
背景
ShardingSphere

MySQL 时间类型简介
ShardingSphere
| 时间类型 | 所需空间(5.6.4前) | 所需空间(5.6.4后) | "0" 值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| YEAR | 1 byte | 1 byte | 0 |
| DATE | 3 bytes | 3 bytes | '0000-00-00' |
| TIME | 3 bytes | 3 bytes + fractional seconds storage | '00:00:00' |
| DATETIME | 8 bytes | 5 bytes + fractional seconds storage | '0000-00-00 00:00:00' |
| TIMESTAMP | 4 bytes | 4 bytes + fractional seconds storage | '0000-00-00 00:00:00' |
01 服务器时区的影响
time_zone
1 bit sign (1= non-negative, 0= negative)17 bits year*13+month (year 0-9999, month 0-12)5 bits day (0-31)5 bits hour (0-23)6 bits minute (0-59)6 bits second (0-59)--------------------------- 40 bits = 5 bytes复制
// 初始化表create table test(id int not nullprimary key,c_timestamp timestamp null,c_datetime datetime null,c_date date null,c_time time null,c_year year null);// 插入一条数据INSERT INTO test (id, c_timestamp, c_datetime, c_date, c_time, c_year) VALUES (1, '2023-07-03 08:00:00', '2023-07-03 08:00:00', '2023-07-03', '08:00:00', 2023);复制
mysql> show global variables like '%time_zone%';+------------------+--------+| Variable_name | Value |+------------------+--------+| system_time_zone | CST || time_zone | +00:00 |+------------------+--------+2 rows in set (0.01 sec)mysql> select * from test;+----+---------------------+---------------------+------------+----------+--------+| id | c_timestamp | c_datetime | c_date | c_time | c_year |+----+---------------------+---------------------+------------+----------+--------+| 1 | 2023-07-03 00:00:00 | 2023-07-03 08:00:00 | 2023-07-03 | 08:00:00 | 2023 |+----+---------------------+---------------------+------------+----------+--------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)mysql> SET SESSION time_zone = "+8:00";Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.00 sec)mysql> select * from test;+----+---------------------+---------------------+------------+----------+--------+| id | c_timestamp | c_datetime | c_date | c_time | c_year |+----+---------------------+---------------------+------------+----------+--------+| 1 | 2023-07-03 08:00:00 | 2023-07-03 08:00:00 | 2023-07-03 | 08:00:00 | 2023 |+----+---------------------+---------------------+------------+----------+--------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)复制
02 特殊的 "0" 值
详情可参考官方文档 :
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/sql-mode.html
// 本地将 sql_mode 清空,即不配置严格模式mysql> show global variables like '%sql_mode%';+---------------+-------+| Variable_name | Value |+---------------+-------+| sql_mode | |+---------------+-------+1 row in set (0.05 sec)mysql> INSERT INTO test (id, c_timestamp, c_datetime, c_date, c_time, c_year) VALUES (2, null, null, '2023-02-30', null, null);Query OK, 1 row affected, 1 warning (0.08 sec)mysql> select * from test;+----+---------------------+---------------------+------------+----------+--------+| id | c_timestamp | c_datetime | c_date | c_time | c_year |+----+---------------------+---------------------+------------+----------+--------+| 1 | 2023-07-03 00:00:00 | 2023-07-03 08:00:00 | 2023-07-03 | 08:00:00 | 2023 || 2 | NULL | NULL | 0000-00-00 | NULL | NULL |+----+---------------------+---------------------+------------+----------+--------+2 rows in set (0.00 sec)复制
严格模式有助于保证数据的完整性,便于数据在不同环境,不同数据库系统中流转。

Pipeline 中对于时间类型的兼容
ShardingSphere
数据迁移,数据一致性校验,CDC 都会依赖 Pipeline 的底层功能,要求保证数据的正确性和完整性。由于时间类型会涉及到时区、精度,这部分相对来会有更多的地方需要兼容处理。
这里比较核心的就是 JDBC 驱动了,程序和数据库都是通过 JDBC 进行交互的,所以 JDBC 的一些参数配置,会影响到数据的展示。
mysql> show global variables like '%time_zone%';+------------------+--------+| Variable_name | Value |+------------------+--------+| system_time_zone | CST || time_zone | +00:00 |+------------------+--------+2 rows in set (0.01 sec)复制
01 时区的注意事项
最好手动指定 serverTimezone,避免出现 MySQL 中的默认时区和 Java 时区含义不一致的情况,比如 CST, 在 Java 的 TimeZone 中指的是 America/Chicago,但是在 MySQL 中却是China Standard Time。
参考:
https://docs.oracle.com/javase/8/docs/api/java/time/ZoneId.html
<dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><version>8.0.23</version></dependency>复制
class TimeTest {@Testvoid testServerTimezone() throws SQLException {System.out.println(TimeZone.getDefault().getID());Timestamp timestamp = Timestamp.valueOf(LocalDateTime.of(2023, 7, 7, 12, 1, 0));System.out.println(timestamp + ", unix timestamp(seconds):" + timestamp.getTime() 1000);int id = 10;try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_0?allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false", "root", "root")) {PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO test (id, c_timestamp, c_datetime) VALUES (?,?,?)");preparedStatement.setInt(1, id);preparedStatement.setTimestamp(2, timestamp);preparedStatement.setTimestamp(3, timestamp);preparedStatement.executeUpdate();}try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_0?serverTimezone=GMT&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false", "root", "root")) {PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO test (id, c_timestamp, c_datetime) VALUES (?,?,?)");preparedStatement.setInt(1, id + 1);preparedStatement.setTimestamp(2, timestamp);preparedStatement.setTimestamp(3, timestamp);preparedStatement.executeUpdate();}}// 输出结果如下Asia/Shanghai2023-07-07 12:01:00.0, unix timestamp(seconds):1688702460复制
mysql> select * from test;+----+---------------------+---------------------+------------+----------+--------+| id | c_timestamp | c_datetime | c_date | c_time | c_year |+----+---------------------+---------------------+------------+----------+--------+| 1 | 2023-07-03 00:00:00 | 2023-07-03 08:00:00 | 2023-07-03 | 08:00:00 | 2023 || 10 | 2023-07-07 12:01:00 | 2023-07-07 12:01:00 | NULL | NULL | NULL || 11 | 2023-07-07 04:01:00 | 2023-07-07 04:01:00 | NULL | NULL | NULL |+----+---------------------+---------------------+------------+----------+--------+3 rows in set (0.01 sec)复制
mysql> select id,unix_timestamp(c_timestamp), unix_timestamp(c_datetime) from test where id in (10, 11);+----+-----------------------------+----------------------------+| id | unix_timestamp(c_timestamp) | unix_timestamp(c_datetime) |+----+-----------------------------+----------------------------+| 10 | 1688731260 | 1688731260 || 11 | 1688702460 | 1688702460 |+----+-----------------------------+----------------------------+2 rows in set (0.00 sec)复制
11 中的时间已经比程序中插入时间多了 8 小时。
通过结果我们来分析下原因,当 JDBC URL 中没有指定 serverTimezone 的时候发生了什么。在一开始获取 Connection 时,com.mysql.cj.protocol.a.NativeProtocol#configureTimeZone 中设置了 session 的 timezone。

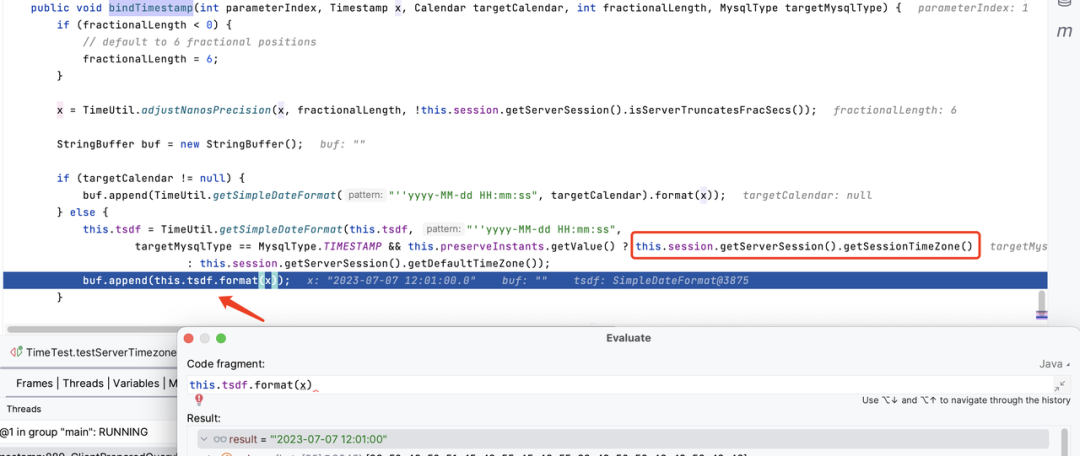
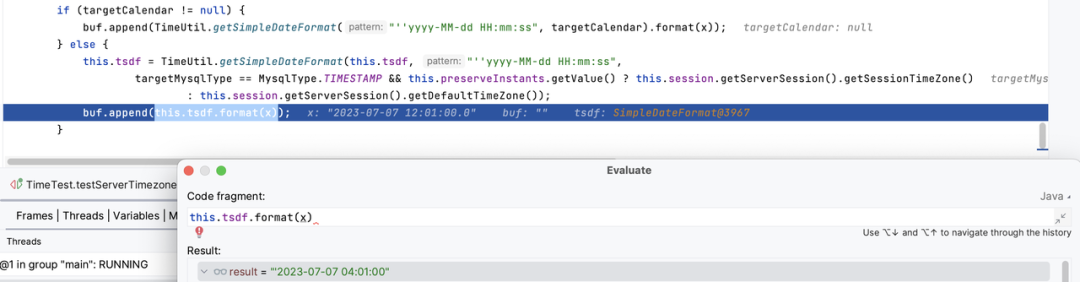
通过设置 C/J 连接属性 serverTimezone,可以覆盖服务器的时区。如果不指定,服务器配置的默认时区会生效。
C/J 5.1 需要同时配置 useLegacyDatetimeCode=false&serverTimezone=XXX这两个参数
C/J 8 只需要配置 serverTimezone=XXX
@Testvoid testServerTimezoneWithString() throws SQLException {int id = 111;Timestamp timestamp = Timestamp.valueOf(LocalDateTime.of(2023, 7, 7, 12, 1, 0));try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_0?serverTimezone=GMT&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false", "root", "root")) {PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO test (id, c_timestamp, c_datetime) VALUES (?,?,?)");preparedStatement.setInt(1, id);preparedStatement.setString(2, "2023-07-07 12:01:02");preparedStatement.setTimestamp(3, timestamp);preparedStatement.executeUpdate();}}复制
mysql> mysql> * from test where id in (11,111);+-----+---------------------+---------------------+--------+--------+--------+| id | c_timestamp | c_datetime | c_date | c_time | c_year |+-----+---------------------+---------------------+--------+--------+--------+| 11 | 2023-07-07 04:01:00 | 2023-07-07 04:01:00 | NULL | NULL | NULL || 111 | 2023-07-07 12:01:02 | 2023-07-07 04:01:00 | NULL | NULL | NULL |+-----+---------------------+---------------------+--------+--------+--------+2 rows in set (0.10 sec)复制
02 精度的注意事项
create table test_fst(id int not nullprimary key,c_timestamp timestamp(6) null,c_datetime datetime(6) null,c_time time(6) null);
@Testvoid testFst() throws SQLException {int id = 1;Timestamp timestamp = Timestamp.valueOf(LocalDateTime.of(2023, 7, 7, 12, 1, 0, 123456789));try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_0?allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false&", "root", "root")) {PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("INSERT INTO test_fst (id, c_timestamp, c_datetime, c_time) VALUES (?,?,?,?)");preparedStatement.setInt(1, id);preparedStatement.setString(2, "2023-07-07 12:01:00.123456789");preparedStatement.setTimestamp(3, timestamp);preparedStatement.setTime(4, Time.valueOf(LocalTime.of(1, 1, 1, 123456789)));// preparedStatement.setObject(4, LocalTime.of(1, 1, 1, 123456789));preparedStatement.executeUpdate();}}复制
mysql> select * from test_fst;+----+----------------------------+----------------------------+-----------------+| id | c_timestamp | c_datetime | c_time |+----+----------------------------+----------------------------+-----------------+| 1 | 2023-07-07 12:01:00.123457 | 2023-07-07 12:01:00.123457 | 01:01:01.000000 |+----+----------------------------+----------------------------+-----------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)复制
c_timestamp 和 c_datetime 的值都包含小数位,最后一位发生了四舍五入,所以小数位变成了 .123457。
c_time 并没有小数位,虽然我们在代码中明确指定了。
mysql> insert into test_fst(id, c_time) values (2, '01:01:01.123457');Query OK, 1 row affected (0.02 sec)mysql> select * from test_fst where id = 2;+----+-------------+------------+-----------------+| id | c_timestamp | c_datetime | c_time |+----+-------------+------------+-----------------+| 2 | NULL | NULL | 01:01:01.123457 |+----+-------------+------------+-----------------+1 row in set (0.00 sec)复制
从 8.0.23 开始 ,JDBC URL 中sendFractionalSeconds 的配置是全局控制所有时间类型发送小数点的。如果 sendFractionalSeconds=false,无论
sendFractionalSecondsForTime 的值如何,都不会发送小数秒。
public class Time extends java.util.Date {// 舍去了 LocalTime 中的小数值public static Time valueOf(LocalTime time) {return new Time(time.getHour(), time.getMinute(), time.getSecond());}// 这里也会舍去 Time 本身中含有的小数值public LocalTime toLocalTime() {return LocalTime.of(getHours(), getMinutes(), getSeconds());}}复制
<dependency><groupId>mysql</groupId><artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId><version>5.1.49</version></dependency>复制
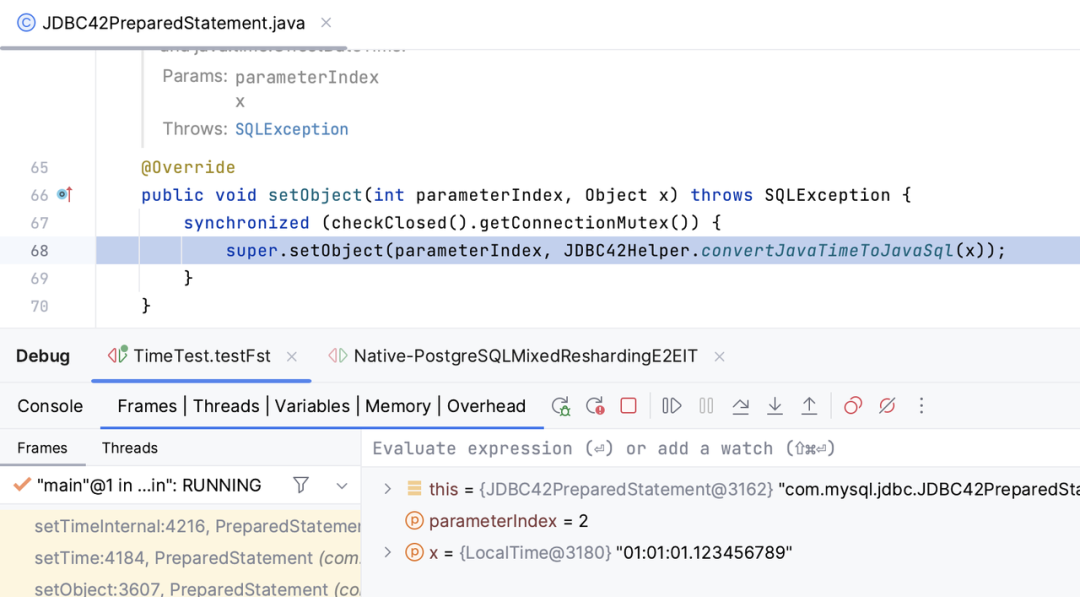
public class JDBC42Helper {/*** JDBC 4.2 Helper methods.*/static Object convertJavaTimeToJavaSql(Object x) {if (x instanceof LocalDate) {return Date.valueOf((LocalDate) x);} else if (x instanceof LocalDateTime) {return Timestamp.valueOf((LocalDateTime) x);} else if (x instanceof LocalTime) {return Time.valueOf((LocalTime) x);}return x;}}复制
@Testvoid testFst() throws SQLException {try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_0?allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false&", "root", "root")) {PreparedStatement queryStatement = connection.prepareStatement("select id, c_time from test_fst where id = ?");queryStatement.setInt(1, 2);ResultSet resultSet = queryStatement.executeQuery();resultSet.next();System.out.println(resultSet.getObject(2).getClass());System.out.println("getObject: " + resultSet.getObject(2));System.out.println("getTimestamp: " + new Timestamp(resultSet.getTime(2).getTime()).getNanos());}}复制
class java.sql.TimegetObject: 01:01:01getTimestamp: 0复制
03 关于数据一致性对比
时区问题(上面已经讨论过,这里不重复了) 数据库字段有特殊值的问题(比如上面提到的 "0" 值) 数据库同一类型的字段在程序中展现的类型不一致(通常和 JDBC 驱动参数有关)
C/J 5:exception,round,convertToNull C/J 8:EXCEPTION,ROUND, CONVERT_TO_NULL
mysql> INSERT INTO test (id, c_timestamp, c_datetime, c_date, c_time, c_year) VALUES (1000, '0000-00-00', '0000-00-00', '2023-02-30', null, null);复制
@Testvoid tesZero() throws SQLException {try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_0?allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false&", "root", "root")) {PreparedStatement queryStatement = connection.prepareStatement("select id, c_timestamp from test where id = ?");queryStatement.setInt(1, 1000);ResultSet resultSet = queryStatement.executeQuery();resultSet.next();System.out.println(resultSet.getObject(2));}}复制
java.sql.SQLException: Zero date value prohibitedat com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.SQLError.createSQLException(SQLError.java:129)at com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.SQLError.createSQLException(SQLError.java:97)at com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.SQLError.createSQLException(SQLError.java:89)at com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.SQLError.createSQLException(SQLError.java:63)at com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.SQLError.createSQLException(SQLError.java:73)at com.mysql.cj.jdbc.exceptions.SQLExceptionsMapping.translateException(SQLExceptionsMapping.java:99)at com.mysql.cj.jdbc.result.ResultSetImpl.getTimestamp(ResultSetImpl.java:933)at com.mysql.cj.jdbc.result.ResultSetImpl.getObject(ResultSetImpl.java:1265)复制
@Overridepublic T createFromTimestamp(InternalTimestamp its) {if (its.isZero()) {switch (this.pset.<PropertyDefinitions.ZeroDatetimeBehavior>getEnumProperty(PropertyKey.zeroDateTimeBehavior).getValue()) {case CONVERT_TO_NULL:return null;case ROUND:return localCreateFromTimestamp(new InternalTimestamp(1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0));default:break;}}return localCreateFromTimestamp(its);}复制
public class SqlTimestampValueFactory extends AbstractDateTimeValueFactory<Timestamp> {@Overridepublic Timestamp localCreateFromTimestamp(InternalTimestamp its) {if (its.getYear() == 0 && its.getMonth() == 0 && its.getDay() == 0) {throw new DataReadException(Messages.getString("ResultSet.InvalidZeroDate"));}......}}复制

结论
ShardingSphere
If set to SYSTEM, every MySQL function call that requires a time zone calculation makes a system library call to determine the current system time zone. This call may be protected by a global mutex, resulting in contention.

参考文章:
MySQL 数据类型存储要求:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/storage-requirements.html
MYSQL时间类型:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/date-and-time-types.html
MySQL Strict Mode:https://dev.mysql.com/blog-archive/improvements-to-strict-mode-in-mysql
MySQL 参数配置列表:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/connector-j/8.0/en/connector-j-reference-configuration-properties.html
MySQL Fractional Seconds:
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/fractional-seconds.html
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/connector-j/8.0/en/connector-j-fractional-seconds.html
关于 Apache ShardingSphere







