




DB2 BACKUP Performance
5墨值下载

Maximizing Performance of IBM DB2 Backups 1
®
Maximizing Performance of IBM DB2 Backups
This IBM
®
Redbooks
®
Analytics Support Web Doc describes how to maximize the performance of IBM
DB2
®
backups.
Backing up a database is a critical part of any disaster recovery plan. Making sure that the backup
completes in a reasonable time frame means that there is always a valid backup available in case of
emergency. This document describes the following elements that are critical to good backup
performance:
The backup process model
z
Basic backup performance concepts
z
Backup performance considerations
z
Monitoring backup performance with the
DB2_BAR_STATS
registry variable
z
This document applies to all versions of DB2 for Linux, UNIX, and Windows.
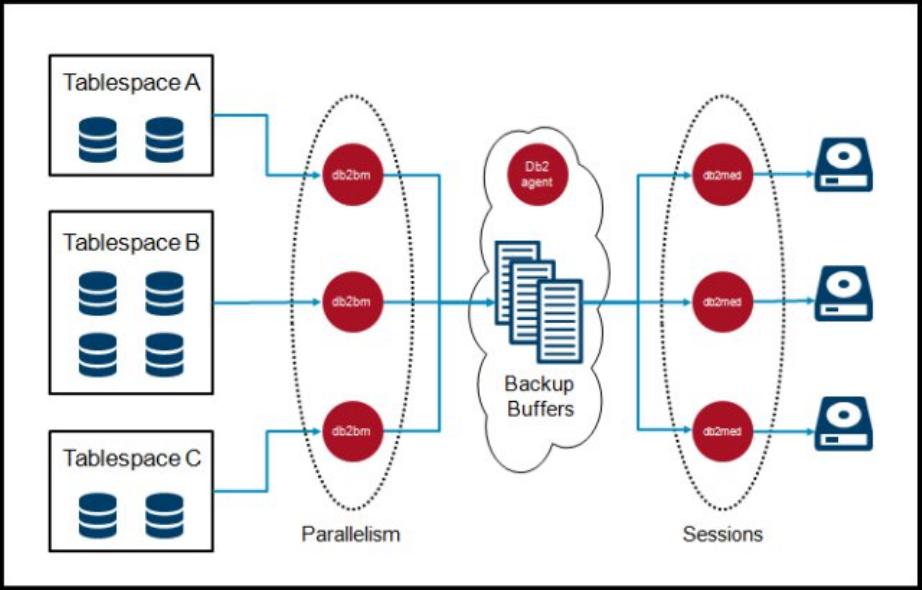
The backup process model
The backup process model consists of the engine dispatchable units (EDUs)
db2agent
,
db2bm
, and
db2med. If the backup uses a storage manager, an additional db2vend process is created. The
db2agent EDU does most of its work during the start of the backup, and then waits for the backup to
complete. The tasks that it performs include the following actions:
Calculate and create an optimal number of
db2bm
and
db2med
EDUs
z
Allocate an optimal number of optimally sized backup buffers
z
Display the selected tunable values to the
db2diag.log
z
Allocate message queues for inter-EDU communication
z
Create a list of table spaces that are sorted by decreasing size
z
Coordinate the backup process by sending control messages to the
db2bm
and
db2med
EDUs
z
The
db2bm
EDU acquires a backup buffer from the empty queue, and then fills the buffer by reading data
from its assigned table space. The db2bm then places the backup buffer on the full queue to be written to
the backup device by the db2med EDU.
The
db2med
EDU is responsible for acquiring a backup buffer from the full queue and writing it to the
backup device. If the backup is being written to disk, it handles the input/output (I/O) directly. If the backup
is being written to a storage manager, it transfers the full buffer to the db2vend process. After
confirmation that the db2vend process successfully saved the contents of the buffer, the db2med EDU
returns the backup buffer to an empty queue for reuse by the next db2bm EDU.
The
db2vend
process is created by the
db2med
EDU if a storage manager is being used. The
db2vend
process receives a full buffer from the db2med, and calls the appropriate vendor application programming
interface (API) for sending the data to the storage manager. A separate process is used so that any crash
or abnormal failure during interaction with the storage manager terminates only the db2vend process,
and does not negatively affect the stability of the DB2 instance.
Maximizing Performance of IBM DB2 Backups 2
Figure 1 is a graphical representation of the backup process model.
Figure 1. Backup process model
Basic backup performance concepts
The following concepts are critical to designing and implementing a successful backup strategy:
Balanced table spaces are the primary factor
z
The primary way to ensure good backup performance is to make sure that the data is evenly
distributed between table spaces. During the backup, DB2 assigns one db2bm EDU to back up each
table space. If most of the data in a database is in one table space, the backup is serialized while only
the one table space is being backed up. Having data equally distributed between multiple table
spaces ensures maximum parallelism throughout the backup.
Difference between system managed space (SMS) and database managed space (DMS) table
z
spaces
When backing up an SMS table space, every page in the table is included in the backup image. When
backing up a DMS table space, only extents that are marked as
used
at the beginning of the backup
are included in the backup image.
What pages are included in an incremental or delta backup
z
An incremental backup includes only pages that were modified since the last
full
backup. Every page
must have its page header scanned to determine whether it belongs in the backup. All large object
(LOB), long varchar, and long vargraphic (LONG) pages are included in the backup image, because
they do not have page headers. A delta backup includes all of the pages that were modified since the
last backup of any type. The delta backup also includes all LOB and LONG pages.
of 10
5墨值下载
【版权声明】本文为墨天轮用户原创内容,转载时必须标注文档的来源(墨天轮),文档链接,文档作者等基本信息,否则作者和墨天轮有权追究责任。如果您发现墨天轮中有涉嫌抄袭或者侵权的内容,欢迎发送邮件至:contact@modb.pro进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,墨天轮将立刻删除相关内容。
下载排行榜


评论