




Apache IoTDB A Time Series Database for Large Scale IoT Applications.pdf
100墨值下载
Apache IoTDB: A Time Series Database for Large Scale IoT
Applications
CHEN WANG, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
JIALIN QIAO, Timecho Ltd, Beijing, China
XIANGDONG HUANG, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
SHAOXU SONG, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
HAONAN HOU, Timecho Ltd, Beijing, China
TIAN JIANG, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
LEI RUI, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
JIANMIN WANG, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
JIAGUANG SUN, Tsinghua University, Beijing, China
A typical industrial scenario encounters thousands of devices with millions of sensors, consistently generating billions of data
points. It poses new requirements of time series data management, not well addressed in existing solutions, including (1)
device-dened ever-evolving schema, (2) mostly periodical data collection, (3) strongly correlated series, (4) variously delayed
data arrival, and (5) highly concurrent data ingestion. In this paper, we present a time series database management system,
Apache IoTDB. It consists of (i) a time series native le format, TsFile, with specially designed data encoding, and (ii) an IoTDB
engine for eciently handling delayed data arrivals and processing queries. We introduce a native distributed solution with
distributed queries optimized by parallel operators. We also explore ecient TsFile synchronization mechanisms, ensuring
seamless data integration without the need for ETL processes. The system achieves a throughput of 10 million inserted values
per second. Queries such as 1-day data selection of 0.1 million points and 3-year data aggregation over 10 million points can
be processed in 100 ms. Comparisons with InuxDB, TimescaleDB, KairosDB, Parquet and ORC over real world data loads
demonstrate the superiority of IoTDB and TsFile.
CCS Concepts: • Information systems → Data management systems.
Additional Key Words and Phrases: time series, data model, database engine, distributed
1 Introduction
In the Internet of Things (IoT), a huge amount of time series is generated by various devices with many sensors
attached. The data need to be managed not only in the cloud for intelligent analysis but also at the edge for
real-time control. For example, more than 20,000 excavators are managed by one of our industrial partners, a
maintenance service provider of heavy industry machines, each of which has hundreds of sensors, e.g., monitoring
Shaoxu Song (https://sxsong.github.io/) and Jianmin Wang are the corresponding authors.
Authors’ Contact Information: Chen Wang, Tsinghua University, Beijing, Beijing, China; e-mail: wang_chen@tsinghua.edu.cn; Jialin Qiao,
Timecho Ltd, Beijing, Beijing, China; e-mail: jialin.qiao@timecho.com; Xiangdong Huang, Tsinghua University, Beijing, Beijing, China;
e-mail: hxd@timecho.com; Shaoxu Song, Tsinghua University, Beijing, Beijing, China; e-mail: sxsong@tsinghua.edu.cn; Haonan Hou,
Timecho Ltd, Beijing, Beijing, China; e-mail: haonan.hou@timecho.com; Tian Jiang, Tsinghua University, Beijing, Beijing, China; e-mail:
jiangtia18@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn; Lei Rui, Tsinghua University, Beijing, Beijing, China; e-mail: rl18@mails.tsinghua.edu.cn; Jianmin Wang,
Tsinghua University, Beijing, Beijing, China; e-mail: jimwang@tsinghua.edu.cn; Jiaguang Sun, Tsinghua University, Beijing, Beijing, China;
e-mail: sunjg@tsinghua.edu.cn.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives International 4.0 License.
© 2025 Copyright held by the owner/author(s).
ACM 1557-4644/2025/3-ART
https://doi.org/10.1145/3726523
ACM Trans. Datab. Syst.
2 • C. Wang et al.
!"#$%&'()
*+,&% '
!"#-'./'.
*+,&% ' *+,&% ' *+,&% ' *+,&% '*+,&% '
-01.2 314550
6!"$
78#,&%'
-9(:
;<=#>4?'#$5@0A)'.
;:=#$%5A4#$%A+)'.
;1=#>(4#!'/&:'
,&%'
-9(:
>*B
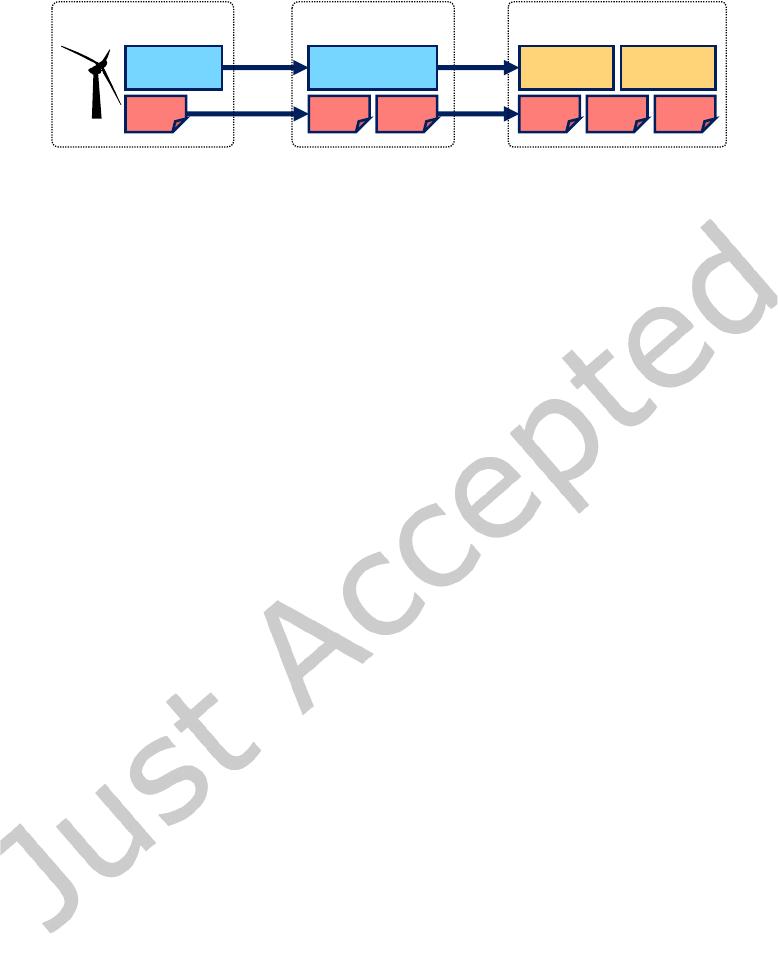
Fig. 1. Data management in IoT scenarios
engine rotation speed. As illustrated in Figure 1, the data are rst packed in devices and sent to the server via a
5G mobile network. In the server, the data are written to a time series database for OLTP queries. Finally, data
scientists may load data from the database to a big data platform for complex analysis and forecasting, i.e., OLAP
tasks.
1.1 IoT Scenarios
The process in Figure 1 poses new requirements to time series database management systems. (1) In the end
device, such as the aforesaid excavator, a lightweight database or a compact le format is needed to save space
and network bandwidth. (2) In the e dge server, a full-function database collects, stores and queries the massive
data of devices, capable of handling delayed arrivals. (3) In the cloud, a database cluster with complete historical
data persistence connects directly to big data analysis systems, such as Spark and Hadoop, and enables OLAP
queries. In addition to the large scale issues, millions of series (columns) and billions of p oints (rows), we highlight
below the unique and urgent features in the IoT scenarios.
1.1.1 Device-defined Ever-evolving Schema. Unlike the traditional relational databases with pre-dened schema,
the schema of time series data in the IoT scenario is dened by sensors in the devices. During the device
maintenance or upgrade, sensors are frequently removed, replaced or augmented, leading to the changed schema.
For instance, as illustrated in Figure 2, sensor FC32 for monitoring fuel consumption is replaced by FC3X, at time
09:06:13. We ne ed a data model that is suciently exible to capture such an ever-evolving schema.
1.1.2 Mostly Periodical Data Collection. Machine-generated sensor data are often collected periodically with a
pre-set frequency. While the time series is expected with a regular time interval, there may be small variations
due to data bus congestion or network delay. Even worse, those values not changed with the previous may be
omitted to save energy. For example, in Figure 2, ES05 is mostly collected every 60 seconds, but with a small
delay from time 09:04:13 to 09:04:20 and an omitted data at time 09:07:13. Data encoding should be able to handle
such variations for ecient storage.
1.1.3 Strongly Correlated Series. It is also worth noting that multiple sensors, e.g., in the same module of a device,
may collect data at the same time. In addition to the same timestamps, their values may also be correlated. For
instance, in Figure 2, the fuel consumption (FC32/FC3X) value should be determined by engine speed (ES05)
and torque (ET03) at the same time. Moreover, the wind spee ds of close turbines in the same wind farm should
be similar with each other. Again, the storage scheme is expected to fully utilize such opportunities in data
compression.
1.1.4 Variously Delayed Data Arrival. While most data points arrive in time order, serious delays may occur, e.g.,
owing to network delay or corruption. For instance, in Figure 2, the data point with timestamp 09:05:13 arrives
after it subsequent points. The delay could b e various, ranging from seconds to days. This issue is unique in time
series data and seriously obstruct the time ordered storage.
ACM Trans. Datab. Syst.
of 45
100墨值下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论