly dened the scope of the information that can be used
in dierent adaptive techniques, nor have they framed a mechanism
to manage the information lifecycle. In a production environment,
information collection, transmission, and storage all lead to addi-
tional overhead. High-performance data warehouse requires such
overhead to be diminished and separated from query execution
process. Moreover, a carefully designed mechanism is necessary to
limit the memory usage of the information storage that the dynamic
statistics does not aect the overall system.
Challenge 3: Coordination with query scheduler. The statistics
information can be holistically leveraged to optimize the adaptive
adjustments. To this end, the scheduler naturally comes into the
picture to orchestrate the execution orders of information consumer
and producer. However, none of the previous studies have clearly
dened a scheduler that is aware of the information dependencies.
In batch processing systems, the transmission of adaptive statis-
tics is mostly implemented as part of the execution process. Some
approaches [
12
,
25
,
32
] add checkp oints in the execution plan that
monitor statistics during execution and trigger re-optimization if
necessary, while others rewrite the provider of information explic-
itly as a sub-expression in the query execution to provide adaptive
statistics as part of the query execution process. Both approaches
tie information transmission strictly with data processing, which
means that the information consumer can only receive information
from its upstream operators without considering the possibilities of
receiving information sideways or discarding information with high
production costs. Some real-time data analytics systems support
passing information sideways, but mostly through tailored services.
For example, Impala [
5
] implements a dynamic lter service to pass
information sideways. Such services are customized for specic use
cases and cannot be easily extended to others. Moreover, the sched-
uler is not aware of such information transmission. The consumer
of the information either waits a static time period for statistics
to arrive or only consumes available statistics before running. As
execution plans become more complicated, useful statistics may not
be consumed to provoke adaptive execution without cooperation
with the scheduler. Therefore, a more sophisticated mechanism is
required to manage the transmission and consumption of adap-
tive statistics, which takes into account the collaboration with the
scheduler.
To this end, a novel information sharing framework, namely
a
daptive i
n
formation
s
haring fram
e
wo
r
k(Anser), is developed in
AnalyticDB . Our major contributions are summarized as follows:
(1)
The framework provides a uniform and eective interface
for dierent modules to share various types and levels of in-
formation. At the operator level, Anser collects various types
and levels of information, classies according to their types
and granularities, and passes to dierent modules across the
query to tune for better performance during execution.
(2)
The framework supports the automatic matching and trans-
mission of the information between information producer
and information consumer once the relationship is registered.
It supports many-to-one and one-to-many information pass-
ing in a complex physical execution tree. The transmission
is both low latency and ecient by the usage of information
merging and push-based communication model.
(3)
In conjunction with the framework, we design an information-
aware scheduler, allowing for prioritization of scheduling se-
quences based on information dependencies. Anser improves
query performance by sending information sideways based
on pre-determined dependencies that the information can b e
3637
of 13
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


文档被以下合辑收录
评论