
大家好, 应广大小伙伴的要求,大表哥这个带来的是 MYSQL中的半连接 semi join.
从MYSQL本身的语法树上来说,是没有直接可以用的关键字 semi join, 但是 一般子查询语句含有 in 或者 exists 关键字会触发mysql 内部进行查询
转换成semi join.
SELECT ... From Outer_tables WHERE expr in (SELECT ... From Inner_tables ...) And ...
SELECT ... From Outer_tables WHERE expr exist (SELECT ... From Inner_tables ...) And ...
简单地说,我们可以把表看成是 数据集合, 表与表的连接,就是数据集的 交集,并集, 补集等操作。
下面的图来自于大厂阿里:

SEMI join 简单来说就是 外层的表的过滤依赖于内层的子查询语句作为过滤条件。
MYSQL 大叔的优化器为semi 设置了如下几种的策略:
DuplicateWeedout strategy
Firstmatch Strategy
Loosescan Strategy
Materialize scan/Materialize lookup Strategy
同样mysql 大叔还贴心的为这几种semi join 的策略提供了对应的hint:
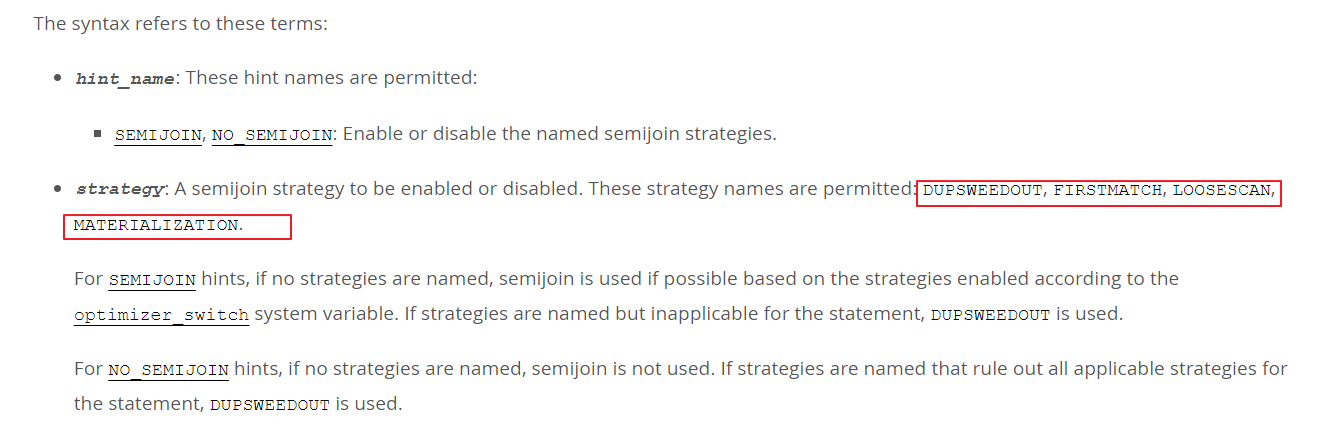
面大表哥带你来看一下:
DuplicateWeedout strategy: 表示的是重复值去重。
现在假设外面的表和IN 子句里面的表的关系是 1对多 的关系, 那么查询出来的就结果集就需要做去重的处理。
核心的去重的操作是 通过建立一张临时表完成的。
create table tmp(
id int primary key
)
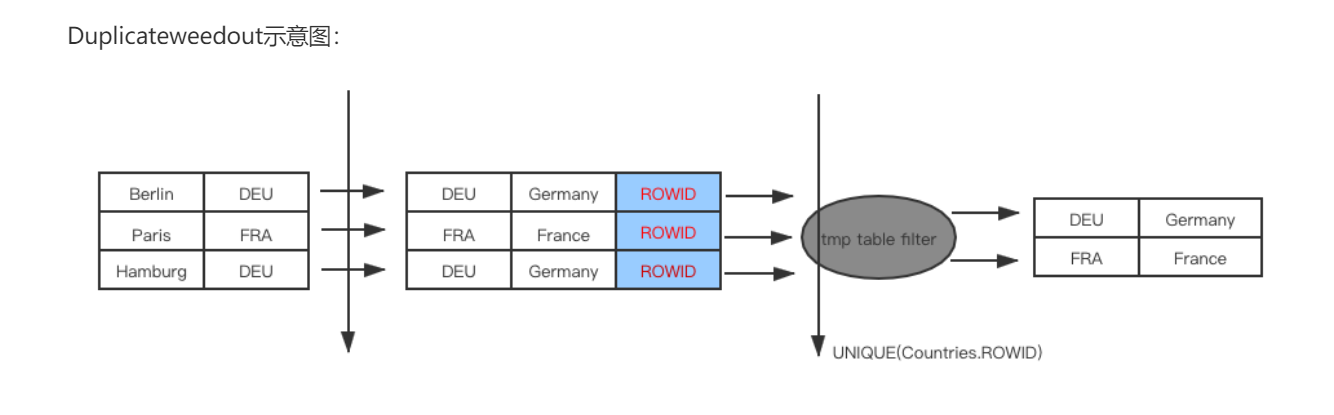
我们来建2张表来测试一下: 他们的关系是1对多的关系:
root@localhost:mysql_uatDB.sock [testdb]> create table tab1 (id int primary key, name varchar(20));
--------------
create table tab1 (id int primary key, name varchar(20))
--------------
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
root@localhost:mysql_uatDB.sock [testdb]> create table tab2 (id int primary key, name varchar(20),pid int);
--------------
create table tab2 (id int primary key, name varchar(20),pid int)
--------------
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.02 sec)
root@localhost:mysql_uatDB.sock [testdb]> alter table tab2 add index idx_pid (pid);
--------------
alter table tab2 add index idx_pid (pid)
--------------
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.03 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
root@localhost:mysql_uatDB.sock [testdb]> insert into tab1 values (1,'Father');
--------------
insert into tab1 values (1,'Father')
root@localhost:mysql_uatDB.sock [testdb]> insert into tab2 values (1,'Son',1);
--------------
insert into tab2 values (1,'Son',1)
--------------
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
root@localhost:mysql_uatDB.sock [testdb]> insert into tab2 values (2,'Daughter',1);
--------------
insert into tab2 values (2,'Daughter',1)
--------------
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
root@localhost:mysql_uatDB.sock [testdb]> insert into tab1 values (2,'Monther');
--------------
insert into tab1 values (2,'Monther')
--------------
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
root@localhost:mysql_uatDB.sock [testdb]> insert into tab2 values (3,'Son',2);
--------------
insert into tab2 values (3,'Son',2)
--------------
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
root@localhost:mysql_uatDB.sock [testdb]> insert into tab2 values (4,'Daughter',2);
--------------
insert into tab2 values (4,'Daughter',2)
--------------
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.00 sec)
我们现在来测试一下查询: 我们采用hint DUPSWEEDOUT 来强制走一下 DuplicateWeedout 这个策略:
我们从执行计划里可以看到 Start temporary; End temporary 这个就是 在建临时表去重的过程
explain select/*+ SEMIJOIN(@subq1 DUPSWEEDOUT) */ * from tab1 where id in (select /*+ QB_NAME(subq1) */ pid from tab2 )
--------------
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+----------------+------+----------+---------------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+----------------+------+----------+---------------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab1 | NULL | ALL | PRIMARY | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab2 | NULL | ref | idx_pid | idx_pid | 5 | testdb.tab1.id | 2 | 100.00 | Using index; Start temporary; End temporary |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+------+---------------+---------+---------+----------------+------+----------+---------------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
Firstmatch Strategy: 这种策略简单来说就是外层表每次取出一条进入到内层表中做匹配,如果可以连接到内层查到记录,则立即返回,进行下一次的外层循环。
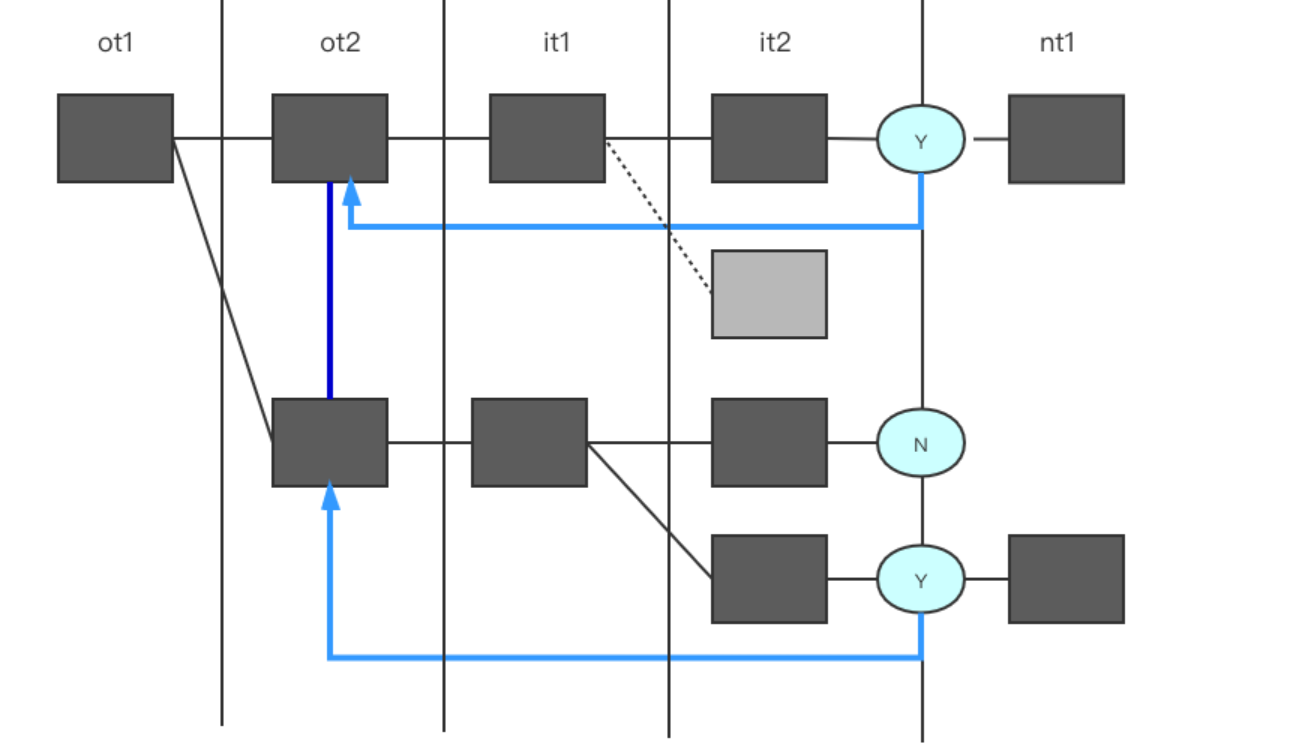
我们从例子中,可以看到 执行计划中 出现了策略 FirstMatch(tab1)
root@localhost:mysql_uatDB.sock [testdb]> explain select * from tab1 where id in (select pid from tab2 where pid =1);
--------------
explain select * from tab1 where id in (select pid from tab2 where pid =1)
--------------
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab1 | NULL | const | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | const | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab2 | NULL | ref | idx_pid | idx_pid | 5 | const | 2 | 100.00 | Using index; FirstMatch(tab1) |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+-------+---------------+---------+---------+-------+------+----------+-------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
Loosescan Strategy: 稀松扫描。触发这个策略的条件是 内层子查询 where 条件进行范围过滤 (pid >= 1) 并且 内外层关联的值就是 内层的范围过滤的值 (select pid from tab2 where pid >= 1)
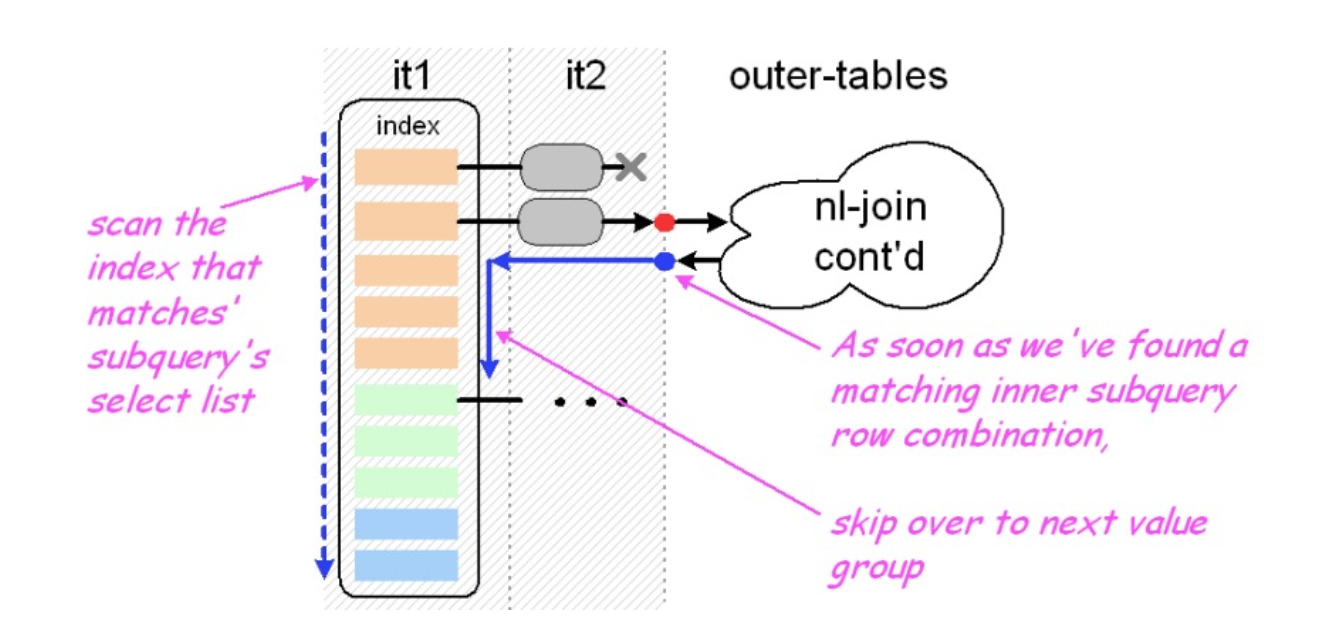
root@localhost:mysql_uatDB.sock [testdb]> explain select * from tab1 where id in (select pid from tab2 where pid >= 1);
--------------
explain select * from tab1 where id in (select pid from tab2 where pid >= 1)
--------------
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+-----------------+------+----------+-------------------------------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+-----------------+------+----------+-------------------------------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab2 | NULL | index | idx_pid | idx_pid | 5 | NULL | 4 | 50.00 | Using where; Using index; LooseScan |
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab1 | NULL | eq_ref | PRIMARY | PRIMARY | 4 | testdb.tab2.pid | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
+----+-------------+-------+------------+--------+---------------+---------+---------+-----------------+------+----------+-------------------------------------+
2 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
Materialize scan/Materialize lookup Strategy:内部表物化策略。
就是说将内部子查询的表进行物化处理,生成临时表:
我们可以看到执行计划里面出现了: MATERIALIZED 的关键字
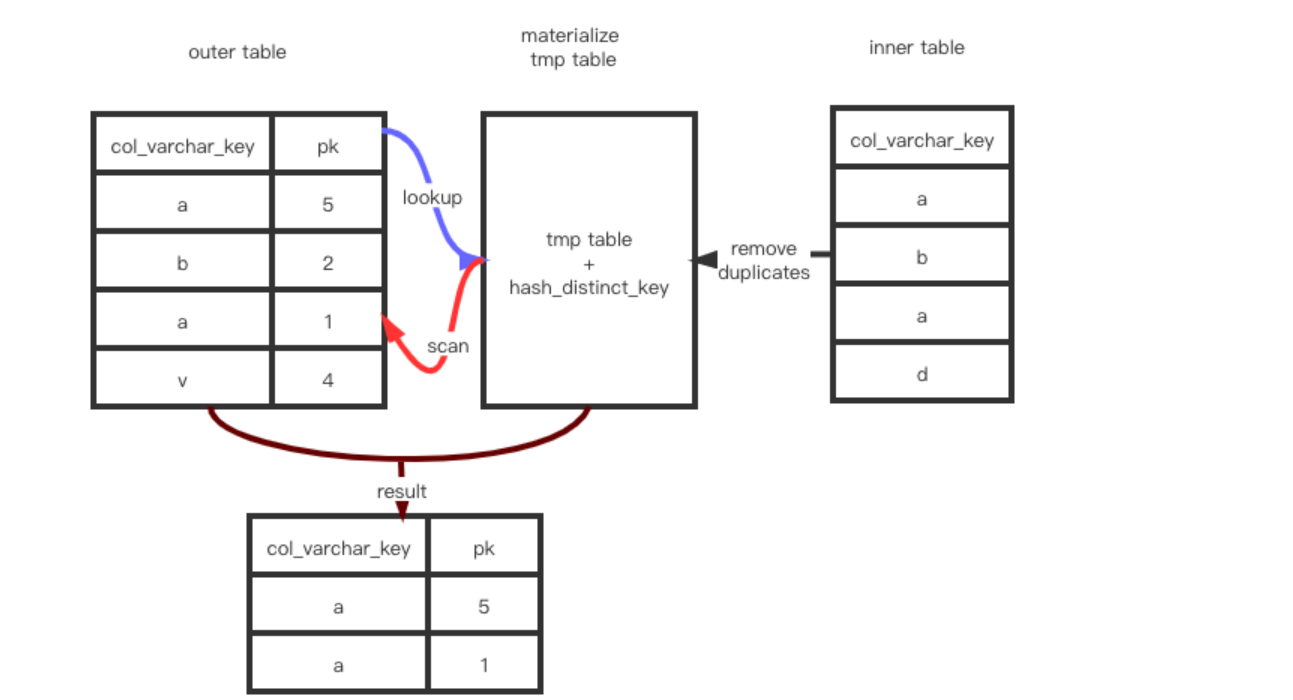
root@localhost:mysql_uatDB.sock [testdb]> explain select/*+ SEMIJOIN(@subq1 MATERIALIZATION) */ * from tab1 where id in (select /*+ QB_NAME(subq1) */ pid from tab2 );
--------------
explain select/*+ SEMIJOIN(@subq1 MATERIALIZATION) */ * from tab1 where id in (select /*+ QB_NAME(subq1) */ pid from tab2 )
--------------
+----+--------------+-------------+------------+--------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+----------------+------+----------+-------------+
| id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra |
+----+--------------+-------------+------------+--------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+----------------+------+----------+-------------+
| 1 | SIMPLE | tab1 | NULL | ALL | PRIMARY | NULL | NULL | NULL | 2 | 100.00 | Using where |
| 1 | SIMPLE | <subquery2> | NULL | eq_ref | <auto_distinct_key> | <auto_distinct_key> | 5 | testdb.tab1.id | 1 | 100.00 | NULL |
| 2 | MATERIALIZED | tab2 | NULL | index | idx_pid | idx_pid | 5 | NULL | 4 | 100.00 | Using index |
+----+--------------+-------------+------------+--------+---------------------+---------------------+---------+----------------+------+----------+-------------+
3 rows in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec)
最后大表哥简单的总结一下mysql semi join 的几种策略:
- DuplicateWeedout strategy: 在外部表和内部表记录存在 1对多 具有重复的数据情况下, 去重的策略采用建立带有唯一主键临时表的方式去重过滤
- Firstmatch Strategy: 外部表的每一条去循环匹配内部表,返回一条记录立即停止,进行外部表的下一次循环
- Loosescan Strategy: 内层子查询是范围过滤,并且过滤的键和外层表连接键是一致的,那么会进行内部表的一次性的范围扫描,缓存到join buffer中
- Materialize scan/Materialize lookup Strategy:直接缓存内部表的子查询为物化表






