




ICDE2024_FedMix Boosting with Data Mixture for Vertical Federated Learning_腾讯云.pdf
免费下载
FedMix: Boosting with Data Mixture
for Vertical Federated Learning
Yihang Cheng
1
, Lan Zhang
12
, Junyang Wang
1
, Xiaokai Chu
3
, Dongbo Huang
3
, Lan Xu
3
1
University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, China
2
Institute of Artificial Intelligence, Hefei Comprehensive National Science Center, China
3
Tencent, Shanghai, China
yihangcheng@mail.ustc.edu.cn, zhanglan@ustc.edu.cn, iswangjy@mail.ustc.edu.cn
chuxiaokai@ict.ac.cn, andrewhuang@tencent.com, lanxu@tencent.com
Abstract—The need to safeguard data privacy and adhere to
regulations such as GDPR creates data silos and has prompted the
emergence and widespread adoption of techniques for distributed
databases. To effectively explore the value of data across multiple
organizations, techniques for data management, data analysis and
data functionality from distributed databases have been proposed.
Recently, Vertical Federated Learning (VFL) has become a
solution with growing interests, which enables collaborative model
training when data features are partitioned into multiple parts
and are held by different parties. However, typical VFL methods
heavily rely on private set intersection (PSI) to align data before
training and only utilize aligned data for training. In this work, we
provide a theoretical analysis to show that unaligned data actually
contains valuable and rich features, and a thoughtful design
that harnesses the potential of unaligned samples to significantly
improve the performance of VFL models. Regrettably, many
existing methods simply discard unaligned data, resulting in an
irrecoverable loss of performance. To address this data sacrifice
problem, we introduce the concept of data mixture, which enables
the utilization of both aligned and unaligned data during training.
Building upon the data mixture idea, we present FedMix, the
first on-the-fly and distribution-agnostic framework designed to
boost the performance of VFL models by leveraging unaligned
data. A data seasoning approach is also designed to utilize
auxiliary data lacking label information. Evaluations on diverse
datasets under different settings demonstrate the effectiveness of
the proposed FedMix compared with various SOTA approaches.
FedMix achieves up to
15%
model performance improvement
and 30.5 hours time cost reduction.
I. INTRODUCTION
In the modern digital era, data has become a critical asset
for organizations. The ability to analyze and extract insights
from data is key to driving business decisions, understanding
consumer behavior, and enhancing operational efficiency. There
are already numerous studies focusing on data management
and mining [1, 30, 33, 24] in the centralized scenario. However,
with regulations such as GDPR [38], the landscape of data
management and analysis has significantly changed, giving rise
to distributed databases characterized by multiple data silos
across various organizations, in which the transfer of raw data
is typically restricted. Consequently, the exploration of methods
for data management, data analysis and data functionality from
distributed databases in a privacy-preserving way without the
exchange of local data has emerged as a pressing topic.
Lan Zhang is the corresponding author.
aligned
unaligned
unaligned
auxiliary
auxiliary
ࣞ
ࣞ
௨
ࣞ
௨௫
ࣳ
ࣳ
௨
ࣳ
ଵ
௨
ࣞ
ଵ
௨
ࣞ
ଵ
ࣞ
ଵ
௨௫
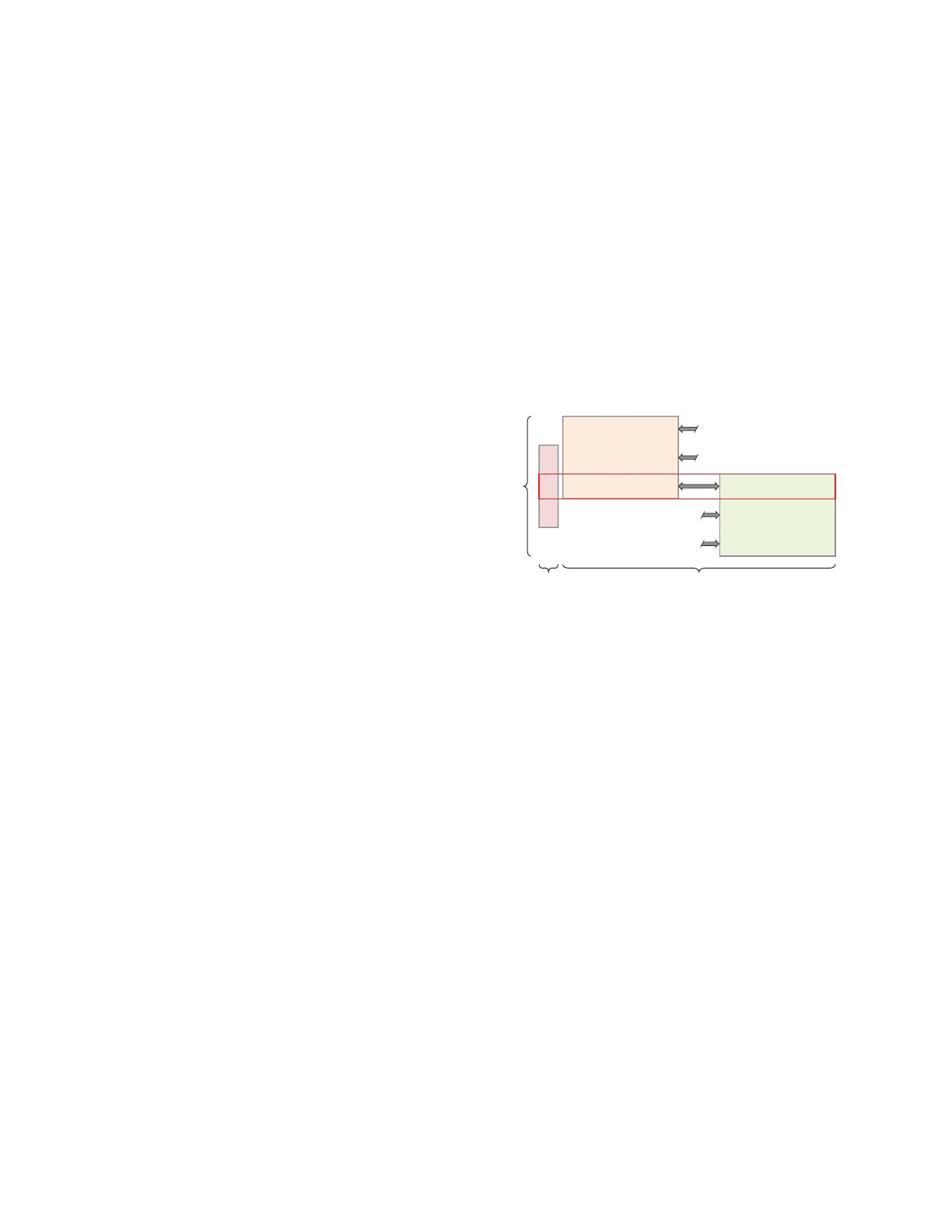
Active Party Passive Party
Sample Space
Label Space Feature Space
Fig. 1: A typical data distribution in VFL. A classic VFL
training process leverages only the aligned data
Y
a
, D
a
0
, D
a
1
(highlighted in the red square) but discards other data.
On the other hand, machine learning has been rapidly
developed and gradually transformed from a simple target
prediction tool into a powerful means of data analysis, capable
of effectively uncovering the potential value in data. And, how
to apply machine learning to distributed databases for data
silos has become a growing area of interest for researchers [29,
45, 25, 16, 26]. Federated Learning (FL) [28], first proposed
by Google in 2016, is one common technique in this area to
enable collaborative model training without revealing any local
data among parties. To accommodate different scenarios, the
concept of FL is subsequently divided into three categories [27]:
Horizontal Federated Learning (HFL), Vertical Federated
Learning (VFL), and Federated Transfer Learning (FTL).
Among them, VFL is designed for situations where data features
are partitioned into multiple parts, each held by different parties.
This mode can effectively break information silos and has been
widely adopted in various industries, such as advertising [35]
and finance [20].
Problem: data sacrifice. However, a typical VFL training
process [48, 27, 41] requires parties to first perform private
set intersection (PSI) [14] to find aligned data, i.e., data with
aligned IDs, which significantly reduces the amount of usable
data. As the example of typical data distribution in VFL in
Fig. 1, only the aligned data
D
a
0
and
D
a
1
as well as the
labels
Y
a
can be utilized for training, and the rest of the
data is discarded, though unaligned data usually contain rich
3379
2024 IEEE 40th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE)
2375-026X/24/$31.00 ©2024 IEEE
DOI 10.1109/ICDE60146.2024.00261
2024 IEEE 40th International Conference on Data Engineering (ICDE) | 979-8-3503-1715-2/24/$31.00 ©2024 IEEE | DOI: 10.1109/ICDE60146.2024.00261
Authorized licensed use limited to: Tencent. Downloaded on April 22,2025 at 08:49:34 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply.

valuable features. We refer to this problem as data sacrifice,
as formally defined in Definition 1. Several methods have
been proposed to mitigate this problem, which can be divided
into two categories: (1) Data completion [19, 47, 43] is the
most straightforward solution. Reconstruction techniques such
as generative adversarial networks (GAN) [10] are applied
to estimate missing features of unaligned data. After that,
all data can be used in the training of VFL. (2) Extractor
improvement [7, 12] leverages unsupervised learning methods
like deep reconstruction-classification network (DRCN) [9] or
autoencoder [14] to improve the performance of extractors
(i.e. the bottom model) of each party. The training of VFL
is then built on top of these extractors. We find that both
data completion and extractor improvement require a preparing
stage for either unaligned data reconstruction or the training of
extractors. The preparing stage is extremely time-consuming,
which takes 30% to 125% of the running time of the whole
training stage as shown in Table V. Besides, those two methods
are hard to apply in cases when the feature distribution is biased
(see Fig. 8) or when the proportion of unaligned data is too
large (see Fig. 9). In these cases, those two methods can only
achieve 0.1% ∼ 3% performance improvement.
In this work, we aim to find a general on-the-fly solution for
the data sacrifice problem to improve the performance of VFL
models by leveraging unaligned data. To find such a solution,
we need to answer three key questions:
1)
Can unaligned data indeed enhance model performance?
Quantitatively characterizing VFL model performance, particu-
larly in relation to the influence of additional unaligned data,
poses significant challenges. This work, to the best of our
knowledge, presents the first attempt to provide a theoretical
analysis of the contribution of unaligned data to the VFL
model. Besides, previous methods addressing the data sacrifice
problem have provided little theoretical guarantees.
2)
How to incorporate unaligned data seamlessly into the
VFL training process, eliminating the need for additional
preparation? Existing methods necessitate an extra preparing
stage, resulting in substantial extra time costs. Besides, they are
difficult to achieve good performance when there is significant
bias in feature distribution. Therefore, it is urgent to seek a
more effective approach to directly utilize unaligned data in
VFL training.
3)
How to deal with the absence of label information for
some unaligned data? Some unaligned data, especially in
passive parties, do not come with label information, and we
refer to them as the auxiliary data. Simply discarding them
means missing out on opportunities for significant improvement,
as shown by the results in Fig. 12 (an approximate
20%
improvement in the overall performance). Therefore, we must
also explore strategies for reconstructing label information.
New framework: FedMix. To tackle the above challenges
and resolve the data sacrifice problem, a series of technical
advancements are required. First, we formalize the data sacrifice
problem and analyze the potential improvements that can be
achieved with unaligned data. We provide a theoretical analysis
of this problem and introduce Theorem 1, demonstrating that
the inclusion of unaligned data in the VFL training results in a
closer alignment of data distribution to the global distribution
(from which all training data are sampled), and indeed improve
the performance of the VFL model. This analysis serves as
the cornerstone of our new framework FedMix. Second, we
introduce the concept of data mixture and design a data mixer
with two distinct random selection strategies. These innovations
enable the efficient utilization of unaligned data during the VFL
training process. Data mixture, as the core idea of our work,
randomly and independently selects one sample to match each
aligned sample and sums them with a weight-average parameter
from Beta distribution. Specifically, the data mixer provides two
random selection strategies to guide the collaborative selection
of samples from the aligned and unaligned datasets within each
party. Third, when dealing with auxiliary data lacking label
information, we design a data seasoning technique to generate
pseudo-labels for such data during the training of VFL and
incorporate them into the unaligned dataset. This enables their
utilization alongside the data mixer. We implement our theory-
backed framework FedMix as a general on-the-fly solution to
address the data sacrifice problem. Our extensive experiments,
conducted on diverse datasets, various data distribution settings,
ablation studies, and comparison with state-of-the-art methods,
consistently demonstrate the superior performance of FedMix.
Contributions. We summarize the three key contributions
of this work as follows:
•
We present a theoretical analysis of the data sacrifice
problem, and to the best of our knowledge, the first theoretical
analysis of the potential improvement brought by unaligned
data to the VFL model.
•
We introduce FedMix, the first on-the-fly and distribution-
agnostic framework designed to address the data sacrifice
problem. Within FedMix, we propose an efficient data mixer
based on the core idea of data mixture, along with a data
seasoning approach, enabling the full utilization of unaligned
and auxiliary data during the VFL training stage.
•
We have implemented FedMix and conducted extensive
evaluations on various datasets. Comparisons with state-of-the-
art methods show the superiority of FedMix in dealing with
the data sacrifice problem, as it shows notable advantages in
both model performance and time cost. Specifically, FedMix
achieves up to
15%
model performance improvement and a
substantial reduction in time cost by
30.5
hours. Our exper-
imental results, conducted across different data distribution
settings, showcase the robustness of FedMix, with consistent
performance improvements ranging from
3%
to
16%
. The
ablation study confirms the significance of the two key modules
within FedMix (data mixer and data seasoning), as they each
contribute to improvements of 12% and 4%, respectively.
II. R
ELATED WORK
Current work about the data sacrifice problem can be mainly
divided into two categories: data completion and extractor
improvement. Below we give a detailed description of them.
Data completion. The most straightforward way is to fill in
missing features of unaligned data and treat them as normal
3380
Authorized licensed use limited to: Tencent. Downloaded on April 22,2025 at 08:49:34 UTC from IEEE Xplore. Restrictions apply.
of 14
免费下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论