前言
前边几篇介绍了pg_hint_plan的主要原理,以及部分hint的原理。
pg_hint_plan技术内幕–01核心原理
pg_hint_plan技术内幕–02 Scan method
修改disable_cost为guc参数–增强干预执行计划
pg_hint_plan技术内幕–03 Join method
pg_hint_plan技术内幕–04 Join order
本文将继续分析hint_table的原理。
什么时候使用hint_table?为什么要使用hint_table?
我们使用hint时,hint是作为sql文本的一部分去执行,那么意味着必须要修改sql文本了。但是往往有些场景下我们无法修改sql文本,例如定制化SAAS软件服务的SQL等,终端用户无法自定义修改。所以我们可以将sql对应的hint写入hint_table,这样在执行sql时就可以从hint_table查询到对应的hint_str,然后走hint的逻辑去影响执行计划。
所以hint_table有两个能力:
1、不改写sql文本影响执行计划;
2、实现全局共享执行计划。
hint_table对应文档:hint_table
比如以下这个sql,默认pu为inner。
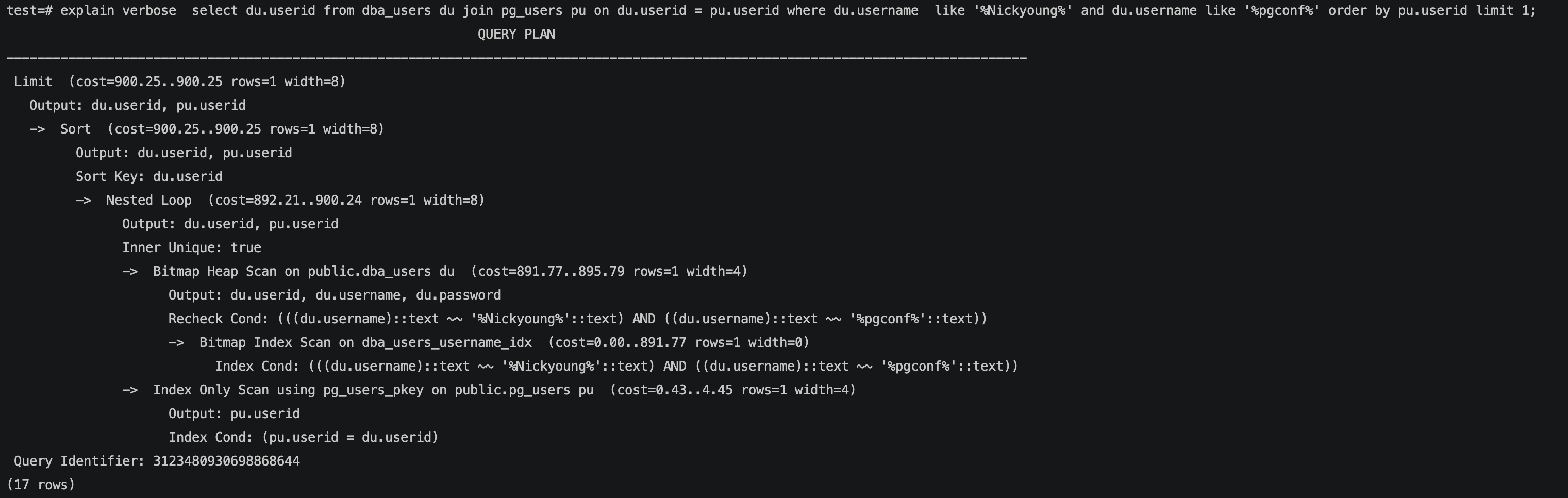
我们使用hint指定du为inner,并且写入到hint_table。
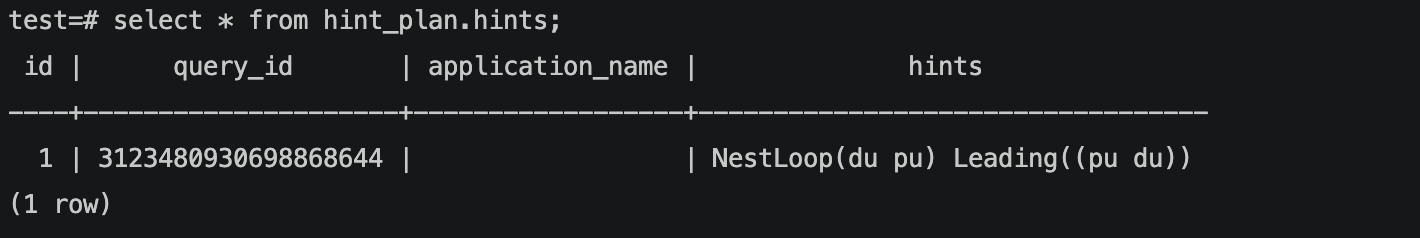
当打开enable_hint_table,可以看到执行计划中确实已将du指定为inner。
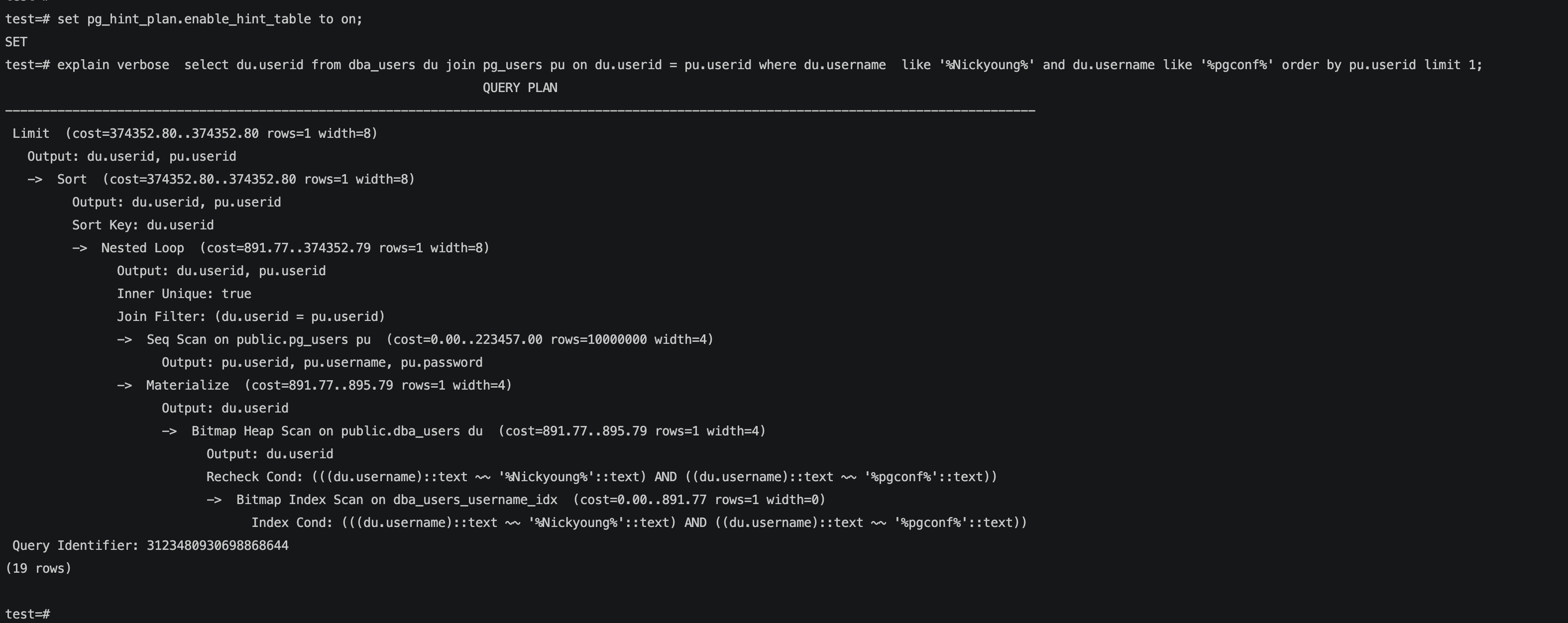
原理
在planner里,当我们开启pg_hint_plan插件时,在pg_hint_plan_planner函数中调用get_current_hint_string获取当前hint_str,且当pg_hint_plan.enable_hint_table为on时,进入get_hints_from_table函数查询hint_table,寻找当前query_id的hint_str。
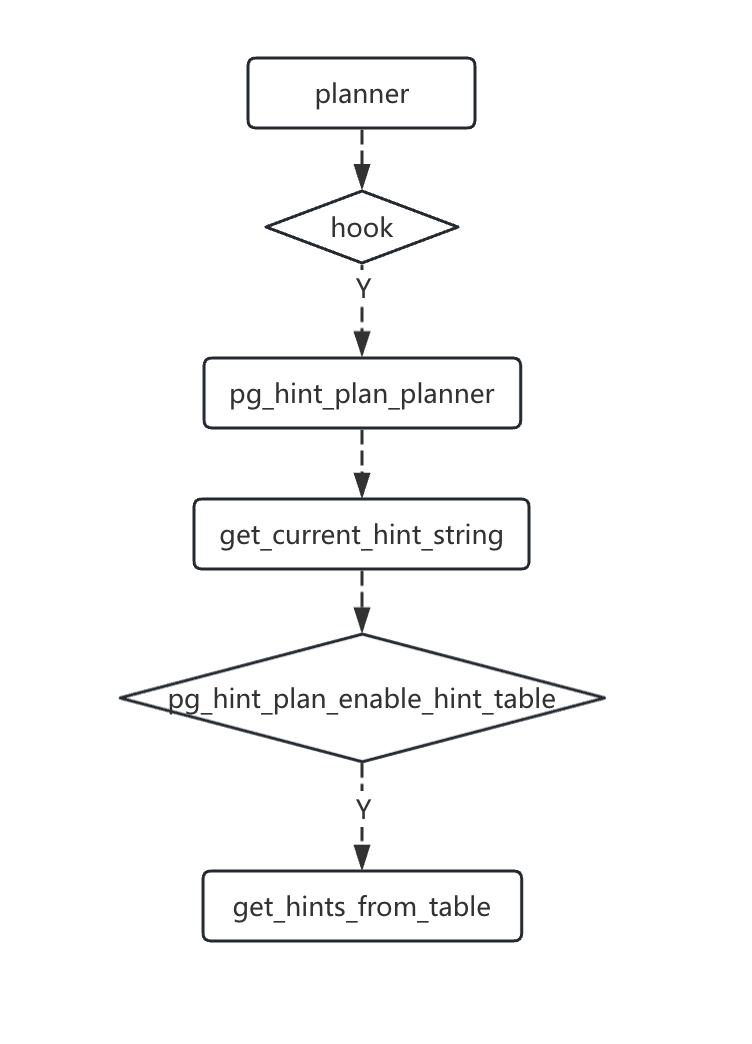
在get_hints_from_table中,可以看到是使用SPI的方式查询hint_plan.hints表,获取当前query_id的hint_str。
/*
* Get hints from table by client-supplied query ID and application name.
*/
static const char *
get_hints_from_table(uint64 queryId, const char *client_application)
{
const char *search_query =
"SELECT hints "
" FROM hint_plan.hints "
" WHERE query_id = $1 "
" AND ( application_name = $2 "
" OR application_name = '' ) "
" ORDER BY application_name DESC";
static SPIPlanPtr plan = NULL;
char *hints = NULL;
Oid argtypes[2] = { INT8OID, TEXTOID };
Datum values[2];
char nulls[2] = {' ', ' '};
text *app;
Oid namespaceId;
bool hints_table_found = false;
/*
* Make sure that hint_plan.hints is found before we attempt to look for
* a hint.
*/
namespaceId = LookupExplicitNamespace("hint_plan", true);
if (OidIsValid(namespaceId) &&
OidIsValid(get_relname_relid("hints", namespaceId)))
hints_table_found = true;
if (!hints_table_found)
{
ereport(WARNING,
(errmsg ("cannot use the hint table"),
errhint("Run \"CREATE EXTENSION pg_hint_plan\" to create the hint table.")));
return NULL;
}
PG_TRY();
{
bool snapshot_set = false;
hint_inhibit_level++;
if (!ActiveSnapshotSet())
{
PushActiveSnapshot(GetTransactionSnapshot());
snapshot_set = true;
}
SPI_connect();
if (plan == NULL)
{
SPIPlanPtr p;
p = SPI_prepare(search_query, 2, argtypes);
plan = SPI_saveplan(p);
SPI_freeplan(p);
}
app = cstring_to_text(client_application);
values[0] = Int64GetDatum(queryId);
values[1] = PointerGetDatum(app);
SPI_execute_plan(plan, values, nulls, true, 1);
if (SPI_processed > 0)
{
char *buf;
hints = SPI_getvalue(SPI_tuptable->vals[0],
SPI_tuptable->tupdesc, 1);
/*
* Here we use SPI_palloc to ensure that hints string is valid even
* after SPI_finish call. We can't use simple palloc because it
* allocates memory in SPI's context and that context is deleted in
* SPI_finish.
*/
buf = SPI_palloc(strlen(hints) + 1);
strcpy(buf, hints);
hints = buf;
}
SPI_finish();
if (snapshot_set)
PopActiveSnapshot();
hint_inhibit_level--;
}
PG_CATCH();
{
hint_inhibit_level--;
PG_RE_THROW();
}
PG_END_TRY();
return hints;
}
/*
复制查询到hint_str后,接下来就是按照hint处理逻辑去修改执行计划。
小结
当我们无法改写sql文本时,可以将hint文本写入到hint_table,在执行sql时会查询hint_table对应当前query_id的hint_str,接着去指定执行计划。因此,也可以说hint_table有两个重要能力:1、不改写sql文本影响执行计划;2、实现全局共享执行计划。
当然hint_table还有优化空间,当前是使用SPI的方式查询插件自定义表,当并发高访问时性能可能不会太好;可以为其创建专用的cache,就像访问其他系统表一样。感兴趣的朋友可以尝试优化下。










